FPSYC3400: Decision-Making & Critical Incident Management (Definitons)
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture 10
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Critical Incident
high-risk, high-stakes, or uncertain events
Critical Incident: Canada
unplanned events such as hostage takings, barricaded persons, workplace violence, and other crisis situations
Critical Incident: UK
any incident where the effectiveness of the police response is likely to have a significant impact on the confidence of the victim, their family and/or the community
Endogenous Features
situational-specific conditions
intense time pressure & risk
prospective cognitive modelling
anticapatory thinking about the future
about the problem environment
stem from the problem itself
Exogenous Features
related to the effectiveness of the response the endogenous features
about the operating system responding to the decision problem
issues affiliated with the management problem and the associate team process
Critical Incident Management (CIM)
is intended to provide a response which satisfies the needs of the victim, their family and the community, but also provides an effective and proportionate outcome to an incident.
Traditional Decision Making (TDM)
Classical decision theory
Rational choice model of decision making
Traditional approach to decision making
Sequence of steps that enhance the probability of attaining a desired outcome
the decision making of individuals within tightly controlled research framework and examine basic cognitive processes
Traditional approach to decision making
Sequence of steps that enhance the probability of attaining a desired outcome
Naturalistic Decision Making (NDM)
an approach to studying decisions made ‘in the field’/real-world situations; exploring the way people use their experience to make decisions
Developed because applied psychologists weren’t happy with classical approaches to decision making
A pragmatic research program that utilizes case studies to examine and analyze the decision-making of officers as they perform their responsibilities in
Hydra: Simulation-Based Training
used to conduct immersive, simulated scenarios for a wide variety of professions (e.g., police, military, emergency personnel, health care professionals)
for the delivery of critical decision-making scenarios
allows flexibility in decision-making as the environment changes within
emulate naturalistic decision-making; replicate practical environments, offer repeated exposure and practice in dealing with critical incidents
Heuristics & Decision-Making
used to speed up the process of finding a satisfactory solution via mental shortcuts to ease the cognitive load of making a decision
Cognitive - typically lead to accurate assessments, but can lead to systematic errors or biases
Representativeness Heuristic
tendency to assess the likelihood of an event occurring based on impressions about similar occurrences
when we try to figure out whether an object belongs to a class
Availability Heuristic
tendency to base decisions on information readily available in memory
estimating the likelihood of an event; people often use this of related information and memory as a cue to its actual probability
Anchor & Adjustment (Judgment) Heuristic
made by starting from an initial value (anchor) and then making adjustments from that point
a person uses a specific target number or value as a starting point (anchor) and then adjusts tha information until an acceptable view is retimed
Confirmation Bias
select information that confirms a current belief
tendency to search predominantly for confirming evidence while failing to look or falsifying evdence; people focus disproportionately on evidence favouring their current position
interpret information consistently with a current belief
people choose an interpretation that is consistent with their prior belief and fail to see that the information may be comptabile with other positions
tend to overestimate the robot of value of non diagnostic evidence
Recognition-Primed Decision-Making (RPD)
Experienced decision-makers use a pattern recognition approach to identify familiar patterns and cues in a given situation
Based on past experiences
Requires learning and expertise
to quickly identify familiar patterns and cues given situation based on their past experiences and expertise, they then use this recognition to generate a set of potential courses of action that may be effective at addressing the problem at hand
Recognition-Primed Decision-Making (RPD): Situation Assessment
Matching current situation to past ones
Determines course of action
pattern matching to match the current situation to once encountered in the past which identifies reasonable courses of action
Recognition-Primed Decision-Making (RPD): Evaluation using Mental Simulation
using mental stimulation to imagine how courses of action might play out and see if it’s going to work
relies on the ability to identify key patterns an cues in a situation quickly and make effective decisions based on that recognition
Decision Avoidance
the passive avoidance of a decision that needs to be made
maintaining the status quo
deferring the choice to another agency
Decision Inertia
redundant deliberation for no positive gain; specific form of indecision in which the decision maker engages in redundant cognitive deliberation of choice fo no postive gain
excessive information searches
inability to decide upon a course of action
uncertainty about the situation
potential optins
projected outcomes can actually hinder, stop, interfere with decision
Least-Worst Decisions
Decisions where every course of action could lead to negative consequences that are equal to another course of action
equally adversive
choosing between the least-worst is very difficult
lack of good option
places decision-maker in a challenging position
Command Teams
interdisciplinary and cross functional
team members who have different backgrounds, different roles and levels of operational expertise
Preparing for critical incidents
requires chief officers to consider current managements structures, ensuring where possible that staff are trained effectively and the necessary resources are available
training
developing protocols and action plans
Managing Critical Incidents
how to identify critical incidents; processes to ensure incidents are notified to the most appropriate person and that they are managed effectively
start with early identification & notification
attention to victims (needs, family and community)
media & communication strategy: based on openness and transparency
monitoring of CI ensures that resources are used effectively and appropriately
Restoring public confidence
how confidence can be rebuilt through community engagement resolution or public inquiry
community members may suffer psyc. or emotional trauma b/c of close proximity to event
involves dealing with issues raised and being seen to deal with them
must be able to learn from their mistakes
Decision Makers
rational and effective decision maker with decision making comprised of a comprehensive search of all available information and the appropriate inferences being derived from that search
proficient decision makers
relevant experience and knowledge to rely on their experiences
process orientation
does not making an attempt to predict which options will be implemented but tries to describe the cognitive processes of proficient decision makers
situation-action matching decisions rules
matching isn’t a generic label; for decisions with the basic structure because it is appropriate for the situation, which means that any options are evaluated one at a time
when presented with several options, no by comparing them against each other
matching relies on pattern matchig
context-bound informal modelling
Driven by experience and knowledge
exert knowledge is dominant and contact specific and decision makers asense tive smeantive indicating that individuals work as well as the suyantiv contexct
the structure of language
empirical-based prescription
actions are baed on experience; options that are optimal in some formal sense but when they cannot be implemented they are considered worthless
Naturalistic Decision Making (NDM) - Field Studies
provide insight into the demand of the environment on decision-making, the affordances and constraints of those environments
provides information regarding the potential sources of difficulty, error or non-optimal performance and how the larger system supports the decision maker
structured or unstructured interviews, retrospective analysis, out loud protocols, videos of incidents
Naturalistic Decision Making (NDM) - Simulations
elicit similar behaviour
realistic feautures can be built in (i.e., temporal parameters, distractions, workload)
subjects’ behaviour can be analyzed as a function of relevant factors (i.e., levels of experience)
Example: Minerva, Hydra, 10Kv
Naturalistic Decision Making (NDM) - Laboratory Techniques
can be used to help further the understanding of decision-making after a level of understanding already exists in a particular domain
generate a hypothesis around the types of decisions being made
10Kv (bolts)
method for running debriefins after simulations or after field studies
electronic focus group; anonymous inpute from all those invovled in the simulations
sit at a compute and shre thei ideas
to be emotiannly honest
provides ideas that they may have done differently
Anchor
how our final judgements depend upon some initial value rather than any kind of objective estimation
Anchoring Bias
when you focus on 1 piece of information when making a decision or solving a problem
Action Script
the decision maker chooses the first option and course of action that does not fall out when they evaluate the various options
as people developing a game fain more expertise in their field; their ability to make these kinds of important decisions in the better option or least worst option improves
are better able to recognize indicators and characteristics of a problem than people who are not
can perform a more reliable mental simulations
choose a more accurate course of action
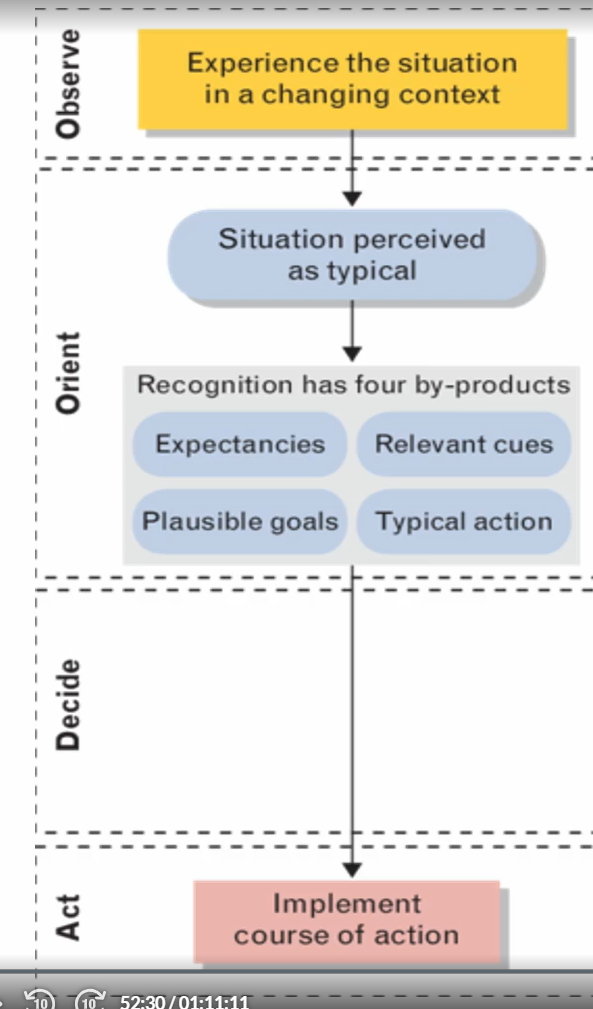
Level 1: Simple Match
familiar situations can be matched with typical actions to facilitate rapid decisions resulting in well-known effects; a sense of tyicality that allows decision makers to quickly categorize situations and recognize how to react as an aspect
simplest case where the situation is recognized
the obvious reaction is implemented here
the decision makers seize the situation and respond with the initial option that they’ve identified
based on the idea that exna epericen decsion maerk can sualer fgenrarte a feasible course of action
perceive the situation as typical cases where certain types of actions are typically appropriate and are usually successful
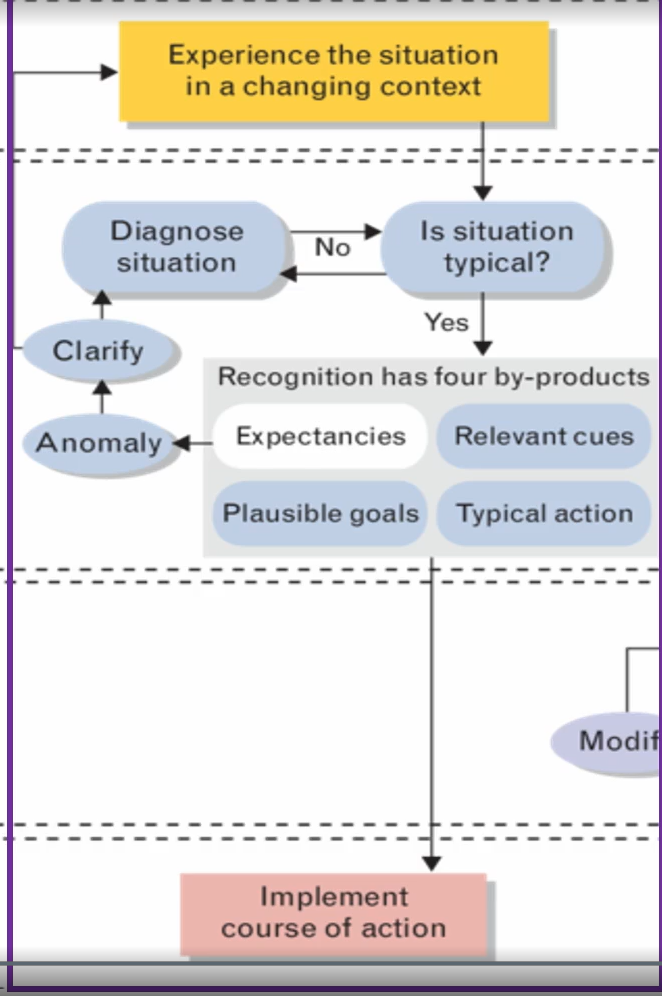
Level 2: Diagnose the Situation
an unfamiliar situation forces the decision into a diagnostic process in order to develop the set of expectancies required to select a course of action from their repertoire; expertise is need to construct the mental models needed to find one explanation more plausible than the next
the decision maker consciously starts to evaluate the reaction, typically using imagery to uncover problems prior to carrying out
often reply on a story
building strategy to mentally simulate the events leading up to the observed features of the situation and try to find one explanation more plausible than another
2nd variation under uncertainty describes how the plausibility of alternative stories can decision maker choose in and categorize a situation and then the simple match method is then engaged
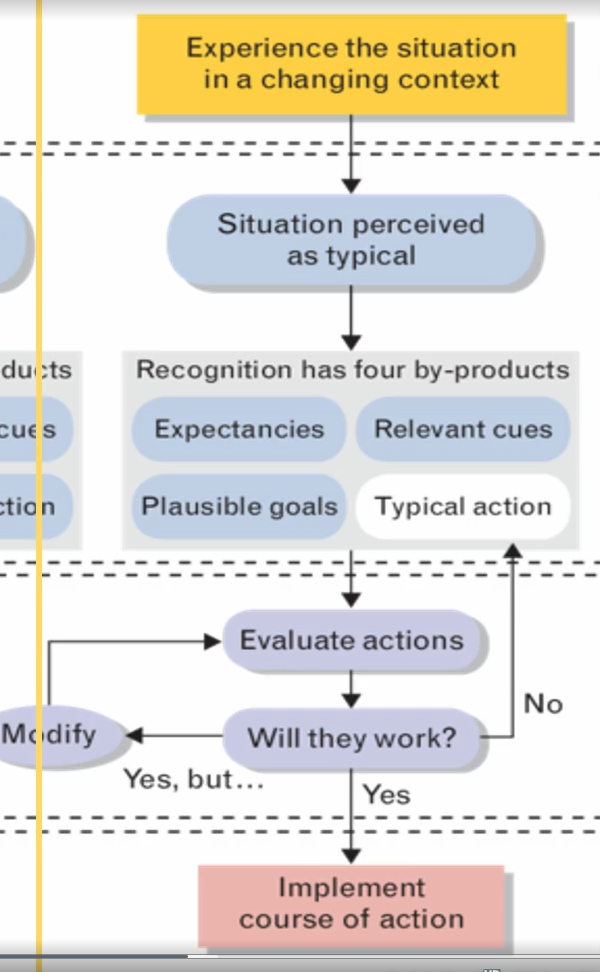
Level 3: Evaluate Course of Action
a satisfactory action may not exist to address even a familiar situation; defined as an ability to mentally stimulate or simulate a course of action in the situation and anticipate how it’s going to play out
a mental stimulation process maybe required to develop an appropriate course of actions
most complex case which allows the decision maker to evaluate a course of action without comparing it to others
evaluation is conducted by mentally simulation the course of action see if it will work and to look if intended consequence that might be unacceptable
RPD Model: Observe
critical incident event
RPD Model: Orient
pattern match, situational understanding recognition
is the situation perceived as typical, yes or no?
Four components:
relevant (critical/important) cues
expectancies
plausible goals
typical actions
RPD Model: Orient - Expectancies
what to expect so that your actions can be smooth
RPD Model: Orient - Plausible Goals
once you’ve identified the situation it tells you what kind of goals you can pursue
RPD Model: Orient - Typical Actions
suggested as a set of actions that are likely to be successful
pattern matching part and tends to happen right away
RPD Model: Decide
evaluation part; done by mentally simulating or imagining the action
do one action at a time and play it out in your mind and if it works you use it and swing into actions
if it almost works you can modify the action and try again
if can’t modify to make it successful, all together and you try the next action in your list until you find on that is successful