physics - waves, topic 6, paper 2
1/76
Earn XP
Description and Tags
year 10 feb-june
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
what is a wave (3)
-transfers energy from 1 place to another
-most waves transfer energy through vibrations (oscillations) of particles in space
-these particles don’t move from 1 place to another but they vibrate around a fixed point
define wave
a vibration (oscillation) that transfers energy from place to place but not matter
transverse waves definition
when the vibration is at a right angle to the direction the energy is moving (perpendicular) e.g electromagnetic waves
longitudinal waves definition
waves when the vibration is parallel to the direction of the wave is moving e.g sound waves
difference between a transverse wave and a longitudinal wave (3)
-longitudinal waves vibration is parallel to the direction of the wave moving
-whereas transverse waves are when the vibration is at a right angle to the direction the energy is moving
-oscillations!!!
longitudinal waves vibration is parallel to the direction of the wave moving whereas transverse waves are ehre when the vibration is at a right angle to the direction the energy is moving
label both waves
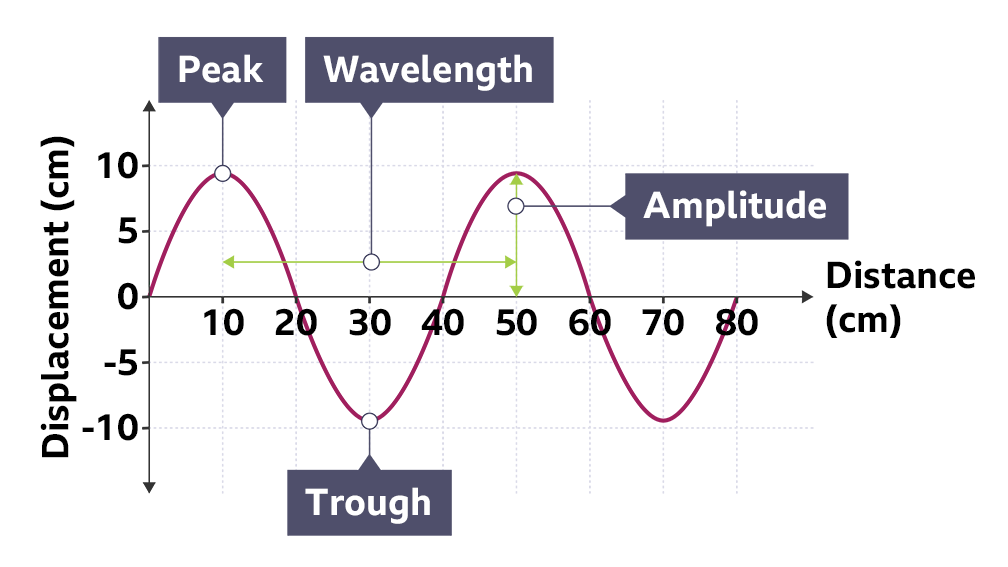
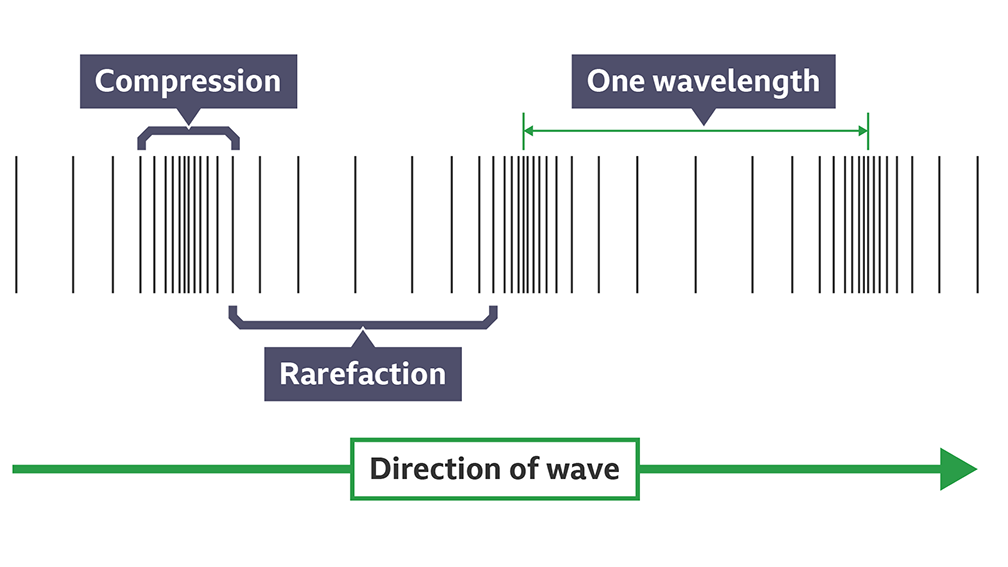
what’s the wavelngth symbol and definition
upside down y
the length between 2 peak/ areas of compression
amplitude symbol unit and definition
A
m
half the hight of the wave
frequency (symbol, unit, def)
f
Hz
the number of waves that pass a point every second
period (symbol, unit def)
T
s
the time it takes for a complete wave to pass a point
why can’t astronaughts hear sounds outside their space suits (2)
-sound can’t travel through empty space
-as there are no particles to vibrate
diff waves travel at diff speeds
what does the speed of a wave depend on
the medium (substance) the wave is travelling through
wave speed, frequency, wavelength equation
wave speed (V)(m/s)= frequency(f)(Hz(are every second) X wavelength(λ)(m)
1, frequency, period equation
frequency (f)(Hz)= 1/period(T)(s)
why do the waves appear stationary during the ripple tank RP
-frequency of waves is equal to frequency of the strobe light
whats the electromagnetic spectrum
spectrum of waves that are of the same type of wave but have slightly diff wave properties (wave length + frequency)
what waves are on the electromagnetic spectrum(7)
radio (highest wavelength, lowest frequency)
microwaves
infrared
visible
ultraviolet
xray
gammarays (shortest wavelength, highest frequency)
radio waves
whats it used for (3)
+description
on earth communication
allow us to listen to music transmitted by radio stations at diff frequencies
-when you tune into diff radio stations, you tune into diff radio frequency and canges the transmission you are listening to
radio communication
microwaves
what they do
+description
-heat food
-food absorbs microwaves-causes our food molecules to vibrate and heat up
-satellite communication- uses microwaves to communicate with other satellites and earth- can easily get through atmosphere
Infrared
what they do
+description
-infrared radiation emitted by warm objects
-used in electrical heaters
-infared cameras- see things when there is little to no visible light
visible light
what they do
+description
-the frequencies of the electromagnetic spectrum that humans can see
-used in high speed communication
-fibre optic cable uses visible light to transmit into at incredibly high speeds
Ultra violet
what they do
+description
-sun emits lots of ultra violet (UV) radiation
-UV radiation is higher frequency than visible light so exposure to too much UV can damage your skin and even cause skin cancer
-UV radiation can also be used in energy efficient lighting and light bulbs
-we also use UV to sterilise medical equiptment and food
X ray
what they do
+description
-medical imaging
-image bones-relatively safe in small doses but it can be damaging to the body if you are exposed to too much- because x-ray radiation is high frequency therefore can cause mutations in your cells which could lead to cancer
gamma rays
what they do
+description
-highest frequency electromagnetic wave
-highly ionising- can damage cells-use gamma rays in cancer treatment
-gamma rays directed at cancer cells in the body in order to kill those cells
-can be used in stronomy-highly penetrating and so we can use it to see things very distant in the universe
speed of light
300,000,000 m/s
OR
3 × 108 m/s
electromagnetic waves in a vacuum equation
C = λ x f
how are radio waves transmitted
how are waves picked up- what do electrons do in the reciever and what does it lead to
how can this be represented
why can radio waves be used for long disrance communication
transmitted- transmitter at a certain frequency
picked up- reciever- where electrons in the receiver vibrate/ oscillate at the same frequency as the radio waves were transmitted at. This leads to an alternating current in the reciever
an oscilloscope can be used to represent this recieved radio transmission
radio waves can be used for long distance communication because their long wavelength allow them to bend around the curvature of the Earth
why are microwaves used for heating food
high frequency microwave radiation is absorbed easily by food molecules, increasing their internal energy and raising their temp
why are infared used forheaters and heating food
certain frequencies can be abdorbed easily by chemiscal bonds, increase their internal energy and raising their temp
why are gamma and xrays used for medical imaging
penetrating so will pass through most body tissues
why are gamma rays used for space exploration
highly penetrating so can pass through clouds of gas/ other objects in universe so we can take pictures from far away
P waves
what does it stand for
what are they
what can they pass through
primary waves
longitudinal waves- fastest of waves produced by earthwuakes
can travel through liquid and solid
S waves
what does it stand for
what are they
what can they pass through
Secondary waves
transverse waves- slower waves
onkly travel through solids
what parts of the earth can P and S waves travel through
Crust- solid so P and S waves
mantle- solid so P and S waves
outer core- liquid so only P waves
inner core- solid so P and S waves
2 waves sound waves and radio waves are diff
radio waves are transverse, soundwaves are longitudinal
radio waves travel at a higher speed than sound waves
reflect definition
where waves ‘bounce back‘/ bounce off a surface
absorb definition
where a surface ‘takes in‘ some of the energy from a wave that hits it
refract definition
where waves change speed and bend at a barrier between two mediums
transmit definition
when an object allows a wave to pass through it
emit definition
where an object gives out a wave
if a object/person absorbs more radiation than they emit will they heat up or cool down
if a object/person emits more radiation than they absorb will they heat up or cool down
heat up
cool down
what are white'/ shiny objects good for
reflecting
bad at absorbing or emitting radiation
what are black/ matte objects good for
absorbing/ emitting
poor at reflecting
out of
matte black
matte copper
shiny copper
matte red
which ones the best emitter of radiation
why
matte black
matte red
matte copper
shiny copper
because matte black has the highest temp as it emitted the most infarred radiation
how does the earth stay warm (4)
most wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation emitted by the sun are transmitted through the earths atmosphere
earth absorbs short wavelengths and warms up. Other wavelengths reflect off the earth
greenhouse gases in the atmosphere absorbs some of the infrared radiation reflected off the earth- warming the lower atmosphere
the longer wavelength infrared is transmitted through the atmosphere and back into space
whats the perfect black body
a (black) object that absorbs all the radiation that hits it so nothing is reflected
would a hotter object
emit a higher/lower wavelength
higher/lower frequency radiation
lower wavelength
higher frequency radiation
would a cooler object
emit a higher/lower wavelength
higher/lower frequency radiation
higher wavekength
lower frequency radiation
is the peak of a hotter object be a shorter or longer wavelength than a cooler object
shorter wavelength
does a hotter object emit a wider or narrower range of wavelngths than a cooler object
wider range of wavelengths
2 diff between electromagnetic waves and sound waves
electromagnetic waves are transverse, whereas sound waves are longitudinal
electromagnetic waves travel at a higher speed compared to sound waves
measuring waves
list the equiptment needed to calculate the speed of water waves (5)
ripple tank
stobescope
ruler
motor
wooden block
describe how to measure the speed of waves in a string (4marks)
-turn up frequency on the single generator
-write down frequency
-use a ruler to measure length of the wave
-use the wave equation to calculate the speed of wave
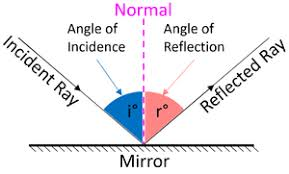
Snell’s law
reflection diagrams can be quite simple to complete, because of Snells law
the angle of incidence = angle of reflection
Seeing colour
why does a red ball appear red to our eyes
when we look through a green filter most things appear green, why
why does a snowman appear white
what do black objects absorb
because it absorbs all other wavelengths except red
this is because the filter only transmits green wavelengths and absorbs all others
because it reflects evry wavelength of visible light, white objects do not absorb any wavelength of light
black objects, absorb every wavelength of visible light, and reflect no wavelength of visible light
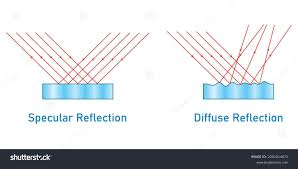
what are the two types of reflection
specular reflection= occurs on mirrors, where surfaces are (almost) entirely smooth. Here the reflection is very orded
diffuse reflection = happens on other objects, that have rougher surfaces. Due to theroughness of the surface the reflections are irregular
ray diagrams and howto describe the motion
what do ray diagrams have (5)
-labelled rays
-directional arrows
-labelled angles
-a normal
-straight linaes
what colour does the ball apear
white light →red filter, white ball
white light→green filter, red ball
ball appears red because the filter only transmits red wavelengths and absorbs all others and reflects of the ball
ball appears black as green is transmitted through the filter, greenlight is absorbed by red ball
investigating retraction diagram
what do you notice when the light ray enters the glass block
the light ray slows down as it enters the glass block. What can we conclude about the density of the block compared to the air
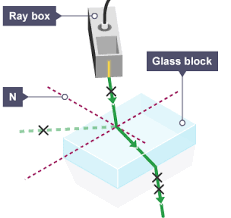
the light ray refracts
the block is denser than air
wave fronts
A wave front diagram is a way of representing multiple waves. Each line on the wave front diagram represents the same point on each of these waves
for example a wavefrontdiagram might represent thr trough or peak of each wave with one straight line
when we use these wave front diagrams to represent refraction we see that the wave front bends when it hits a boundary at an angle LOOK IN BOOK 30 APRIL
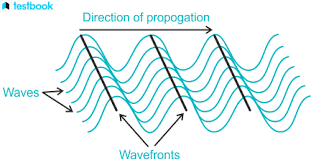
what happens to the wavelength during reflection
what happens to the frequency
wavelength gets smaller and the waves slow down so the frequency stays the same
speed = smaller too
what is sound
-sound waves transfer energy from one place to another
-sound is a longitudinal wave with areas of rarefraction and compression
-sound involves the oscillation of particles, parallel to the direction that the energy is moving
-sound can only travel where there are particles to vibrate
the ear: how we hear
in the same way that our eyes are able to convert electromagnetic waves into brain signals (allowing us to see), the ear converts sound waves into brain signals that allow us to hear
sound waves hit the ear drum, causes small bones in the inner ear to vibrate. The cochlea then converts these vibrations to nerve signals - allowing our brain to work out what we have heard
what are oscilloscopes used for
converting sound waves into viewable transverse waves
moving sounds
objects that are emitting waves - arent always stationary
The doppler effect
when a wave emitting object moves towards you the wave frequency inc causing the sound to seem higher pitched
when wave emitting objects move away from you the wave frequency decreases causing the sound to seem lower pitched
Ultrasound - image babies in the womb
-humans can hear 20-20,000 Hz (but other factors can impact the range an individual can hear e.g listening to loud music, age)
-ultrasound = a sound that is a higher frequency than what humans can hear
-a transducter = a piece of electronic equipment that emits ultrasound into the womb, this ultrasound hits the baby + reflects back
-reciever = what the reflected ultrasound is picked up by. The length of time between the ultrasound is emitted and when its recieved allows us to image the baby
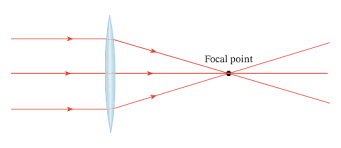
convex / converging lenses
-parallel rays of light are refracted inwards and meet at the focus
-focus is infront of the lens
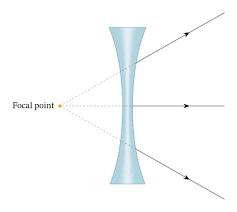
concave/diverging lens
-spreads light rays out
-focus behind the lens
-used for short sighted
Practicle: measuing focal length
method
we measured the focal length for the convex lense by using a ray block and the slit card on the 3 hole side. We put the convex lense when the light is still parallel and draw an X (this is the focus) in the middle of where the light rays meet. Trace around the convex lense. Take of the lense and measure from the middle of thw width of the lense to the focus. THis is the focal length
we measured the focal length for the concave lense by using the ray block. Put the concave lense where the light is still parallel and trace the lense. Trace the 3 rays and remove the lense. Measure where the rays meet behind the lense (side closer to ray box) abd put an X (focus) then measure from the focus tpoint to the middle of the width of lense. This is the focal length
Practicle: measuing focal length
equipment
-ruler
-paper
-power bank
-ray box
-lenses
-rubber
-slit
-pencil
magnification equation
if magnification is >1
if magnification <1
magnification = image height/object height
if magnification >1 then object will be magnified (bigger)
if magnification <1 object will be dimminished (smaller)
Real vs Virtual images
LOOK IN BOOK FOR DIAGRAM 11 JUNE
-real images are locations where light actually converges (rays being brought together)
-real images would be visible if a screen is placed there
-virtual images are located where light appears to come from
-virtual images can only be seen when looking through the lense
upright vs inverted images
LOOK IN BOOK FOR DIAGRAM 11 JUNE
-upright images would appear the same way up as the object
-inverted images would appear upside down
-if the object is moved further away from the lense the size of the image will decrease
convex lense thats futher than 2 focal points
convex lense thats between F and 2F
convex less than F
concave at any location
are they diminished or magnified, upright or inverted, virtual or real
DIR
MIR
MUV
DUV
wave speed on a string
experiment
A string is attached to a vibrator and passes over a pulley. The weights on the end of the string keep the strings in tension.
The signal generator is used to change the frequency of the vibrator
when the signal generator is switched on, the vibrator “shakes” the string and sets up a wave pattern. (This is just the same as a vibrating string on a guitar)
becuase the ends of the string are fixed, it can only vibrate so that there are a whole number of half wavelengths on the string
FInd the frequencies at which these patterns occur and use the ruler to measure the wavelength (count the number of half wavelengths on the string)
Wave speed on a string
theory
The wave patterns on the string are called “stationary waves” or “standing waves”
they form because a wave travels along the string and reflects at the end. The two waves, moving in opposite directions, add together to form the stationary wave pattern
to find the speed of the wave, use the formular: = frequency x wavelength