Trends of the periodic table
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What is electronegativity?
the tendency of an atom to attract a shared paired of electrons in a covalent bond.
Provide the names of all the group names and their respective group numbers
1: Alkali metals
3-11 : transition elements
17: Halogens
18: Noble gases
Define atomic radius
The distance from an atom's nucleus to the outermost orbital of one of its electrons.
half of the distance between two adjacent nuclei.
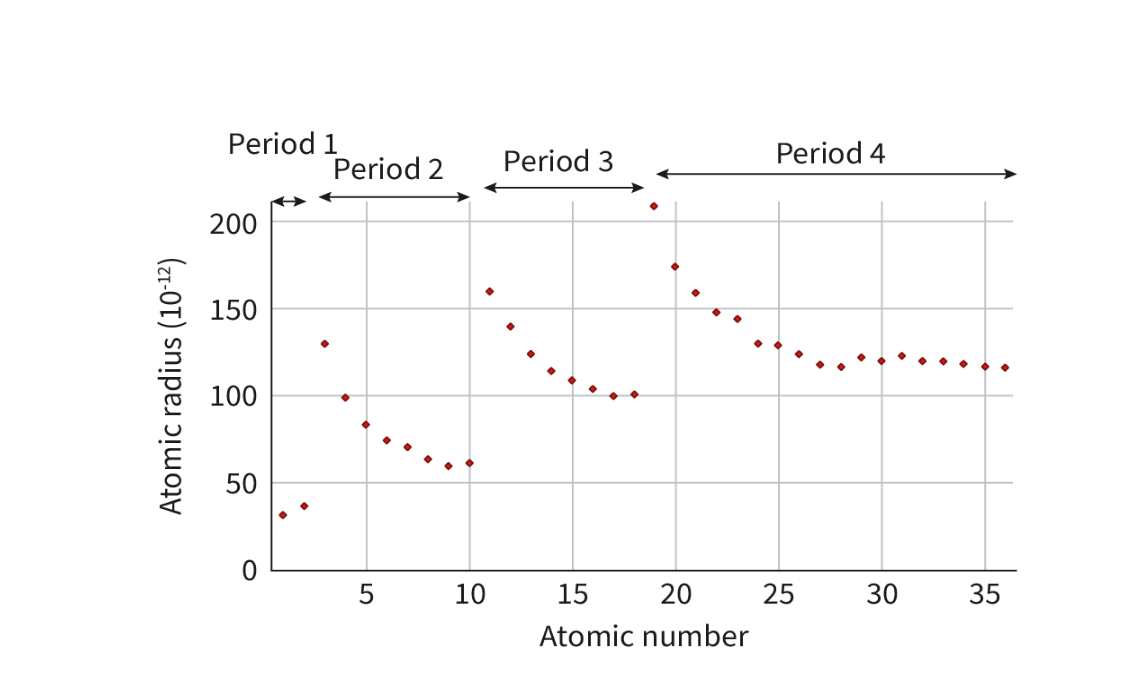
Explain the trend of atomic radius across a period.
Draw its graph
Decreases.
Each successive element has an additional proton
. hence a higher nuclear charge
means that there is greater attraction between the valance electrons and the nucleus so they become smaller
as the electrons are added to the same energy level each there is no increase in shielding by inner electrons
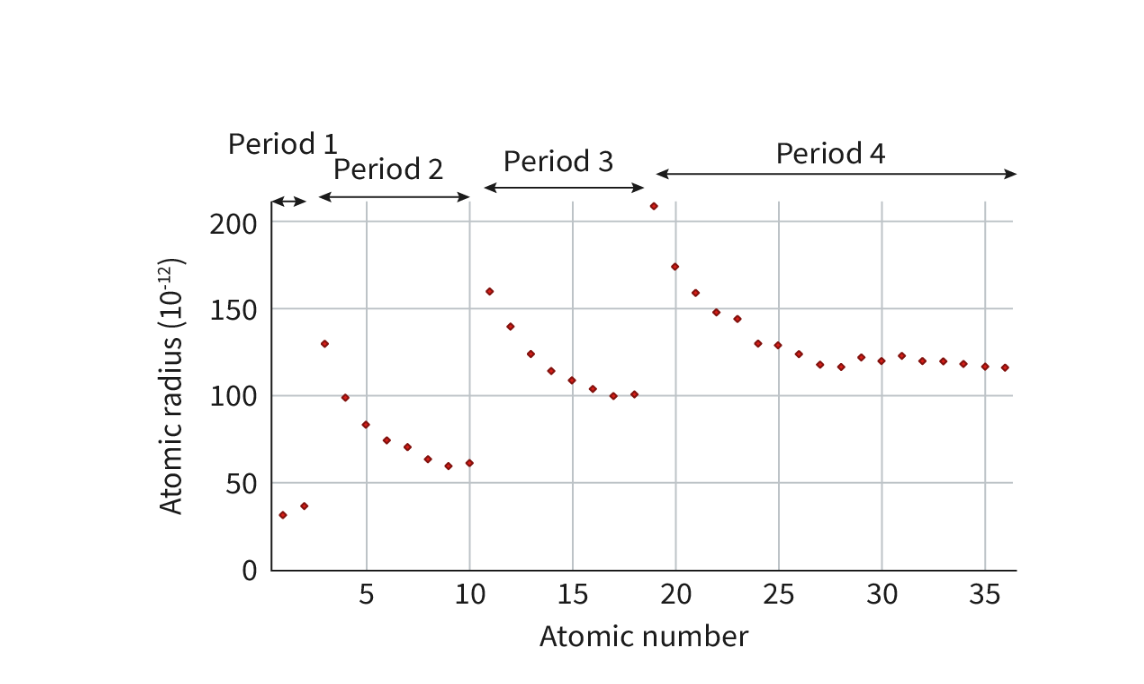
Explain the trend of atomic radius down a group.
Draw its graph.
Increases
number of occupied energy shells increases.
. Although the number of protons increases, and therefore the nuclear charge also increases, the valence electrons are added to a higher energy level.
results in the outermost electrons being shielded from the attractive electrostatic force of the nucleus by a greater number of inner levels of electrons.
Explain the trend of ionic radius across a period in group 1,2 and 3.
Draw its graph.
Loss of electrons (typically all electrons) from outermost energy level.
forms Cations (positive ions)
have increased attraction between nucleus and valance shell electrons
The greater the number of electrons removed, the smaller the ionic radius.
Exlain the trend of ionic radius across a period in group 15.16 and 17.
forms anions (negative ions)
ionic radius increases because as the valance shell gain electrons
it increases the repulsion between electrons which causes
a decreased attraction between nucleus and valance shell electrons.
(the greater the amount of electron gained the larger the ionic radius)
Larger in size than their parent atom.
Explain the trend of ionic radius down a group.
Draw its graph.
ionic radius increases for both cations and anions due to the increasing number of electron energy levels and increased shielding of the nucleus.
(similar to the trend for ionic radius)
How does nuclear charge effect the radius of an atom and what is the nuclear charge.
The greater the effective nuclear charge, the stronger the force of attraction between the nucleus and the outer electrons, therefore the smaller the radius.
(The net positive charge from the nucleus experienced by outer valence shell electrons once the screening effect of the core electrons has been considered.)
What are metalloids and where are they located?
An element located between metals and non-metals in the periodic table and shows intermediate properties between them.
They can form both ionic and covalent bonds
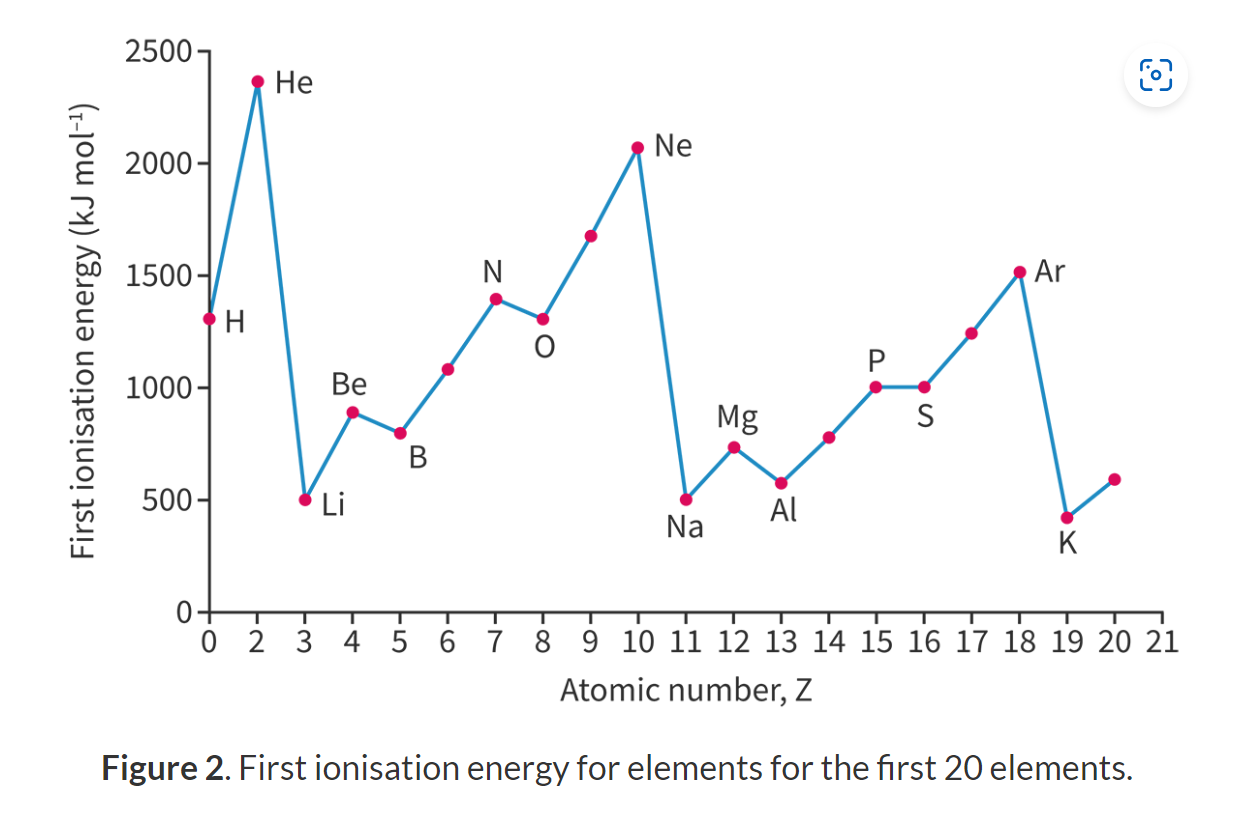
Explain the trend of ionisation energy down a group.
Draw its graph.
Decreases down a group.
The number of energy level increases (atomic radii increases) down a group and the shielding becomes greater (electrons in higher energy level have a weaker attraction to the nucleus) so less energy is required to ionize atoms/to remove an electron.
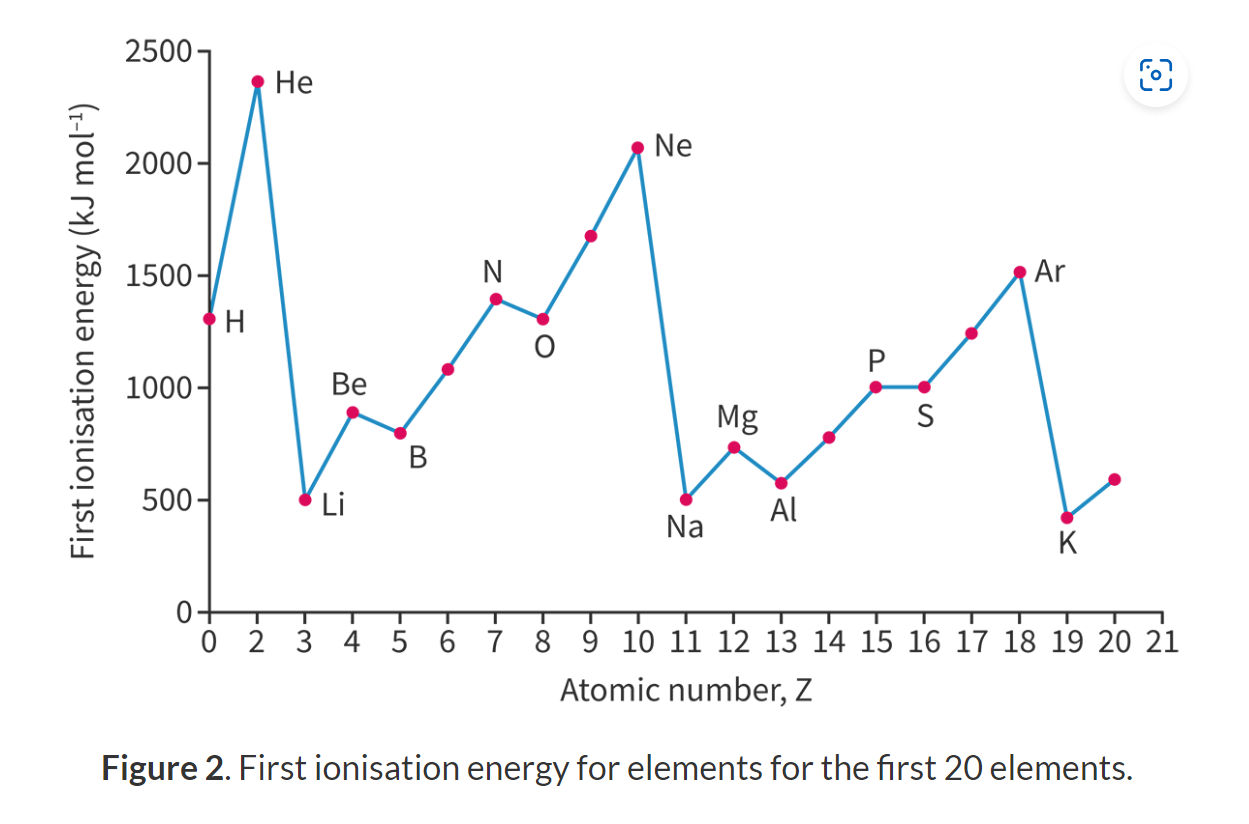
Explain the trend of ionization energy across a period.
Draw its graph.
Increases across a period.
more protons in the nucleus (increasing effective nuclear charge)
and more electrons occupying the outermost energy level resulting in a stronger attraction to the nucleus.
while shielding effect remains nearly constant (because the number of inner electrons does not change)
so more energy is required to remove an electron.
How to differentiate between isoelectronic species and what are they?
(not in the spec)
isoelectronic species are the ones with the same electronic configuration.
But because they are formed from different elements , with a different proton number, their size varies depending on the ratio of protons to electrons because they have different nuclear charges.
(the species with the greatest number of protons will have the greatest effective nuclear charge).(the greater the effective nuclear charge, the strongest the stronger the force of attraction between the molecules and the outer electrons so the smaller the radius.)
Explain the differences in ionisation energy and atomic radius in terms of it changing across a period and down a group.
Opposite trends.
Both relies on the attraction of the outer valance shells to the nucleus.
the stronger the attraction the smaller the radius and the more energy required to remove an electron.
and vice versa.
(the weaker the attraction, the larger the atomic radius and the less energy required to remove an electron)
What is electron affinity and Explain the trend of it across a period.
Electron affinity (EA) is the energy released when an additional electron is attached to a neutral atom or molecule. {elements with larger electron affinity are those with great tendency to gain electrons}
Increases across a period. (higher affinity for gaining an electron)
higher effective nuclear charge
stronger attraction between the added electrons and the nucleus so more energy s released when electrons are added.
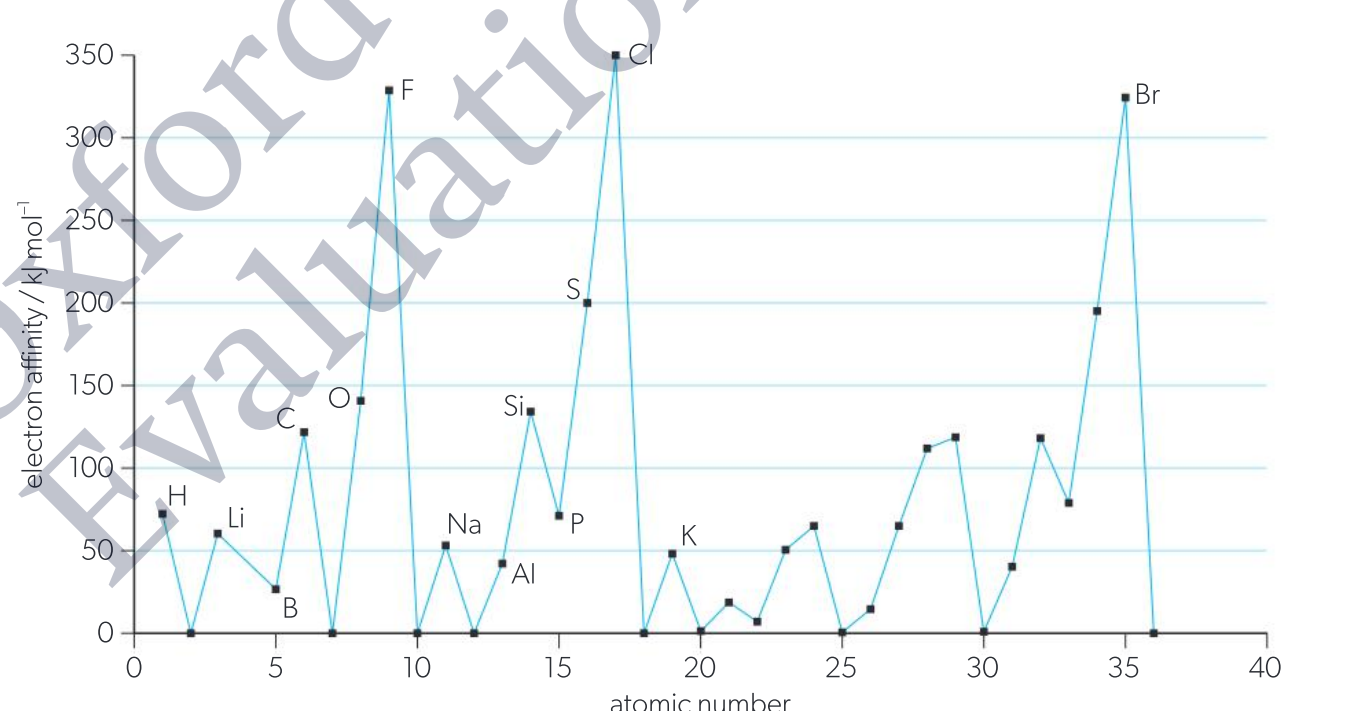
Why is energy released during electron affinity?
due to the small forces of attraction between the nucleus and the incoming electron.
What is electron affinity and Explain the trend of it down a group
Electron affinity (EA) is the energy released when an additional electron is attached to a neutral atom or molecule. {elements with larger electron affinity are those with great tendency to gain electrons}
decreases down a group. (similar to ionisation energy) lower affinity for gaining an electron.
larger atomic radius with outer valance shells further away from the nucleus.
Weaker attraction between the added electrons and the nucleus.
From the book tho:
Only applicable for group one because for some elements adding an electron results in a less stable electron configuration which reduces the energy released.
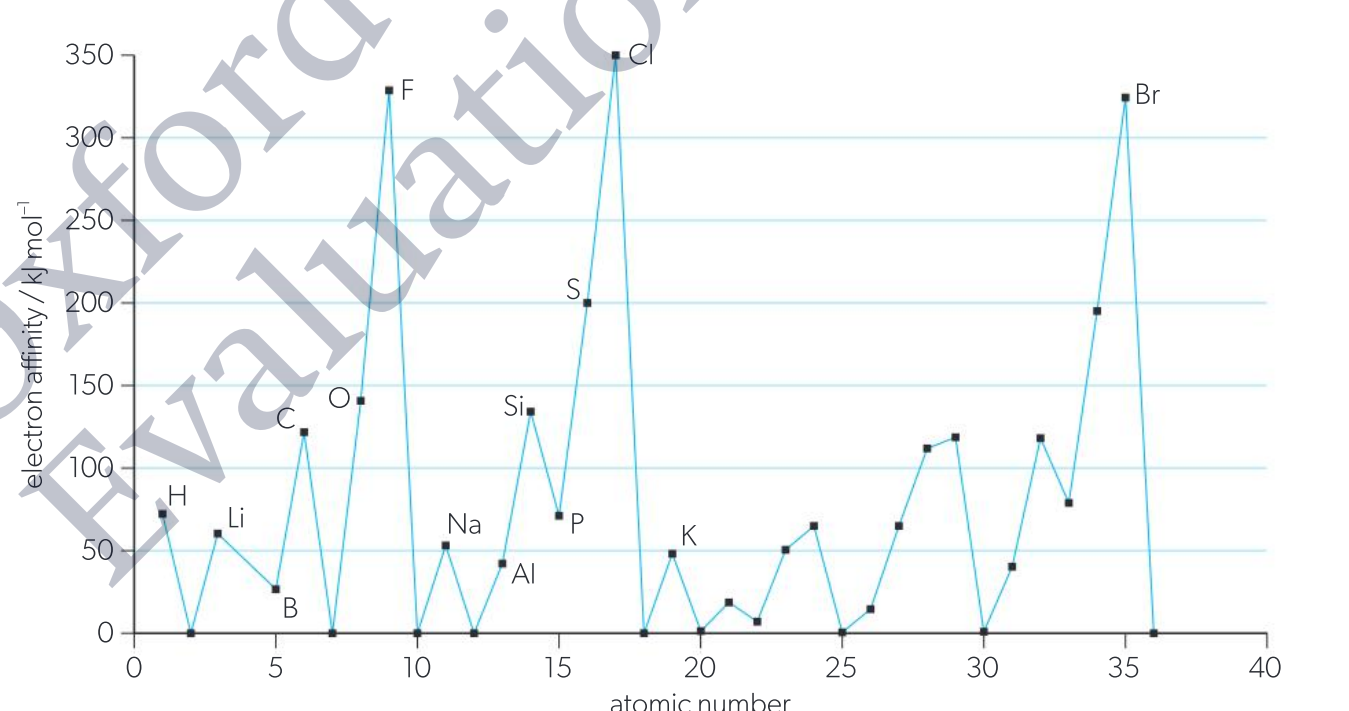
What is electronegativity and Explain the trend of it across a period.
the tendency of an atom to attract a shared paired of electrons in a covalent bond.
Increases across a period.
Effective nuclear charge increases so stronger attraction between the nucleus and the shared pair of electrons.
What is electronegativity and Explain the trend of it down a group.
the tendency of an atom to attract a shared paired of electrons in a covalent bond.
Decreases down a group.
Atomic radius increases due to additional energy levels
weaker attraction between the nucleus and the Shared pair of electrons due to shielding.
Describe the trend of everything in a periodic table and what is responsible for it all.
the attraction between the nucleus and the outer valance shell
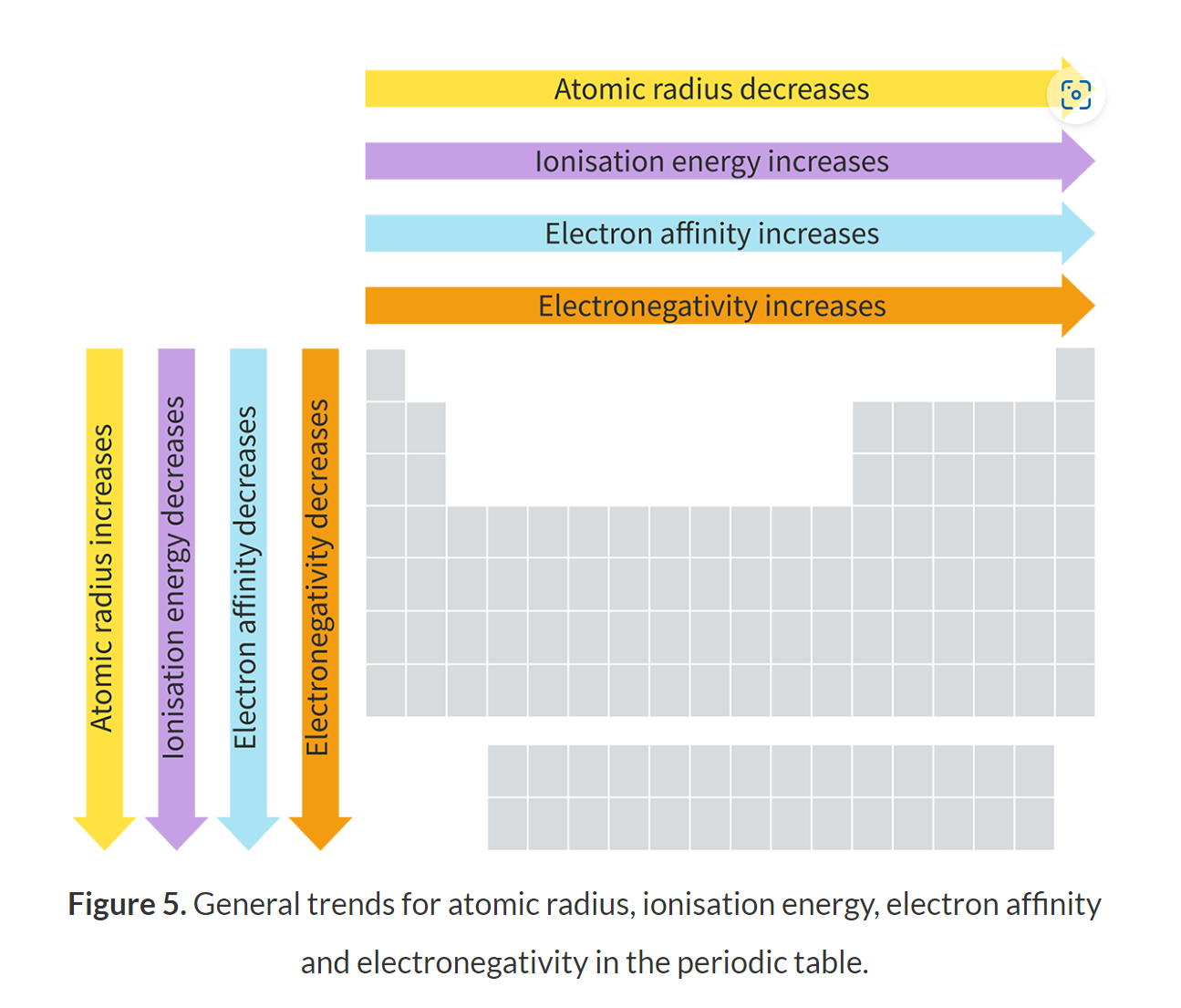
What does a group 1 metal produce when it reacts with water?
Hydrogen gas
Hydroxide metal