waves
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
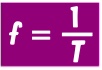

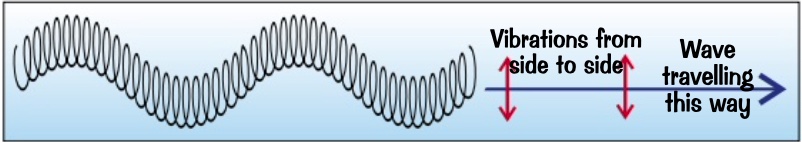
e.gs:
* light and all other EM waves
* a slinky spring wiggled up and down
* waves on strings
* ripples on water
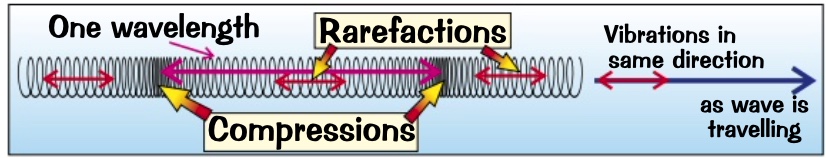
e.g’s?
* sound and ultrasound
* shock waves egg some seismic waves
* a slinky spring when you push the end
e.g microwaves in an oven make things warm up - their energy is transferred to the food your cooking.
sound waves can make things vibrate or more e.g loud bangs can start avalanches.
e.g light in optical fibres or radio waves travelling through the air
* there are multiple waves moving together in the same direction
* the distance between each wavefront is = to one wavelength
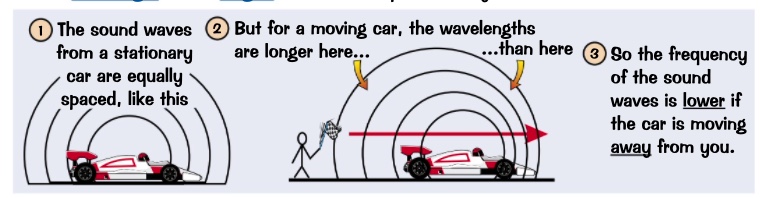
the waves produced by a source which is moving towards or away from an observer will have a different wavelength that they would if the source were stationary.
this is bc the wavespeed is constant . the wavefronts will bunch up in front of the moving source and spread out behind it.
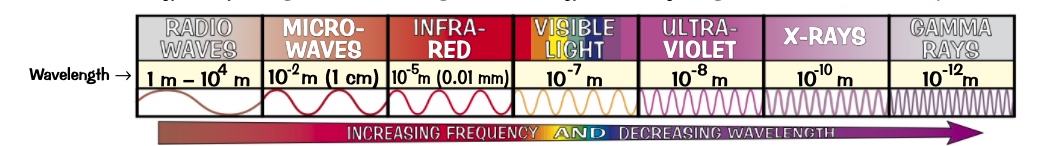
violet has the shortest wavelength high freq
radio waves are EM radiation with wavelength longer than about 10cm.
used for TV and FM radio broadcasting very short wavelength.
\
* wavelength 1-10cm
tv- signal from a transmitter is transmitted into space where it is picked up by the satellite receiver dish orbiting. satellite transmits signal back to earth received by satellite dish on ground.
mobile phone also travel as microwaves from your phone to nearest transmitter
* microwaves are absorbed by the water molecules in the food.
* they penetrate a few centimetre in the food before being absorbed.
* energy is conducted or convected to the other parts of the food
* known as heat radiation.
* electrical heaters radiate IR to keep us war and grill use IR to cook food
* the hotter the object the more IR radiation gives out
* IR radiation given out by injects can be detected in the dark by nigh vision equipment
* electrical signal displayed on the screen as a picture which would be hidden in the dark e.g criminal on the run
* visible light can be used for communication using optical fibres
work by bouncing waves off the sides of a very narrow core
pulse of light enters the fibre at a certain angle at one end and is reflected again and again until it emerges at the other end
used for medical purposes to see inside the body without having to operate
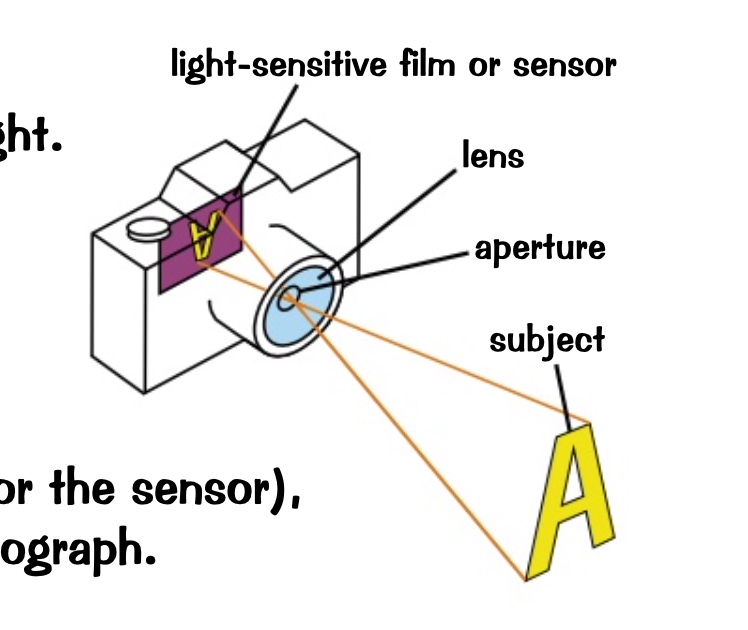
* came uses a lens to focus visible light onto a light sensitive film or sensor
* the lens aperture controls how much light enters the camera
* the shutter speed determines how long the film or seniors is exposed to the light
\
* fluorescence is a property of certain chemicals where ultraviolet radiation UV is absorbed and then visible light is emitted.
* they emit light
* fluorescent light use UV radiation to emit visible light. There safe to use as nearly all the UV radiation is absorbed by a phosphor coating on the inside of the glass which emits visible light instead
* fluorescent lights are more energy efficient than filament light bulbs
* X-rays are directed through the body onto a detector plate.
* radiographers in hospitals take X-ray photographs to help doctors diagnose broken bone
* easily pass through flesh but not through denser material like bones
* can cause mutations which lead to cancer
2- food by killing microbes and keeping them fresh for longer
\
mostly passes through soft tissue without being absorbed
other type are absorbed and cause heating of the cell
some radiation can cause cancerous changes in living cell
microwaves heat human body tissue
that is why they need to have shielding to prevent microwaves reaching the user
higher frequency carries more energy than microwave radiation.
if too much infrared radiation skin burns
protect yourself using insulating materials to reduce the amount of IR reaching your skin
\
some frequencies of UV radiation are ‘ionising’- carry enough energy to knock electrons off atoms.
can cause cell mutation or destruction and cancer.
wear sunscreen with uv filters when in sun
stay out of strong sunlight to protect skin from UV radiaiton
\
much more damaging and can penetrate further into body.
cause cell mutation destruction leading to tissue damage or cancer.
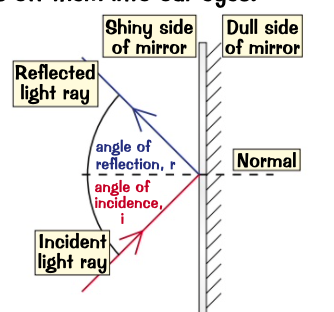
shown as a dotted line
\
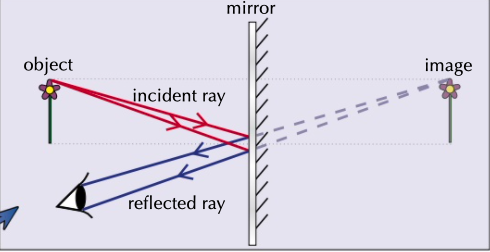
EM waves travel more slowly in denser media
sound waves travel faster in denser substance
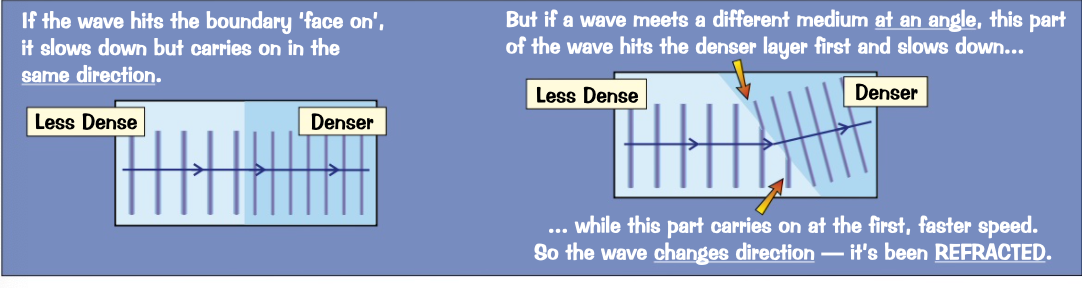
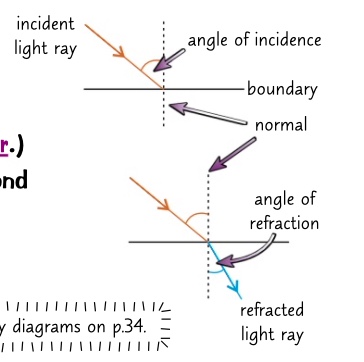
* draw an incident ray that meets the normal at the boundary
* draw the refracted ray on the other side.
* if the second material is denser than the first the refracted ray will bends towards the normal.
* the angle between the refracted ray and the normal is smaller than the angle of incidence
* if the second material is less dense the angle of refraction is larger than the angle of incidence.
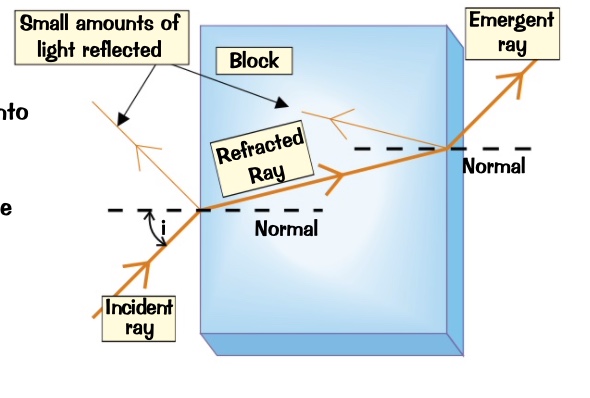
shine a light ray at an angle into the block .
some light will reflect but a lot passes through the glass and gets refracted
trace the incident and emergent rays onto the piece of paper and remove the block
draw in the refracted ray through the block by joining the ends of the other two rats with a straight line
as the light passes from the air into the block it bends towards the normal as it slows down
when the light reaches the boundary on the other side of the block it’s passing into a less dense medium. speeds up and bends away from normal
experiment with refraction using a light source and a rectangular block

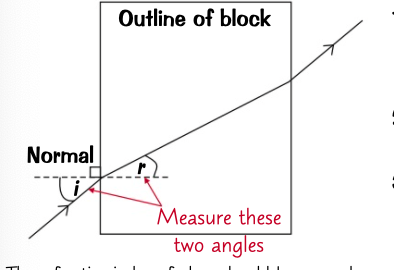
* Draw around a rectangle glass block on a piece of paper and direct a ray of light though it at an angle
* trace the incident and emergent rays, remove the block then draw in the refracted ray between them.
* draw in the normal at 90 degrees to the edge of the block at the point where the rays enter the block
* use a protractor to measure the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction.
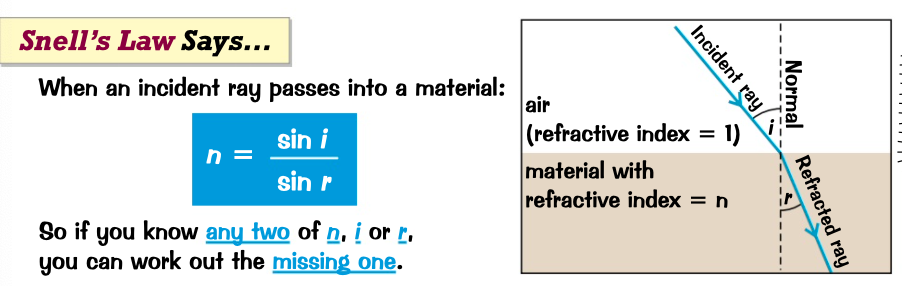
* calculate the refractive index using snell’s law?
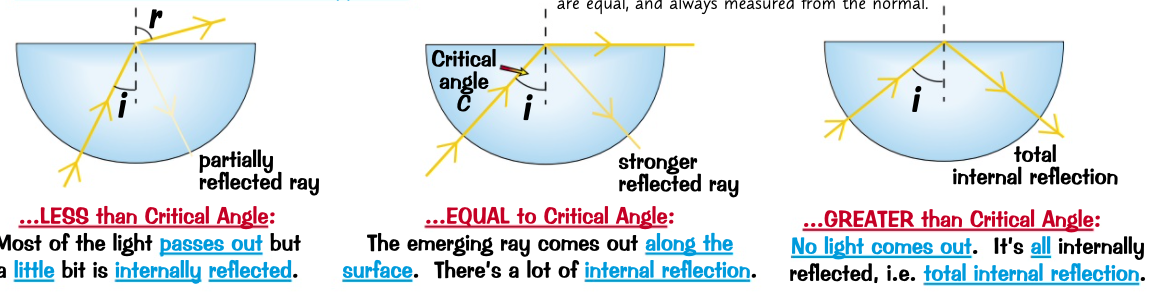
* incident light ray is aimed at the curved edge of the block
* always enters at right angle to the edge
* doesn’t bends as it enter only bend when it leaves
* mark the positions of the rays and the blocks on paper use a protractor

optical fibres and prisms
2 uses of internal reflection?
made of plastic or glass consists of a central core surrounded by cladding with a lower refractive index
what are optical fibres made out of?