NURS 3444. Exam 5 (Hematologic and Oncologic)
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Who is at the highest risk for iron deficiency anemia?
- Preemies
- 12-36 months
- Teens
Why are preemies at risk for iron deficiency anemia?
Do not have the whole time to get maternal iron stores
- normally stores would last for 6 months
Why are 12-36 months at risk for iron deficiency anemia?
transition to table food
- whole milk is not a source of iron
- should not have more than 24 oz of milk a day
Why are teens at risk for iron deficiency anemia?
heavy menstrual period
Treatment for iron deficiency anemia
Iron supplementation (ferrous sulfate or ferrous fumarate)
- liquid form for babies
- enteric coated pills for older
- increase iron-rich food
- transfusion in severe cases
When do you start treating iron deficiency anemia?
HGB < 10
What to take iron with?
vitamin C (orange juice)
- administer between meals (HCL acid helps with absorption)
- no milk with meds
Symptom of iron deficiency anemia
- spoon (concave) nails
- irritability
- headache
- dizziness
- weakness
- SOB
- pallor
- fatigue
Side effects of iron supplementation
- Black stools
- teeth staining
- constipation
Risk factors for lead poisoning
- Infants and toddlers → use mouth to explore world, crawling around
- Older homes → lead in paint (old windows → can form lead dust)
- Old pottery → often has lead paint (in bright colors)
- Lead pipes that lead to home → let water run before using
Effects of lead on hematologic system
interferes with synthesis of heme leading to anemia
Effects of lead on renal system
damage cells of proximal tubules leading to renal impairment
- glycosuria
- proteinuria
- ketonuria
- decreased vitamin D
Effects of lead on neurologic system
- increased membrane permeability
- increased ICP
- atrophy
- low exposure (distractibility, impulsivity, hyper, hearing impairment
- high exposure (cognitive impairment, death, coma, convulsions, blindness)
Interventions for blood levels less than <3.5
Provide education on sources and exposure prevention; assess developmental milestones and diet (iron/calcium intake); conduct f/u testing as age/risk appropriate
- Best ways to get rid of dust → damp mopping (do NOT vacuum)
Interventions for blood levels 3.5 to 19
Report test to state/local health department; obtain environmental exposure history to identify potential sources; arrange environmental investigation of the home, per local regulations; assess developmental milestones and diet (iron/calcium intake); parent/caregiver education on decreasing lead exposure
- Follow-up test in 1-3 months (then q 3-9 months, if levels declining)
Interventions for blood levels 20-40
Perform complete history/physical exam, assess for signs/symptoms related to lead exposure; conduct environmental investigation of home and complete lead hazard reduction program; consider radiology for lead-based foreign body ingestion; contact poison control as needed
- Follow-up test in 2 weeks – 1 month (then q 1-3 months, if levels declining)
Interventions for blood level >44
Conduct a detailed neuro exam and admit to the hospital if the child exhibits neuro signs/symptoms of lead poisoning or if continued lead exposure in home cannot be avoided. Ensure lead is removed from the home.
- Initiate treatment plan: (A) chelation therapy; and/or (B) GI decontamination for removal of swallowed lead
- Follow-up testing as soon as possible and per treatment plan.
Hemophilia A
- X-linked recessive bleeding disorder (only affects men)
- Deficiency of factor VIII
When is hemophilia A often diagnosed?
- Circumcision may show
- Often shown when teething (>6 months)
Hemarthrosis
bleeding into a joint space
- sign of hemophilia A
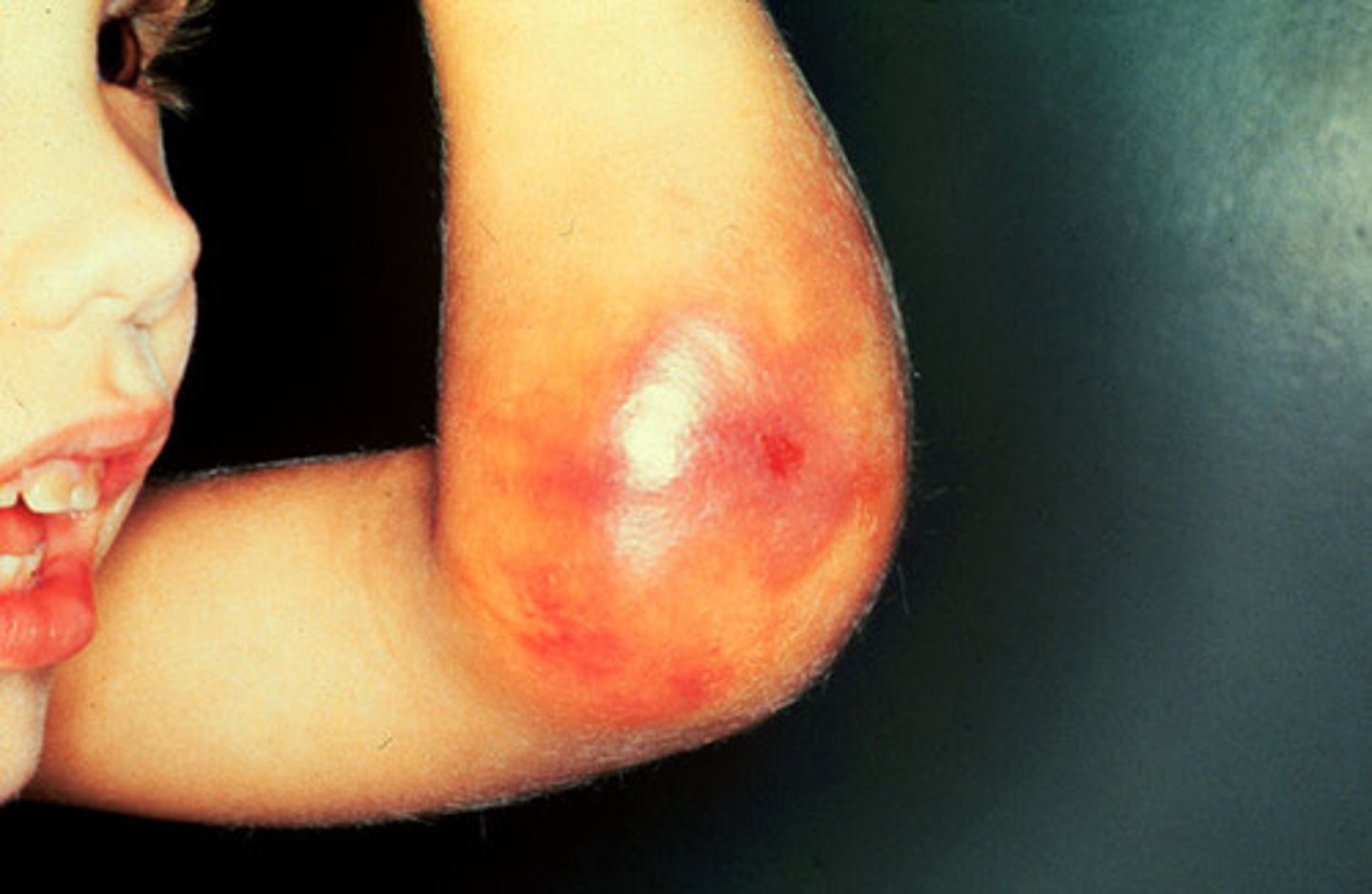
Symptoms of Hemophilia A
- prolonged bleeding
- hemorrhage
- excessive brusing
- hemarthrosis
- hematuria
Manifestations of hemophilia A
- Hemarthrosis of knees, ankles, elbows
- Circumcision bleeding
- Ecchymosis
- Epistaxis
- Hematuria
- Dental procedure bleeding
- Neck, mouth, chest, brain bleeding
Prevention of bleeding
- Electric razor
- Soft toothbursh
- No rectal temp or suppositories
- BP checks only as needed
- Only injections and venipunctures as needed
- Peripheral fingerstick for labs can cause bleeding
- Paper or silk tape
- Padding as needed
Treatment of hemophilia A
DDAVP or Factor VIII Concentrate
- pain management (Tylenol or opioids if needed)
- avoid aspirin and NSAIDs
Meds for hemophilia A
- Replace missing factor (factor VIII) → now synthetically made
- DDVAP → decrease bleeding with procedures
- Steroids → decrease swelling in joints
- Hemlibra
- Cryoprecipitate → blood product used for clotting
Von Willebrand Disease
Deficiency of von Willebrand factor (VWF)
- less severe than hemophilia
- can effect females and males
Clinical presentation of VWD
- Bruising
- Epistaxis
- Monrrhagia
Treatment of VWD
- VWF (factor replacement therapy)
- Desmopressin (DDAVP)
Idiopathic Thrombocytopenia Purpura cause
Antibodies destroy platelets
- Follows viral infection (respiratory, measles, chickenpox)
- May also follow vaccination (ex. MMR)
Symptoms of ITP
- Multiple ecchymosis and petechiae (purpura)
- Bleeding
- Low platelet count (thrombocytopenia) <50,000
Treatment of ITP
- Steroids
- IVIG
- If not resolved (splenectomy)
ITP resolves
typically resolves within months
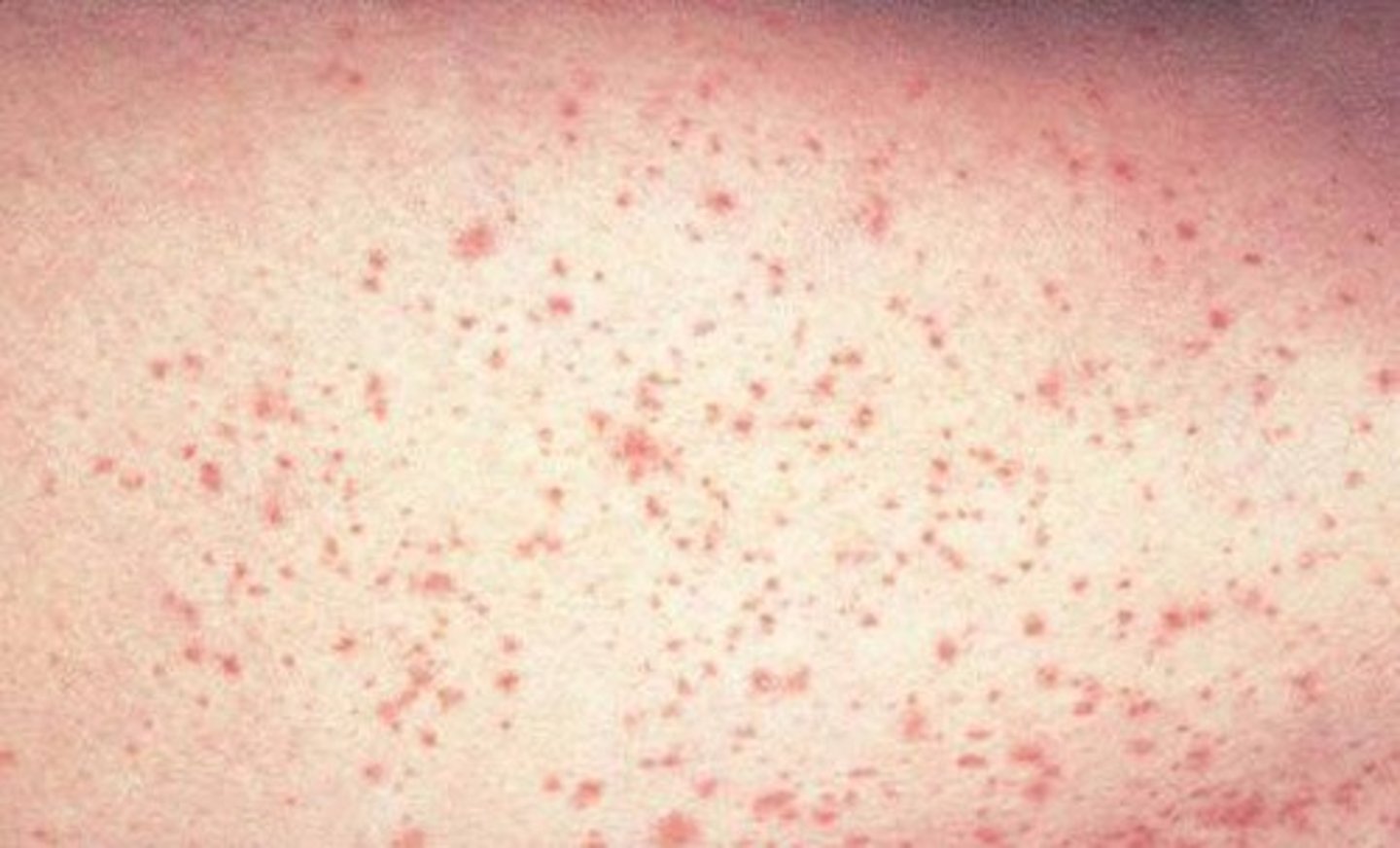
Petechia
pinpoint hemorrhage that occur anywhere on the body and do not blanch to pressure
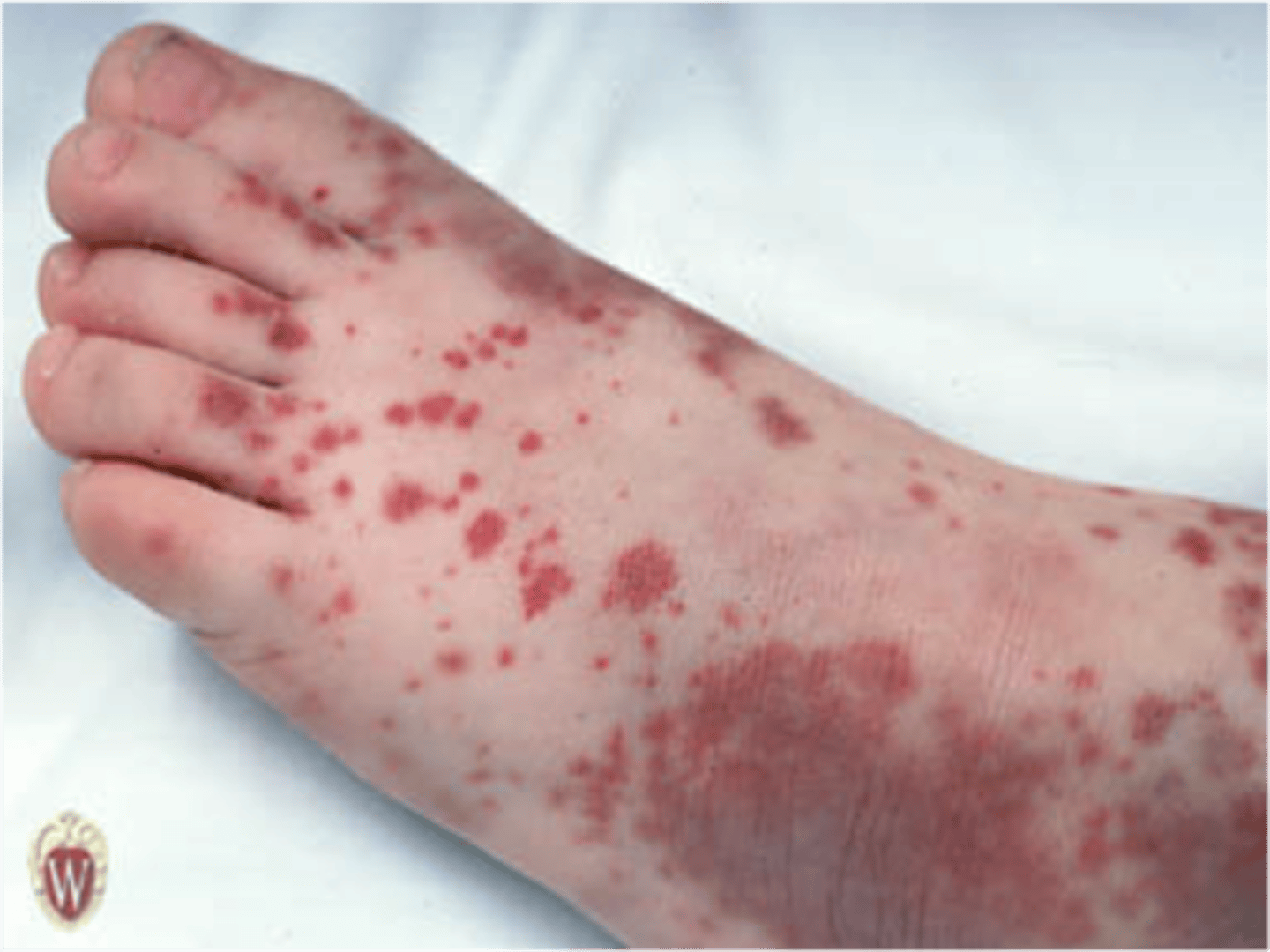
Purpura
larger areas of hemorrhage in which blood collects under tissues (purplish) not blanchable
Nursing care for ITP
- Self limiting → typically resolves after steroids and IVIG
- Medications → Steroids and IVIG
- Limit activities with low platelet count
- No contract sports
- No NSAIDs → in order to prevent bleeding
Sickle cell anemia
- Inherited → RBC do not carry the normal adult hemoglobin, but instead carry less effective type (hemoglobin SS disease)
- Elongated RBC with crescent shape
- RBC clump and occlude
What causes vaso-occlusive episodes
- Any stress
- Traumatic event (infection, fever, dehydration, physical exertion, excessive cold exposure, hypoxia)
Treatment of vaso-occlusive episodes
- Pain control
- Oxygen → maximize oxygen carrying capacity of normal RBC
- Adequate hydration
- Close monitoring of Hgb, Hct, and reticulocytes
- Electrolyte analysis
- Antibiotics therapy
Medication Treatment of SCD
- Hydroxyurea and L-glutamine
- Hydroxyurea → helps to increase normal hemoglobin
- Blood transfusions
- Splenectomy if needed
Cardinal S/Sx of Cancer
- Unusual mass or swelling
- Unexplained paleness and loss of energy
- Prolonged, unexplained fever or illness
- Frequent headaches, often with vomiting
- Sudden tendency to bruise
- Sudden eyes or vision changes
- Persistent, localized pain or limping
- Excessive, rapid weight loss
Treatment of Cancer
- Surgery: tumor removal
- Radiation therapy: kill tumor cells or shrink prior to surgery
- Chemotherapy / Immunotherapy: drugs that destroy cancer cells at different cycles
- Hematopoietic stem cell transplant: stem cells infused, followed by chemotherapy/irradiation
Nadir
bone marrow suppression us at greatest → therefore neutrophil count is at its lowest
- Child's immunity is at its lowest
Cancer and fever
- Any fever warrants lab work and IV antibiotics immediately
- Always get blood culture before administering antibiotics
- Blood culture and give antibiotics right after
- Fever and neutropenia is an EMERGENCY
Absolute neutrophil count (ANC)
Correlated with the ability to fight infection
- Should have their own room on a CLEAN floor
Dental if ANC > 500
- Regular brushing
- Flossing
- Fluoride
- Dental checkups
Dental if ANC < 500
- Toothette
- Wiping gums/teeth
- Fluoride rinse
Immunizations with Cancer
- Omit live vaccines until 3 months post treatment
- Encourage vaccinations in family members
- Administer immune globulin if exposed
- Antivirals if disease develops
- Delay inactivated vaccines when possible
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
Immature lymphoblasts lack infection-fighting capabilities (replace normal cells in bone marrow depriving body of normal cells)
- higher WBC count at diagnosis = worse the prognosis
Therapeutic Management of ALL
Chemotherapy
- 3 stages of chemo to eradicate leukemic cells and restore normal bone marrow function
Signs and Symptoms of Brain Tumor
- Headache (upon awakening)
- Exacerbated by sneezing, straining
- Visual changes
- Vague symptoms
- May have CNS effects
- Unsteady gait
- Irritability, failure to thrive, developmentql delay
Treatment of Brain Tumor
- Surgery
- Radiation
Post-operative care for brain tumor surgery
- Do not position on the side where the tumor was removed
- Hyperextension of neck and legs (backward C is an abnormal finding)
Complications of Wilms' Tumor
metastasis
Nursing Care for Wilms' Tumor
- Surgical removal of tumor
- Surgical removal of affected kidney (nephrectomy)
- Radiation and/or chemo (pre or post op)
Complications of Sickle Cell Disease
- Vaso occlusive pain crisis
- Stroke
- Sepsis
- Priaprisms
- Delayed growth and puberty
Brain tumor diagnostic tests
- CT, MRI, PET scans
- Lumbar puncture (may show positive tumor markers)
Staging of Wilms Tumor
- Stage I: better prognosis
- Stage V: poor prognosis