Pathology
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Medical Examiner (ME)
Pathologist who specializes in forensic (legal) medicine related to criminal issues. performs autopsies.
Mechanism of Death
The specific body failure that leads to death.
Asphyxia
Deprivation of oxygen for tissue use; suffocation. A mechanism of death.
Algor Mortis
The temperature of the body after death. Used to calculate TOD.
Initial Decay
Corpse appears normal on the outside, but is starting to decompose from the actions of bacteria and autolysis.
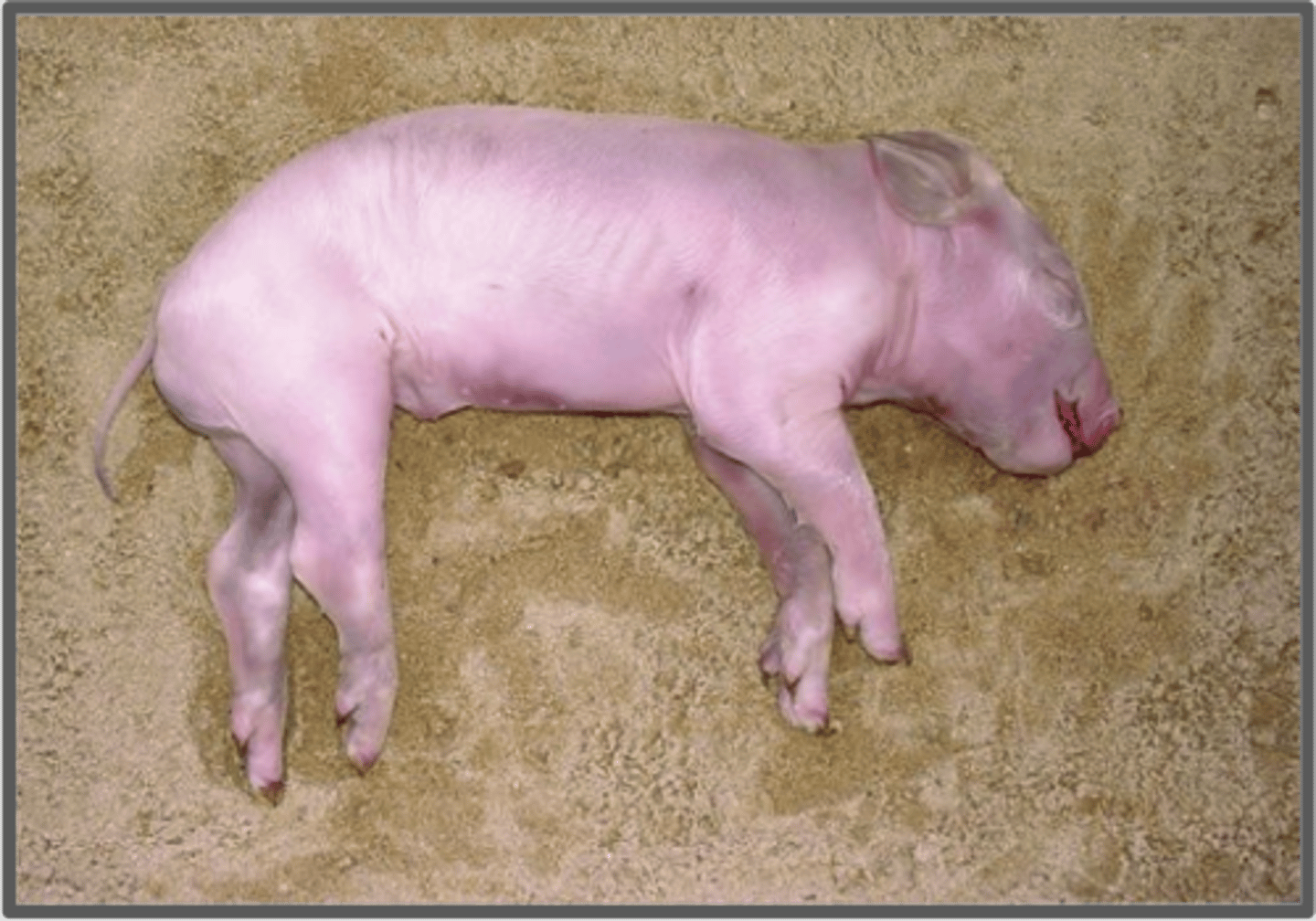
Butyric Fermentation
Corpse is beginning to dry out. Most of the flesh is gone.

Entomology
The scientific study of insects. Can be used to calculate TOD using blow flies.
Dry Decay
Corpse is almost dry. Further decay is very slow from lack of moisture.

Putrefaction
Known as the bloat stage. Gas from the previous stage starts to build up. This pressure inflates the body and forces fluids out of cells and blood vessels and into the body cavity.
Ambient Temperature
The temperature of the surrounding environment.
Livor Mortis
The pooling of the blood in tissues after death resulting in a discoloration of the skin. Starts at 2 hours and becomes permanent (no shifting) at about 8 hours.

Time of Death (TOD)
When the person died
Manner of Death
One of four means by which someone dies (natural, accidental, suicidal, or homicidal).
Coroner
A public official who investigates death. They file death certificates and request autopsies.
Death
The cessation, or end, of life.
Cause of Death
The immediate reason for a person's death (such as heart attack, kidney failure).
Exsanguination
Loss of blood to the point where life can no longer be sustained. A mechanism of death.
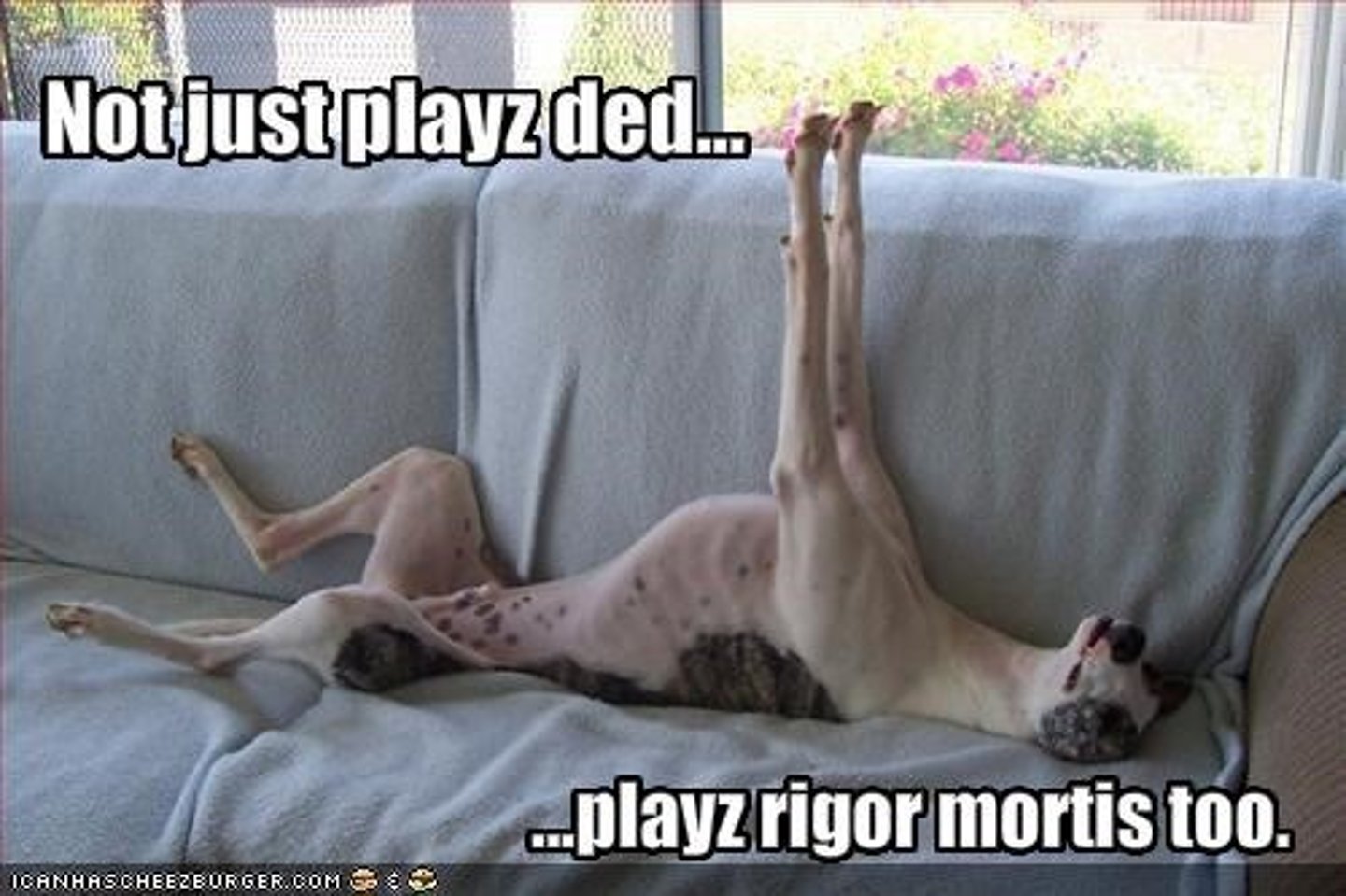
Rigor Mortis
Stiffness of the body that sets in several hours after death. A body follows the 12-12-12 rule. Full rigor at 12 hours.

Decomposition
A chemical reaction that breaks down compounds into simpler products.
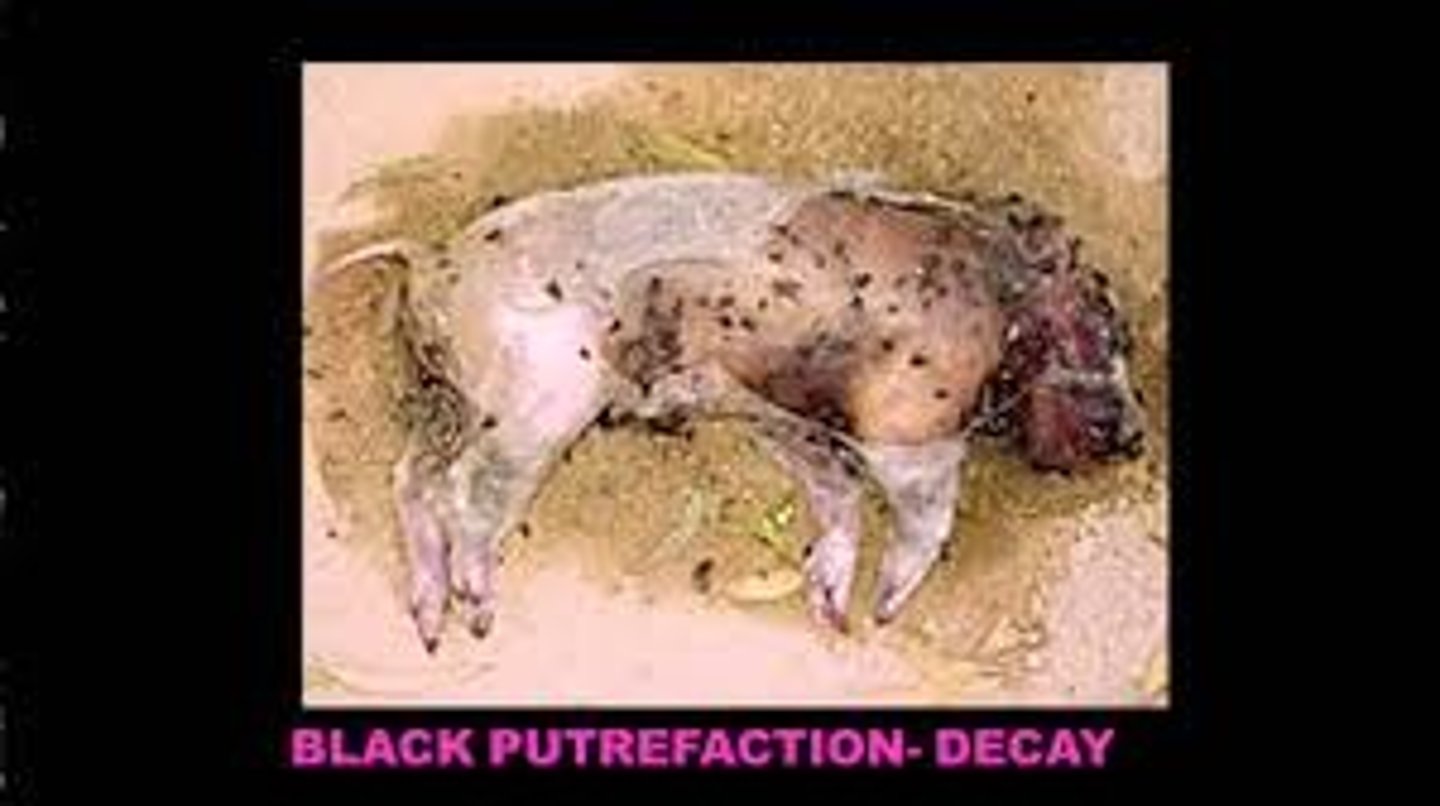
Black Putrefaction
Very strong odor; parts of skin appear black, gases cause the chest and abdominal cavities to burst and collapse, fluids leak out of body cavities, eyeballs liquefy, skin sloughs off.
Autolysis
Self-destruction of cells; decomposition of all tissues by enzymes of their own formation without microbial assistance/
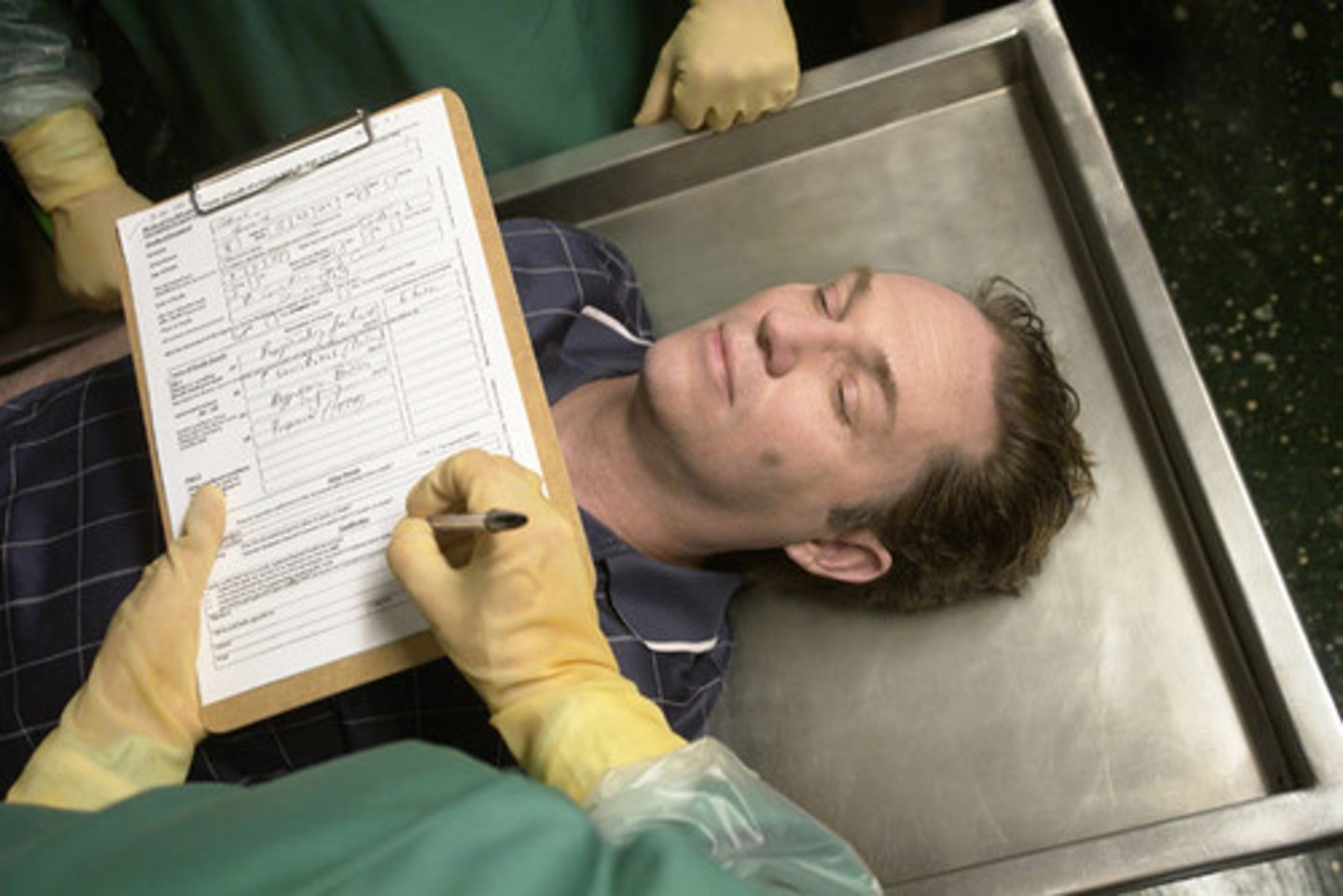
Autopsy
An examination of the body after death usually with such dissection as will expose the vital organs for determining the cause of death.
Pathology
A medical field that studies death disease.
Post Mortem Interval (PMI)
How long between death and the discovery of the body.
Saponification
A chemical process that causes the fat of the body to form into a soapy material and preserves the body.
Adipocere
Waxy fat; happens with bodies under water
Forensic Taphonomy
Concerned with study of decomposition of human remains, particularly in context of burial sites.