Lecture 8: Multivariate OLS in Political Science Research
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Multivariate Regression
Statistical method including multiple independent variables.
Endogeneity
Bias caused by omitted variable correlation.
Omitted Variable Bias
Error from excluding relevant variables in analysis.
Random Assignment
Method to ensure unbiased treatment effects in experiments.
Independent Variable (IV)
Variable manipulated to observe effects on dependent variable.
Dependent Variable (DV)
Outcome variable affected by independent variables.
Hypothesis (H0)
Null hypothesis stating no effect exists.
Hypothesis (HA)
Alternative hypothesis suggesting a significant effect exists.
Control Variables
Factors included to isolate the effect of IV.
Descriptive Statistics
Summary statistics to explore and describe data.
Statistically Significant
Results unlikely due to chance, typically p < 0.05.
Robustness Checks
Tests ensuring results hold under various conditions.
Reverse Causation
Situation where outcome influences the independent variable.
Measurement Error
Inaccuracies in data collection affecting results.
Political Participation
Engagement in political activities like voting.
Victimization
Experience of being a victim of crime.
Confounder
Variable influencing both independent and dependent variables.
Placebo Test
Test to check if results hold without treatment.
Empirical Measurement
Collecting data to quantify variables in research.
Research Question
Inquiry guiding the focus of a study.
Data Sources
Origins of data, such as surveys or records.
Bateson's Research
Study linking crime victimization to political activism.
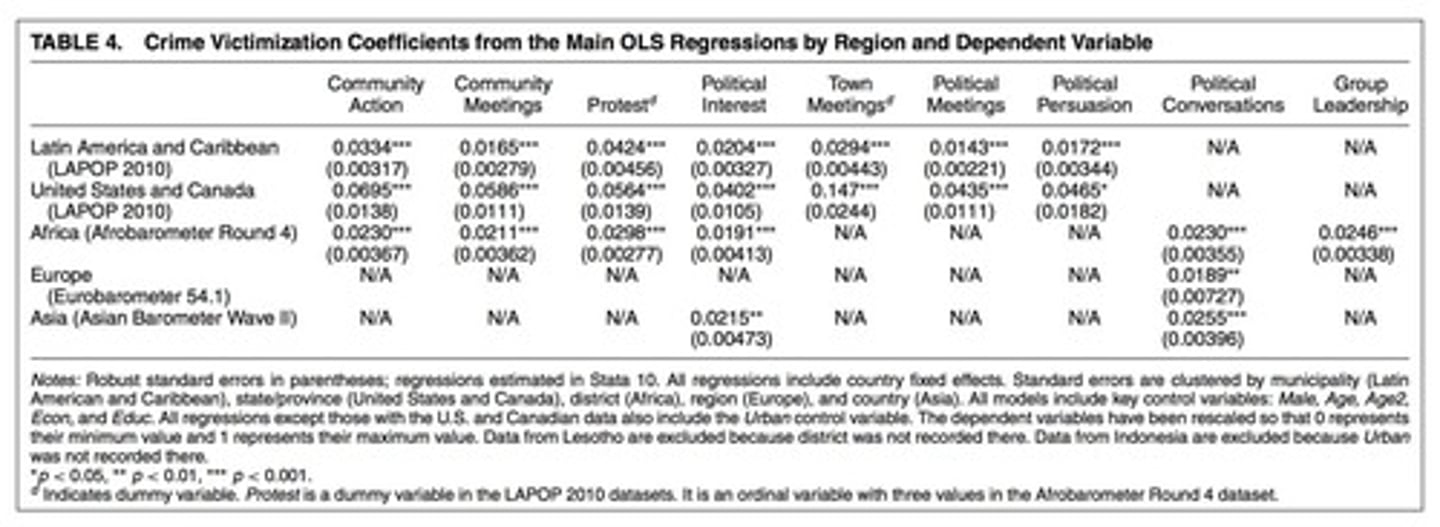
Model Specification
Defining the structure and variables of a regression model.
Political Violence
Use of force to achieve political goals.