Histology self-study 3: Muscle and Cartilage
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
Skeletal muscle diameter and length
Diameter: 10-100µm
Length: 1mm-30cm
Cardiac muscle diameter and length
Diameter: 15-30 micrometres
Length: 85-120 micrometres
Smooth muscle diameter and length
Diameter: 3 - 15µm
Length: 20 - 200 µm
Skeletal muscle structure
long, cylindrical cells
cytoplasm filled with contractile filaments
multinucleated with many peripheral nuclei
exhibit cross-striations
skeletal muscle control?
voluntary control - innervated by motor neurones from the somatic nervous system
respond quickly to stimuli
skeletal muscle stem cell name
Satellite cells
Cardiac muscle structure?
Short branched cells
Form a syncytium
Single, central nucleus (occasionally binucleate)
Intercalated discs join cells end-to-end
Cardiac muscle control?
Involuntary - innervated by the autonomic nervous system
Cardiac muscle pigment?
Lipofuscin - end-stage lysosomes containing undigested material
Cardiac muscle lifespan?
Poor capacity for regeneration
Automatic rhythmic conditions for life
Smooth muscle purpose
Apply pressure to organs (e.g. stomach, intestines, uterus)
Blood vessels
Smooth muscle structure
spindle-shaped cells of various size
single centrally located nucleus
non-striated
retain ability to divide
smooth muscle control
Involuntary control - innervated by the autonomic nervous system
Also under hormonal control
responds slowly to stimuli - capable of long, sustained contractions
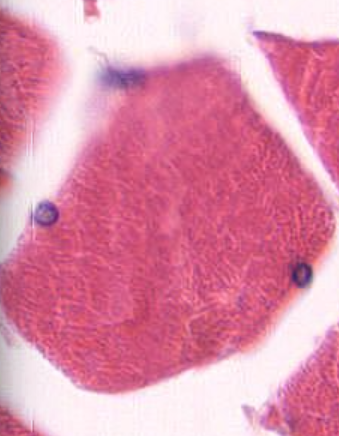
What muscle cell is this and how can you tell? (Transverse section)
Skeletal muscle cell
Polygonal cross-sections
Nuclei at periphery
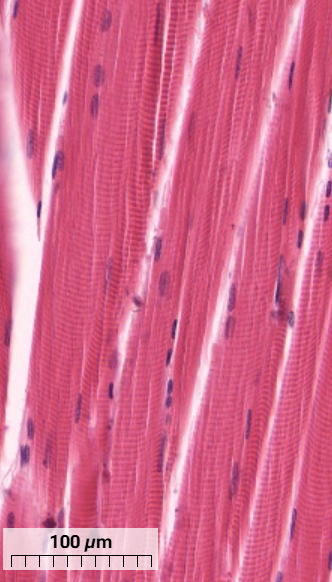
What muscle cell is this and how can you tell? (Longitudinal section)
Skeletal muscle cells
Can see sarcomere striations from thick and thin filaments
Satellite cell nuclei of mostly heterochromatin can be seen on the surface of muscle cells
Bundle of muscle cells
Fascicle
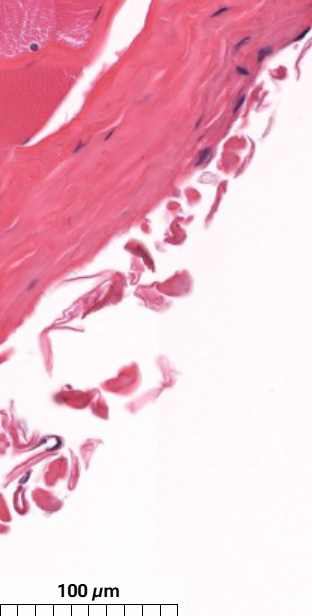
What part of the skeletal muscle is this?
Epimysium - dense connective tissue that surrounds the entire muscle and is usually continuous with a tendon
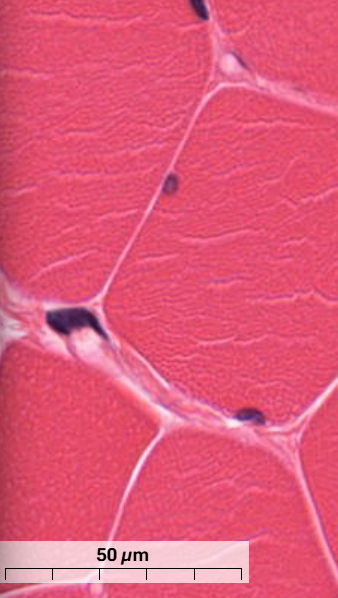
What are the white-line structures shown in the skeletal muscle?
Endomysium - thin layer connective tissue that surrounds each muscle cell
Capillaries seen at the corners of the muscle cells
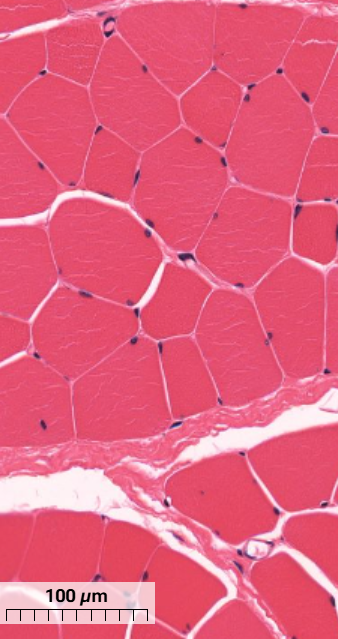
What thick tissue layer is seen in the skeletal muscle?
Perimysium - thick layer of connective tissue that surrounds a group of muscle cells to form fascicles.
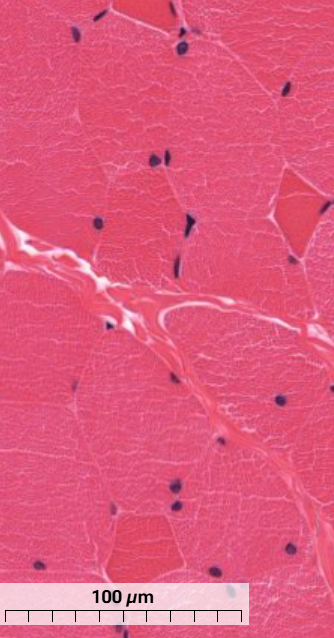
What type of muscle are the dark muscle fibres and what are the light ones in this skeletal muscle?
Type I - dark, smaller muscle cells that specialise in long, slow contraction
Type II - light, larger muscle cells, specialise in fast contraction (majority of muscle in picture)
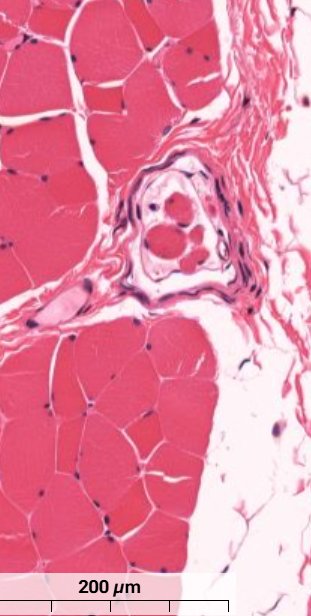
What feature is shown in the skeletal muscle?
Muscle spindle - sensory receptors within a muscle that detect change in length of the muscle.
Main composition of tendons
Dense, collagenous connective tissue
What is sarcoplasmic reticulum?
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum but in muscle cells
Thick filament
Myosin arranged as bipolar filaments anchored at the M-line.
Thin filaments
Actin arranged as unipolar filaments anchored at the Z-line.
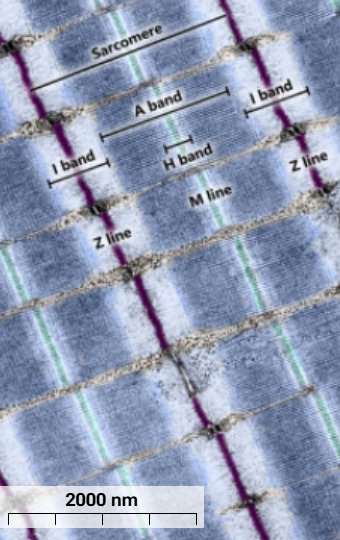
A band
Dark blue - thick myosin filaments and parts of thin actin filaments where they overlap.
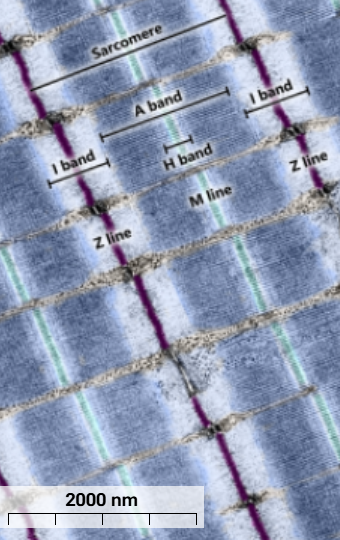
I Band
Light blue - only thin actin filaments, narrows with contraction
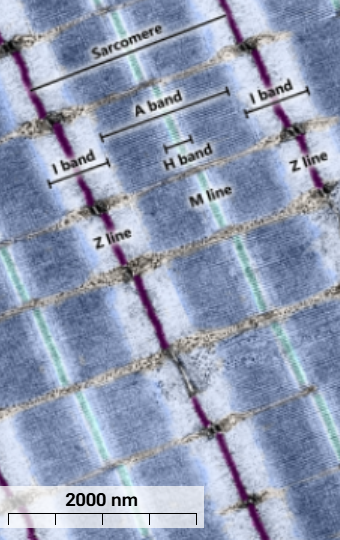
Z line
Purple - thin actin filaments anchor to Z lines
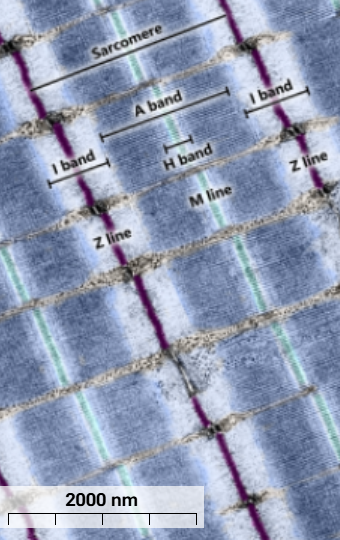
H bands
Light blue - only myosin filaments without overlapping actin filaments
M line
cyan - holds myosin filaments together
I meaning
isotropic
A meaning
anisotropic
What 2 internal membrane systems play a role in excitation-contraction coupling?
The sarcoplasmic reticulum
Transverse tubular system (T-tubules)
T system
Tubular invaginations of sarcolemma
Terminal cisternae
Flattened vesicular structures formed by sarcoplasmic reticulum on either side of each T tubule.
Triad
Formed by a pair of terminal cisternae and a T tubule
Describe the steps of skeletal muscle stimulation
Action potentials propagate from the sarcolemma to the interior of the muscle fibre via the T tubules
At the triads, depolarisation of the T tubules triggers the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum into the sarcoplasm surrounding the myofibrils.
Rise in calcium concentration - interaction between myosin motors and actin filaments initiated
Myofibril contraction
What allows for a rapid response during skeletal muscle stimulation?
T tubule and skeletal muscle arrangement reduces diffusion pathway for calcium.
Where is calcium released from during skeletal muscle contraction?
Terminal cisternae
Where is calcium accumulated during skeletal muscle contraction?
Fenestrated network of sarcoplasmic reticulum - largest surface area for calcium pumps.
Red fibre properties
Slow twitch upon stimulation
Sustained contraction
Aerobic metabolism
Numerous mitochondria
Rich in myoglobin
Profuse capillary network
Found in muscle that maintains body posture
White fibre properties
Fast twitch response
Cannot sustain contractions for long periods of time
Anaerobic metabolism
Few mitochondria
Little myoglobin
Abundant in muscle for intense but sporadic contraction
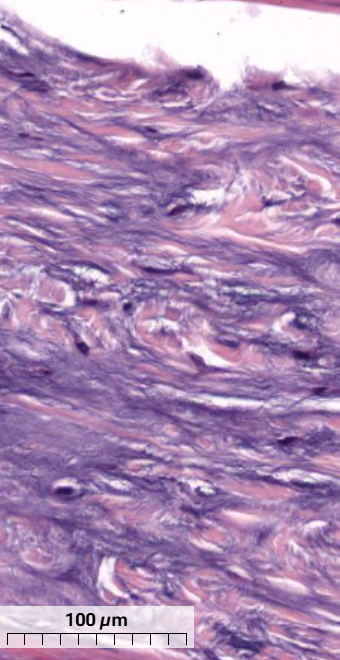
What type of cartilage is in this tendon and how can you tell?
Fibrocartilage
Collagen fibres have irregular arrangement
Chondrocytes round/oval with a clear space surrounding the nuclei
External lamina function
Contractile forces from internal contractile proteins transmitted to external lamina via link proteins
Link proteins on muscle cell membrane
Binds individual cells into single functional mass
Satellite cells function
Enter mitosis after damage to muscle
Fuse to form differentiated muscle fibres
Muscle fibres formed after damage often have nuclei in the centre of the fibre rather than at the periphery
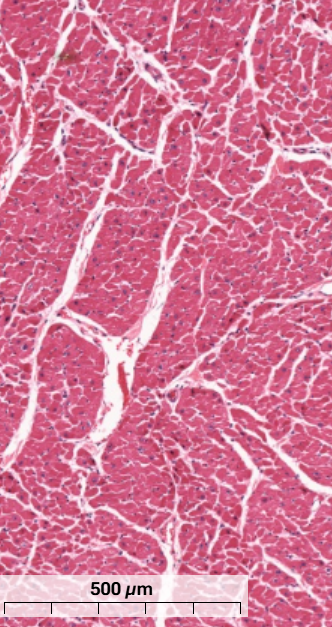
What type of muscle is this and how do you know? (transverse section)
Cardiac muscle cells have rounded cross-sections
Centrally located nucleus
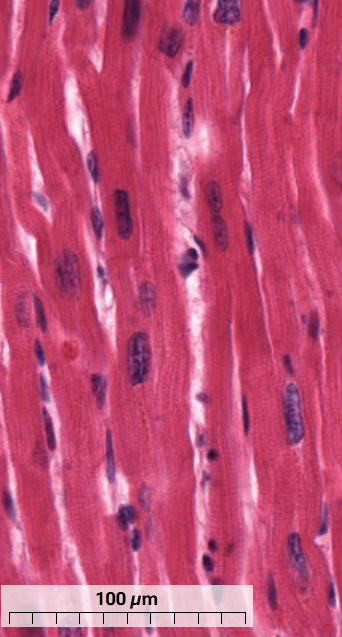
What type of muscle is this and how do you know? (longitudinal section)
Cardiac muscle - cells are joined end to end and often branched
Intercalated discs perpendicular to direction of muscle fibres
Lipofuscin pigment can be seen near nucleus of some cells.
What is the purpose of intercalated discs?
Enable synchronisation and contraction of cardiac fibres by providing both mechanical and electrical coupling.
3 types of membrane to membrane contact
Adherens junctions
Desmosomes
Gap junction
Adherens junctions
Contain cell adhesion molecule cadherin
Anchor actin filaments at the end of terminal sarcomeres
Allows contractile forces to be transmitted from cell to cell
Desmosomes
Provide anchorage for intermediate filaments in cytoskeleton
Prevent cardiac muscle detaching during contraction
Gap junctions
intercellular channels
allow ions and small molecules to pass from cell to cell
structural basis for electrical transmission between cells
Diad (or dyad)
Single terminal sac of sarcoplasmic reticulum closely apposed to T tubule.
Purkinjie fibres
conducting system of modified cardiac muscle fibres
larger than cardiac muscle cells
sometimes binucleated
contain numerous mitochondria
few, irregularly arranged myofibrils
lack T tubules and intercalated discs
connect via gap junctions and desmosomes
cytoplasm rich in glycogen
Unitary (visceral) smooth muscle
Individual muscle fibres linked by gap junctions
act as a unit
predominantly in walls of hollow viscera
Multi-unit smooth muscle
individual units without gap junctions
unlinked fibres - each contract independently
found where fine graded contractions occur, e.g. iris
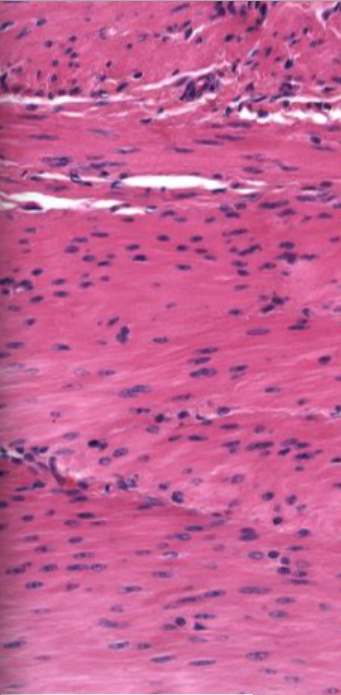
Which muscle is this and how can you tell? (longitudinal section)
relaxed smooth muscle - nuclei elongated with rounded ends
when contracted nuclei spiral, kink or twist
cytoplasm pink, non-striated, little detail
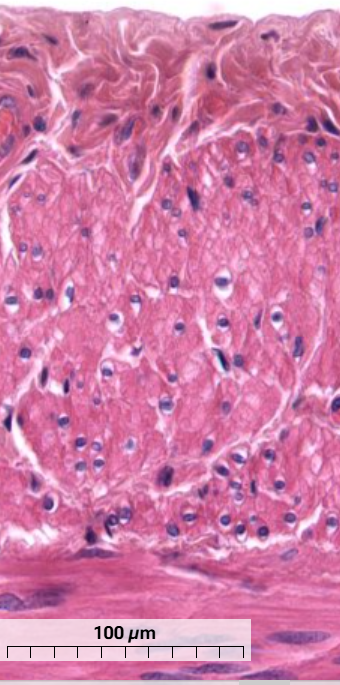
What muscle is this and how can you tell? (transverse section)
smooth muscle - individual cells vary in diameter
cross sections have centrally located nuclei surrounded by unstained region
Caveolae
small invaginations of the plasma membrane involved in the regulation of ion channels and calcium signalling.
Dense bodies
Points of attachment for actin filaments and intermediate filaments of the cytoskeleton.
found in cytoplasm and areas adjacent to the plasma membrane
What forms cartilage
chondroblasts, chondrocytes, collagen fibres, hydrated proteoglycans.
Collagen in cartilage
provides strength to resist stretch
proteoglycan trapped water in cartilage
generates turgor pressure that allows cartilage to spring back to shape following deformation
Components of cartilage
perichondrium
chondroblasts
chondrocytes
perichondrium
connective tissue sheath that surrounds cartilage
vascularised
rich in collagen
inner layer contains fibroblasts/mesenchyme that can differentiate to form chondroblasts
chondroblasts
immature cartilage cells
secrete extracellular matrix
not rigidly embedded in matrix
chondrocytes
mature cartilage cells
embedded in extracellular matrix
reside in small spaces within the matrix called lacunae
may be more than one cell per lacuna
chondrocytes in hyaline cartilage grouped together called isogenic groups
3 types of cartilage
hyaline, elastic, fibrocartilage
hyaline cartilage
type II collagen and chondromucoprotein
found in nose, trachea, where ribs join sternum and at epiphyseal plate of long bones
contains no blood vessels or nerves
elastic cartilage
matrix contains abundant branching and anastomosing elastic fibres
type II collagen
found in external ear and epiglottis
contains no blood vessels or nerves
fibrocartilage
large amounts of well-ordered type I collagen fibres
found where tendons attach to bone, intervertebral discs, within pelvic pubic symphysis
mixture of regular dense connective tissue and hyaline cartilage
chondrocytes dispersed singularly, in columns or in isogenous groups
there is no perichondrium