MCAT Biology Study Material - Chapter 1: The Cell Flashcards
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Robert Hooke
Created the first microscope to visualize cells
Also, Hooke's Law (F=-kx)
Cell Theory
1. All living things are composed of cells
2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things
3. New cells are produced from existing cells
More Recent Addition:
4. Cells carry genetic information in the form of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). This genetic material is passed on from parent to daughter cell.
serial endosymbiosis theory
attempts to explain the formation of some of the membrane bound organelles
posits that these organelles formed by engulfing of one prokaryote by another and the establishment of a symbiotic relationship between the two
in addition to mitochondria, chloroplasts in plant cells and organelles of motility (flagella) are believed to have evolved through this process
Cilia
Hairlike projections that extend from the plasma membrane and are used for locomotion
eukaryotic have a 9+2 Structure
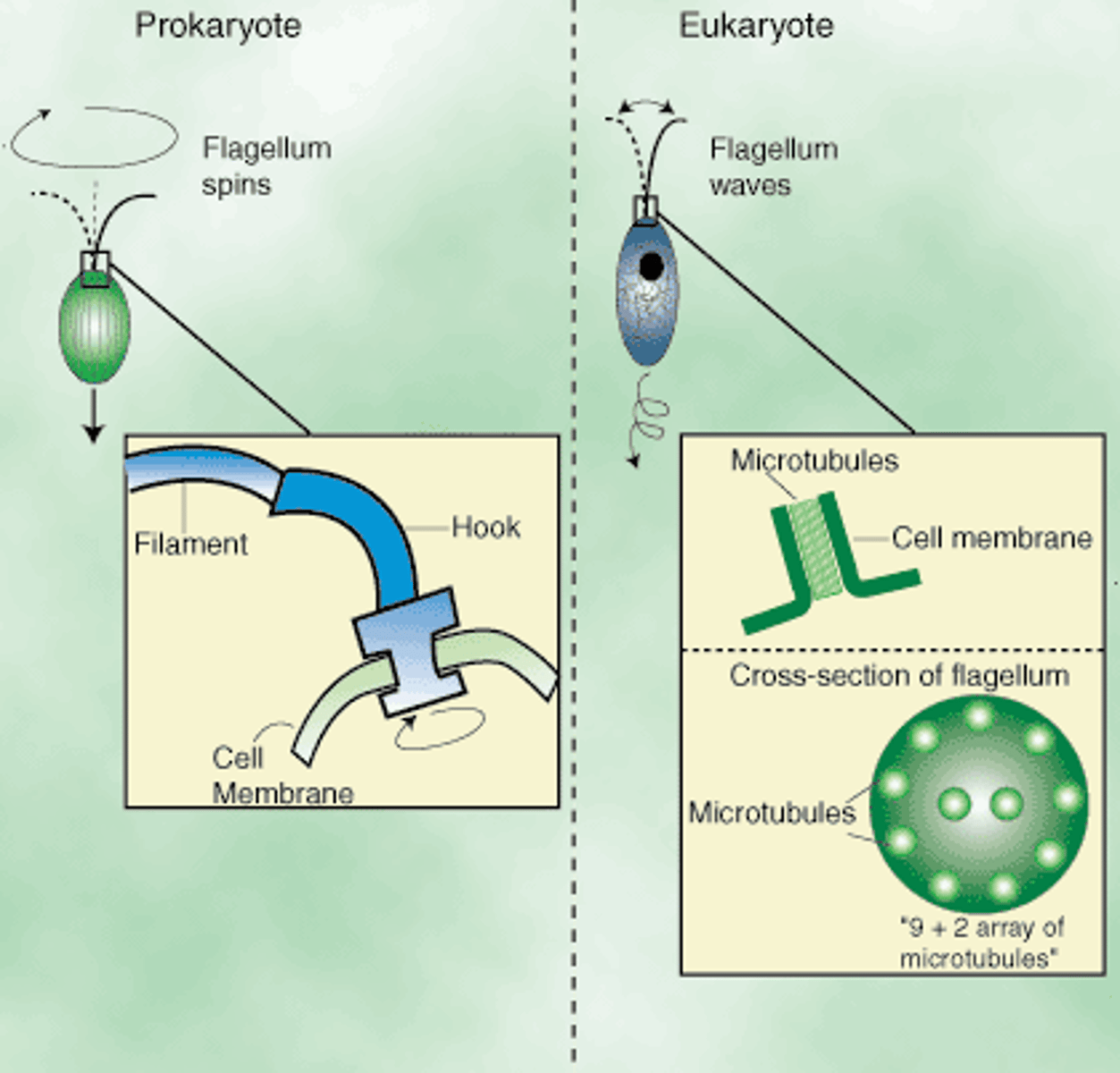
Flagella
structures involved in the movement of the cell
eukaryotic have a 9+2 Structure
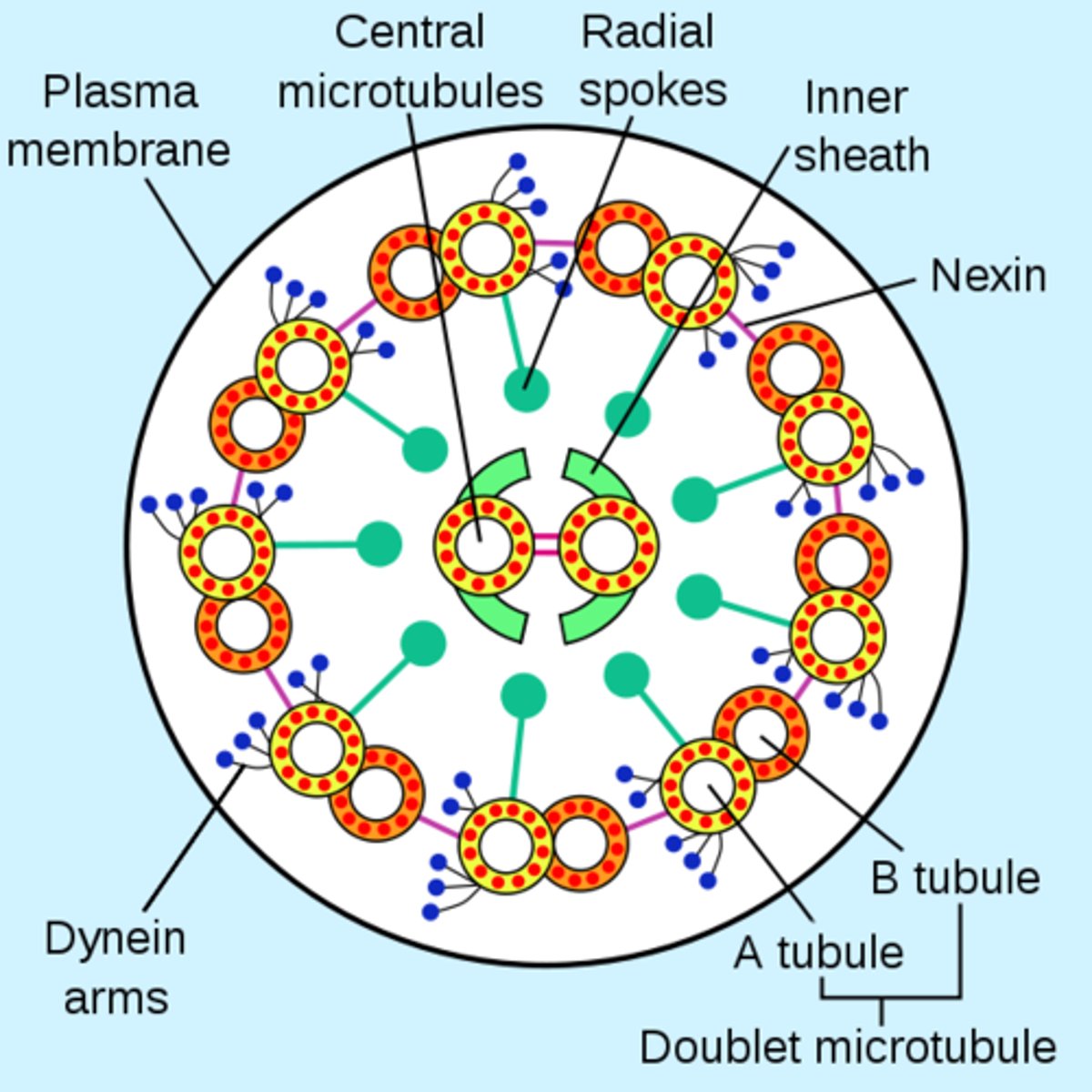
9+2 structure of cilia and flagella
Eukaryotic cilia and flagella have 9 pairs of microtubules creating an outer ring which surrounds two microtubules in the center
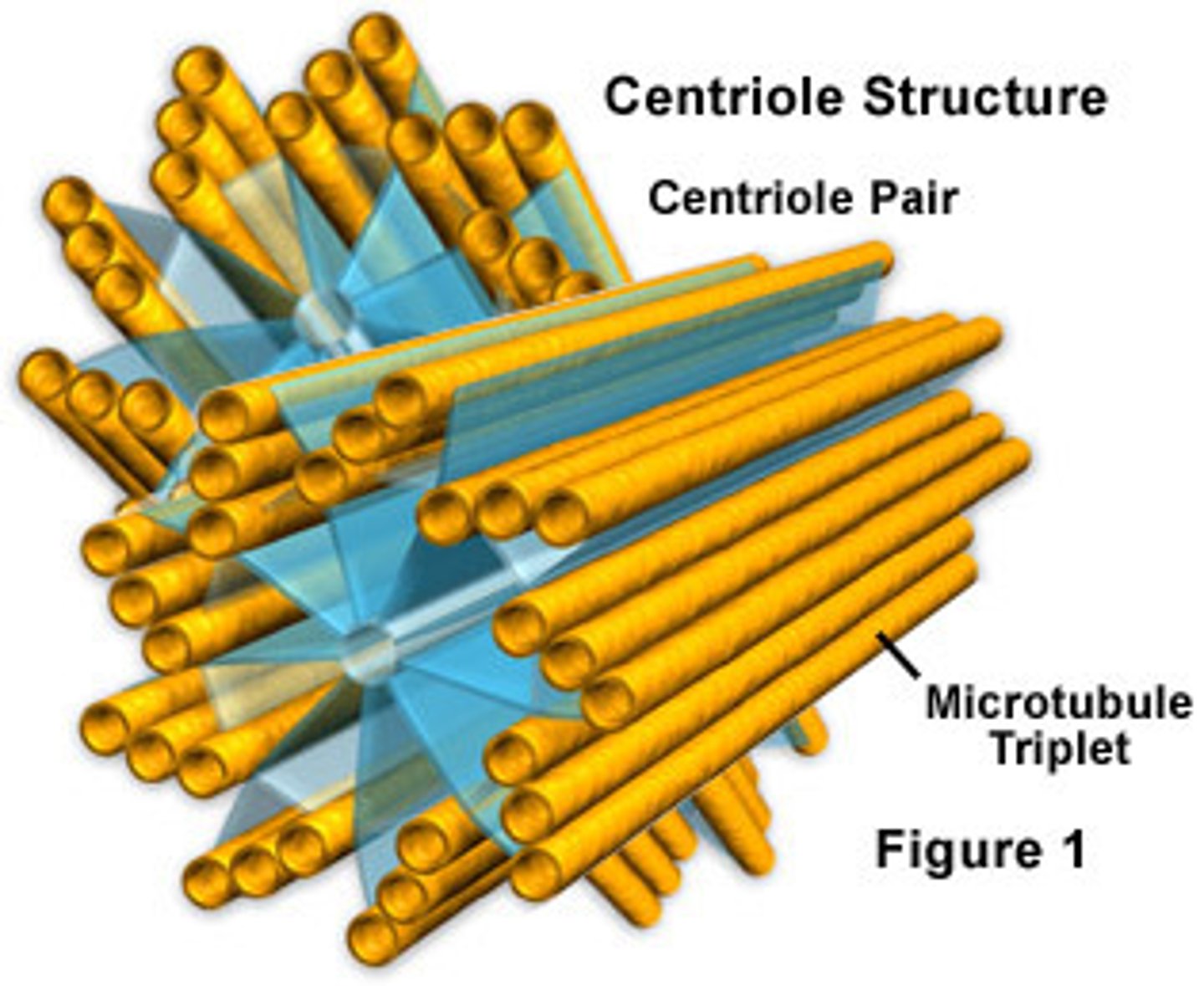
Centrioles
Structures located in the centrosome
organizing centers for microtubules
nine triplets of microtubules surrounding a hollow core
Nucleus
Stores genetic information
Site of transcription
Mitochondria
Involved in ATP production and apoptosis
Lysosomes
break down cellular waste products and endocytosed molecules
also involved in apoptosis
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
lipid synthesis
detoxification
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
synthesizes proteins
Golgi apparatus
Packages, modifies, and distributes cellular products
Peroxisomes
break down fatty acids
synthesize lipids
contribute to the pentose phosphate pathway
produce hydrogen peroxide
A child is diagnosed with an enzyme deficiency that prevents the production of hydrogen peroxide. What would the likely outcome be of such a deficiency?
Peroxisome would not be able to digest long chain fatty acids
undigestible long chain fatty acids would build up in the peroxisome displacing cellular contents and resulting in cell death
What are the predominant proteins of microfilaments?
actin
What are the predominant proteins of microtubules?
tubulin
What are the predominant proteins of intermediate filaments?
keratin
desmin
vimentin
lamins
etc
How do the structures of centrioles differ from that of flagella?
Centrioles: 9 triplets of microtubules with hollow center
Flagella: 9 pairs of microtubules with 2 individual microtubules in the center
Classify as epithelial cells or connective tissue:
Fibroblasts, which produce collagen in a number of organs
Connective tissue
Classify as epithelial cells or connective tissue:
Endothelial cells, which line blood vessels
epithelial cells
Classify as epithelial cells or connective tissue:
alpha-cells, which produce glucagon in the pancreas
epithelial cells
Classify as epithelial cells or connective tissue:
Osteoblasts, which produce osteoid, the material that hardens into bone
Connective tissue
Classify as epithelial cells or connective tissue:
Chondroblasts, which produce cartilage
Connective tissue
Archaea
often extremophiles
harsh environments
alternative energy sources (chemical)
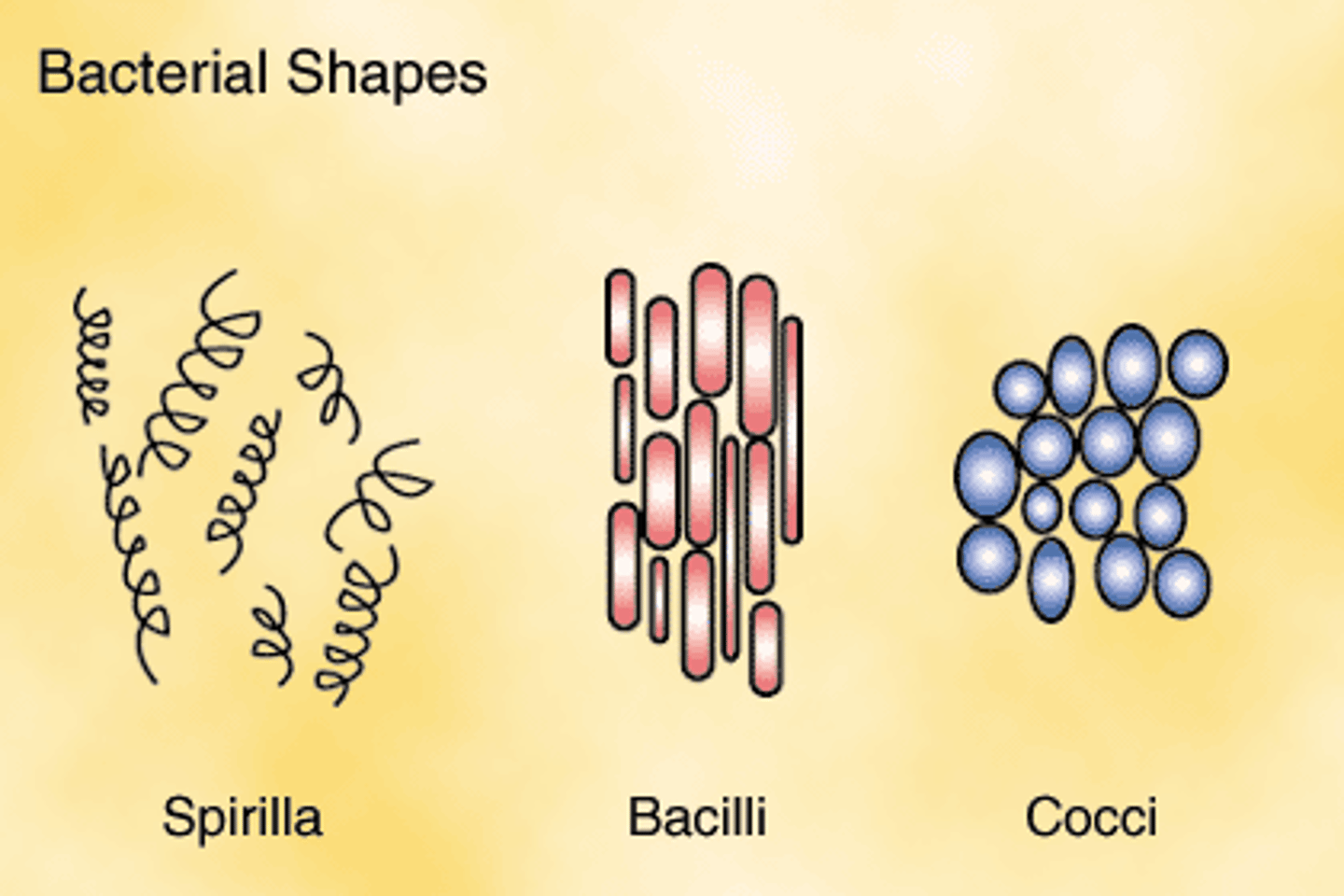
Bacterial shapes
Cocci: spherical
Bacilli: rod-shaped
Spirilli: Spiral-shaped
Facultative anaerobe
can survive with or without oxygen, can use oxygen
Aerotolerant anaerobes
can survive with or without oxygen, but do not use oxygen
Obligate anaerobes
Cannot survive in the presence of oxygen
Obligate aerobes
require oxygen
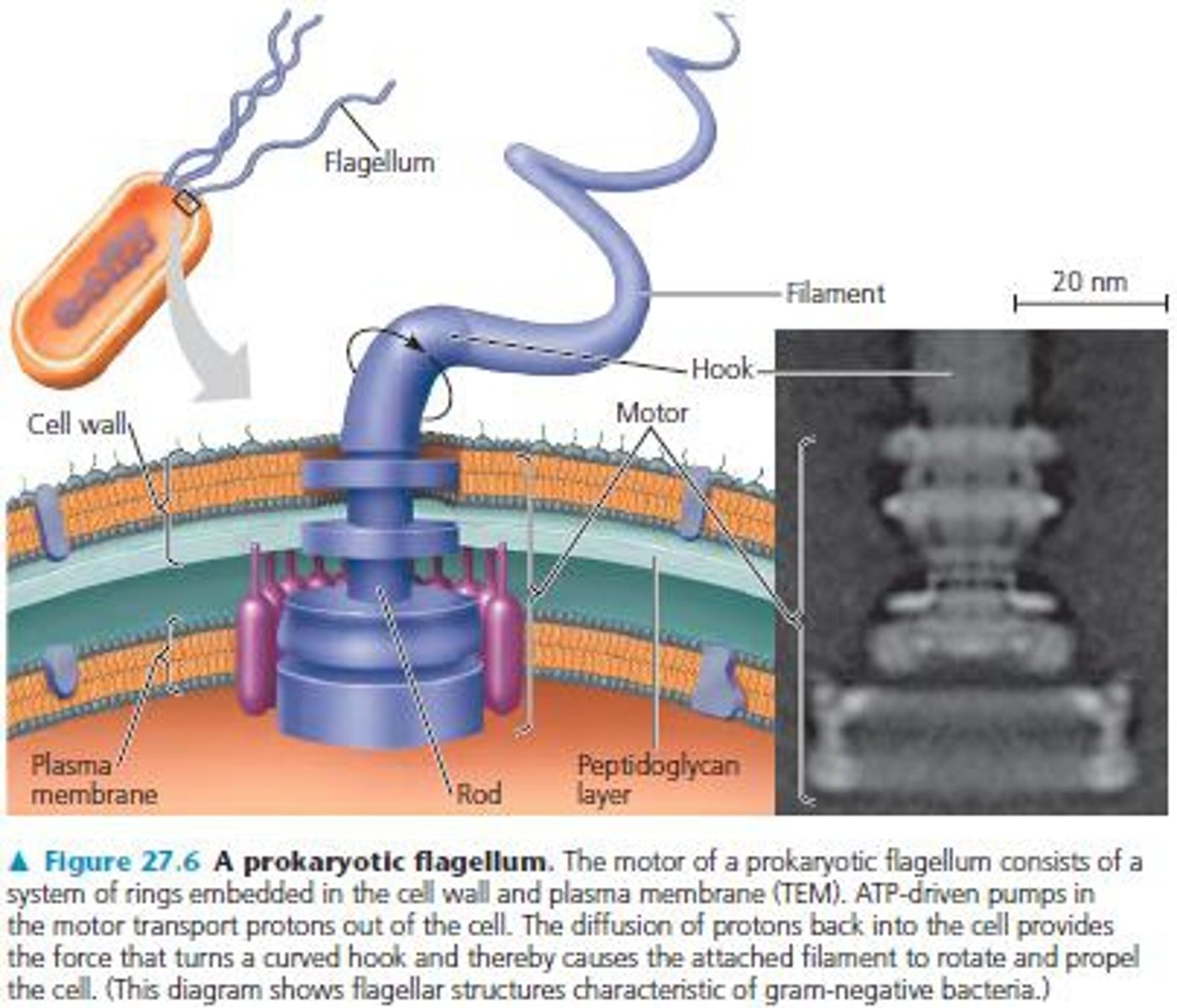
Prokaryotic flagella
longer projections that propel the prokaryotic cell through its liquid environment
In what ways are Archaea similar to bacteria?
both are single-celled organisms that lack a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles
contain a single circular chromosome
divide by binary fission or budding
In what ways are Archaea similar to eukaryotes?
Start translation with methionine
contain similar RNA polymerases
associate their DNA with histones
What difference between the envelopes of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria make gram-positive bacteria more susceptible to antibiotics such as penicillin?
Penicillin targets the enzyme which cross-links peptidoglycan
Gram-positive bacteria have a thick layer of peptidoglycan, but no outer membrane
Gram-negative bacteria have a thin layer of peptidoglycan, but do have an outer membrane
Antibiotics like penicillin can more easily reach the peptidoglycan layer of the gram-positive bacteria
How do the structures of eukaryotic and prokaryotic flagella differ?
Eukaryotic: 9+2 microtubules
Prokaryotic: Filament + hook + basal body made of flagellin
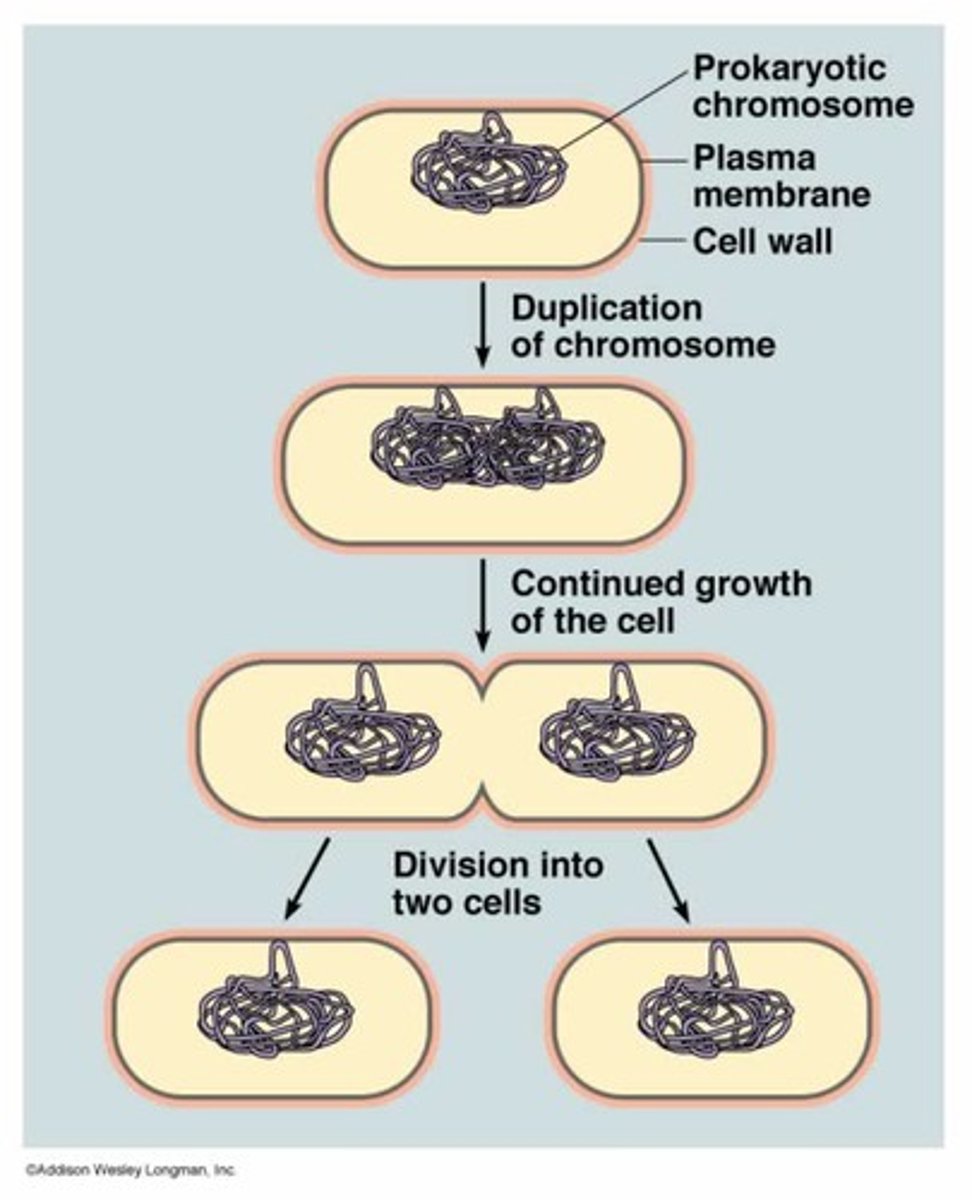
Binary fission
A form of asexual reproduction in single-celled organisms by which one cell divides into two cells of the same size
Transformation
integration of foreign genetic material into the host genome
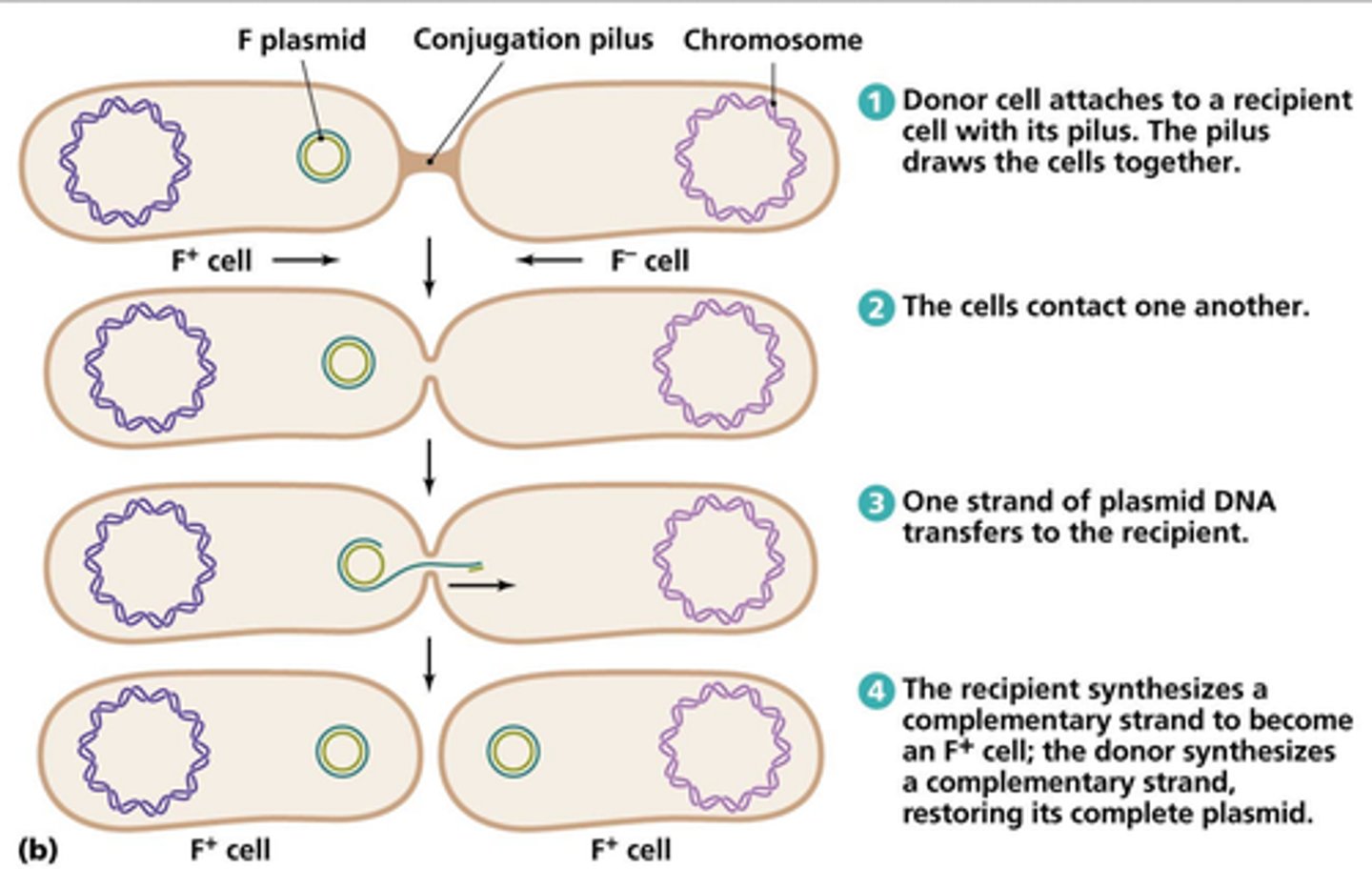
Conjugation
bacterial form of mating
formation of conjugation bridge and transfer of genetic material from the "donor male" to the "recipient female"
requires the sex factor for formation of the conjugation bridge
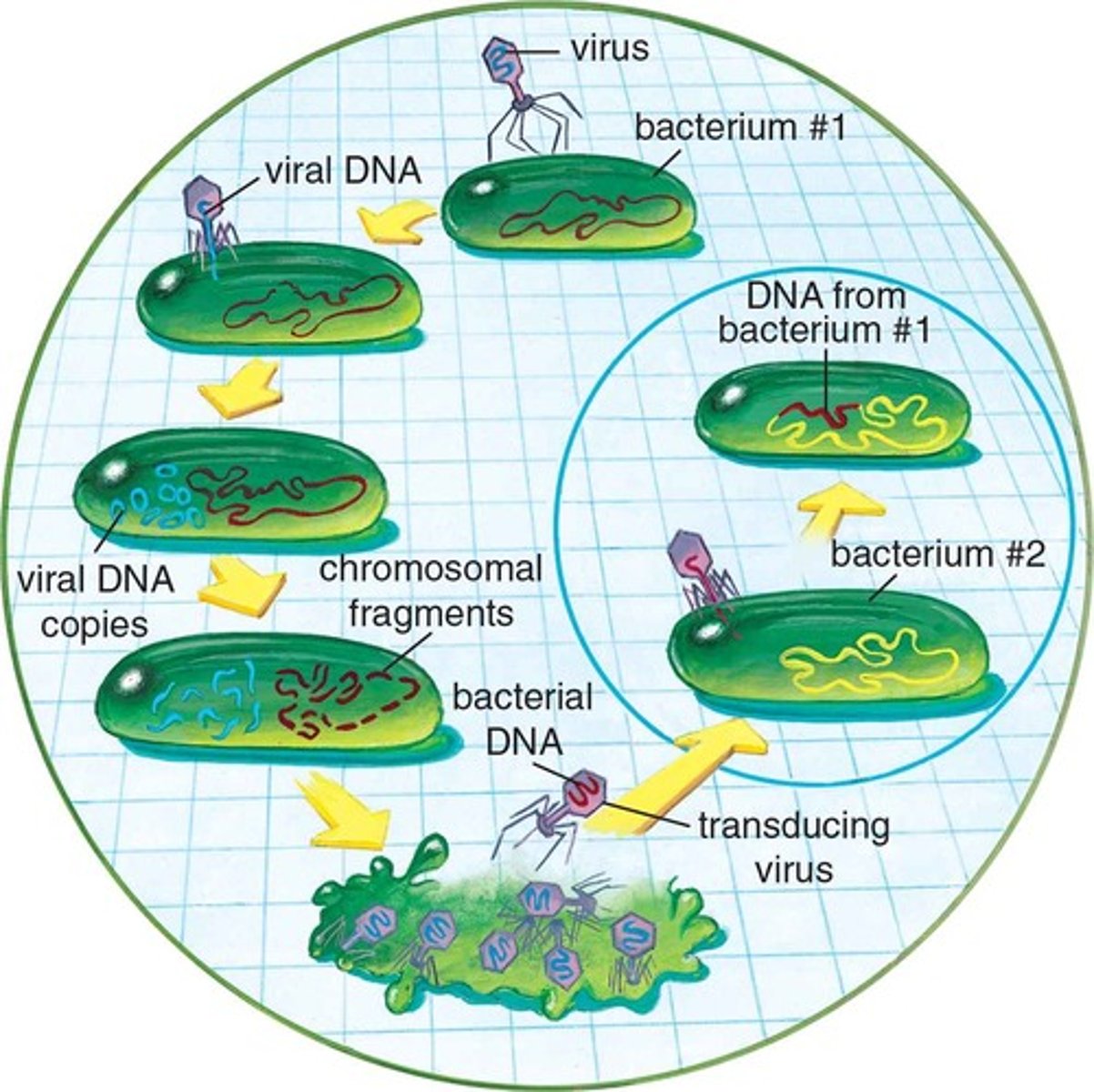
Transduction
Genetic recombination that requires a vector
Bacteriophage carries genetic info from one bacteria to another by mistake
Bacterial Growth Curve
A semilog plot
Lag phase
Exponential phase
Stationary phase
Death phase
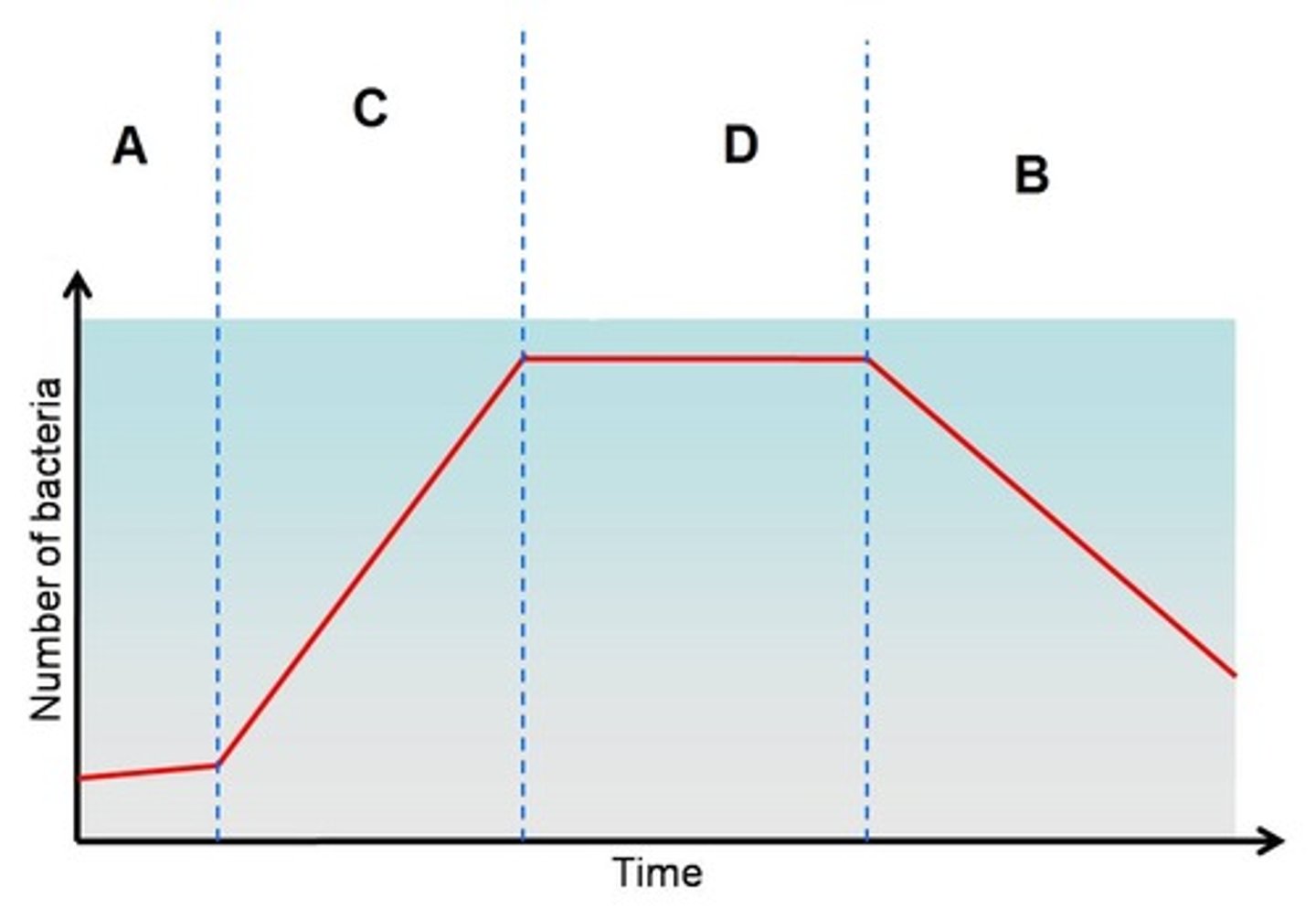
Lag phase
bacteria adapt to new environment, little growth
log/exponential phase
bacteria use available resources to multiply at an exponential rate
stationary phase
bacterial multiplication slows as resources are used up
Death phase
Bacteria die as resources become insufficient to support the colony
Viral life cycle
infection, translation and progeny assembly, progeny release
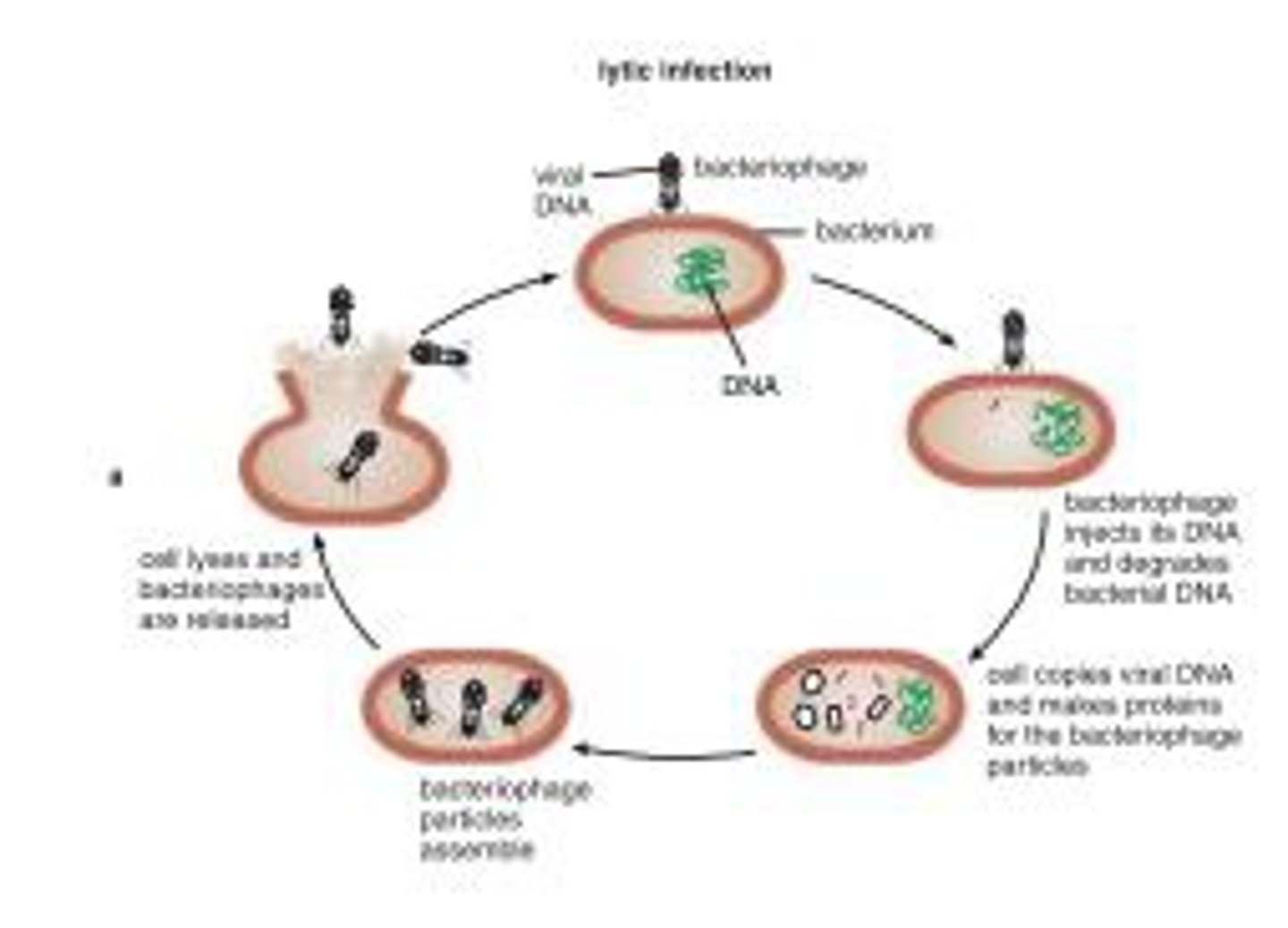
Lytic cycle
a viral reproductive cycle in which copies of a virus are made within a host cell, which then bursts open, releasing new viruses
Lysogenic cycle
a viral reproductive cycle in which the viral DNA is added to the host cell's DNA and is copied along with the host cell's DNA
Prions
infectious proteins
cause disease by triggering misfolding of other proteins
Viroids
small pathogens consisting of a very short circular single-stranded RNA that infect plants
Why are viruses considered obligate intracellular parasites?
Viruses do not contain organelles such as ribosomes for production of proteins and reproduction, so they must hijack the machinery of a host cell
Coronavirus, which causes the common cold, is described as an enveloped, single-stranded positive-sense RNA virus. What does this description indicate about the virus?
The virus is weaker due to the envelope rather than a protein capsid
The RNA does not have to enter the nucleus to be used by the host cell machinery
Briefly describe the pathway of retroviral nucleic acids from infection of a host cell to release of viral progeny
ssRNA to dsDNA to mRNA to Proteins and replicated viral ssRNA
What are the differences between the lytic and lysogenic cycles?
Lytic: Bacteriophage replicates in extremely high numbers causing the host to rupture
Lysogenic: Bacteriophage genome is incorporated into the host genome and replicates with the host cell, can be used to synthesize new virions upon the appropriate signal
How do prions cause disease?
Prions cause disease by triggering a change in the conformation of a protein from an alpha helix to a beta pleated sheet
This change reduces solubility of the protein and makes it highly resistant to degradation.
Hyperbaric oxygen may be used as a treatment for certain types of bacterial infections. In this therapy, the patient is placed in a chamber in which the partial pressure of oxygen is significantly increased, increasing the partial pressure of oxygen in the patient's tissues. This treatment is most likely used for infections with:
A. obligate aerobic bacteria
B. facultative anaerobic bacteria
C. aerotolerant anaerobic bacteria
D. obligate anaerobic bacteria
D. obligate anaerobic bacteria
Which of the following does NOT describe connective tissue cells?
A. They account for most cells in muscles, bones, and tendons
B. They secrete substances to form the extracellular matrix
C. In organs, they tend to form the stroma
D. In organs, they provide support for epithelial cells
A. They account for most cells in muscles, bones, and tendons
Which of the following types of nucleic acid could form the genome of a virus?
I. Single-Stranded RNA
II. Double-stranded DNA
III. Single-stranded RNA
A. I only
B. II only
C. I and II only
D. I, II, and III
D. I, II, and III
Which of the following activities occurs in the Golgi apparatus?
A. Synthesis of proteins
B. Modification and distribution of proteins
C. Breakdown of lipids and carbohydrates
D. Production of ATP
B. Modification and distribution of proteins
Mitochondrial DNA is:
I. circular
II. self-replicating
III. single-stranded
A. I only
B. II only
C. I and II only
D. I, II, and III
C. I and II only
Which of the following is NOT a function of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
A. Lipid synthesis
B. Poison detoxification
C. Protein synthesis
D. Transport of proteins
C. Protein synthesis
What is the main function of the nucleolus?
A. Ribosomal RNA Synthesis
B. DNA Replication
C. Cell Division
D. Transport of Proteins
A. Ribosomal RNA Synthesis
Which of the following organelles is surrounded by a single membrane?
A. Lysosomes
B. Mitochondria
C. Nuclei
D. Ribosomes
A. Lysosomes
Which of the following is NOT a difference that would allow one to distinguish a prokaryotic and a eukaryotic cell?
A. Ribosomal subunit weight
B. Presence of a nucleus
C. Presence of a membrane on the outside surface of the cell
D. Presence of membrane-bound organelles
C. Presence of a membrane on the outside surface of the cell
Which of the following does NOT contain tubulin?
A. Cilia
B. Flagella
C. Microfilaments
D. Centrioles
C. Microfilaments
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) enters the human body and remains dormant in the nervous system until it produces an outbreak after exposure to heat, radiation, or other stimuli. Which of the following statements correctly describes HSV?
A. While it remains dormant in the nervous system, the virus is in its lytic cycle.
B. During an outbreak, the virus is in the lysogenic cycle.
C. Herpes simplex virus adds its genetic information to the genetic information of the cell.
D. The herpes simplex virus contains a tail sheath and tail fibers.
C. Herpes simplex virus adds its genetic information to the genetic information of the cell
A and B have the terms flip-flopped. D describes bacteriophage features, not present in human viruses
Resistance to antibiotics is a well-recognized medical problem. Which mechanism(s) can account for a bacterium's ability to increase its genetic variability and thus adapt itself to resist different antibiotics?
I. Binary fission
II. Conjugation
III. Transduction
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II, and III
C. II and III only
A bacterial cell is noted to be resistant to penicillin. The bacterium is transferred to a colony that lacks the fertility factor, and the rest of the colony does not become resistant to penicillin. However, the penicillin-resistant cell has also started to exhibit other phenotypic characteristics, including secretion of a novel protein. Which of the following methods of bacterial recombination is NOT likely to account for this change?
A. Conjugation
B. Transformation
C. Transduction
D. Infection with a bacteriophage
A. Conjugation
In Alzheimer's disease, a protein called the amyloid precursor protein (APP) is cleaved to form a protein called beta-amyloid. This protein has a beta-pleated sheet structure and precipitates to form plaques in the brain. This mechanism of disease is most similar to which of the following pathogens?
A. Bacteria
B. Viruses
C. Prions
D. Viroids
C. Prions
After infection of a cell, a viral particle must transport itself to the nucleus in order to produce viral proteins. What is the likely genomic content of the virus?
A. Double-stranded DNA
B. Double-stranded RNA
C. Positive-sense RNA
D. Negative-sense RNA
A. Double-stranded DNA
A virus that requires nuclear transport likely requires use of the nuclear RNA polymerase to create mRNA. Thus only DNA viruses need to be transported to the nucleus to produce viral proteins