Smartwork chapter 3
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What is the measure of disorder in a system called?
A. enthalpy
B. second law of thermodynamics
C. entropy
D. catabolism
E. free energy
Entropy
Reactions that use energy to drive the synthesis of molecules inside the cell are most specifically considered:
Anabolic
Catabolic
Metabolic
Anabolic
Carbon atoms cycle continuously through the biosphere. What is a by-product of cell respiration, and what does this by-product represent?
A. CO2; completely oxidized carbon
B. CO2; a reduced version of carbon
C. C6H12O6; completely oxidized carbon
D. C6H12O6; a reduced version of carbon
CO2; completely oxidized carbon
What is the origin of the energy that animals acquire by eating plants or other animals?
A. heat
B. carbohydrates
C. fats
D. sugars
E. sunlight
Sunlight
Which energy conversion characterizes photosynthesis?
A. electromagnetic (light) energy → oxidation energy
B. electromagnetic (light) energy → CO2
C. electromagnetic (light) energy → kinetic energy
D. electromagnetic (light) energy → chemical bond energy
E. electromagnetic (light) energy → heat energy
Electromagnetic (light) energy → chemical bond energy
Which of the following does not describe an oxidation reaction?
A. the conversion of a chlorine atom to Cl–
B. the removal of electrons from a molecule
C. the conversion of Fe2+ to Fe3+
D. the addition of oxygen atoms to a molecule
The conversion of a chlorine atom to Cl–
Which of the following statements is not true?
A. When a sugar molecule is oxidized to CO2 and H2O, the O2 molecules involved in forming the H2O are reduced.
B. Oxidation and reduction reactions always occur simultaneously.
C. Hydrogenation reactions are oxidations, and dehydrogenation reactions are reductions.
D. When a carbon atom in a C–H bond has somewhat more than its share of electrons, it is said to be reduced.
Hydrogenation reactions are oxidations, and dehydrogenation reactions are reductions
The cell regulates its metabolism through a vast interconnected web of anabolic and catabolic chemical pathways. Which of the following would be expected to release energy and generate activated carriers to drive energetically unfavorable reactions?
A. Gluconeogenesis, a pathway where one molecule of glucose is generated from two molecules of pyruvate.
B. Glycolysis, where each glucose molecule is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate.
C. Translation, where proteins are assembled from amino acid building blocks.
D. Photosynthesis, where sugars are produced from atmospheric carbon dioxide molecules.
Glycolysis, where each glucose molecule is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate.
Your company has developed an organic molecule with commercial potential and you know how to produce it in the lab. You want to increase production and make as much of the molecule as possible, but the reaction has a positive ΔG°. What can you do to try to drive the reaction toward your desired product?
Choose one or more:
A.increase the concentration of reactants
B.add an enzyme that does not couple to another reaction
C.continually remove products
D.add some products initially to get the reaction primed
Increase the concentration of reactants
Continually remove products
Compared to adding heat to the system, what is the advantage of using an enzyme to overcome an energy barrier?
A. An enzyme speeds up a reaction more than heat does.
B. An enzyme is specific for one desired pathway and end product.
C. An enzyme can catalyze a reaction in many different ways.
D. An enzyme generates multiple different products using multiple pathways.
An enzyme is specific for one desired pathway and end product.
All four possible reactions in the animation are energetically favorable; the energy of the four products is lower than the energy of the original starting molecule. Why does the starting molecule not completely and quickly convert to its possible products before the addition of heat or an enzyme?
A. An activation energy barrier exists that must be overcome for conversion to products.
B. When heat was added to the reaction, only some of the products were produced.
C. The starting substrate does quickly convert to the four products.
D. The starting molecule can only form some of the products quickly.
An activation energy barrier exists that must be overcome for conversion to products.
In thermodynamics, what does the term “free energy” refer to?
A. excess energy from a reaction that a cell does not use
B. energy required to initiate a chemical reaction
C. energy that cells borrow from the environment
D. energy that can be harnessed to do work or drive chemical reactions
E. energy that cannot be harnessed to do work or drive chemical reactions
Energy that can be harnessed to do work or drive chemical reactions
Which statement about enzymes is not true?
A. Enzymes can help build large polymers.
B. Enzymes can speed up energetically favorable reactions.
C. An enzyme can force an energetically unfavorable reaction to take place inside the cell.
D. Enzymes reduce the activation energy required to initiate a spontaneous reaction
An enzyme can force an energetically unfavorable reaction to take place inside the cell.
Is the following statement true, false, or either depending on the situation?
After an enzyme catalyzes a reaction, the enzyme has been altered and cannot perform additional reactions.
A. always true
B. always false
C. true or false, depending on the enzyme
Always false
True or false: Energetically unfavorable reactions can occur if they are coupled to a second reaction with a negative ΔG so large that the net ΔG of the entire process is negative.
True
Which is not true of a chemical reaction at equilibrium?
A. The net concentrations of substrate and product do not change.
B. Both the forward and reverse reactions have stopped
C.ΔG is equal to zero.
D.The rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal
Both the forward and reverse reactions have stopped.
A reaction A → B has a negative ΔG under experimental conditions. Which statement is true about this reaction?
A. The formation of product B will decrease the entropy of the universe.
B. The reaction cannot proceed until it is coupled to a reaction with a positive ΔG.
C. The reaction is energetically unfavorable.
D. Increasing the concentration of B will increase the ΔG, making it less negative.
E. The reaction will proceed spontaneously and rapidly.
Increasing the concentration of B will increase the ΔG, making it less negative
Two molecules will bind to each other by means of noncovalent bonds if the ΔG° of the interaction is which of the following?
A. negative (the free energy of the product is less than the sum of the free energies of the unbound partners)
B. zero (the free energy of the product is the same as the sum of the free energies of the unbound partners)
C. positive (the free energy of the product is greater than the sum of the free energies of the unbound partners)
Negative (the free energy of the product is less than the sum of the free energies of the unbound partners)
Throughout the 1920s, Otto Meyerhof, A. V. Hill, and colleagues investigated how cells use energy to power muscle contraction. They determined that during muscle contraction, glycogen is broken down into lactic acid, a product of fermentation. Originally Meyerhof thought that the conversion of glycogen into lactic acid directly powered muscle contraction. This idea was overturned by experiments performed by Einar Lundsgaard. What evidence did Lundsgaard provide to suggest that glycogen breakdown and lactic acid production did not directly power muscle contraction?
A. Creatine phosphate infusions into muscle cells inhibited muscle cell contraction.
B. A pulse of electricity caused muscle contraction in isolated frog muscle tissue.
C. Inhibition of fermentation immediately halted muscle contraction.
D. Muscle contraction could continue for some time after inhibition of fermentation.
Muscle contraction could continue for some time after inhibition of fermentation
True or false: In isolation, the formation of an activated carrier, such as ATP, NADH, or NADPH, is an energetically unfavorable reaction.
True
What is the difference between NAD+ and NADH?
A. NADH is involved in biosynthetic reactions.
B. NADH is the oxidized form, while NAD+ is the reduced form.
C. NADH carries an extra phosphate group.
D. NADH carries an extra proton and two high-energy electrons.
E. NADH is an electron acceptor, whereas NAD+ is an electron donor.
NADH carries an extra proton and two high-energy electrons.
What is true of the breakdown of polymers inside living cells?
A. It occurs without the need for enzymes.
B. It is energetically unfavorable.
C. It is associated with a negative change in free energy.
It is associated with a negative charge in free energy
Which statement about polymers is true?
A. Polymer synthesis requires an input of free energy and involves the consumption of water.
B. Polymer breakdown requires an input of free energy and involves the consumption of water.
C. Polymer synthesis requires an input of free energy and involves the release of water.
D. Polymer breakdown requires an input of free energy and involves the release of water.
Polymer synthesis requires an input of free energy and involves the release of water
Which carrier is in its activated state as used in the cell?
A.CoA
B.NADP+
C.ADP
D. FAD
E.NADH
NADH
Consider the image and then answer the question.
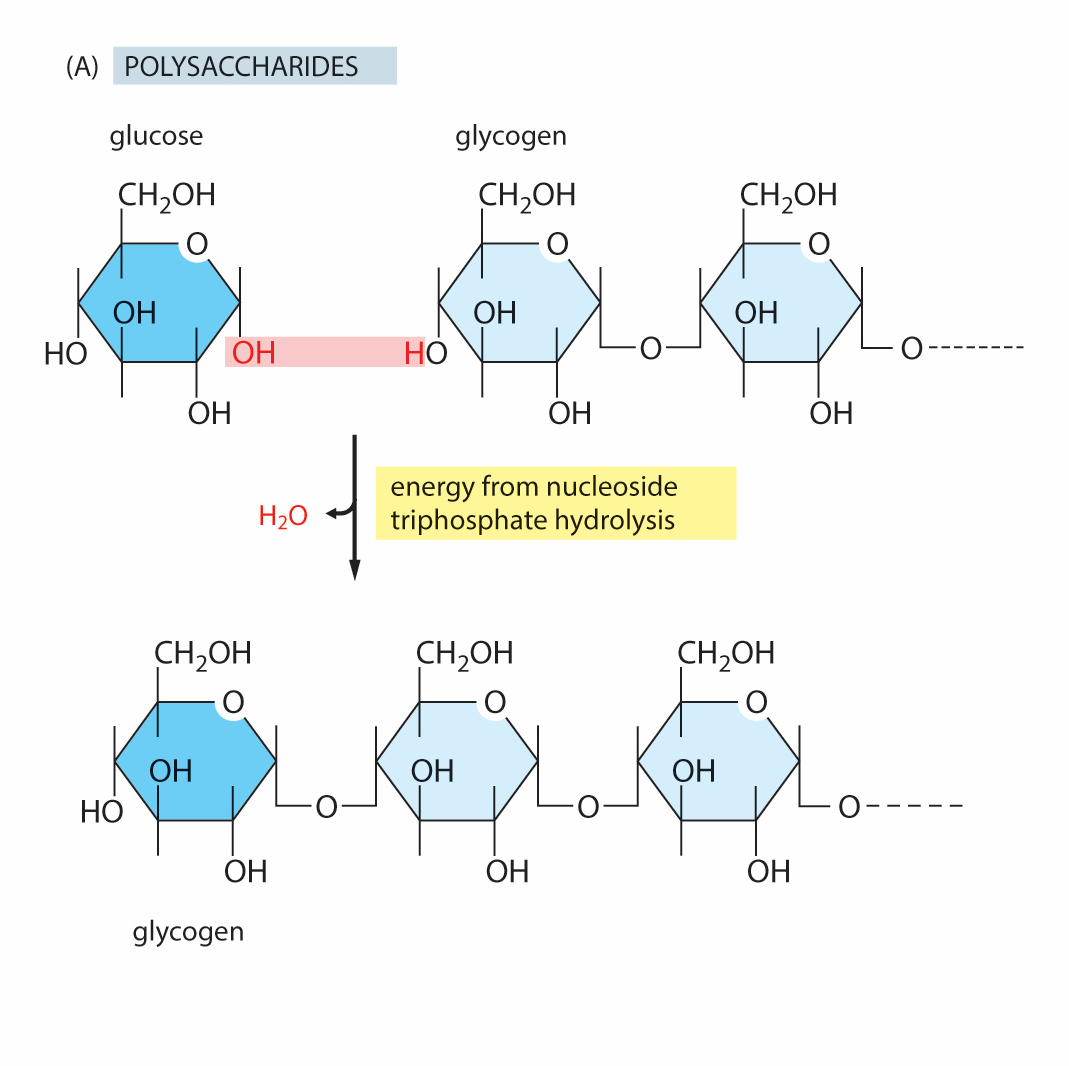
Which of the following best describes this reaction?
A. condensation
B. hydrolysis
C. redox
Condensation
Reactions that build larger molecules in the cell are called ___________; reactions that break down molecules into smaller ones are called ___________.
A. metabolic; anabolic
B. anabolic; metabolic
C. catabolic; anabolic
D.anabolic; catabolic
Anabolic; catabolic
Living systems can generate and maintain order without violating the second law of thermodynamics because they generate
A.order.
B. heat.
C. decreased entropy.
D.macromolecules.
Heat
In an enzymatic reaction, a molecule gains an electron. This is known as a(n) ___________ reaction.
A.oxidation
B. hydrogenation
C. electronegative
D. reduction
Reduction
Why is CO2 an end product of cellular respiration?
A. because it is the most stable form of carbon in our atmosphere
B. because it can accept electrons and produce a reduced form of carbon
C. because plants can use it for respiration
D. because it captures light energy for photosynthesis
Because it is the most stable form of carbon in our atmosphere
Enzymes increase the speed of a chemical reaction because they
A. lower the activation energy needed to start the reaction.
B. make the reaction more energetically favorable.
C. make the reaction spontaneous.
D. increase the temperature to provide the necessary boost of energy.
Lower the activation energy needed to start the reaction
What is the role of activated carriers in cells?
A. They are enzymes that catalyze biosynthetic reactions and make them feasible at the temperature of a cell.
B. They capture energy from energy releasing reactions and transfer it to other reactions.
C. They carry energy from anabolic reactions for use in catabolic reactions.
D. They are enzymes that catalyze the reactions that break down foodstuffs for energy generation in the cell.
They capture energy from energy releasing reactions and transfer it to other reactions.
Which of the following has a higher concentration in the cell to allow it to be available to accept electrons from oxidation of food molecules?
A.NADH
B. NADPH
C. NAD+
D. NADP+
NAD+