C4 Chemical Change
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
oxidation
reduction (oilrig)
loss of electron gain oxygen gain of electron loss of oxygen
some ___ is ____ using ______ the ______ gains ______. This can only happen with metals below _____ in the reactivity series
ores reduced carbon carbon oxygen carbon
reactivity series mnemonic …
purple slime can make a careless zebra insane try learning how camels surprise gorillas
potassium sodium calcium magnesium aluminium carbine zinc iron tin lead hydrogen copper silver gold platinum
learn (transition metals e.g iron)
yes
______ is pure because
gold, platinum its unreactive is is cleaned with chemical processes
acid + metal oxide
acid + base
acid + metal carbonate
acid+ metal
salt+ water
salt + water
salt + water + carbon dioxide
salt + hydrogen
Making soluble salts: (crystals)
Pick the right insoluble____ or ________ ____ and _____
2) Gently warm the dilute _____ a bit at a time using a Bunsen Buner. then ___ __ ___
3) add the ______ or _____ ____ to the acid until the ____ is in excess or no ______ are ______ indicating that the ____ has ______
4) Then _____ out the excess solid
5)To get crystals gently ____ the solution using a _____ _____ to ______ some of the water. Then stop ______ and let the solution ___. Crystals should form which can be filtered and dried
base metal carbonate acid acid turn it off. base metal carbonate base bubbles produced acid reacted filter heat water bath evaporate heating cool
aa more accurate way of measuring pH
pH probe
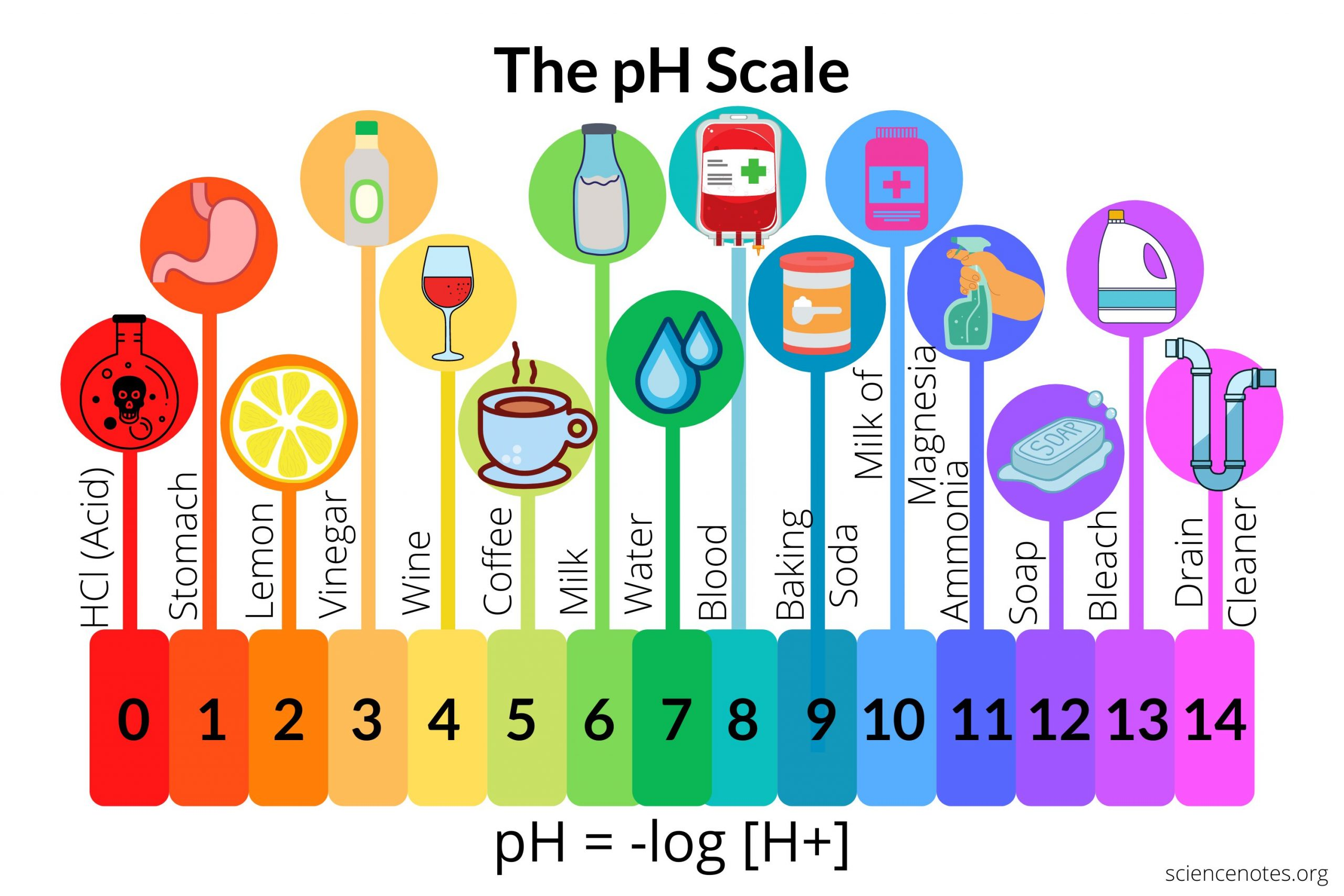
acids form _____ alkalis form ______ only in ______ this is called ______
H+ OH- ions in water neutralisation
Pipette
burette
measures only one volume of a certain solution measure different volume and let you add the solution drop by drop
Titration required practical:
Please fill this in later i cant do this right now sos.
acids produce ___ in water. They ____ in ______ ______ - producing ____.
SO HYDROCHLORIC GAS IS NOT ACIDIC
protons ionise aqueous solutions H+ ions
strong acids ____ ______, all the acid particles _______ to release ____ ___. whereas weak acids don’t fully ____. Only some _____ _____ ______ to release _____ ___.
ionise completely disassociate H+ ions dissociate acid particles dissociate H+ ions
ionisation of a weak acid is ______
reversible
acid reactions involve ____ ____ reacting with other substances. if the ____ of ___ ___ is higher, the ___ ___ _____ is _____ so strong acids are more ___ than weak acids of the same ______.
H+ ions concentration H+ ions rate of reaction faster reactive concentration
pH of an acid or alkali is the measure of ____ ___ in the solution. Every _______ on the pH scale of _____ the concentration of _ ___ ________ by a factor of ____.
H+ ions decrease 1 H + ions increases 10
concentrated
strength
how much acid in a certain volume of water what proportion f acid molecules ionise in water