BCH4024 Lecture 4
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
proteins are stabilized by ___ interactions
noncovalent
function is based on the ____ structure
tertiary or 3D
native
functional, stabilized by weak interactions but with decent stability
H bonds, Hphobic effect, ionic interactions
disulfide bonds rare but important
solvation layer
shell of H2O structure around Hphobic molecule
decreases with np clusters, causes increase in entropy
repeating units optimize ____
H bonding and salt bridges
R groups are (in/out) of the plane of a peptide group
out
alpha helix
simplest, common, maximizes H bonds
each helical turns 3.6 residues or 5.4A
1 pitch per helix
proline
introduces destabilizing kink
glycine
has high conformational flex and takes up coiled structures
right-handed
R groups protrude away
most common;
backside arrow faces right
extended left-handed heliz
theoretical but not stable enough;
backside arrow faces left
beta conformation
backbone extends into zigzag, organizes into sheets
strand = single protein segment
sheet = several strands
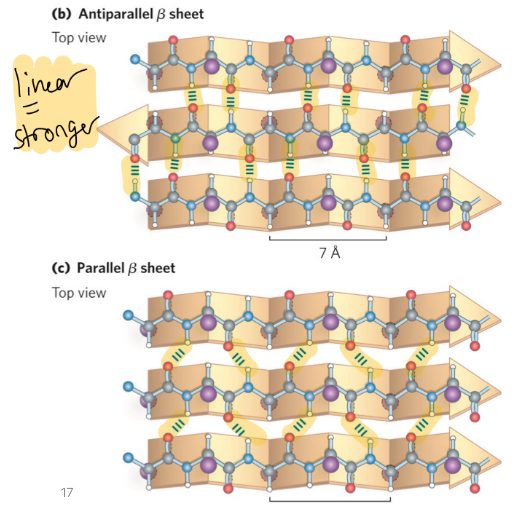
anitparallel beta sheet
more frequent, H bonds are linear = stronger, upside down next to right side up
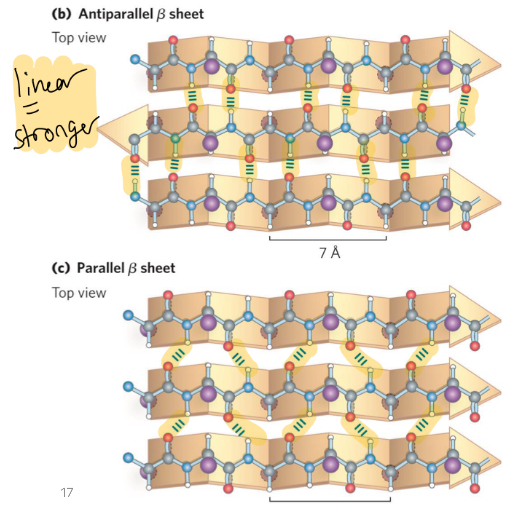
parallel
copy paste, go same direction, less stable
beta turns
connect ends of 2 antiparallel sheets;
4 residues and 180 turn
often involves Pro and Gly
Ramachandran plots
visualize phi and psi angles to test quality of structure
!!ci

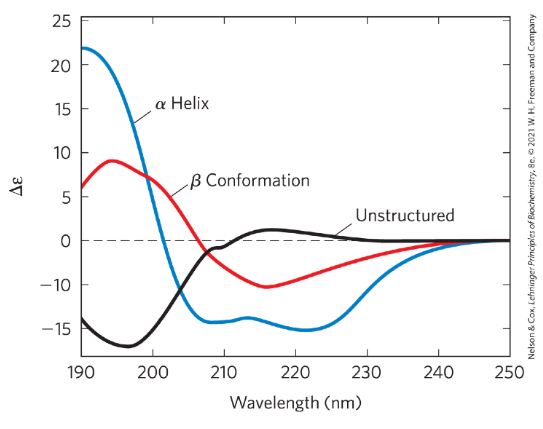
circular dichroism (cd) spec
measures diff in molar absorption of left v right handed light
delta epsilon = epison L - epsilon Rch
chromophore
peptide bond, can absorb light
membrane proteins
embedded in Hphobic lipid membranes
intrinsically disordered proteins
lack stable tertiary structures;
lack Hphobic core;
lots of charged residues which helps multiple binding partners;
can change structure
fibrous protein
long strand or sheets;
give strength and flex;
simple repeating element, H2O insol
alpha helix crosslinked by disulfide bonds (fibrous proteins)
tough, insol, protection, hardness, flex;
keratin
beta conformation (fibrous proteins)
soft, flex filaments;
silk fibron
collagen triple helix (fibrous proteins)
high tensile strength, no stretch;
tendon collagen, bone matrix
alpha keratin in hair
right hand alpha heliz;
2 strands of alpha keratin parallel and supertwisted to the left bc of their Hphobic side chains;
rich in Hphobic residues ala, val, leu, ile, met, phe;
cross link stabilized by disulfide
collagen in connective tissue
left handed tripeptide Gly-Pro-Hyp;
right trwisting of 3 poly;
fibrils cross linked by covalent bonds with Lys or His
scurvy
lack of vitamin C
degeneration of connective tissue
vit c required for hydroxylation of proline and lysine in collagen
globular proteins
folded into spherical or globular shape;
fold back onto each other to be super compact
enzymes, transport, motor, regulation, immunoglobulins
myoglobin
alpha helical regions, binding pocket, and Hphobic R chains
motif
fold with 2+ elements of secondary structure
beta-alpha-beta loop or beta barrel
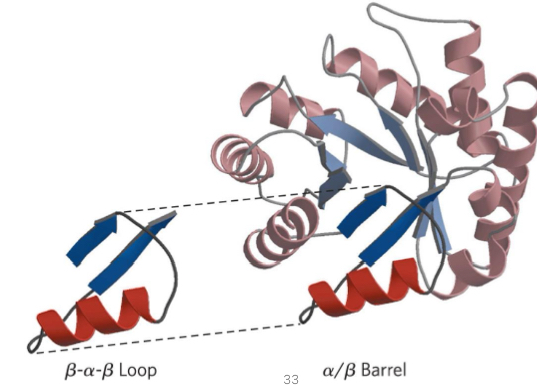
domain
polypeptide chain part that is independently stable
protein folding rules
bury Hphobic R groups with 2+ layers of secondary
a helix and b sheets are in diff. layers
beta conformation best with right hand connections
alpha-beta barrel
series of alpha-beta-alpha loops so B forms barrel
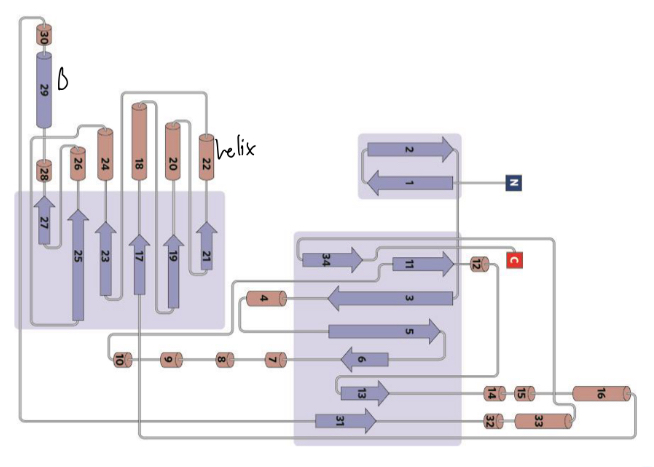
!
topology diagram
!
families
same primary functions and or tertiary structure
superfamily
2+ families with similar structural motif and function but not sequence
oligomer
multimer = multi-subunit protein