Ancient Civilizations: Mesopotamia, Egypt, and the Indus Valley
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key concepts from Mesopotamia, Old Kingdom Egypt, and the Indus Valley, focusing on urbanism, architecture, and societal structures.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
What geographic region spawned a great system of cities during the fifth through third millennia BCE?
Mesopotamia
What material was the most available medium of expression in Mesopotamia?
Clay
What are the earliest urban settlements in Mesopotamia, dating from 5000 BCE, located in?
Sumer, the southern delta area
What shared features did Mesopotamian cities exhibit?
A set of double walls, at least one towering temple as the center, and dikes, canals, and irrigation systems
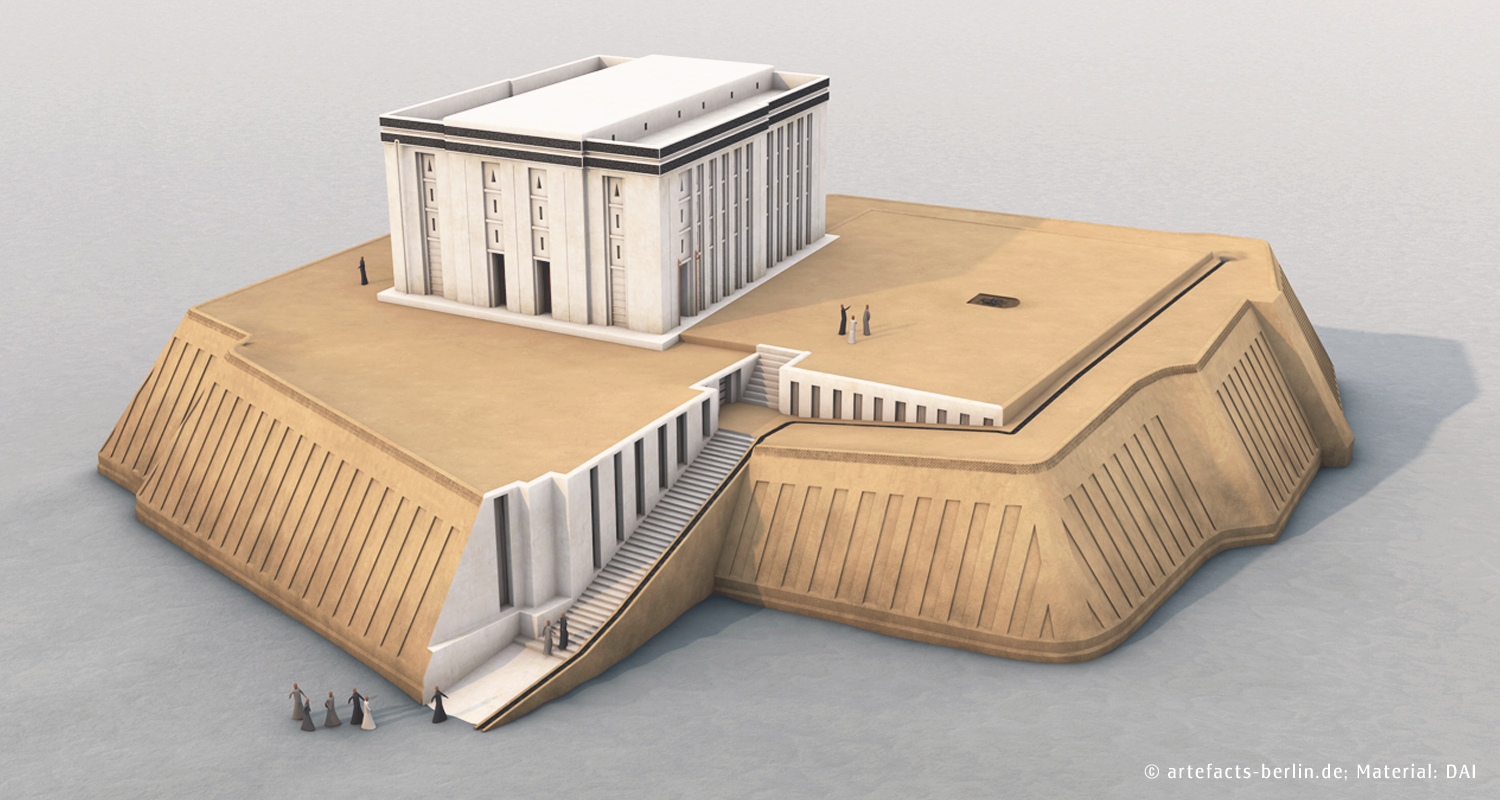
What is the term for the stepped temples designed by Sumerian architects that rose on platforms?
Ziggurats

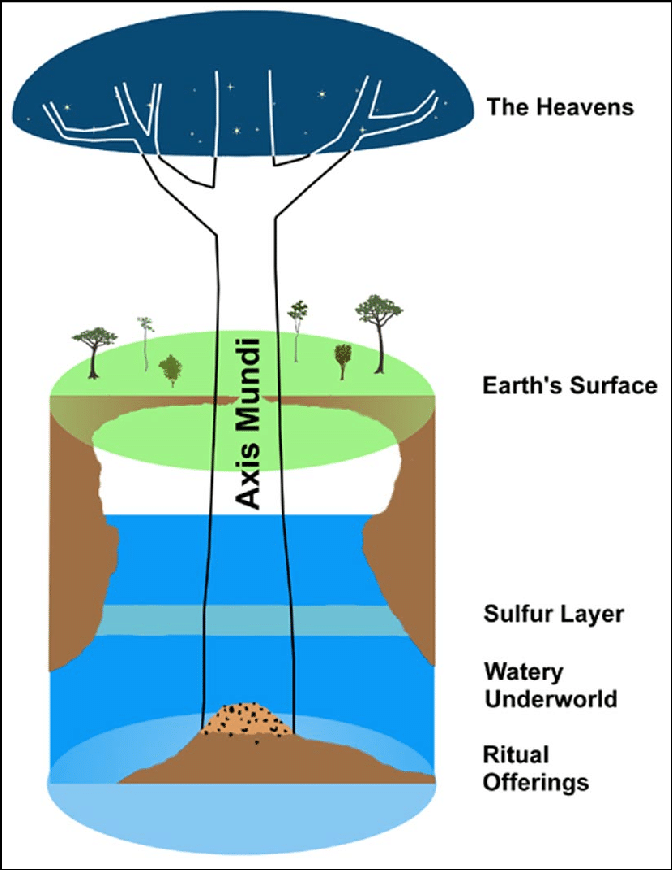
What is an "Axis Mundi" in the context of ancient architecture?
A sacred marker indicating a local culture's center of the world
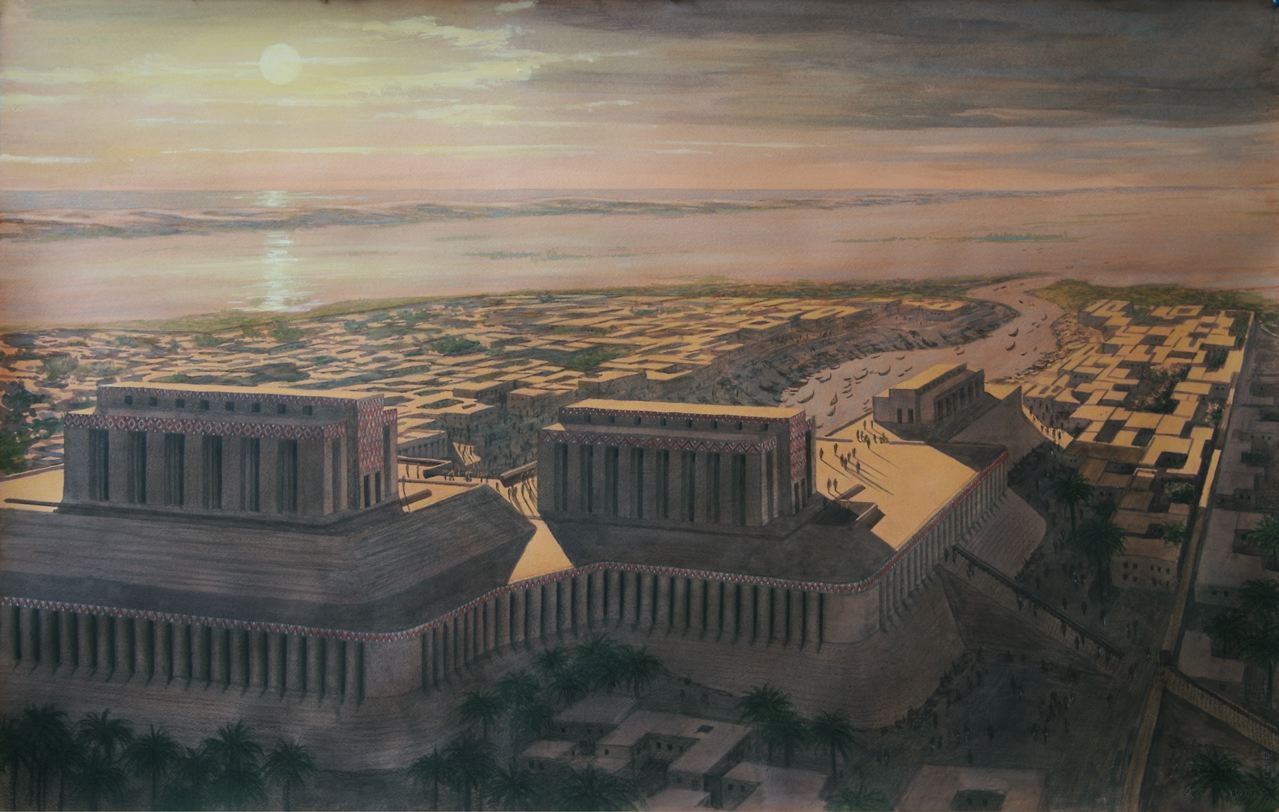
Which Mesopotamian city is considered the oldest settlement in the region and featured a temple to Enki?
Eridu

Which Uruk temple, built between 3400 and 3000 BCE, became the focus of the city's religion and government?
White Temple
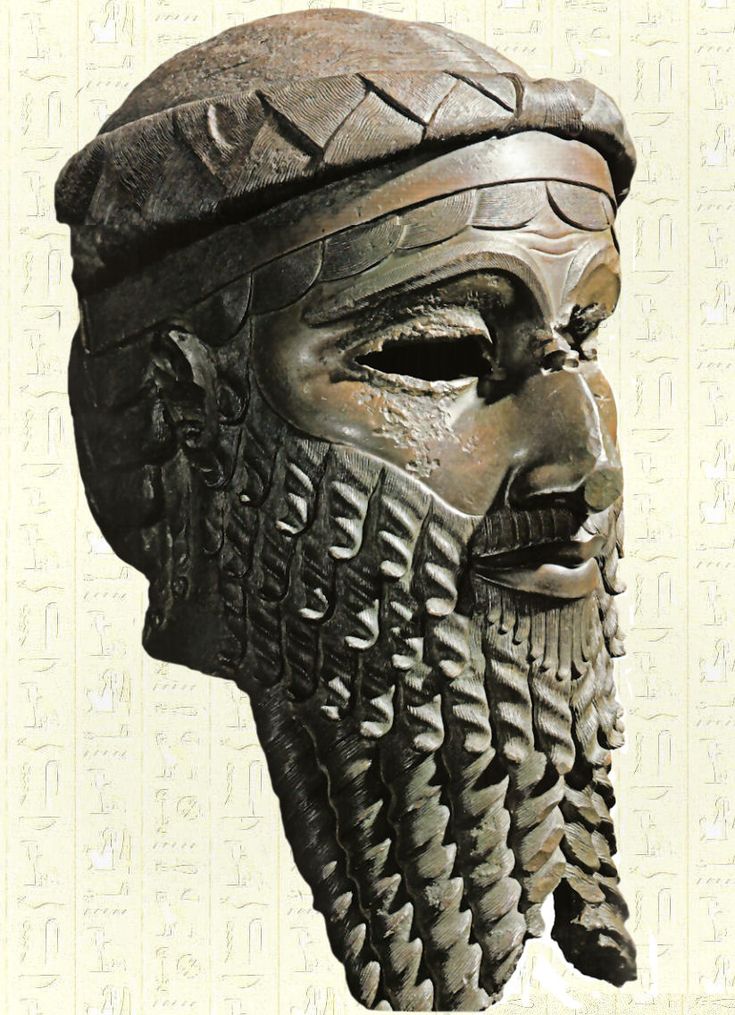
Who was Sargon the Great?
A ruler who seized power in Kish and controlled as many as sixty-five cities, leading to the development of royal palaces

What material did the heat from fires convert the clay walls and cuneiform tablets of sacked palaces (like Ebla and Mari) into?
Terra-cotta
After the demise of Sargon's Akkad, which city emerged as the largest in Bronze-Age Mesopotamia?
Ur
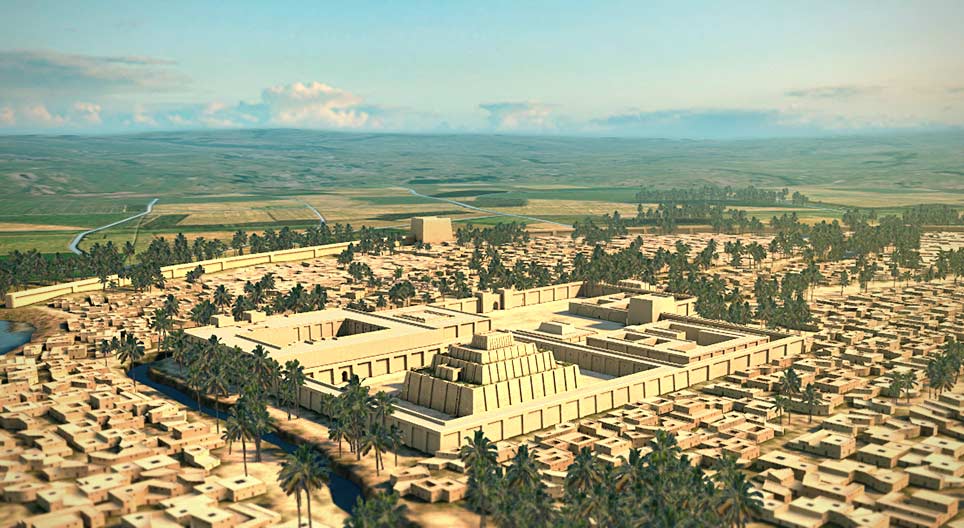

Which king of Ur published the first code of laws, later revised as the Code of Hammurabi?
King Ur-Nammu

What was a distinguishing feature of the temple district in Ur's layout?
It was planned as a solemn void with orthogonal coordinates, contrasting order and disorder
What encouraged the ancient Egyptians' belief in an eternal order?
The Nile's reliable annual floods
Where were all ancient Egyptian burial grounds confined?
To the west bank of the Nile, the land of the setting sun
What was the initial loaf-shaped rectangular royal tomb type known as in ancient Egypt?
Mastaba

Which king transformed the Old Kingdom royal tomb type into Egypt's first pyramid?
King Djoser
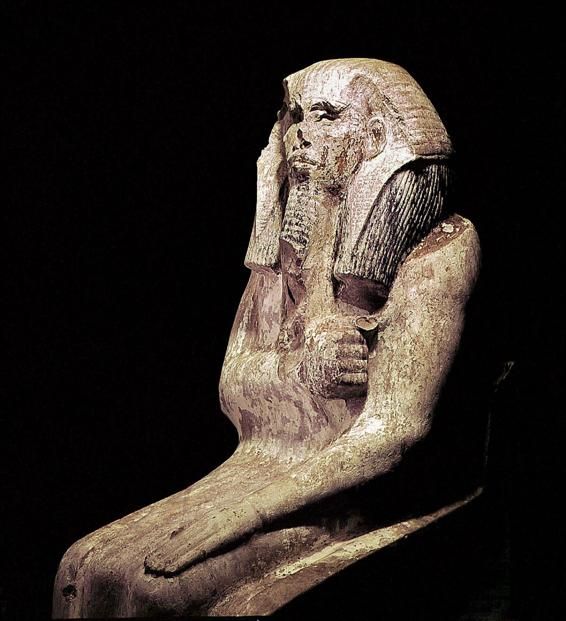

Who was the architect who designed the precinct of Djoser's tomb complex?
Imhotep

What festival, celebrated every thirty years, was a key ritual within Djoser's tomb complex to test the pharaoh's capacity to rule?
The Heb-Sed festival

Who was the pharaoh who made three attempts to smooth the stepped pyramid structure, eventually creating the first perfectly prismatic pyramid and the first valley temple?
Sneferu
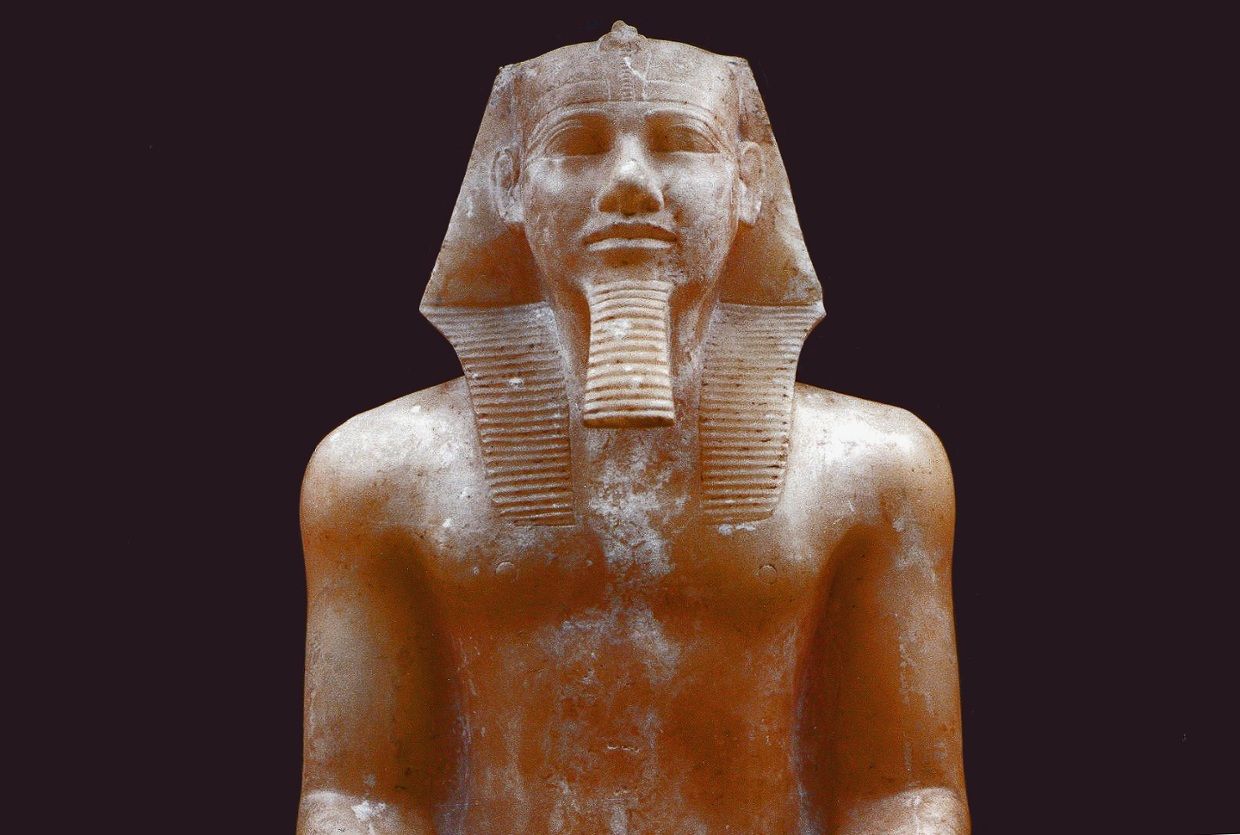

Which pharaoh commissioned the first and largest of the pyramids at Giza?
Khufu

What did the pyramids at Giza represent for the ancient Egyptians?
Monuments of hope and a necessary link to the realm of the gods
What major environmental disaster did Egypt suffer in the 22nd century BCE, similar to Ur's decline?
The Nile refused to flood, leading to famine, disorder, and political shifts
Who was the founder of the eleventh dynasty who reunited the two lands of Egypt and sponsored a new type of platform funeral memorial?
Mentuhotep I

What was distinctive about the Harappan (Indus Valley) urban society compared to Mesopotamians and Egyptians?
They were the first urban society to intentionally avoid building religious and dynastic monuments.
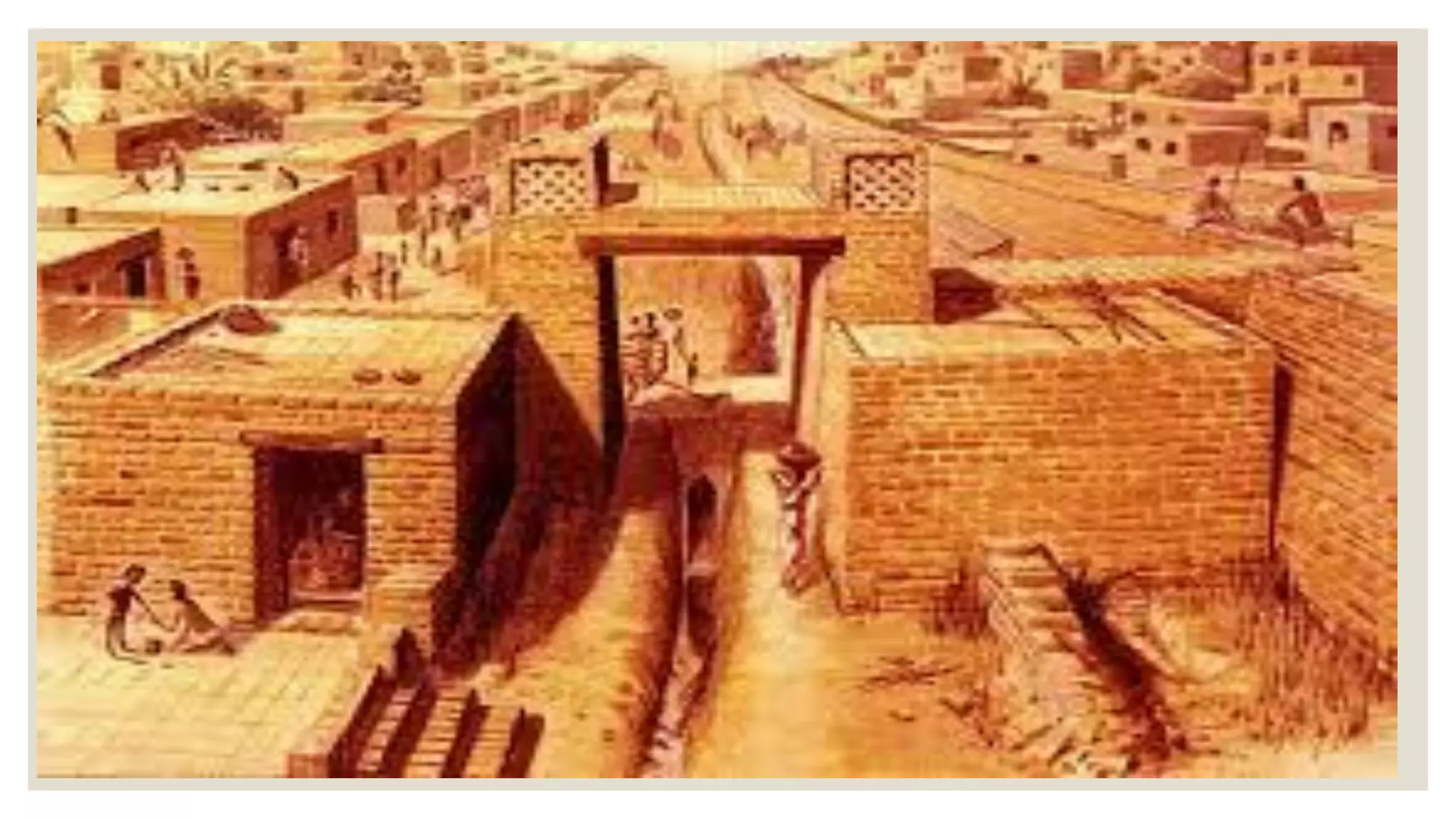

What is the earliest known settlement in the Indus Valley region, dating from the seventh millennium?
Mehrgarh
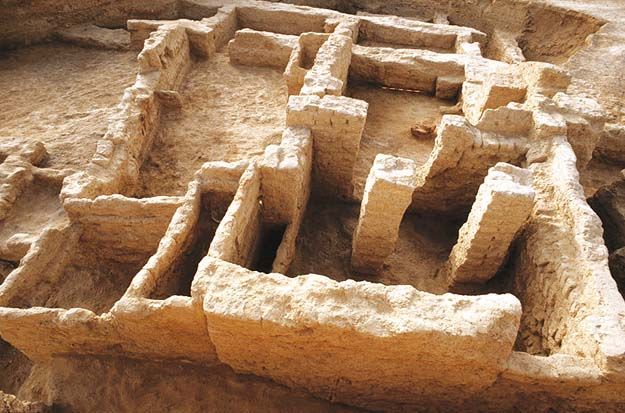

What aspect of Harappan cities' infrastructure was more prominent than their monumental architecture?
Unusually thick city walls, well-planned reservoirs, and sophisticated systems of brick-lined drains

What does the absence of large structures for high priests, monarchs, or powerful rulers in Harappan cities imply about their society?
A relatively horizontal society run by assemblies
What was the likely function of the Great Bath in Mohenjo-daro?
It may have had religious functions as a structure for ritual bathing.
