STS chap 2
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 10:48 AM on 8/26/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
1
New cards
**Revolution**
denotes a drastic change in what is established, believed and embraced by the society.
2
New cards
**Heretics**
outcasts of society, people who shared revolutionary ideas Many were ostracized, imprisoned and prevented fom publishing their writings.
3
New cards
**Nicolaus Copernicus**
an astronomer of the Renaissance period who challenged the previous notion about the cosmos, led the so-called Scientific Revolution.
4
New cards
**Epitome of Ptolemy's Almagest**
Johann Muller's Epitoma in Almagestum
5
New cards
**Disputations against divinatory astrology**
Disputationes adversus astrologiam divinatricem
6
New cards
**PRE-COPERNICAN SYSTEM**
Came about in response to the questions that cannot be addressed by the geocentric model of the universe
7
New cards
**Ptolemy**
Popularized the term “ geocentrism”, Earth as the center of the universe
8
New cards
**Anaximander**
He drew the first map of the world during 6th century BC
9
New cards
**Pythagoras**
First to suggest that the earth was a sphere
10
New cards
**Anaximander**
Earth taking the shape of a cylinder floating in the center of the universe
11
New cards
**Pythagoras**
The conclusion was after studying the constellations and the Earth's circular shadow on the moon during lunar eclipse.
12
New cards
**Anaximander**
Sun and Moon were hollow rings of fire and the eclipses were the results of these rings closing
13
New cards
**Map of the world according to Anaximander during 600 BC**
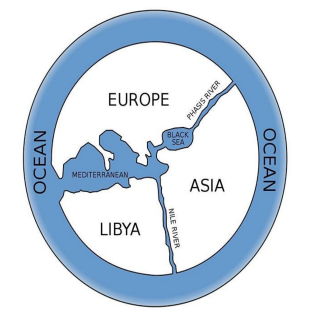
14
New cards
**Plato**
Student of Socrates
15
New cards
**Aristotle**
Studied under Plato
16
New cards
**Plato**
Believed that the cosmos is made up of matter in geometric shapes
17
New cards
**Aristotle**
\- Posited that the Earth was at the center of the universe with all other celestial bodies arranged in concentric crystalline spheres around it
18
New cards
**Geocentric Model**
\
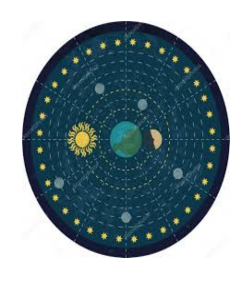
19
New cards
**Heliocentric Model**
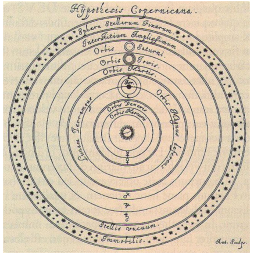
20
New cards
**Geocentric Model**
By Ptolemy, redined explanation behind the movements of planets
21
New cards
**Heliocentric Model**
By Copernicus “Father of Modern Astronomy”
22
New cards
**Geocentric Model**
Earth was unmoving while the Sun, planets and stars revolved around it
23
New cards
**NICOLAUS COPERNICUS**
For him, the geocentric model did not discuss the occasional backward movement of the planets or RETROGADE MOTION.
24
New cards
**Earth's rotation**
causes the rising and setting of the Sun and the seasons
25
New cards
**Earth's revolution**
causes the movements of the stars
26
New cards
**NICOLAUS COPERNICUS**
University of Krakow, studied astronomy, mathematics, philosophy and sciences. Proposed that the earth is not the center of the universe but the Sun.
27
New cards
**Nicolaus Copernicus**
According to him the movement of the earth sometimes cause the retrograde motion and planets travel in perfect circles
28
New cards
**Nicolaus Copernicus**
He finished his research in 1532, although he is hesitant to publish his ideas and took almost a hundred years before his theory formally gained respect and recognition
29
New cards
**Tycho Brahe (1546-1601)**
Rejected that the Earth is not the center of the universe. According to him, The earth is the fixed center, with the Sun and Moon orbiting the Earth, and the other planets revolving around the Sun.
30
New cards
**Tycho Brahe (1546-1601)**
proposed his own model, geoheliocentrism or the Tychonic System. Combination of Copernican and Ptolemaic systems
31
New cards
**`The Tychonic Model by Tycho Brahe (1546-1601)**
gues what revolution model and proposed by who?
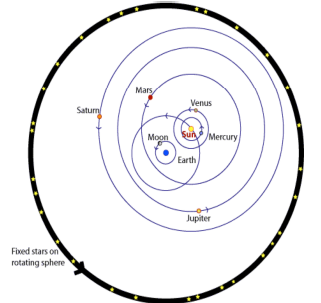
32
New cards
**JOHANNES KEPLER**
proposed the law of planetary motions in 1609. According to him, planets move in elliptical orbits with the Sun at one focus.
33
New cards
**Galileo Galilei**
Best known for his works in the field of astronomy, cosmology, philosophy, mathematics and physics. Proposed that Earth orbited around the Sun.
34
New cards
**GALILEO GALILEI**
First person to observe craters of the moon using telescope. Using a telescope, he was able to observe movements of the Moon, Venus, Jupiter and its satellites. Discovery of existence of sunspots
35
New cards
**Sir Isaac Newton**
First one to provide mathematical equations that could prove Copernicus, Brahe and Kepler have explained
36
New cards
**GALILEO GALILEI**
Persecuted and put on trial by the Inquisition in Rome. Found guilty of heresy
37
New cards
**Sir Isaac Newton**
Philosopiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica
38
New cards
**Giordano Bruno**
Martyred Italian monk who spread Copernicus’s theory of a heliocentric and scientific universe
39
New cards
**Anton Van Leeuwenhoek**
\-Father of Microbiology. Discovered bacteria
40
New cards
**Robert Boyle**
Father of Modern Chemistry. Extensive experiment and use of Scientific method
41
New cards
**Francis Bacon**
Supporter of the empirical method and inductive reasoning which provide that people understand truths according to their experience
42
New cards
**Rene Descartes**
Practiced deductive reasoning and the scientific method in solving problems and whose idea of the human consciousness dominated until the 20th century
43
New cards
**Evolution**
is the change in characteristics of a species over several generations, relying on the idea that all species are related and gradually change over time.
44
New cards
**PRE-DARWINIAN BELIEF**
It has always been controversial.
45
New cards
**Creationism**
the view that the universe originated from “specific acts of divine creation
46
New cards
**Carolus Linnaeus**
He subscribed to the Judeo-Christian version of creationism and saw their work as a mere representation of the unchanging order of life created by God.
47
New cards
**Erasmus Darwin**
a physician and a discreet evolutionist (transmutationist – one who believed evolution occurred in living things)
48
New cards
**Zoonomia; or the Laws of Organic Life**
contained theories about evolution and suggested that the Earth could have been much older than the timeline based on the biblical origin
49
New cards
**Charles Darwin**
At age 16, he entered Edinburgh University to study medicine
50
New cards
**Robert Grant**
* A radical evolutionist and a follower of French biologist, Jean-Baptiste Lamarck.
* Darwin’s mentor.
* growth and relationship of primitive marine invertebrates
* Darwin’s mentor.
* growth and relationship of primitive marine invertebrates
51
New cards
**CHARLES DARWIN**
Also influenced by **ADAM SEDWICK** and **JOHN STEVENS HENSLOW**
52
New cards
**CHARLES DARWIN**
* Summer of 1931, Adam Sedgwick and Darwin traveled to Wales
* December 27, 1831, Henslow and Darwin went on a voyage to Tierra del Fuego
* HMS Beagle with Captain Robert Fitzroy
* December 27, 1831, Henslow and Darwin went on a voyage to Tierra del Fuego
* HMS Beagle with Captain Robert Fitzroy
53
New cards
**England in 1836**
Charles Darwin wrote his findings in the Journal of Researches
54
New cards
**Charles Darwin**
Was published as part of Robert Fitzroy’s narrative of the voyage (Zoology of the Voyage of the HMS Beagle)
55
New cards
**Darwin’s observations**
the similarities of different species in different parts of the globe and their variations in specific areas led him to believe that they evolved from common ancestors
56
New cards
**Natural selection**
a process where species that adapt to the changing environment survive, whereas those that do not simply die out On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection
57
New cards
**Charles Darwin**
Father of Evolution
58
New cards
**Richard Owen and John Gould**
Darwin’s findings were scrutinized by experts
59
New cards
**Darwin's publication**
steered the intellectual history of humanity in a new direction
60
New cards
**Darwinian Revolution**
* completed the Copernican Revolution
* radically changed the perception of humans of their place in the universe
* drew out for biology the notion of nature as an orderly system governed by natural laws , where the origin of humanity itself could be explained
* following this theory, the contemporary study of DNA of different species showed evidence of his theorization of evolution
* radically changed the perception of humans of their place in the universe
* drew out for biology the notion of nature as an orderly system governed by natural laws , where the origin of humanity itself could be explained
* following this theory, the contemporary study of DNA of different species showed evidence of his theorization of evolution
61
New cards
**Darwinism**
Darwin's theory of biological evolution, paved the way not only for developments in evolutionary biology but also a foundation for the philosophy of biology
62
New cards
**Evolutionary Biology**
sub-discipline of biological sciences that has to do with the origin of life as well as diversification and adaptation of life forms through time
63
New cards
**JULIAN HUXLEY**
coined the term modern synthesis or NeoDarwinism, reconciling Darwin's theory with that of Gregor Mendel's idea on heredity
64
New cards
**Philosophy of Biology**
* A branch of philosophy of science that has to do with biology
* It makes biology relevant to classic issues in the philosophy of Science such as causation and explanation, progress, reductionism, and chance.
* It makes biology relevant to classic issues in the philosophy of Science such as causation and explanation, progress, reductionism, and chance.
65
New cards
**PRE-FREUDIAN PSYCHOLOGY**
* Psychology as a branch of philosophy
* Psychology’s development into an independent scientific field
* Psychology’s development into an independent scientific field
66
New cards
**Priest, Shamans, Spiritual Leaders**
Since the dawn of the civilization and establishment of the earliest religions and spiritual beliefs. People were dependent on:
67
New cards
A formal study of the mind
But as time passed by, psychology developed and was defined as ________ and a more systematic approach to understanding and curing mental conditions
68
New cards
**Plato (427- 347 BCE)**
Proposed that “psyche” was the seat of all human knowledge
69
New cards
**Aristotle (384 – 322 BC)**
Wrote “Para Psyche” (About Human Mind). Proposed that the human mind was the primary reason for the existence and functioning of the body.
70
New cards
**Psyche**
word used to describe mind and soul
71
New cards
**Anamnesis**
process of unlocking and utilizing knowledge in our human mind
72
New cards
**Para Psyche**
the first known text in the history of psychology
73
New cards
**Late 1870s**
psychology developed into an independent scientific field
74
New cards
**Wilhelm Wundt (1832-1920)**
\- founder of first laboratory dedicated to psychological research
75
New cards
**Wilhelm Wundt (1832-1920)**
“Founder of Experimental Psychology”
76
New cards
**Principles of Physiological Psychology**
This sought to investigate the immediate experiences of consciousness including sensations, feelings, volitions and ideas
77
New cards
**William James**
* “Father of American Psychology”
* Known for “pragmatism”
* Known for “pragmatism”
78
New cards
**Ivan Pavlov**
Known for discovering Classical Conditioning
79
New cards
**Hermann Ebbinghaus**
\- Developed the first scientific approach to the study of a higher psychological process (memory)
80
New cards
**René Descartes (1596–1650)**
* 17th century philosopher
* known for his "Cartesian paradigm"
* known for his "Cartesian paradigm"
81
New cards
Dualism
What Cartesian paradigm called?
82
New cards
mind-mind problem
Mind in relation to itself
83
New cards
mind-body problem
mind in relation to the body
84
New cards
Dualism
asserts that mind and body are two entities that interact to form human experience
85
New cards
**René Descartes (1596–1650)**
According to a philosopher, humans are immediately aware of their own cognitive states and process out of necessity, and such self-aware mind is distinct to the body.
86
New cards
Mind
______ is a mere non-physical thing that interacts with the physical body through the brain as medium.
87
New cards
brain
Mind is a mere non-physical thing that interacts with the physical body through the _______ as medium.
88
New cards
During 19th century
* Cartesian paradigm came under pressure
* Studies of disorders caused by brain lesions showed that mental faculty for language is connected to a
* Studies of disorders caused by brain lesions showed that mental faculty for language is connected to a
89
New cards
**Charles Darwin’s Evolution Theory**
This theory states that every aspect of humans including their mental capacities, evolved in response to the physical selection process
90
New cards
**Sigmund Freud**
All cognitive processes are unconscious.
91
New cards
**Sigismund "Sigmund" Scholomo Freud**
* His interest in laboratory work shifted from microscopic studies to living patients
* He spent most of his life studying human psychology.
* He spent most of his life studying human psychology.
92
New cards
Psychoanalysis
Freud created his magnum opus called _____ which includes: methodology of treating mental illnesses
93
New cards
**Sigismund "Sigmund" Scholomo Freud**
He earned the title “Father of Psychoanalysis”
94
New cards
Psychoanalysis
\*It is anchored on the concept that human behavior is determined by: Unconscious motivation and biological and instinctive drives
95
New cards
Eros
refers to the survival instincts like hunger, thirst, and sexual impulses
96
New cards
Thanatos
Aggressive and self-destructive instincts driven toward death.
97
New cards
ID
\- Unconscious aspect of personality like untamed instincts, impulses, and desires.
98
New cards
Ego
\- It is responsible for dealing in reality
99
New cards
ID
present since birth and operates by the pleasure principle
100
New cards
EGO
\- Its main function is to be the referee between id and the demands and expectation of the society