mastering biology chapter 4
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/132
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
133 Terms
1
New cards
cell theory
-all living things are composed of cells
-cells are the basic units of structure & function in living things
-new cells are produced from existing cells
-cells are the basic units of structure & function in living things
-new cells are produced from existing cells
2
New cards
cell
-basic unit of structure and function in living things
-constantly in motion
-all cells contain chromosomes & ribosomes
-the cytoplasm is the interior of all cells
-between 1 & 100 micrometers (µm) in length
-constantly in motion
-all cells contain chromosomes & ribosomes
-the cytoplasm is the interior of all cells
-between 1 & 100 micrometers (µm) in length
3
New cards
Robert Hooke
-used a crude microscope to study a piece of cork
-compared the structures he saw to "little rooms" (cellulae)
-coined the term "cell"
-compared the structures he saw to "little rooms" (cellulae)
-coined the term "cell"
4
New cards
Cellulae
"little rooms"
5
New cards
Antoni van Leeuwenhoek
-discovered bacteria using the microscope
-his reports to the Royal Society of London included drawings & descriptions of his discoveries
-his reports to the Royal Society of London included drawings & descriptions of his discoveries
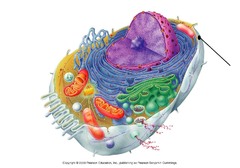
6
New cards
Magnification
An increase in the apparent size of an object
7
New cards
micrograph
A photograph taken through a microscope.
8
New cards
resolution
-A measure of the clarity of an image
-The ability to see two objects as separate
-The ability to see two objects as separate
9
New cards
light microscope
-Visible light passes through specimen (microorganism/thin slice of animal or plant tissue) through glass lenses
-Lenses bend light so that the image of specimen is magnified as it is projected into eye/camera
-Can effectively magnify objects up to 1,000 times
-Cannot resolve detail finer than 2 micrometers (µm)
-Lenses bend light so that the image of specimen is magnified as it is projected into eye/camera
-Can effectively magnify objects up to 1,000 times
-Cannot resolve detail finer than 2 micrometers (µm)
10
New cards
electron microscope
-Focuses a beam of electrons through a specimen or onto its surface
-Can distinguish biological structures as small as 2 nanometers (nm)
-Cannot study living specimens, as the methods to prepare the specimen kills the cells
-Can distinguish biological structures as small as 2 nanometers (nm)
-Cannot study living specimens, as the methods to prepare the specimen kills the cells
11
New cards
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
-An electron microscope used to study cell surfaces
-Uses an electron beam to scan the surface of a cell, exciting the electrons
-Surface is usually coated by a thin film of gold
-Electrons are detected by a device to translate their pattern onto an image projected onto a video screen
-Produces images that look 3D
-Uses an electron beam to scan the surface of a cell, exciting the electrons
-Surface is usually coated by a thin film of gold
-Electrons are detected by a device to translate their pattern onto an image projected onto a video screen
-Produces images that look 3D
12
New cards
Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
-An electron microscope used to study cell ultrastructure
-Aims an electron beam through a very thin section of the specimen
-Section is stained w/ atoms of heavy metals
-Electrons are scattered by the more dense parts, creating an image by the pattern of the transmitted electrons
-Electromagnets bend the paths of electrons, magnifying & focusing an image onto a viewing screen/photographic film
-Aims an electron beam through a very thin section of the specimen
-Section is stained w/ atoms of heavy metals
-Electrons are scattered by the more dense parts, creating an image by the pattern of the transmitted electrons
-Electromagnets bend the paths of electrons, magnifying & focusing an image onto a viewing screen/photographic film
13
New cards
cell ultrastructure
cellular anatomy revealed by an electron microscope
14
New cards
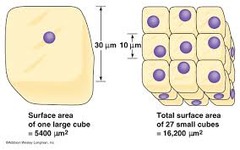
surface-to-volume ratio
-Amount of surface area per unit volume
-Smaller cells have a greater SA:V ratio, allowing for greater efficiency in diffusion & transport of nutrients across the cell's surface
-Smaller cells have a greater SA:V ratio, allowing for greater efficiency in diffusion & transport of nutrients across the cell's surface
15
New cards
cell diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
16
New cards
plasma membrane
-A thin, flexible boundary between a living cell and its surroundings
-Regulates the flow of material in and out of a cell
-Some proteins form tunnels that shield ions & polar molecules as they pass through the interior
-Regulates the flow of material in and out of a cell
-Some proteins form tunnels that shield ions & polar molecules as they pass through the interior
17
New cards
Fusion of a Transport Vesicle (Golgi) w/ the Plasma Membrane
-the contents of the transport vesicle are secreted from the cell
-the membrane of the transport vesicle is added to the plasma membrane
-the membrane of the transport vesicle is added to the plasma membrane
18
New cards
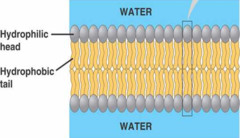
phospholipid bilayer
-A two-layer sheet of phospholipid molecules
-Composed of 2 regions
-Head w/ negatively charged phosphate group
-2 non-polar fatty acid tails
-Non-polar molecules can move across the hydrophobic interior
-Composed of 2 regions
-Head w/ negatively charged phosphate group
-2 non-polar fatty acid tails
-Non-polar molecules can move across the hydrophobic interior
19
New cards
head w/ negatively charged phosphate group
-hydrophilic
-faces outward, exposed to aqueous solutions on both sides of the membrane
-faces outward, exposed to aqueous solutions on both sides of the membrane
20
New cards
non-polar fatty acid tails
-hydrophobic
-faces inward, mingling together and shielded away from the aqueous solutions
-embeds proteins
-faces inward, mingling together and shielded away from the aqueous solutions
-embeds proteins
21
New cards
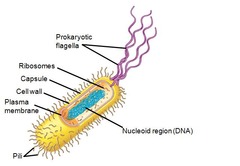
prokaryotic cells
-cells that do not have a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles.
-evolved before eukaryotic cells
-evolved before eukaryotic cells
22
New cards
Prokaryote
"before nucleus"
23
New cards
examples of prokaryotes
-bacteria
-archaea
-archaea
24
New cards
eukaryotic cells
cells that contain a membrane-enclosed nucleus & other membrane-bound organelles
25
New cards
Eukaryote
"true nucleus"
26
New cards
examples of eukaryotes
-protists
-fungi
-plants
-animals
-fungi
-plants
-animals
27
New cards
Frimbriae
attachment structures on the surface of some prokaryotes
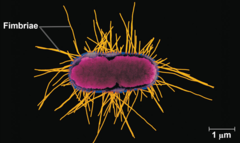
28
New cards
chromosomes
threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain the genes
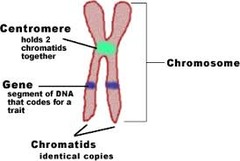
29
New cards
chromatin
-Clusters of DNA, RNA, & proteins in the nucleus of a cell
-Before cell division, chromatin fibers coil up, becoming thick enough to be visible by a light microscope
-Before cell division, chromatin fibers coil up, becoming thick enough to be visible by a light microscope
30
New cards
ribosomes
-Synthesizes polypeptides (proteins) according to instructions from the nucleus
-Can be free/bound
-Can be free/bound
31
New cards
free ribosomes
-Suspended in the fluid of the cytoplasm
-Most proteins made on free ribosomes function within the cytoplasm
-Most proteins made on free ribosomes function within the cytoplasm
32
New cards
bound ribosomes
-Attached to the outside of the endoplasmic reticulum/nuclear envelope
-Synthesizes proteins that could be inserted in the growing ER membrane, transported to other organelles, or secreted by the cell
-Synthesizes proteins that could be inserted in the growing ER membrane, transported to other organelles, or secreted by the cell
33
New cards
cytoplasm
-Jelly-like fluid inside the cell that suspends the organelles
-Only refers to the region between the nucleus and plasma membrane in prokaryotic cells
-Only refers to the region between the nucleus and plasma membrane in prokaryotic cells
34
New cards
nucleoid
-A dense region of DNA in a prokaryotic cell
-Not surrounded by a membrane
-"Nucleus-like"
-Not surrounded by a membrane
-"Nucleus-like"
35
New cards
nucleus
-Control center of the cell
-Houses most of cell's DNA
-Directs protein synthesis to organize/coil DNA
-Replicates DNA
-Synthesizes RNA (rRNA & mRNA)
-Houses most of cell's DNA
-Directs protein synthesis to organize/coil DNA
-Replicates DNA
-Synthesizes RNA (rRNA & mRNA)
36
New cards
DNA
-deoxyribonucleic acid
-associated w/ chromosome proteins
-associated w/ chromosome proteins
37
New cards
RNA
ribonucleic acid
38
New cards
types of RNA
-messenger RNA (mRNA)
-ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
-transfer RNA (tRNA)
-ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
-transfer RNA (tRNA)
39
New cards
messenger RNA (mRNA)
-Carries instructions from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosomes
-Moves through the pores in the nuclear envelope to the cytoplasm
-Is translated by the ribosomes in the cytoplasm into the amino acid sequence of proteins
-Moves through the pores in the nuclear envelope to the cytoplasm
-Is translated by the ribosomes in the cytoplasm into the amino acid sequence of proteins
40
New cards
ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
makes up part of the ribosome
41
New cards
transfer RNA (tRNA)
carries amino acids to the ribosome
42
New cards
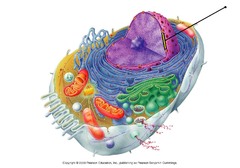
nuclear envelope
-Double membrane that encloses the nucleus of a cell
-Each membrane is a phospholipid bilayer w/ associated proteins
-Controls flow of material in & out of the nucleus
-Perforated w/ protein-lined pores
-Each membrane is a phospholipid bilayer w/ associated proteins
-Controls flow of material in & out of the nucleus
-Perforated w/ protein-lined pores
43
New cards
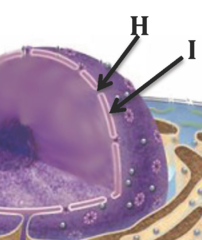
protein-lined pores (nuclear pores)
-Small holes in the nuclear envelope
-Regulates the movement of molecules in the nucleus
-Connects the nucleus w/ the ER
-Regulates the movement of molecules in the nucleus
-Connects the nucleus w/ the ER
44
New cards
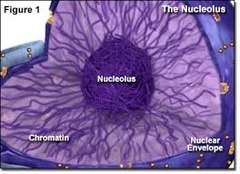
Nucleolus
-Found inside the nucleus
-Synthesizes rRNA according to DNA instructions
-Assembles ribosomal subunits
-Synthesizes rRNA according to DNA instructions
-Assembles ribosomal subunits
45
New cards
step 1 of ribosomal subunit synthesis
Proteins brought in through nuclear pores of the cytoplasm are assembled w/ nucleolus rRNA, forming ribosomal subunits
46
New cards
step 2 of ribosomal subunit synthesis
Subunits then exit through the pores of the cytoplasm, joining to form functional ribosomes
47
New cards
capsule
jelly-like outer coating of prokaryotes
48
New cards
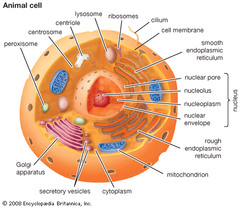
organelles
-"Little Organs"
-Cellular structures that perform specific functions
-Each bounded by a membrane in eukaryotes
-Enzymes essential for metabolic processes are built into the membrane
-Cellular structures that perform specific functions
-Each bounded by a membrane in eukaryotes
-Enzymes essential for metabolic processes are built into the membrane
49
New cards
fluid-filled spaces in organelles
-Maintains chemical conditions
-Chemical conditions vary among organelles
-Chemical conditions vary among organelles
50
New cards
cellular metabolism
All the chemical activities of all the organelles in a cell
51
New cards
1st basic functional group
Nucleus & ribosomes carry out genetic control of the cell
52
New cards
2nd basic functional group
Golgi apparatus; lysosomes; peroxisomes; & vacuoles function in the manufacture, distribution, & breakdown of molecules
53
New cards
3rd basic functional group
Mitochondria in all cells & chloroplasts in plants function in energy processing
54
New cards
4th basic functional group
Cytoskeleton; plasma membrane; & plant cell wall function in the structural support, movement, & communication between cells
55
New cards
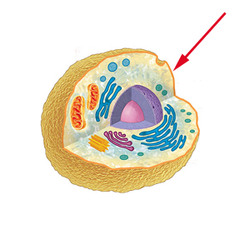
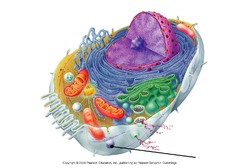
animal cell
eukaryotic cells that contain lysosomes & centrioles not found in plant cells
56
New cards
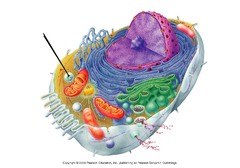
lysosome
-"Breakdown Body"
-A membranous sac of digestive enzymes contained in an acidic environment
-Enzymes & membranes are made by rough ER & processed in the Golgi
-Protists engulf food particles into vacuoles
-Lysosomes fuse & digest food vacuoles, releasing the nutrients in the cell fluid
-Digests damaged organelles, bacteria, macromolecules
-Serves as recycling centers in animal cells
-A membranous sac of digestive enzymes contained in an acidic environment
-Enzymes & membranes are made by rough ER & processed in the Golgi
-Protists engulf food particles into vacuoles
-Lysosomes fuse & digest food vacuoles, releasing the nutrients in the cell fluid
-Digests damaged organelles, bacteria, macromolecules
-Serves as recycling centers in animal cells
57
New cards
hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) production & degradation in lysosomes
-Enzymes transfer hydrogen from various compounds to oxygen, producing hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) as a byproduct
-Other enzymes convert this to water, degrading H2O2
-Other enzymes convert this to water, degrading H2O2
58
New cards
step 1 of the lysosome recycling process
Damaged organelles/small amounts of cell fluid become surrounded by a membrane
59
New cards
step 2 of the lysosome recycling process
A lysosome fuses w/ such vesicle, dismantling its contents, & making organic molecules for reuse
60
New cards
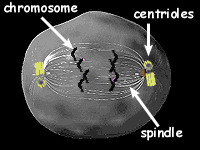
Centriole
-Helps organize cell division in animal cells
-Found in the microtubule-organizing center
-Found in the microtubule-organizing center
61
New cards
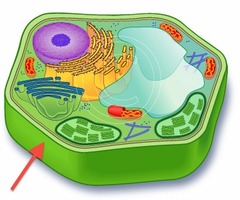
plant cell
-Eukaryotic cells that contain a cell wall, chloroplast, plasmodesmata, & central vacuole not found in animal cells
-Pectins glue adjacent plant cells together
-Pectins glue adjacent plant cells together
62
New cards
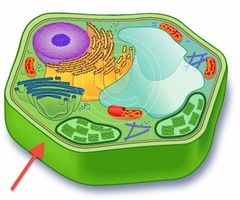
cell wall
-A rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants & some other organisms.
-Consists of cellulose fibers embedded in polysaccharides & proteins
-Functions as skeletal support, keeping plants upright on land
-Protects the cells
-Binds cells in tissues
-Consists of cellulose fibers embedded in polysaccharides & proteins
-Functions as skeletal support, keeping plants upright on land
-Protects the cells
-Binds cells in tissues
63
New cards
cell wall construction
-Plant cells initially lay down a thin, flexible primary cell wall that allows the cell to continue to enlarge
-Some cells add a secondary cell wall, deposited in layers
-Construction is similar to that of fiber glass
-Some cells add a secondary cell wall, deposited in layers
-Construction is similar to that of fiber glass
64
New cards
chloroplast
-Photosynthetic organelle of plants & algae
-Enclosed by an inner & outer membrane
-Membranes are separated by an intermembrane space
-Inner membrane holds the stroma
-Holds thylakoids, a circular DNA molecule, & ribosomes
-Enclosed by an inner & outer membrane
-Membranes are separated by an intermembrane space
-Inner membrane holds the stroma
-Holds thylakoids, a circular DNA molecule, & ribosomes
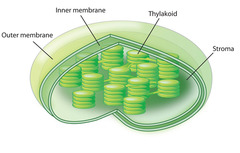
65
New cards
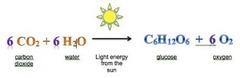
Photosynthesis
-Process in which light energy converts carbon dioxide & water into oxygen & glucose
66
New cards
stroma
thick fluid containing chloroplast DNA, ribosomes, & other enzymes
67
New cards
thylakoids
-Network of interconnected membrane sacs inside the chloroplast
-Converts light energy into chemical energy of glucose
-Converts light energy into chemical energy of glucose
68
New cards
thylakoid space
compartment inside thylakoid
69
New cards
granum (grana)
-stack of thylakoids
-green chlorophyll molecules embedded in the membrane trap solar energy
-green chlorophyll molecules embedded in the membrane trap solar energy
70
New cards
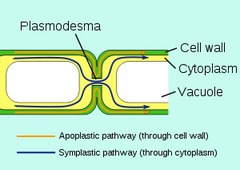
plasmodesma (plasmodesmata)
-Cytoplasmic channels through cell walls that connect adjacent cells
-Cytoplasm & plasma membrane extend through the plasmodesmata
-Allows plant tissue cells to share water, nourishment, & chemical messages
-Cytoplasm & plasma membrane extend through the plasmodesmata
-Allows plant tissue cells to share water, nourishment, & chemical messages
71
New cards
central vacuole
-Helps the cell grow in size by absorbing water, enlarging
-Stockpiles vital chemicals
-Acts as a trash can, safely storing toxic waste products
-Stockpiles vital chemicals
-Acts as a trash can, safely storing toxic waste products
72
New cards
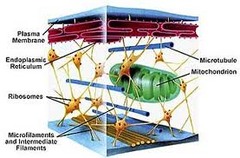
cytoskeleton
-A network of protein fibers that extend throughout the cytoplasm
-Aids in structural support, cell motility, & movement of organelles within cells
-Anchors organelles
-Includes microfilaments, microtubules, & intermediate filaments
-Aids in structural support, cell motility, & movement of organelles within cells
-Anchors organelles
-Includes microfilaments, microtubules, & intermediate filaments
73
New cards
structural support (cytoskeleton)
-Holds the cell together
-Helps the cell keep its shape
-Helps the cell keep its shape
74
New cards
cell motility
-Internal movement of cell parts
-Locomotion of the cell
-Requires the interaction of the cytoskeleton w/ motor proteins
-Locomotion of the cell
-Requires the interaction of the cytoskeleton w/ motor proteins
75
New cards
examples of cell motility
-Crawling
-Muscle contraction
-Bending of cilia & flagella
-Muscle contraction
-Bending of cilia & flagella
76
New cards
microfilaments (actin filaments)
-Thinnest
-Composed of solid rods of actin arranged in a Twisted Double Chain
-Microfilaments form a 3D network inside the plasma membrane to support cell shape
-Involved in cell movements
-Can disassemble & reassemble elsewhere
-Composed of solid rods of actin arranged in a Twisted Double Chain
-Microfilaments form a 3D network inside the plasma membrane to support cell shape
-Involved in cell movements
-Can disassemble & reassemble elsewhere
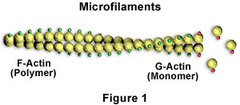
77
New cards
intermediate filaments
-In between thickness
-Composed of fibrous proteins that supercoil into thicker cables
-Reinforces cell shape
-Anchors certain organelles
-Holds the nucleus in place in a cage
-Are permanent fixtures in a cell
-Composed of fibrous proteins that supercoil into thicker cables
-Reinforces cell shape
-Anchors certain organelles
-Holds the nucleus in place in a cage
-Are permanent fixtures in a cell
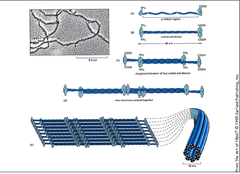
78
New cards
microtubules
-Thickest
-Are straight, hollow tubes composed of tubulins
-Elongates by the addition of tubulin proteins
-Shapes/supports cell
-Acts as tracks where organelles equipped w/ motor proteins can move
-Guides movement of chromosomes during cell division
-Are readily assembled in a reverse manner
-Are straight, hollow tubes composed of tubulins
-Elongates by the addition of tubulin proteins
-Shapes/supports cell
-Acts as tracks where organelles equipped w/ motor proteins can move
-Guides movement of chromosomes during cell division
-Are readily assembled in a reverse manner
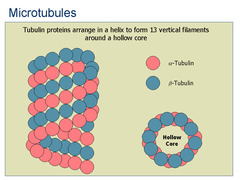
79
New cards
tubulins
-Globular proteins that make up microtubules
-Consists of 2 subunits
-Can be reused elsewhere in the cell
-Consists of 2 subunits
-Can be reused elsewhere in the cell
80
New cards
microtubule-organizing center
-growth center of microtubules in animal cells
-contains a pair of centrioles within this region
-contains a pair of centrioles within this region
81
New cards
flagellum (flagella)
-Whip-like tails found in one-celled organisms
-Aids in movement
-Most animals & some plants have flagellated sperm
-Composed of microtubules wrapped in an extension of plasma membrane
-Aids in movement
-Most animals & some plants have flagellated sperm
-Composed of microtubules wrapped in an extension of plasma membrane
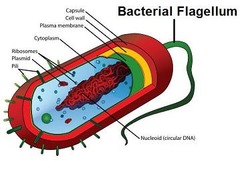
82
New cards
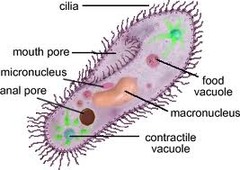
cilium (cilia)
-Hair-like projections that extend from the plasma membrane
-Used for locomotion
-Propels protists
-Sweeps mucus containing debris in lungs
-Composed of microtubules wrapped in an extension of plasma membrane
-Used for locomotion
-Propels protists
-Sweeps mucus containing debris in lungs
-Composed of microtubules wrapped in an extension of plasma membrane
83
New cards
primary cilium
-a single, nonmotile attachment which acts as a signal sensor
-lacks the central pair of microtubules
-only one per cell (in vertebrate animals)
-lacks the central pair of microtubules
-only one per cell (in vertebrate animals)
84
New cards
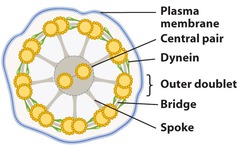
9+2 pattern
-The arrangement of microtubules in cilia and flagella
-9 microtubule doublets surround a central pair of microtubules
-9 microtubule doublets surround a central pair of microtubules
85
New cards
basal bodies
-a ring of 9 microtubule triplets
-anchors cilia/flagella
-anchors cilia/flagella
86
New cards
dynein protein
-Motor protein
-Drives the bending movements of microtubules in cilia & flagella
-Attached along each microtubule doublet
-Drives the bending movements of microtubules in cilia & flagella
-Attached along each microtubule doublet
87
New cards
movement of dynein proteins
-Has 2 "feet" that "walk" along adjacent footing
-1 foot maintains contact; the other foot releases & reattaches 1 step farther along its neighboring microtubule
-Outer doublets are held in place by flexible cross-linking proteins & radial spokes, preventing sliding
-1 foot maintains contact; the other foot releases & reattaches 1 step farther along its neighboring microtubule
-Outer doublets are held in place by flexible cross-linking proteins & radial spokes, preventing sliding
88
New cards
Endomembrane system
-A network of membranes inside and around a eukaryotic cell
-Related through direct physical contact or by transfer of membranous vesicles
-Divides the cell into separate functional compartments
-Related through direct physical contact or by transfer of membranous vesicles
-Divides the cell into separate functional compartments
89
New cards
organelles of the endomembrane system
-nuclear envelope
-endoplasmic reticulum
-golgi apparatus
-lysosomes
-vacuoles
-plasma membrane
-endoplasmic reticulum
-golgi apparatus
-lysosomes
-vacuoles
-plasma membrane
90
New cards
peroxisome
-Metabolic compartments that do not originate from the endomembrane system
-Breaks down fatty acids to be used as cellular fuel
-Detoxifies alcohol & other toxic compounds in liver cells
-Breaks down fatty acids to be used as cellular fuel
-Detoxifies alcohol & other toxic compounds in liver cells
91
New cards
vesicles
small membranous sacs that specialize in moving products into, out of, & within a cell
92
New cards
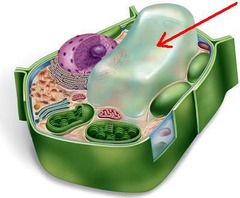
vacuole
-Vesicle that stores materials such as water, salts, proteins, or carbohydrates
-Vacuoles in plants can have a digestive function similar to lysosomes
-Vacuoles in flower petals contain pigments that attract pollinating insects
-Can contain poisons/unpalatable compounds (nicotine, caffeine) for protection against herbivores
-Vacuoles in plants can have a digestive function similar to lysosomes
-Vacuoles in flower petals contain pigments that attract pollinating insects
-Can contain poisons/unpalatable compounds (nicotine, caffeine) for protection against herbivores
93
New cards
food vacuole
forms as a cell ingests food
94
New cards
large central vacuole
stores water & other chemicals
95
New cards
contractile vacuole (paramecium)
-balances water
-spokes collect water from the cell
-hub expels it to the outside
-spokes collect water from the cell
-hub expels it to the outside
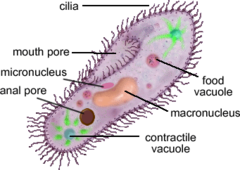
96
New cards
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
-Network of flattened sacs & tubules
-Forms a maze of passageways in which proteins & other materials are carried from one part of the cell to another
-Continuous w/ the nuclear envelope
-Can be smooth/rough
-Forms a maze of passageways in which proteins & other materials are carried from one part of the cell to another
-Continuous w/ the nuclear envelope
-Can be smooth/rough
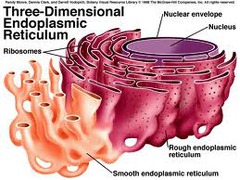
97
New cards
endoplasmic
"within the cytoplasm"
98
New cards
reticulum
"little net"
99
New cards
smooth ER
-ER that is free of ribosomes
-Functions in metabolic processes
-Synthesizes lipids
-Detoxifies drugs & alcohol in liver cells, increasing body tolerance
-Stores Ca2+ (muscle cells)
-Functions in metabolic processes
-Synthesizes lipids
-Detoxifies drugs & alcohol in liver cells, increasing body tolerance
-Stores Ca2+ (muscle cells)
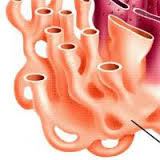
100
New cards
examples of lipids
-oils
-phospholipids
-steroids
-phospholipids
-steroids