Structure & Function of Cells (2)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Based on the book 'Human Biology' by Michael Johnson
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
1
New cards
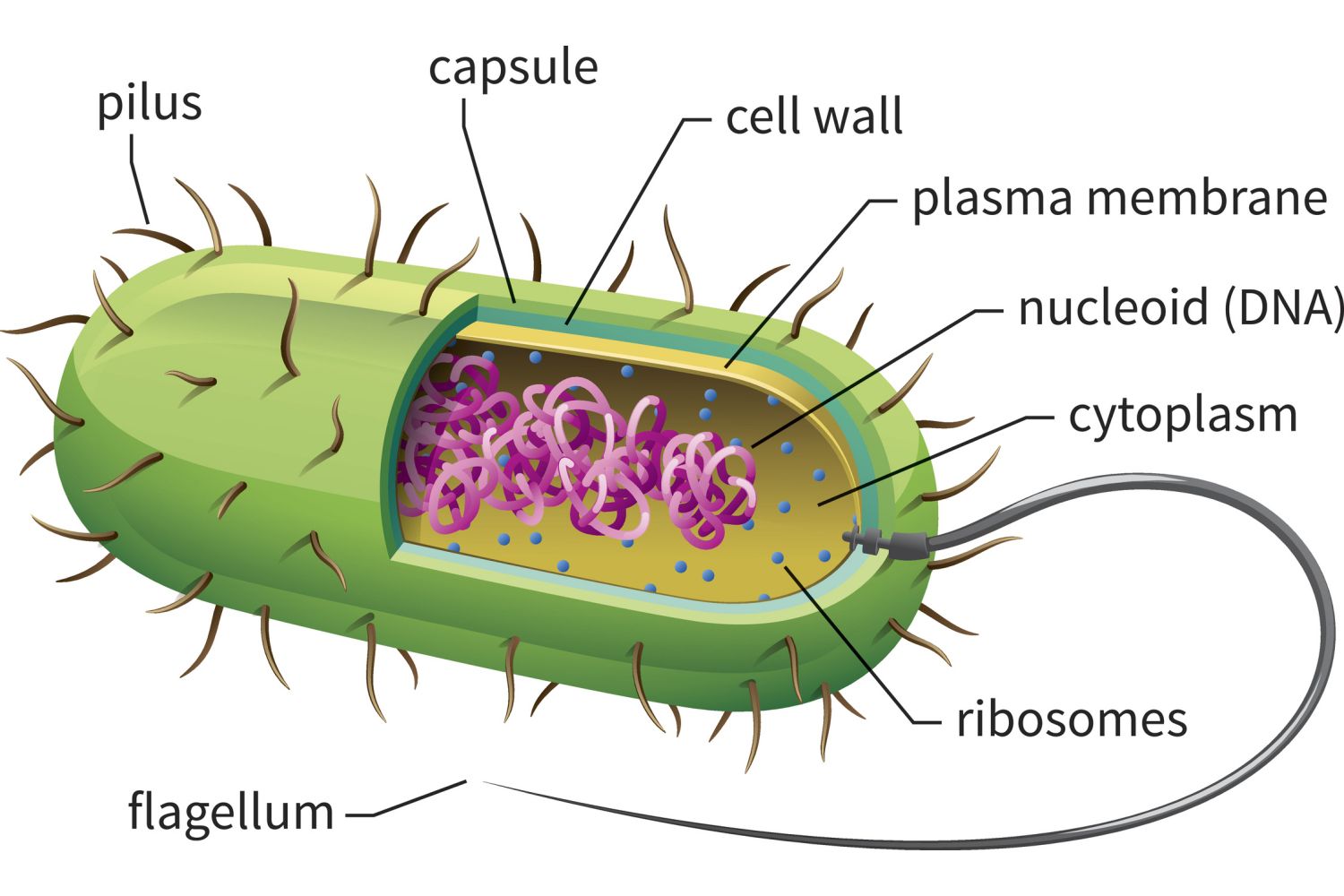
Name the main parts a prokaryotic cell consists of
Plasma membrane
Cytoplasm
* fluid within membrane
Cell wall
Genetic material
Bacterial cells are prokaryotic
Cytoplasm
* fluid within membrane
Cell wall
Genetic material
Bacterial cells are prokaryotic
2
New cards
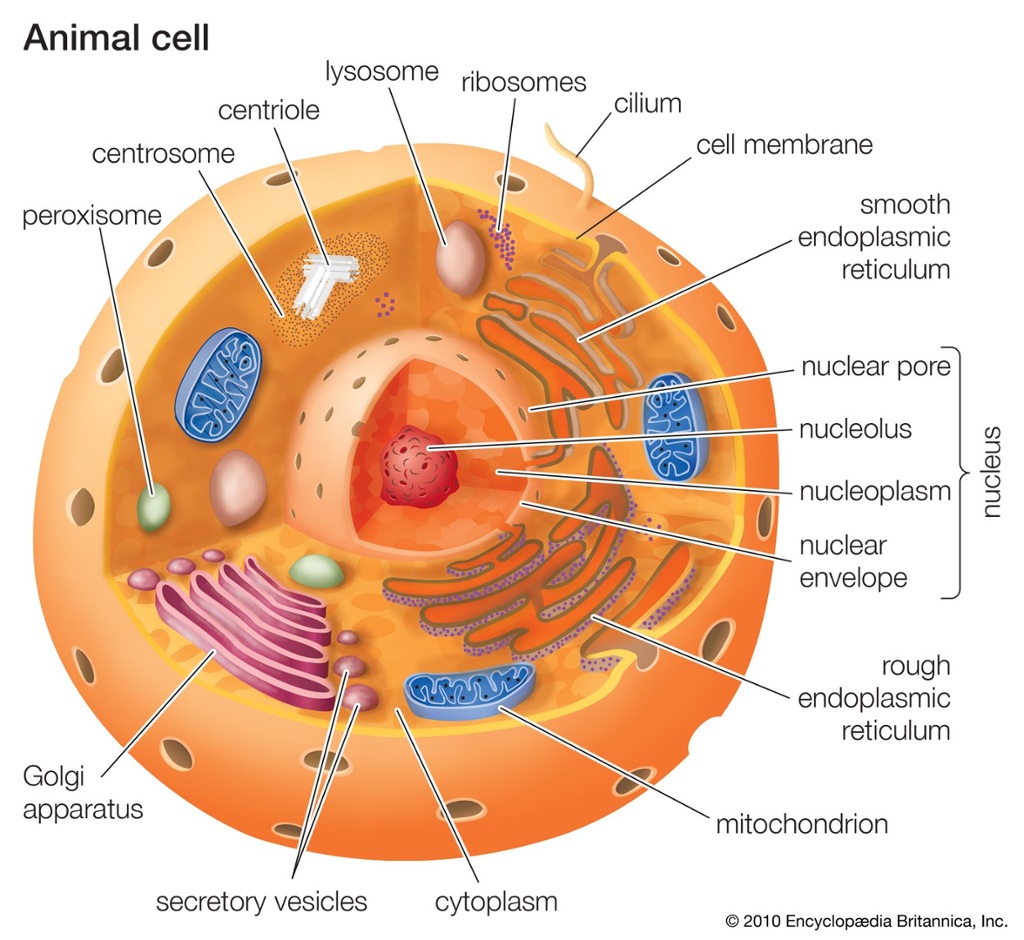
Name the main parts an eukaryotic cell consists of
Plasma membrane
Nucleus
* membrane bound information center
Cytoplasma
Organelles
* membrane bound structures with specialized functions
All human cells are eukaryotic
Nucleus
* membrane bound information center
Cytoplasma
Organelles
* membrane bound structures with specialized functions
All human cells are eukaryotic
3
New cards
What’s the main difference between prokaryotic & eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic
* primitive
* no organelles
* no nucleus
* no distinct structures
* \
\
Eukaryotic
* no cell wall
* ‘incorporation of prokaryotic cells in one big cell’
* cytoplasm enclosed by flexible plasma membrane
* primitive
* no organelles
* no nucleus
* no distinct structures
* \
\
Eukaryotic
* no cell wall
* ‘incorporation of prokaryotic cells in one big cell’
* cytoplasm enclosed by flexible plasma membrane
4
New cards
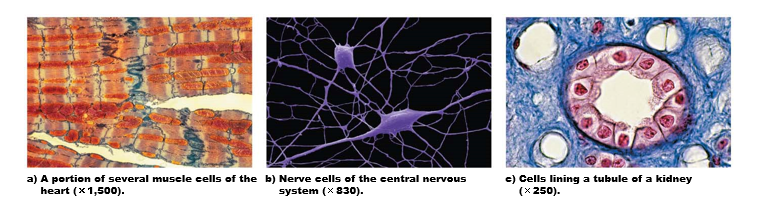
How does (eukaryotic) cell structure reflect cell function?
Eukaryotic cells remarkably similar, but structural differences
* **muscle cells**: contain many organelles providing energy needed for muscle contraction
* **nerve cells**: long & thing to carry impulses over distance
Small size = efficient
* **muscle cells**: contain many organelles providing energy needed for muscle contraction
* **nerve cells**: long & thing to carry impulses over distance
Small size = efficient
5
New cards
Why is the small size of cells efficient?
Small cells have higher surface-to-volume ratio
→ Promotes efficiency in
* acquisition of nutrients
* disposal of water
→ Promotes efficiency in
* acquisition of nutrients
* disposal of water
6
New cards
Which aspects of the cell can affect surface area & volume?
Cell size
Plasma membrane shape
Plasma membrane shape
7
New cards
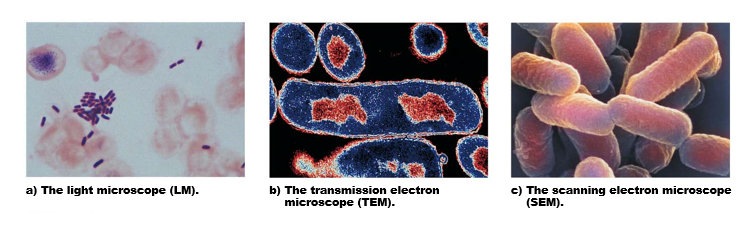
What are the 3 different types of microscopes & what can be seen with them?
Light microscope
* magnifies up to 1K x
* used to view living specimens
\
Transmission electron microscope
* magnifies up to 100K x
* without light
* can reveal internal details of cell structure
\
Scanning electron microscope
* magnifies up to 100K x
* without light
* provides 3D view of cell surface
* magnifies up to 1K x
* used to view living specimens
\
Transmission electron microscope
* magnifies up to 100K x
* without light
* can reveal internal details of cell structure
\
Scanning electron microscope
* magnifies up to 100K x
* without light
* provides 3D view of cell surface
8
New cards
Name all the parts of a typical animal (eukaryotic) cell
Nucleus
Ribosomes
Endoplasmic reticulum (rough & smooth)
Golgi apparatus
Vesicles
Mitochondria
Cytoskeleton
Cilia
Flagella
Centrioles
Plasma membrane
Ribosomes
Endoplasmic reticulum (rough & smooth)
Golgi apparatus
Vesicles
Mitochondria
Cytoskeleton
Cilia
Flagella
Centrioles
Plasma membrane
9
New cards
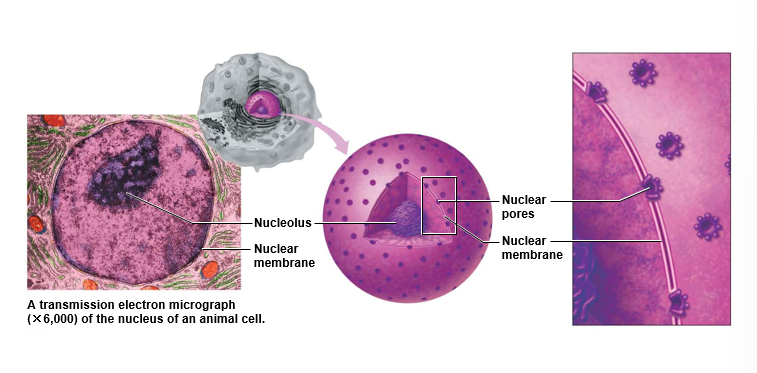
What is the function of the nucleus & what are the structural features?
Function
* contains genetic information of the cell
* controls all activities of the cell
\
Structural features
* double-layered nuclear membrane
* nuclear pores
* chromosomes/chromatin
* nucleolus
* contains genetic information of the cell
* controls all activities of the cell
\
Structural features
* double-layered nuclear membrane
* nuclear pores
* chromosomes/chromatin
* nucleolus
10
New cards
What’s the function of ribosomes & how does their location reflect that?
Responsible for protein synthesis
\
Location
**Free**: floating in cytoplasm
* these ribosomes synthesize proteins for immediate use in the cell
**Bound**: attached to outer surface of ER
* these ribosomes synthesize proteins that will be transported to other organelles or exported from the cell
\
Location
**Free**: floating in cytoplasm
* these ribosomes synthesize proteins for immediate use in the cell
**Bound**: attached to outer surface of ER
* these ribosomes synthesize proteins that will be transported to other organelles or exported from the cell
11
New cards
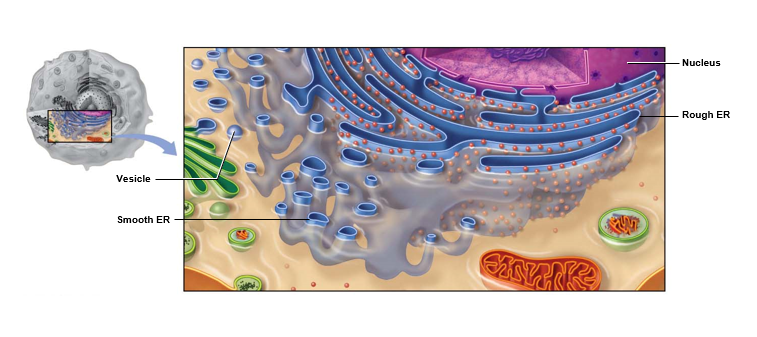
What 2 types of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) are there & what’s their function?
= Manufacturing center
Highly folded membranous network
\
Rough ER
* has ribosomes on surface
* Manufactures proteins, particularly those that’ll be secreted from the cell
\
Smooth ER
* no ribosomes on surface
* lipid synthesis, incl. synthesis of some hormones
* packages proteins & lipids for delivery to Golgi apparatus
Highly folded membranous network
\
Rough ER
* has ribosomes on surface
* Manufactures proteins, particularly those that’ll be secreted from the cell
\
Smooth ER
* no ribosomes on surface
* lipid synthesis, incl. synthesis of some hormones
* packages proteins & lipids for delivery to Golgi apparatus
12
New cards
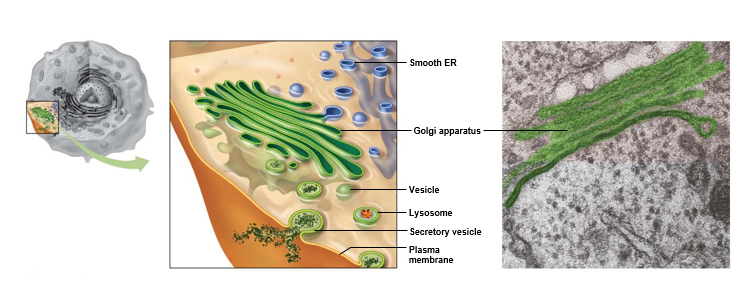
What does the Golgi apparatus do?
**Refines** synthesized products
**Packages** products into vesicles
**Ships** packaged products to other locations within cell or to the cell membrane for export
**Packages** products into vesicles
**Ships** packaged products to other locations within cell or to the cell membrane for export
13
New cards
What are vesicles?
Membrane-bound storage & shipping containers
14
New cards
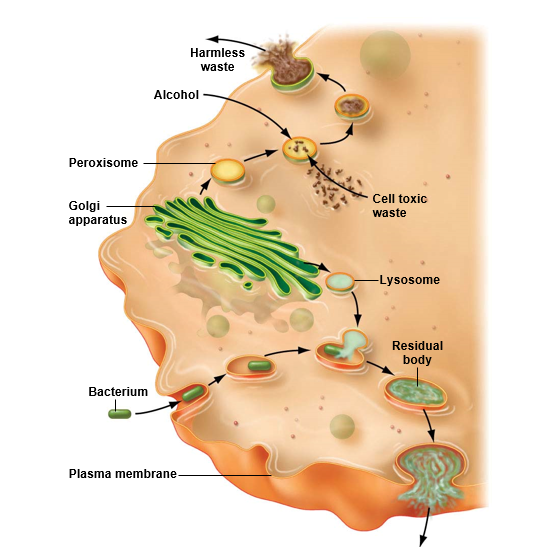
What are the 4 types of vesicles & what do they contain?
**Secretory** vesicles
* contain products destined for export from the cell
**Endocytic** vesicles
* contain substances imported from the external environment
**Peroxisomes**
* contain enzymes that detoxify wastes produced by the cell
**Lysosomes**
* contain digestive enzymes
* contain products destined for export from the cell
**Endocytic** vesicles
* contain substances imported from the external environment
**Peroxisomes**
* contain enzymes that detoxify wastes produced by the cell
**Lysosomes**
* contain digestive enzymes
15
New cards
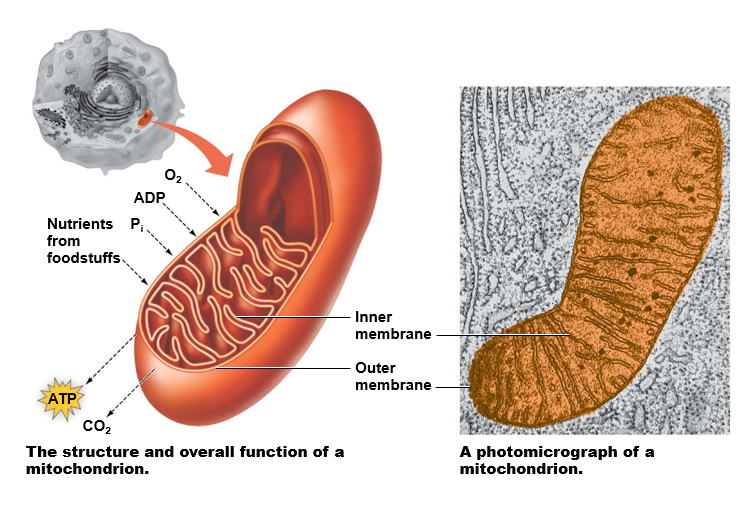
What’s the function of the mitochondrion & how is it structured?
Provides energy
* ‘power plant’ of the cell
Number of mitochondria within cell varies with cell’s energy requirement
Site of cellular respiration
* utilizes O2
* produces CO2
Generates ATP
\
Structure
* surrounded by double membrane
* inner membrane is highly folded
* ‘power plant’ of the cell
Number of mitochondria within cell varies with cell’s energy requirement
Site of cellular respiration
* utilizes O2
* produces CO2
Generates ATP
\
Structure
* surrounded by double membrane
* inner membrane is highly folded
16
New cards
What are the sources of energy?
Fat
* triglycerides
* **long-term** energy storage in animals
\
Glycogen
* carbohydrate storage
* **short-term** energy storage in animals
* stored in muscle & liver cells
* triglycerides
* **long-term** energy storage in animals
\
Glycogen
* carbohydrate storage
* **short-term** energy storage in animals
* stored in muscle & liver cells
17
New cards
What structures give cells support & enable movement?
Cytoskeleton
* internal scaffolding helps maintain cell shape
Enable movement
* cilia
* flagella
* centrioles
* internal scaffolding helps maintain cell shape
Enable movement
* cilia
* flagella
* centrioles
18
New cards
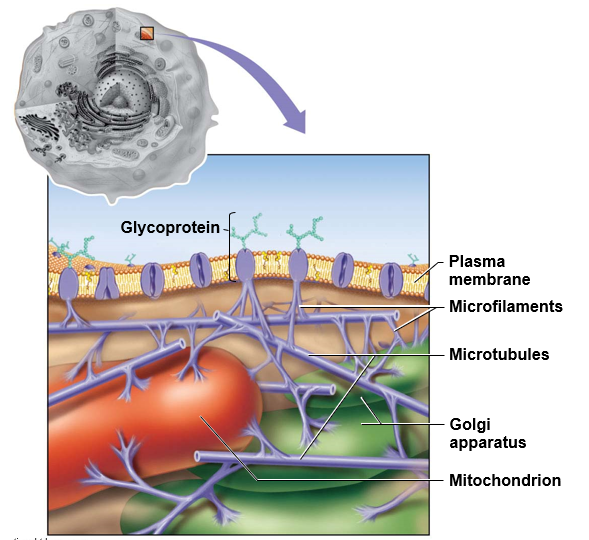
What is the cytoskeleton made of & what are the functions?
Microtubules
* tiny hollow tubes of protein
Microfilaments
* thin solid fibers of protein
\
Microtubules & -filaments form framework that supports cell
Cytoskeleton also supports & anchors other cellular structures
* some proteins from membrane bound to cytoskeleton
* tiny hollow tubes of protein
Microfilaments
* thin solid fibers of protein
\
Microtubules & -filaments form framework that supports cell
Cytoskeleton also supports & anchors other cellular structures
* some proteins from membrane bound to cytoskeleton
19
New cards
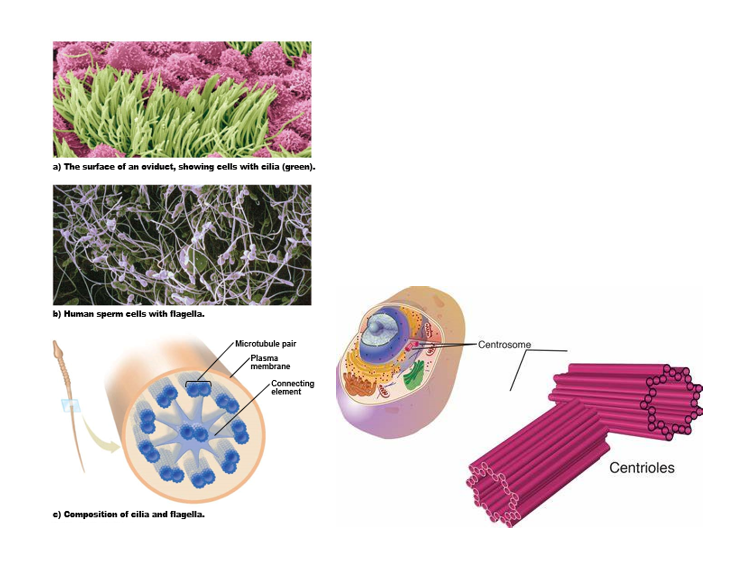
How are cilia, flagella & centrioles structured & what are their functions?
Cilia
* short, many
* found on cells lining airways
\
Flagella
* long, single
* similar internal structure to cilia
* enable spermatozoa to swim
\
Centrioles
* short rod-like microtubular structures near nucleus
* play important role in cell division
* short, many
* found on cells lining airways
\
Flagella
* long, single
* similar internal structure to cilia
* enable spermatozoa to swim
\
Centrioles
* short rod-like microtubular structures near nucleus
* play important role in cell division
20
New cards
What’s the function of the plasma membrane?
Separates cell from its environment
Selectively permeable
* permits movement of some substances into & out of cell
* blocks others
Enables transfer of information between environment & cell
Selectively permeable
* permits movement of some substances into & out of cell
* blocks others
Enables transfer of information between environment & cell
21
New cards
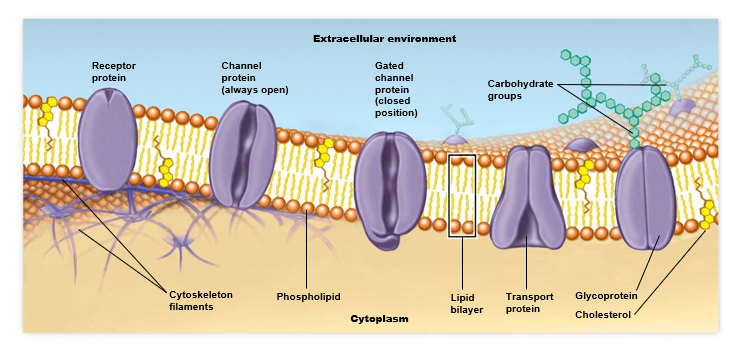
How is a plasma membrane structured?
= Lipid bilayer
* **phospholipids**: polar head & nonpolar tail
* **cholesterol**: makes membrane more rigid
* **proteins**: provide means of transport through membrane
* **carbohydrates**: recognition patterns for cells & organisms, provide communication system for outside of cell
Non-rigid
Fluid mosaic
* **phospholipids**: polar head & nonpolar tail
* **cholesterol**: makes membrane more rigid
* **proteins**: provide means of transport through membrane
* **carbohydrates**: recognition patterns for cells & organisms, provide communication system for outside of cell
Non-rigid
Fluid mosaic
22
New cards
What types of transport are there for molecules crossing the plasma membrane?
Passive transport: cell doesn’t need to expend energy for this
* diffusion
* osmosis
\
Active transport: cell must expend energy
\
Bulk transport: involves membranous vesicles to move larger substances
* endocytosis
* exocytosis
* diffusion
* osmosis
\
Active transport: cell must expend energy
\
Bulk transport: involves membranous vesicles to move larger substances
* endocytosis
* exocytosis
23
New cards
What is passive transport & how does it work?
Transports substance without having to expend energy
Relies on diffusion
High concentration → low concentration
‘Down’ the gradient
Relies on diffusion
High concentration → low concentration
‘Down’ the gradient
24
New cards
What is diffusion?
Movement of molecules from e region of high concentration to a region of low concentration
25
New cards
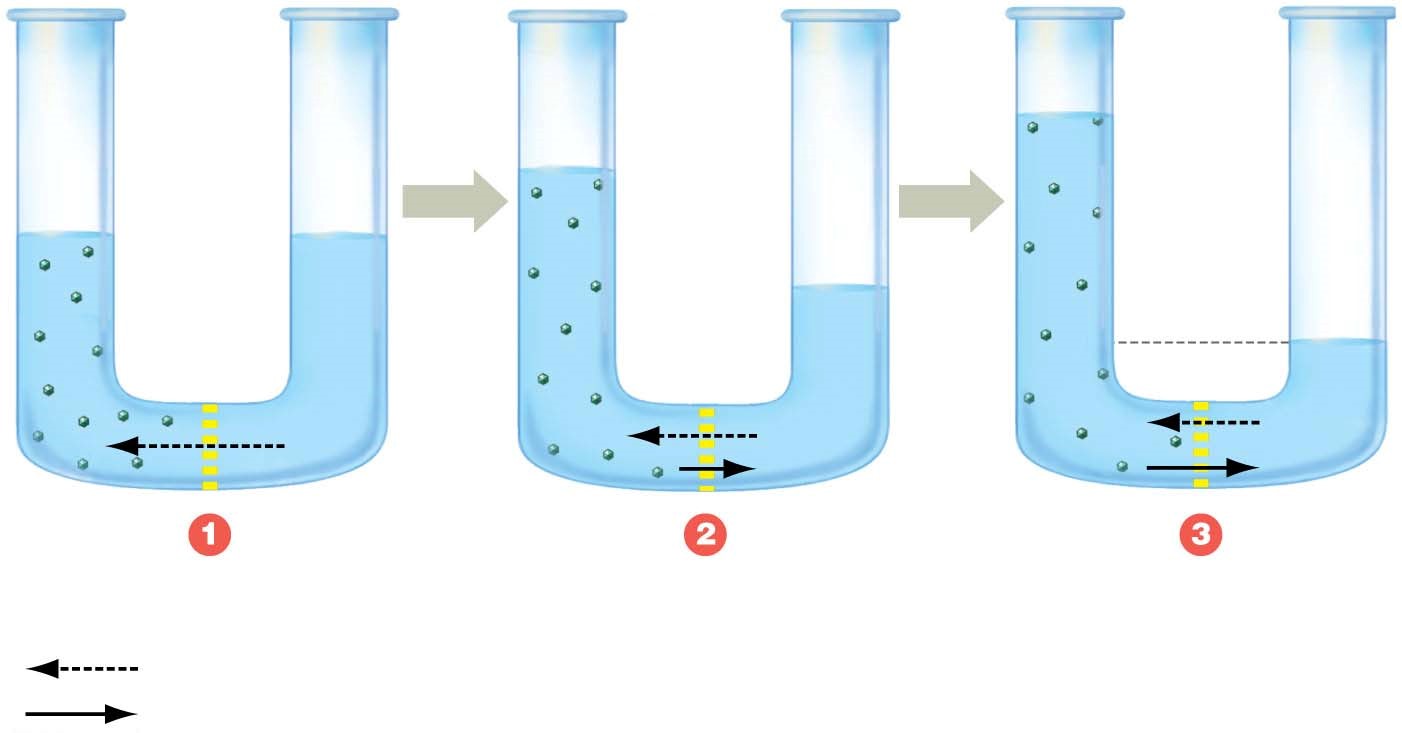
What is osmosis?
Diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane
Water moves from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration
Water moves from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration
26
New cards
What is osmotic pressure?
Fluid pressure required to exactly oppose osmosis
27
New cards
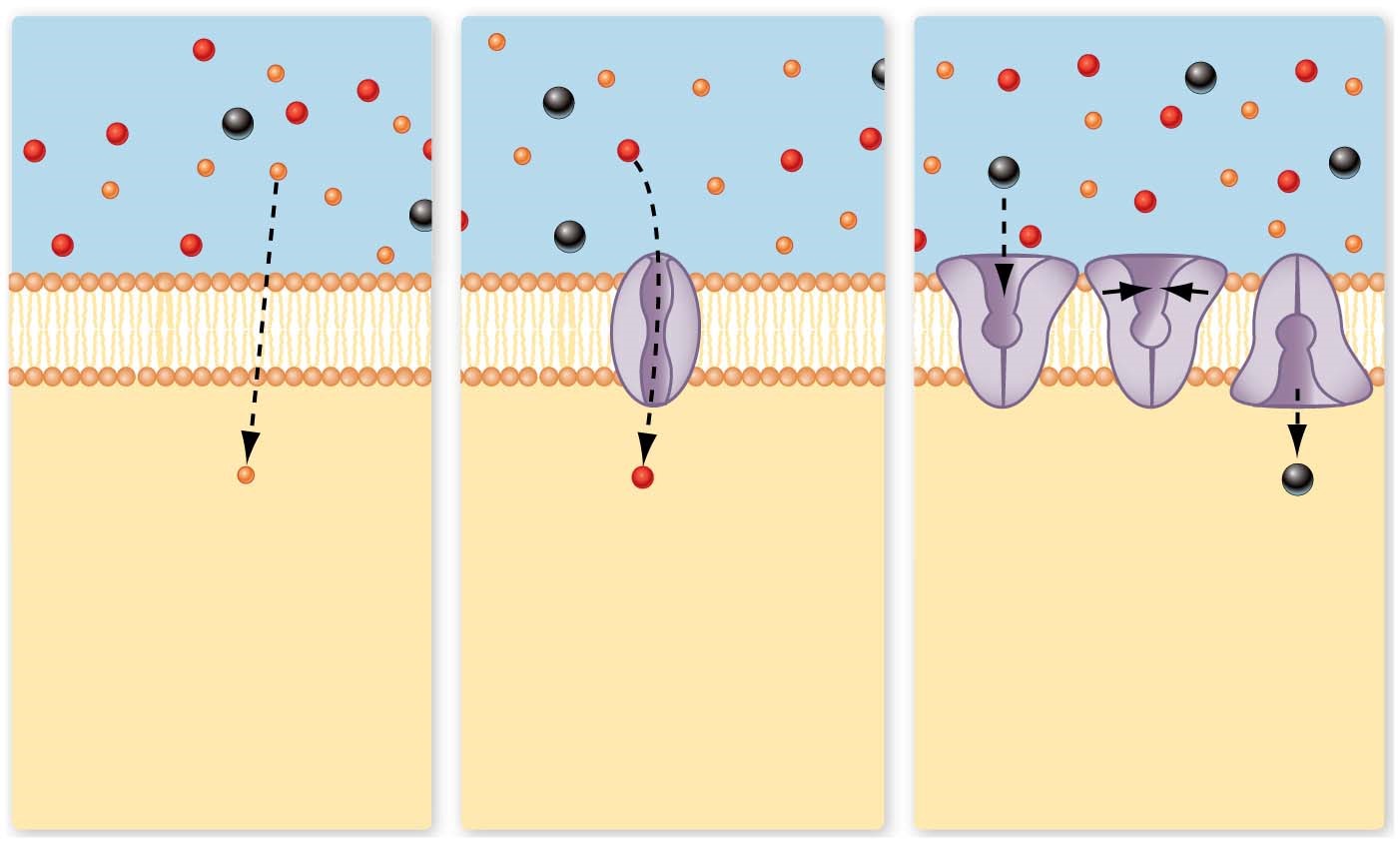
What are the 3 forms of passive transport?
Directly through lipid bilayer
* small uncharged nonpolar molecules
Through protein channels in bilayer
* some always open, others ‘gated’
Facilitated transport
* membrane transport protein changes shape & transports molecule through bilayer
* highly specific
* eg. glucose
* small uncharged nonpolar molecules
Through protein channels in bilayer
* some always open, others ‘gated’
Facilitated transport
* membrane transport protein changes shape & transports molecule through bilayer
* highly specific
* eg. glucose
28
New cards
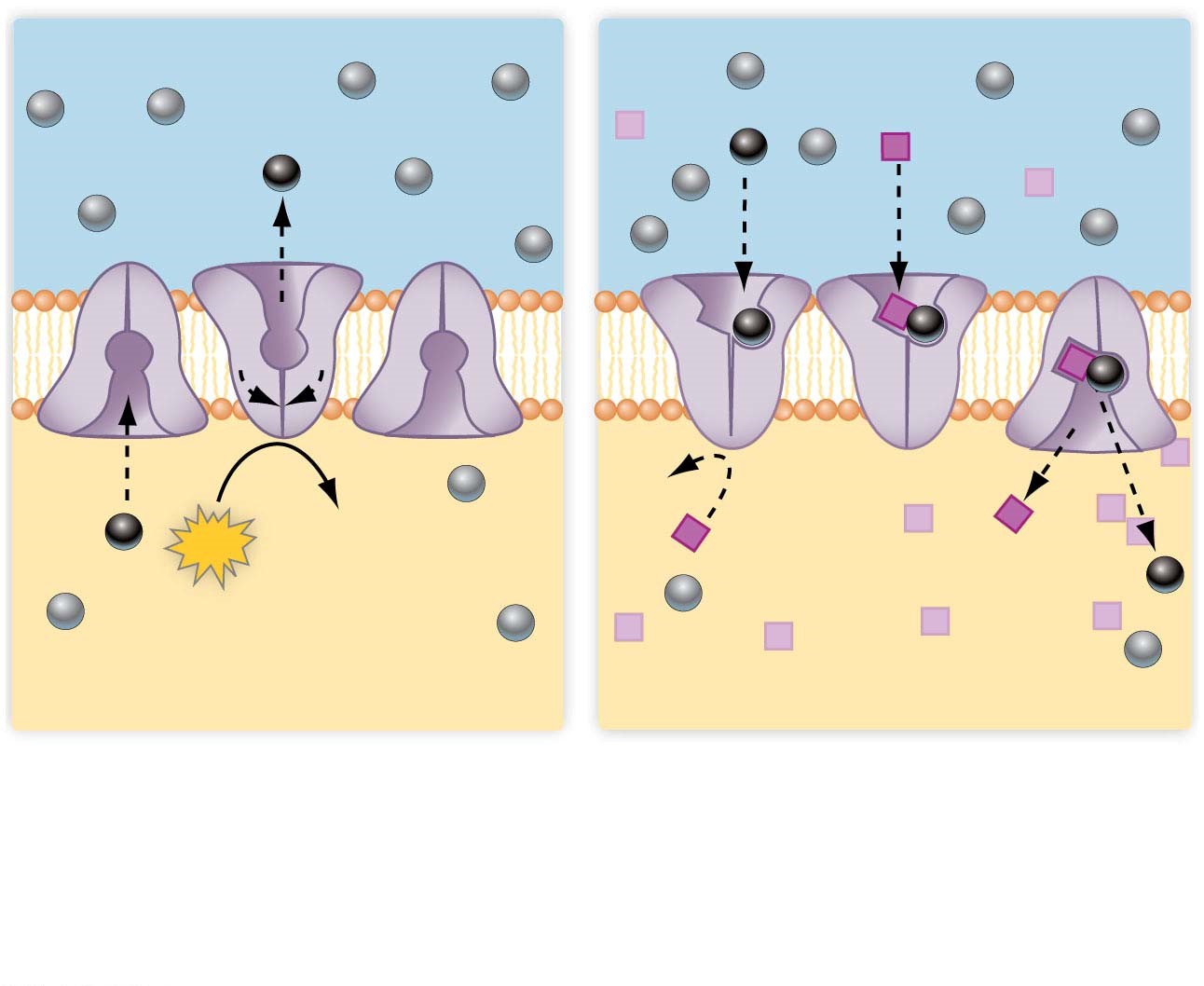
How does active transport work?
Moves substance from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration
* transported substance moves against concentration gradient
* transported substance moves against concentration gradient
29
New cards
What does active transport require?
Membrane protein (transporter) & ATP or other energy source
30
New cards
What is bulk transport used for?
Used to move larger molecules
31
New cards
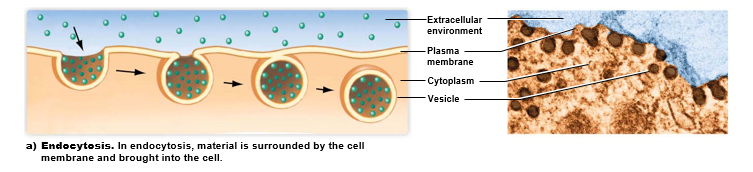
What is endocytosis?
Brings substances into cell
* as substance enters, it’s surrounded by a membrane, forming a membrane-bound vesicle
* as substance enters, it’s surrounded by a membrane, forming a membrane-bound vesicle
32
New cards
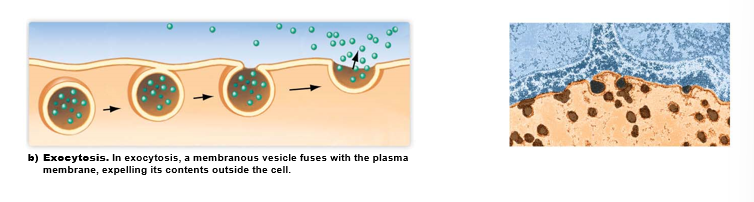
What is exocytosis?
Expels substances from the cell
* substance contained within membranous vesicle, which then fuses with the membrane, releasing the substance to the external environment
* substance contained within membranous vesicle, which then fuses with the membrane, releasing the substance to the external environment
33
New cards
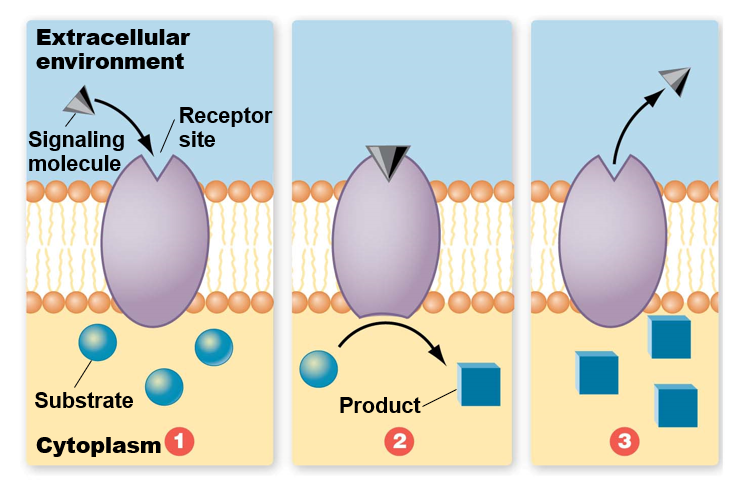
How is information transferred across plasma membrane?
Receptor proteins span membrane
* required for transmission of information to & from cell
Receptor sites (on receptor proteins) interact specifically with signal molecules
Change is triggered within cell as result of binding of signal molecule to receptor site
Different cell types have different receptor proteins
* required for transmission of information to & from cell
Receptor sites (on receptor proteins) interact specifically with signal molecules
Change is triggered within cell as result of binding of signal molecule to receptor site
Different cell types have different receptor proteins
34
New cards
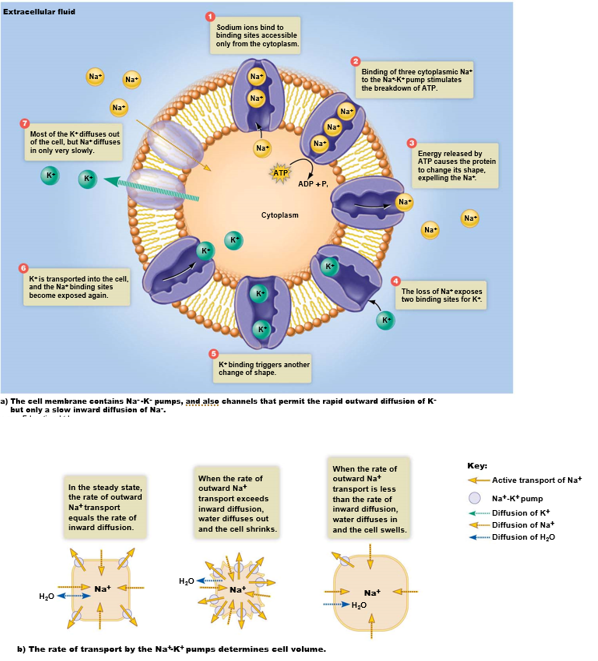
What does the Sodium-Kotassium pump do?
Expels unwanted ions, stockpiles needed ones & maintains cell volume
ATP is used to expel 3 Na+ for every 2 K+ brought into the cell
ATP is used to expel 3 Na+ for every 2 K+ brought into the cell
35
New cards
What is happening when the cell volume is increasing?
More water in cytoplasm, accomplished by **decreasing** pumping & allowing more sodium inside cell
36
New cards
What is happening when the cell volume is decreasing?
Less water in cytoplasm, accomplished by **increasing** pumping & expelling more sodium ions
37
New cards
What else maintains cell volume?
Isotonic extracellular fluid
38
New cards
What is tonicity & what are the different types?
= Relative concentration of solutes in 2 fluids
Isotonic
Hypertonic
Hypotonic
Isotonic
Hypertonic
Hypotonic
39
New cards
What are characteristics of isotonic extracellular fluids?
Extra- & intracellular solute concentrations are **equal**
Cells maintain normal volume
Regulatory mechanisms maintain extracellular fluid that is isotonic with intracellular fluid
Cells maintain normal volume
Regulatory mechanisms maintain extracellular fluid that is isotonic with intracellular fluid
40
New cards
What happens to the cell volume when extracellular fluids are HYPERtonic?
Extracellular solute concentration **higher** than intracellular solute concentration
Water will diffuse out of cell
Cell may shrink & die
Water will diffuse out of cell
Cell may shrink & die
41
New cards
What happens to the cell volume when extracellular fluids are HYPOtonic?
Extracellular solute concentration lower than intracellular solute concentration
Water will diffuse into cell
Cell may swell & burst
That’s why we don’t inject people with pure water
Water will diffuse into cell
Cell may swell & burst
That’s why we don’t inject people with pure water
42
New cards
What is the metabolism?
Sum of all chemical reactions in an organism
43
New cards
What are the 2 types of metabolic pathways?
Anabolism
* larger molecules assembled from smaller ones
* requires energy (ATP input)
\
Catabolism
* larger molecules broken down
* releases energy (ATP output)
* larger molecules assembled from smaller ones
* requires energy (ATP input)
\
Catabolism
* larger molecules broken down
* releases energy (ATP output)
44
New cards
What do chemical reactions/metabolical activities require?
Specific enzyme
A lot of energy
* often provided by catabolism of ATP
* ATP
A lot of energy
* often provided by catabolism of ATP
* ATP
45
New cards
What is glucose used for? Link this with ATP
Provides cell with energy
Energy in glucose used to generate ATP
* 1 glucose molecule → 36 ATP
Absence of glucose → other carbohydrates, fats & proteins can be catabolized to generate ATP
ATP = more readily used ‘pocket change’ form of energy
Glucose & other fuel molecules must be ‘cashed in’ for ATP
ATP can then be used to do cellular work
Energy in glucose used to generate ATP
* 1 glucose molecule → 36 ATP
Absence of glucose → other carbohydrates, fats & proteins can be catabolized to generate ATP
ATP = more readily used ‘pocket change’ form of energy
Glucose & other fuel molecules must be ‘cashed in’ for ATP
ATP can then be used to do cellular work
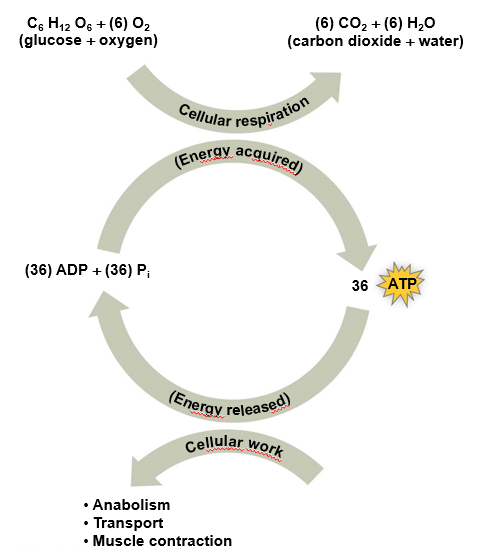
46
New cards
What is cellular respiration?
Breakdown of glucose in the presence of **oxygen** to yield ATP
Cellular process that uses O2 & produces CO2 in process of making ATP
Cellular process that uses O2 & produces CO2 in process of making ATP
47
New cards
What are the 4 stages of cellular respiration?
1. Glycolysis
2. Preparatory step
3. Citric acid cycle
4. Electron transport system
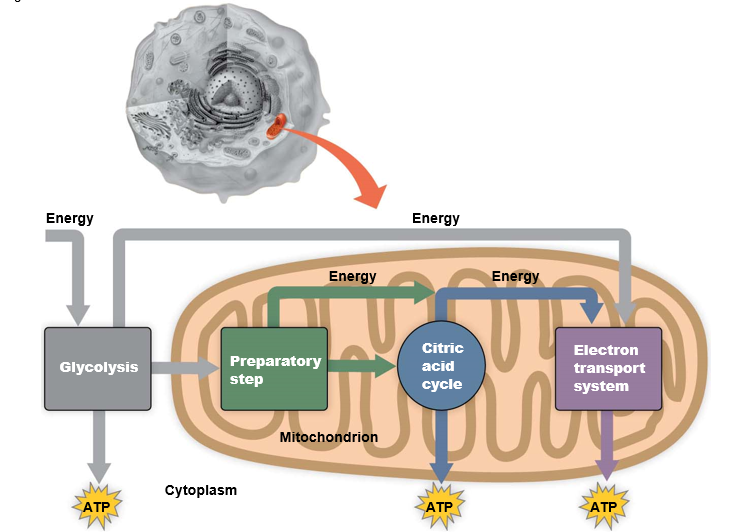
48
New cards
What happens during glycolysis?
Occurs in **cytoplasm**
Series of 10 reactions that **split** glucose into 2 molecules of **pyruvic acid (pyruvate)**
Requires investment of 2 ATP; 4 ATP produced
* netto ATP yield: 2
High-energy electrons & hydrogen ions removed & picked up by coenzyme NAD+
→ NADH formed
Later in process, NADH used to generate additional ATP
Series of 10 reactions that **split** glucose into 2 molecules of **pyruvic acid (pyruvate)**
Requires investment of 2 ATP; 4 ATP produced
* netto ATP yield: 2
High-energy electrons & hydrogen ions removed & picked up by coenzyme NAD+
→ NADH formed
Later in process, NADH used to generate additional ATP
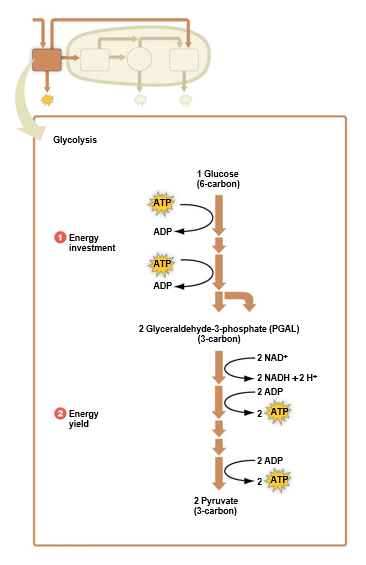
49
New cards
What happens during the preparatory step?
Pyruvate
* enters mitochondria
* converted to **acetyl group** & CO2
High-energy electrons & hydrogen ions removed & picked up by coenzyme NAD+
→ NADH formed
Acetyl group joined to coenzyme A to form **acetyl CoA**
Acetyl CoA will enter citric acid cycle
* enters mitochondria
* converted to **acetyl group** & CO2
High-energy electrons & hydrogen ions removed & picked up by coenzyme NAD+
→ NADH formed
Acetyl group joined to coenzyme A to form **acetyl CoA**
Acetyl CoA will enter citric acid cycle
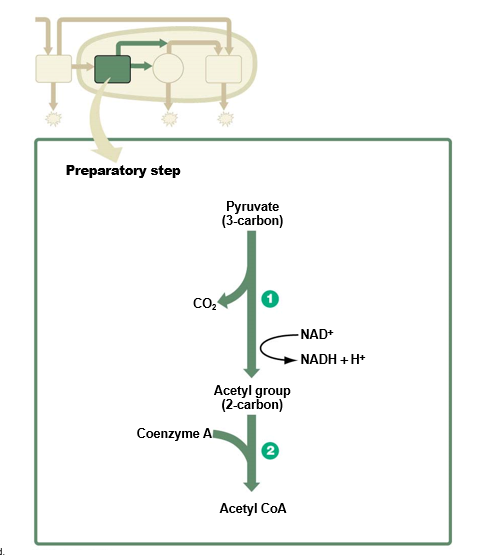
50
New cards
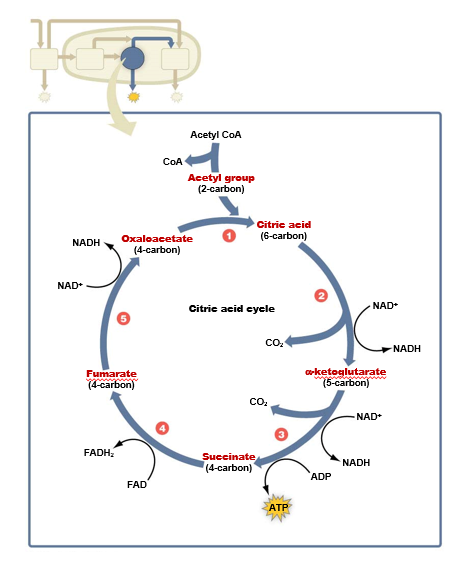
What happens during the citric acid cycle?
Occurs in **mitochondria**
Cyclic series of **8** reactions which **break down acetyl CoA**
Molecule that accepts acetyl CoA regenerated at the end of 1 full turn of the cycle
High-energy electrons extracted to form **NADH & FADH2**
Produces **2 ATP & 4 CO2** per glucose molecule
Cyclic series of **8** reactions which **break down acetyl CoA**
Molecule that accepts acetyl CoA regenerated at the end of 1 full turn of the cycle
High-energy electrons extracted to form **NADH & FADH2**
Produces **2 ATP & 4 CO2** per glucose molecule
51
New cards
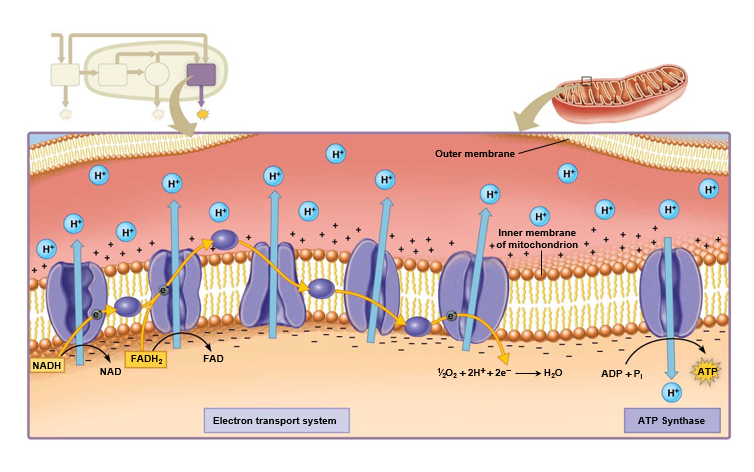
What does the electron transport system do?
Located in **inner mitochondrial membrane**
Takes electrons from NADH & FADH2
Movement of electrons from 1 electron carrier to the next **releases** energy to **generate ATP**
Final electron acceptor: O2
* forms water upon receiving electrons & hydrogen ions
* more hydrogen ions on one side = diffusion process
ATP generated by ATP **synthase enzyme**
* diffusion force by enzyme & stream of hydrogen ions used to produce ATP
Takes electrons from NADH & FADH2
Movement of electrons from 1 electron carrier to the next **releases** energy to **generate ATP**
Final electron acceptor: O2
* forms water upon receiving electrons & hydrogen ions
* more hydrogen ions on one side = diffusion process
ATP generated by ATP **synthase enzyme**
* diffusion force by enzyme & stream of hydrogen ions used to produce ATP
52
New cards
What’s the electron transport system process also known as?
Oxidative phosphorylation
53
New cards
How many **different enzyme-catalyzed reactions** take place during the energy production from glucose?
Over 20
54
New cards
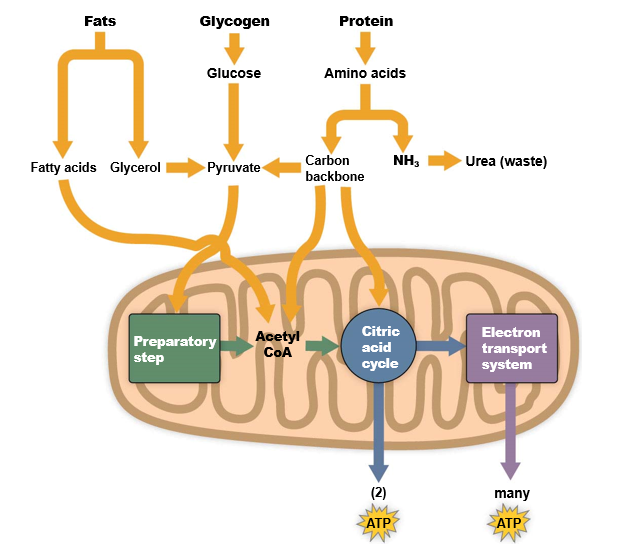
What are the additional energy sources?
__Fats__
* 78% of total energy reserves
* **triglycerides** have **twice** the energy of carbohydrates
\
__Proteins__
* 21% of total energy reserves
* same amount of energy as carbohydrates
\
__Glycogen__ (storage form of glucose)
* 1% of total energy reserves
* can be quickly catabolized to glucose, which then participates in cellular respiration
* 78% of total energy reserves
* **triglycerides** have **twice** the energy of carbohydrates
\
__Proteins__
* 21% of total energy reserves
* same amount of energy as carbohydrates
\
__Glycogen__ (storage form of glucose)
* 1% of total energy reserves
* can be quickly catabolized to glucose, which then participates in cellular respiration
55
New cards
What are the functions of **anaerobic pathways**?
Make energy available **without** oxygen
* cellular respiration cannot continue without O2
* happens when blood can’t catch up with intense labor
* glycolysis will continue, pyruvate will build up
* **lactic acid** buildup in muscles → burning sensation → muscle ache
* 2 ATP produced per glucose molecule
When O2 available, lactic acid metabolized aerobically
* cellular respiration cannot continue without O2
* happens when blood can’t catch up with intense labor
* glycolysis will continue, pyruvate will build up
* **lactic acid** buildup in muscles → burning sensation → muscle ache
* 2 ATP produced per glucose molecule
When O2 available, lactic acid metabolized aerobically