origin and regulation of the heart and cardiac cycle
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
cardiac conduction system
SA node→R and L atrial cardiomyocytes→AV node→bundle of his→purkinje fibre network→R and L ventricular cardiomyocytes
non contractile cardiac cells
larger than standard cardiomyocytes
fewer contractile protein
more glycogen and mitochondria
connected by desmosomes and gap juntions
no intercalated disks
pacemaker action potentials
pacemaker cells are myocardial cells of the SA and AV nodes
SA nodal cells depolarise and set the rate
synchronisation- the action potential is conducted down the conduction system as an electrical impulse and between cardiomyocytes via gap junctions
rate of depolarisation
sa node - 75 bpm
av node- 50 bpm
bundle and purkinje- 30bpm
features of cardiac muscle
Cardiac muscle is a functional syncytium - cells (myocytes) are electrically and mechanically coupled.
• Self-contracting.
• Single nucleus
. • Intercalated discs located between cardiac muscle cells
. • Gap junctions provide passage for ions and small molecules.
• Desmosomes and adheren junctions provide mechanical continuity.
High mitochondrial density - a continuous supply of ATP is needed to support contraction
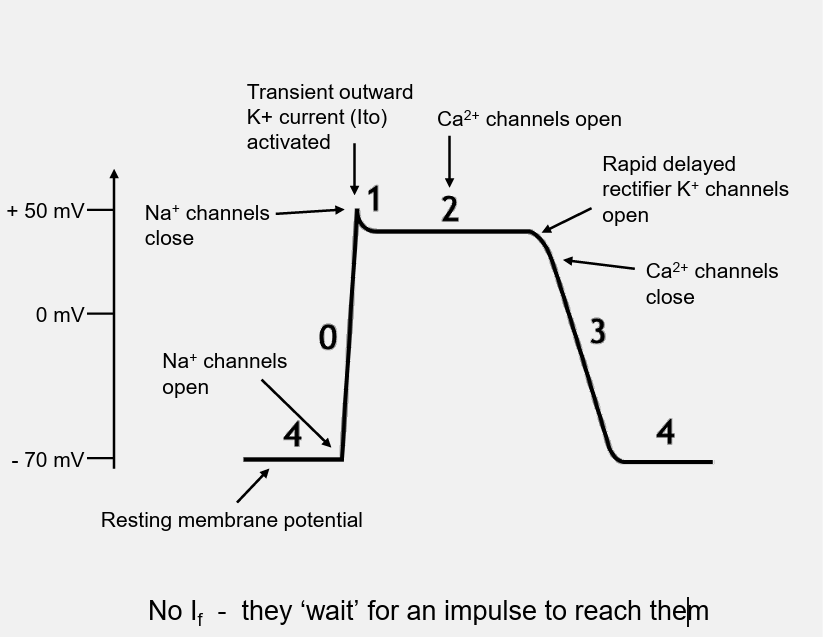
ventricular action potential
4- resting potential
0- rapid depolarisation. sodium channels open and membrane potential positive
1- slow release potassium current, small drop in membrane potential
phase 2- plateau phase. calcium influx balances out potassium efflux. calcium influx stimulates intracellular calciium ions releasing initiating contraction, no further action potential can occur- refracotry period
3-Repolarisation Rapid K+ efflux returns membrane potential back to -70 mV.
cardiac contraction
action potential conducted to contractile myocytes through gap junctions
AP travels between sarcomeres activating calcium ion channels in the t tubules leading to the influx of calcium ions
DHPRs are voltage gated calcium channels in skeletal muscle initiate relase from the SR.
Conformational change of the DHPRs in excitation contraction coupling causes nearby RYRs to open releasing stored calcium ions.
calcium ions binds to troponin c which exposes actin binding site allowing contraction
cardiac relaxation
calcium removed through sr uptake and efflux through membrane channels
calcium removal returns troponin complex to inhibitng position on actin, ending contraction, actin returns to original
enzyme SERCA 2a returns calcium ions back into SR
ECG
p wave- atrial depolarisation
qrs- ventricle depolarisation
t wave- repolarisation of ventricles
pr interval- av conduction time
st segment- isoelectric period- both ventricles completely depolarised
qt interval- time for both ventricular depolarisation and repolarisation to occur- average duration of ventricular action potential
rr interval- measure of cardiac cycle length
what can an ecg show
heart rate
heart rhythm
origin of excitation
anatomical orientation of heart
relative size of heart chambers
spread of impulse
decay of excitation
no info about contractile properties and pumping action
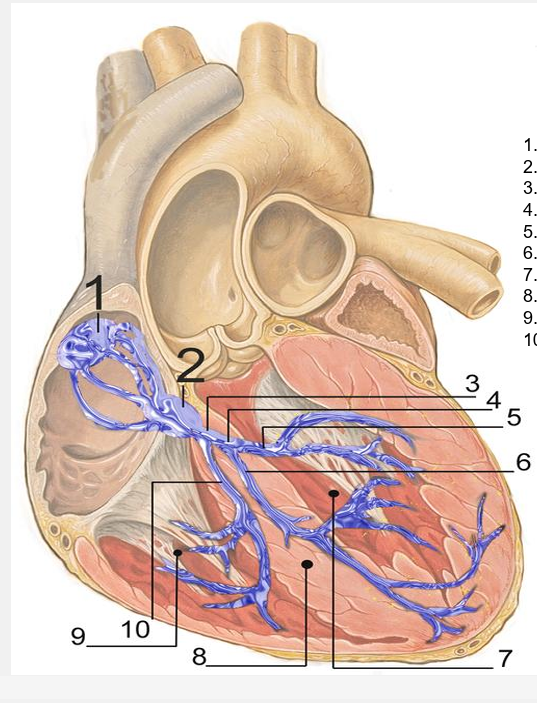
SA node
AV node
bundle of his
left bundle branch
left posterior fascicle
left anterior fascicle
left ventricle
ventricular septum
right ventricle
right bundle branch
cardiac cycle
atrial contraction
isovolumetric contraction (AV valve closure and increase in pressure without any volume change)
rapid ejection
reduced ejection
isovolumetric relaxation (period after ventricular contraction where aortic valve has closed but mitral valve has not opened yet)
rapid filling
reduced filling