BY 124L Topic 6: Kingdom Animalia Part 2
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Bonus Question: A Portuguese Man-O-War is Comprised of 4 what?
tightly connected individuals that are nearly identical genetically
Bonus Question: The 4 individuals on a Portuguese Man-O-War are born _________ and form as growth continues
together
Bonus Question: Each of the individuals on a Portuguese Man-O-War have 4 specialized functions, what are they?
Floating, Capture of Prey, Reproduction, Digestion
What Domain are animals in?
Eukarya
What Kingdom are we?
Kingdom Animalia
What Sub-Kingdom are we in?
Eumetazoa
What are three phylums under Eumetazoa (deuterostomes)?
Brachiopoda, Echinodermata, Hemichordata
What does the blastopore become in Deuterostomes?
blastopore becomes anus
What are characteristics of Deuterostomes pertaining to symmetry, organs, germ layers/body cavity, body plan? (advanced organisms)
bilateral symmetry, organs are present, 3 germ layers/coelomates, tube-in-tube body
What are some characteristics pertaining the the Phylum Brachiopoda? (example and unique feature)
Lamp Shell, Has a "U" shaped lophophore (Tentacle that surround the mouth)
What are the five classes under the Phylum Echinodermata?
Ophiuroidea, Asteroidea, Echinoidea, Crinoidea, Holothuroidea
What are characteristics of the Phylum Echinodermata? (unique symmetries, unique system, feet type, nerve type, skeleton type, sex type, where live, capable of what)
Radial symmetry as adults, Bilateral symmetry for larva; water vascular system; tube feet; nerve ring; Ossicles (Calcareous endoskeleton); separate sexes; ALL marine, capable of regeneration
What is the water vascular system used for in the Phylum Echinodermata? (4 things)
Feeding, locomotion, respiration, sensory
What is a nerve ring? (Phylum Echinodermata)
A ring of nervous cells
What are Ossicles in the Phylum Echinodermata?
Calcareous endoskeleton (Fancy for calcium endoskeleton)
What are some characteristics of the Class Asteroidea? Phylum Echinodermata (example, feet on what, where mouth, special about arm, unique feature)
Sea Stars (NOT STAR FISH); Tube Feet on suckers; Mouth on ventral side; Arm regeneration; Madreporite
What is Madreporite? (Sea Star)
the entrance for sea water to enter the sea star (to keep its shape/sucking abilities)
What are some characteristics of the Class Ophiuroidea (Phylum Echinodermata)? (example, feet?, arm type)
Brittle Stars; No tube feet on suckers; Long, flexible arms
What are some characteristics of the Class Echinoidea? Phylum Echinodermata (2 examples and their types)
Sea Urchins (regular echinoids) and Sand Dollars (Irregular Echinoids)
What are some characteristics of the Class Holothuroidea? Phylum Echinodermata (example, capable of what, defense mechanism!)
Sea Cucumbers; Capable of regeneration; Defense? Evisceration
What is evisceration?
protrusion of visceral organs through a wound opening
What are some characteristics of the Class Crinoidea? Phylum Echinodermata (examples, age, mouths)
Feather stars and Sea lilies; Oldest and most primitive echinoderms; Mouths are pointed upward (on dorsal side)
What are some characteristics of the Phylum Hemichordata? (example, unique gills? slits?, cord?, regrow?)
Acorn worm; has gills or pharyngeal gill slits; has dorsal nerve cord ; can regrow any part of their bodies
What is the first animal with Chordate traits, but is not considered a chordate? What does it have?
Animals in the Phylum Hemichordata, dorsal nerve cord
What are the three sub-Phyla under the Phylum Chordata?
Urochordata, Cephalochordata, Craniata
What are the four characteristics specific to Chordates?
Has pharyngeal gills/slits; Has notochord; Has muscular post-anal tail; Dorsal, hollow nerve chord
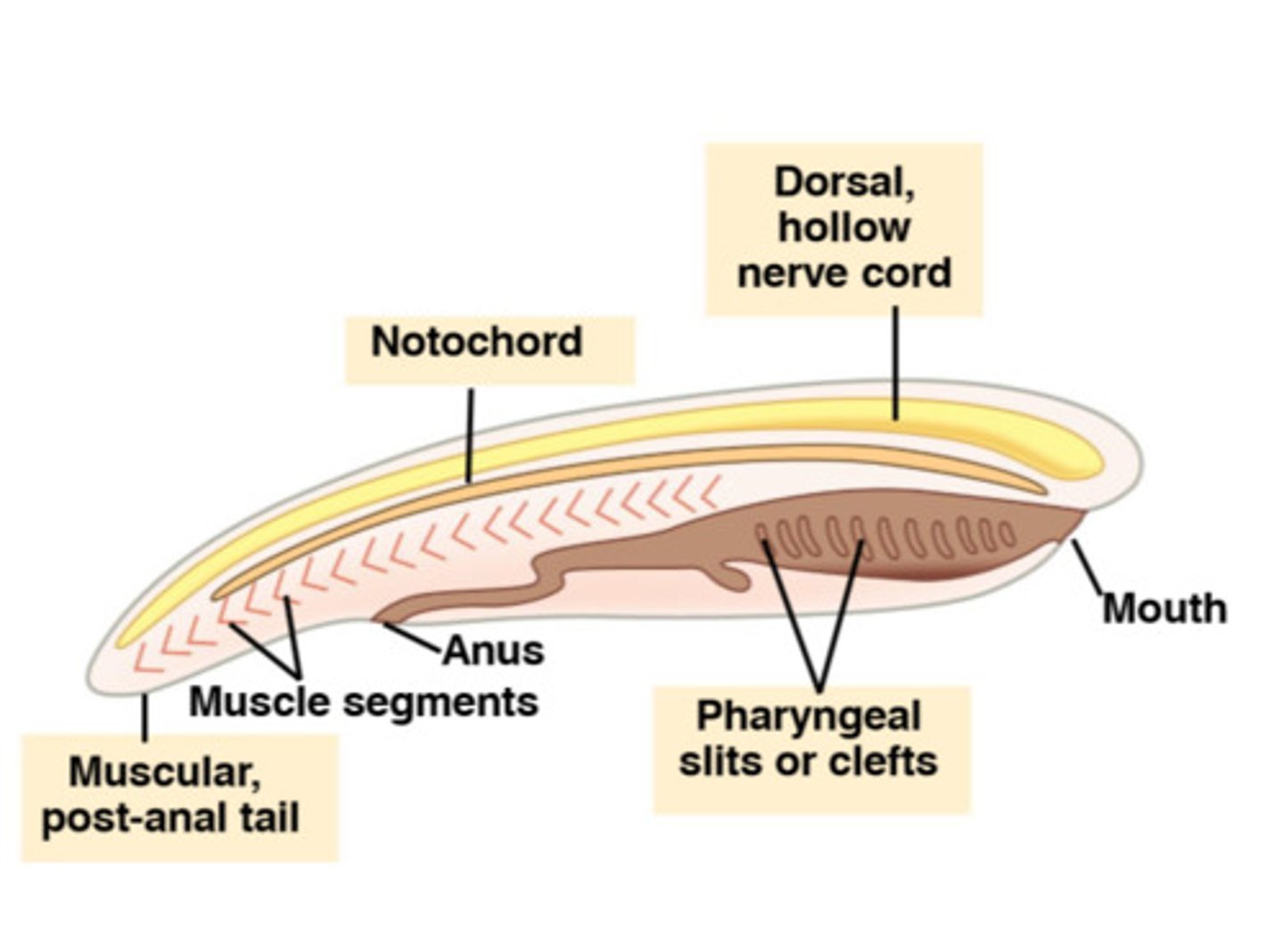
What are some general characteristics of Phylum Chordata? (body cavity, symmetry, body plan, germ layers, segmented?, organs?)
Coelomate, Bilateral symmetry, Tube-in-Tube, 3 germ layers, Segmented body, Organs present
What are some characteristics of the Subphylum Urochordata? Phylum Chordata (examples, movement or sedentary?, body plan, how feed, gill type, larva characteristics and what adults retain)
Tunicates and Sea Squirts; Adults are sessile, sac-like bodies; Filter feeders; Gill Slits; Larva have bilateral symmetry with ALL 4 chordate characteristics; Adults ONLY retain their gill slits
What are some characteristics of teh Subphylum Cephalochordata (Phylum Chordata)? (example, how feed, characteristics of chordates)
Lancelet (Amphioxus); Filter Feeders; All 4 characteristics of Chordates
Is the notochord or dorsal hollow nerve cord on top?
dorsal hollow nerve cord
What are some characteristics of the subphylum Craniata? (Phylum Chordata) (backbone?, where segmentation, gill slits retained?, tail present?)
Vertebrates ("back-boned animals"); Segmentation seen in muscles and vertebrae; Gill slits retained in some adults, others have different structures; Tail is present in some classes, but present during the embryonic stage only for others
What does the backbone replace in vertebrates?
notochord
What are two things the backbone can be?
cartilaginous or calcified
Vertebrates under go a process called neoteny, what is it?
Retention of juvenile traits into adult life
What are the two groupings under the Subphylum Craniata? (not taxonomic)
Pisces (fish) and tetrapods
What are the classes under the Sub Phylum Craniata? (Grouping Pieces)
myxini, Cephalospidomorphi, Placodermi, Chondricthyes, Osteichthyes
What are the two sub classes under the Class Osteichthyes? (Subphylum Craniata - Pieces)
Actinopterygii and Sarcopterygii
What are some characteristics of the Class Myxini? (Subphylum Craniata - Pieces) (example, type of fish, feed on what, skeleton type, heart?, defense)
Hagfish, "Jawless" fish, Feeds on detritus, Cartilaginous skeleton, 2 chambered heart, ALL THE SLIME
What is the first organism we see with a heart?
Hagfish (Class Myxini)
What type of animals have a 2 chambered heart? 3 chambered? 4 chambered? (deals with living in water)
2 - permanently in water, 3 - live in water half the time, 4 - do not live in water at all
What are some characteristics of the Class Cephalospidomorphi? Subphylum Craniata - Pieces (example, fish type, parasitic?, skeleton type, heart type)
Lamprey, "Jawless" fish, Parasitic, Cartilaginous skeleton, 2 chambered heart
What two classes of fish are jawless?
Class Cephalospidomorphi (lamprey) and Class Myxini (hagfish)
What are some characteristics of the Class Placodermi? Subphylum Craniata - Pieces (living or nah?, example)
ALL EXTINT, Armored Fish (Dunkleosteus)
What are some characteristics of the Class Chondrichthyes? Subphylum Craniata - Pieces (common name, examples, swimbladder/lungs?, urea?, line type, teeth are modified what, how fertilization)
Cartilaginous fish; Sharks, skates, and rays; NO swim bladder or lungs; Urea within blood helps osmoregulation; Lateral Line- Detection of water vibrations; Teeth are modified scales; Internal fertilization
What are the two forms of Internal fertilization for the Class Chondrichthyes?
Oviparous and Ovoviviparous
What is Oviparous? Class Chondrichthyes
Lays eggs, hatch outside of body
What is Ovoviviparous? Class Chondrichthyes
Retains eggs inside body, eggs hatch within body, hatchlings are then released
What are some characteristics of the Class Osteichthyes? Subphylum Craniata - Pieces (example, skeleton made of what, gill?, swim what?, heart type, fertilization how)
bony fish, -Skeleton contains calcium phosphate (Replaces the cartilage during development), operculum - gill coverings, swim bladder - depth adjustment, 2 chambered heart, external fertilization
What are some characteristics of the Subclass Sarcopterygii? Class Osteichthyes - Subphylum Craniata - Pieces (what type of fish, example)
Fleshy finned fish, Coelacanths (First thought to be extinct until found 1997 off of Africa)
What are some characteristics of the Subclass Actinopterygii? Class Osteichthyes - Subphylum Craniata - Pieces (what type of fish, example)
Ray-finned fish, Catfish
What are some classes under the Sub-Phylum Craniata, tetrapod grouping?
Amphibia, Reptilia, Aves, mammalia
What are some characteristics of the Class Amphibia? Sub-Phylum Craniata - tetrapod (lungs and skin, heart type, fertilization, metamorphosis?, neoteny?, warm or cold blooded?)
Have lungs, but some use moist skin for gas exchange; 3 chambered heart; External fertilization, water ties them for reproduction; undergo metamorphosis; Neoteny in some salamanders (by choice, or always); ectothermic (cold blooded)
Class Amphibia uses external fertilization, what do some of them have and what are these?
Spermatophores- packets of sperm laid for females to pick up
What are the three stages of Amphibia metamorphosis?
egg -> tadpole -> adult
What are the three orders under the Class Amphibia? Sub-Phylum Craniata - tetrapod
Anura, Urodela, Apoda
What are some characteristics of the Order Anura? Class Amphibia - Sub-Phylum Craniata - tetrapod (two types and differences)
frogs (smooth skin) and toads (rough, warty skin)
What are some characteristics of the Order Urodela? Class Amphibia - Sub-Phylum Craniata - tetrapod (two types and how different)
Newts are different than salamanders based on their skin and tail
What are some characteristics of the Order Apoda? Class Amphibia - Sub-Phylum Craniata - tetrapod (example, name meaning, worm?)
Caecilians, Name literally means "without legs", Looks like a worm
What are some characteristics of the Class Reptilia? Sub-Phylum Craniata - tetrapod (warm or cold blooded, heart type and exception, adapted for what)
Ecothermic, 3 chambered hearts EXCEPT FOR CROCODILES, Adapted for land
How are Reptilia better adapted for land? (limb type, skin type, lungs?, protect internal organs, fertilization type, egg type)
Advanced limbs, Scaled skin to prevent water loss (Keratinized skin), Better lungs, Ribcage to protect internal organs, Internal fertilization, Amniotic egg
What are 4 Orders under Class Reptilia?
Chelonia, Rhychocephalia, Squamata, Crocodilia,
What are two examples of Order Chelonia? Class Reptilia - Sub-Phylum Craniata - tetrapod
turtle and tortoises
Bonus Question: What are the two parts of a turtle's shell? can they remove their shell? how does temperature impact sex?
Carapace (top) and Plastron (bottom, cannot remove shell, dudes are cool and chick are hot
What are some characteristics of the order Rhychocephalia? Class Reptilia - Sub-Phylum Craniata - tetrapod (example, survivor, 3rd what)
Tuatara (Sphenodon- SOLE SURVIVOR OF AN EXTINCT ORDER), 3rd eye on tip of head
What are the two types of reptiles under the order squamata? Class Reptilia - Sub-Phylum Craniata - tetrapod
lizards and snakes
What is the difference between poison and venom?
poison is something you ingest, venom is something you are injected with
How to tell if a snake is venomous? (body type, eyes, head shape, colors, scales divided where)
Stalky body (THEY THICC), Cat-like eyes, Arrow-shaped head, Bright colors, Scales are NOT divided past the cloaca
What are some characteristics of the Order Crocodilia? Class Reptilia - Sub-Phylum Craniata - tetrapod (examples and heart type)
Crocodiles, alligators, caimans, and gavials; Crocodiles developed a "4 chambered heart"
If you are being attacked by an alligator what should you do and why?
run in a zig zag, they can't most fast enough to pivot
Bonus Question: If you climb up a tree are you safe from an alligator?
No, they can jump out of the water as long as they are tall
What are some characteristics of the Class Aves? Sub-Phylum Craniata - tetrapod (example, heart type, air sacs what, warm or cold blooded, feathers?, care for what, egg type and where scales, unique feature?)
4 chambered hearts; Air sacs are highly efficient for gas exchange; ENDOTHERMIC; Feathers; Care for young; Amniotic egg and scales on LEGS; Has Keel- Part of the sternum that provides muscle attachment for flight
What are some characteristics of the Class Mammalia? Sub-Phylum Craniata - tetrapod (hair?, glands (2 types), teeth, brain, breathing muscle, heart type, warm or cold blooded, ear bones)
Hair is keratin, Mammary glands, Sweat Glands, Tooth Differentiation, Well Developed Brain, Muscular Diaphragm, 4 chambered heart, Endothermic, 3 Bones in middle ear: Malleus, Incus, Stapes
What are the three groupings of mammals?
monotremes, marsupials, placentals
What are monotremes?
Primitive mammals that lay eggs
What are marsupials?
Gives birth but embryo must climb up into pouch to complete development
What are placentals?
Advanced mammals, mother nourishes embryo through placenta
What are the five Orders to know under the Class Mammalian? Sub-Phylum Craniata - tetrapod
Marsupialia, Artiodactyla, Cetacea, Xenarthra, Sirenia
What are some examples of the Order Marsupialia? Class Mammalian Sub-Phylum Craniata - tetrapod
Kangaroos, Opossum
What are some examples of the Order Artiodactyla? Class Mammalian Sub-Phylum Craniata - tetrapod (Quiz Question)
Sheep, Cattle, Pigs, Deer
What are some examples of the Order Cetacea? Class Mammalian Sub-Phylum Craniata - tetrapod
Whale, Dolphins
What are some examples of the Order Xenarthra? Class Mammalian Sub-Phylum Craniata - tetrapod
Sloths, Armadillos, Anteaters
What are some examples of the Order Sirenia? Class Mammalian Sub-Phylum Craniata - tetrapod
Manatees