AT1 Receptor Antagonists
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What are AT1 receptor antagonists also known as?
ARBs
How does the renin-angiotensin system work?
Renin is secreted into the kidneys and cleaves angiotensinogen to give angiotensin 1. ACE cleaves angiotensin 1 to give angiotensin 2 during passage through the lungs
What is renin?
Proteolytic enzyme that is secreted into the kidneys
How is renin secreted in the kidneys?
Juxtaglomerular apparatus if there is a fall in sodium levels or in renal perfusion pressure
What is angiotensinogen?
High molecular weight protein produced by the liver
What does angiotensin 2 do in the body?
Constricts efferent arteriole greater than afferent and increases/maintains glomerular filtration pressure
Increases sympathetic activity
Tubular Na+ and Cl- reabsorption and K+ excretion, water also retained
Aldosterone secreted and the retention of Na+ and H2O increases blood volume
Arteriolar vasoconstriction which increases blood pressure
ADH secretion.
What is a diagram showing the renin angiotensin system?
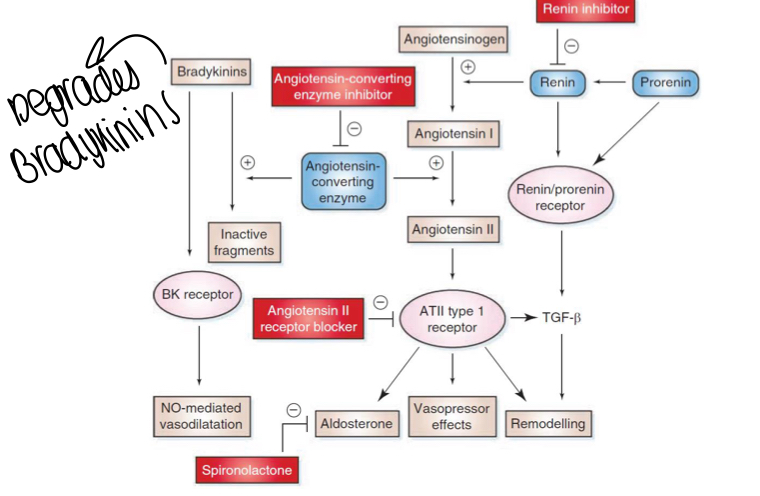
Where do AT1 receptor antagonists act?
Antagonist angiotensin II receptor and inhibits vascular growth
Where is the AT1 receptor found?
Throughout the body but found mostly in vasculature and angiotensin 2 is usually ligand
What type of receptor is the AT1 receptor?
GPCR
How does the AT1 receptor usually get activated?
Signal transduction by G protein
Activates phospholipase C to generate diacylglycerol and inositol triphosphate
Release of inositol triphosphate causes release of Ca from intracellular stores
Ca2+ and diacylglycerol activate protein kinases to phosphorylate proteins and effect cell function
What is a diagram showing how AT1 acts as a GPCR?
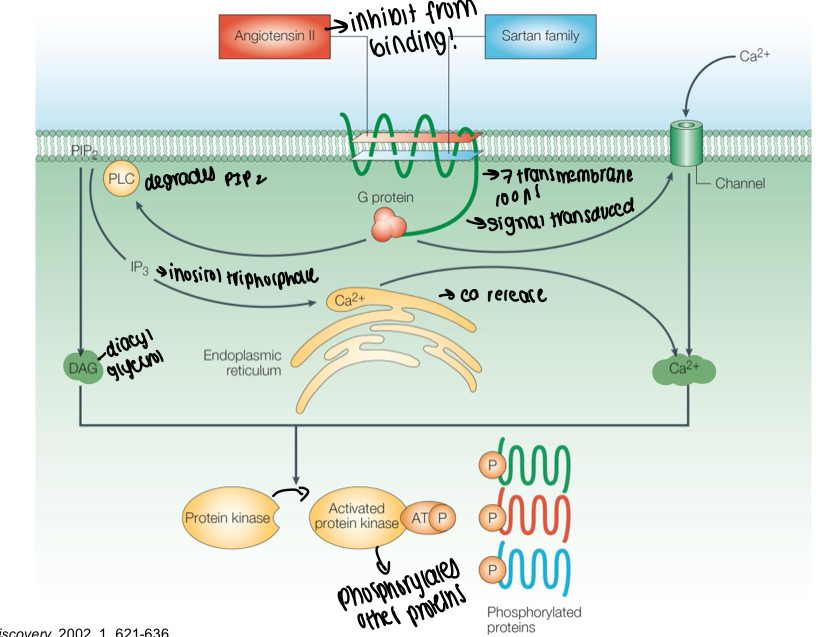
How do AT1 receptor antagonists work?
Block AT1 receptors and prevent angiotensin 2 to bind - allow angiotensin 2 to be produced but binding, therefore inhibit vasoconstriction and aldosterone secretion
What side effects are not observed as frequently as in ACE inhibitors as a result of AT1 receptor antagonists not effecting bradykinins?
Reduced cough and angioedema
What are some examples of angiotensin 2 receptor antagonists?
Losartan, irbesartan, valsartan, candesartan
What are the physiochemical values of the Sartan at1 receptor antagonists?
Around 4.68-5.39 in range for log P, PKa of 3.44 for candesartan in acids to 5.85, basic PKa of 1.51 for candesartan to 4.12 in irbesartan
What structural properties do the sartans have in common?
All have a tetrazole ring for lipophilicity and two benzene rings
What functional group is tetrazole a bioisostere for?
Carboxylic acids
What are the advantages of telmisartan as an at1 receptor antagonists?
Interacts with the tyrosine receptor using the benzydimidazole group and has strong TT-TT interactions
What is a way to remember telmisartan?
Tell me something else