MBB EXAM 2
1/203
Earn XP
Description and Tags
neuromuscular, motor, parkinsons, alzheimers, stroke, ALS
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
204 Terms
Polyneuropathy
Damage to terminal branches on multiple nerves
parkinsons
decreased dopamine signaling in basal ganglia due to DEGENERATION of DOPAMINE producing cells
diabetes, vitamin B 12 deficiency, GBS
conditions associated with POLYNEUROPATHY
Mononeuropathy
Damage to single peripheral nerve
Mononeuropathy multiplex
Damage to ≥ 2 peripheral nerves
Radiculopathy
Damage to nerve root
lumbar disc and GBS
conditions associated with RADICULOPATHY
Plexopathy
Damage to a nerve plexus
Axonal neuropathy
a disorder affecting AXONS leading to muscle weakness and sensory loss
Demyelinating neuropathy
disorder that damages MYELIN sheath, causing weakness, numbness, and impaired coordination
Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS)/ AIDP
Immune-mediated inflammation leads to damage of nerve myelin or axons
Areflexia
absence of reflexes, often associated with GUILIAN BARRE SYNDROME (GBS)
radiculopathy and polyneuropathy
neuropathies associated with GBS
pharyngeal-cervical-brachial variant
severe form of Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) that affects BULBAR FUNCTION
bulbar
functions related to the cranial nerves that control chewing, swallowing, and speech
Guilain-Barré syndrome (GBS)
Antibodies against GANGLIOSIDES
Guilain-Barré syndrome (GBS)
Molecular mimicry by campylobacter jejuni
Myasthenia gravis
Antibodies against ACETYLCHOLINE RECEPTORS
Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome
Antibodies against voltage-gated CALCIUM channels
botox
Toxin inhibiting ACETYLCHOLINE RELEASE into synapse
amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
A patient presents with arm weakness. He is hyperreflexic in his right arm, but also has atrophy and fasciculations in the muscles of his right hand. You are concerned about what motor neuron disease?
motor neuron involvement/damage
what does arm weakness indicate?
Hyperreflexia
an exaggerated reflex response
hyperreflexia, spasticity, and stiffness
sign of UPPER MOTOR NEURON (UMN) lesions
Atrophy and fasciculations
signs of LOWER MOTOR NEURON (LMN) damage
Hereditary myopathies
MYOPATHIES that are chronic, SLOWLY progressive, family history, no inflammation, often structural changes in muscle
Acquired myopathies
MYOPATHIES that are more RAPID onset, systemic associations, may respond to treatment, often inflammatory or toxic
ALS
Progressive weakness which can involve bulbar,extremity, respiratory muscles
frontotemporal dementia
what disease is ALS sometimes associated with?
ALS
progressive degeneration of both UPPER and LOWER motor neurons
neuropathy
a disorder affecting the peripheral nerves, causing weakness, numbness, and pain
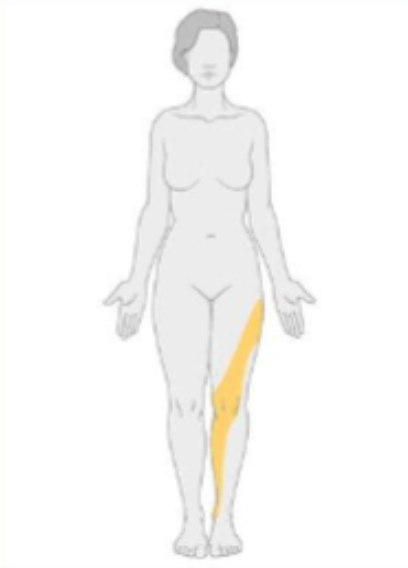
mononeuritis multiplex
what type of neuropathy would have the following distribution?
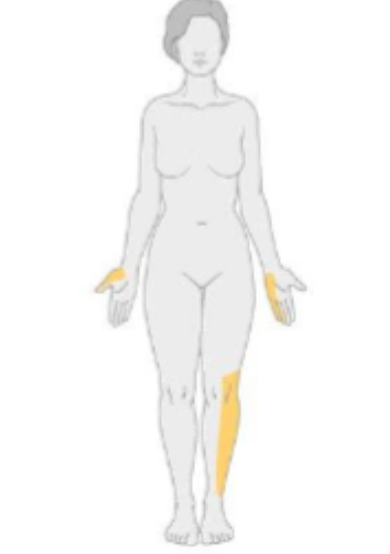
mononeuropathy
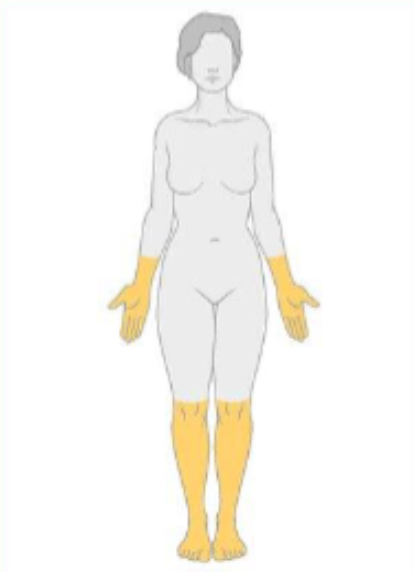
what type of neuropathy would have the following distribution? $
polyneuropathy
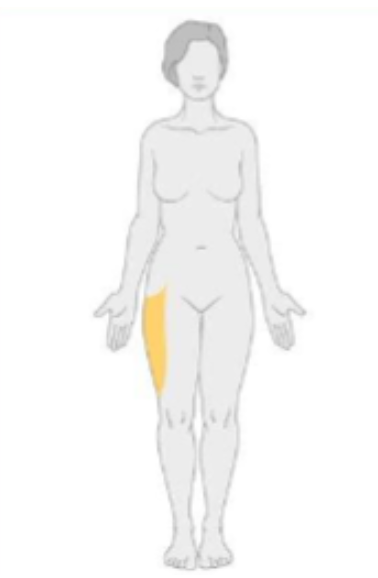
what type of neuropathy would have the following distribution?
plexopathy
what type of neuropathy would have the following distribution?
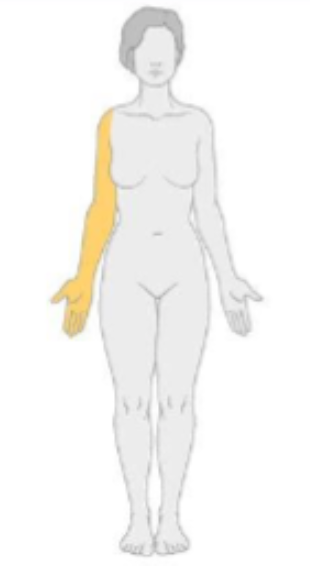
radiculopathy
what type of neuropathy would have the following distribution?
Frontal lobe
Controls executive functions (planning, judgment, decision-making), voluntary movement (primary motor cortex), speech production (Broca's area, left hemisphere), working memory, and aspects of personality
dominant (left) hemisphere
controls language, logical reasoning, math, praxis, and verbal memory
non-dominant (right) hemisphere
controls visuospatial, emotional processing, emotional language, auditory and visuospatial memory, and muscle perception
Temporal lobe
involved in processing auditory information, language comprehension (Wernicke's area), memory, and emotional responses
Parietal lobe
involved in processing sensory information, spatial awareness, attention, and integrating sensory input.
hemispatial neglect
a condition where an individual fails to attend to stimuli on one side of space, typically due to damage to the RIGHT PARIETAL lobe.
left hemispatial neglect
what can damage to RIGHT PARIETAL (nondominant) lobe cause
Occipital lobe
Interprets visual information from both eyes; each lobe processes vision from the opposite field
Cerebellum
Coordinates fine motor movement and balance, posture, and motor learning
ipsilateral
what is the coordination of the cerebellum (ipsilateral or contralateral)
brainstem
Vital for basic life functions (breathing, heart rate, arousal), transfers information between brain and body, and houses nuclei for most cranial nerve
corpus callosum
A thick band of nerve fibers that connects the left and right cerebral hemispheres, facilitating INTERHEMISPHERIC communication
association cortex
integrates signals from widspread connection across brain to allow for higher cognitive functions such as perception, language, and decision making
gerstmann syndrome
damage to LEFT sensory association cortex (parietal) resulting in agraphia, acalculia, finger agnosia, and left-right disorientation
Aphasia
disorder of LANGUAGE, due to damage to language-related cortex (usually left hemisphere)
Dysarthria
speech ARTICULATION dysfunction
Broca's aphasia
can't produce fluent speech, but comprehension mostly spared
Wernicke's aphasia
speech fluent but nonsensical; poor comprehension
Conduction aphasia
difficulty in repeating phrases; fluent speech
Global aphasia
severe impairment of BOTH comprehension and production
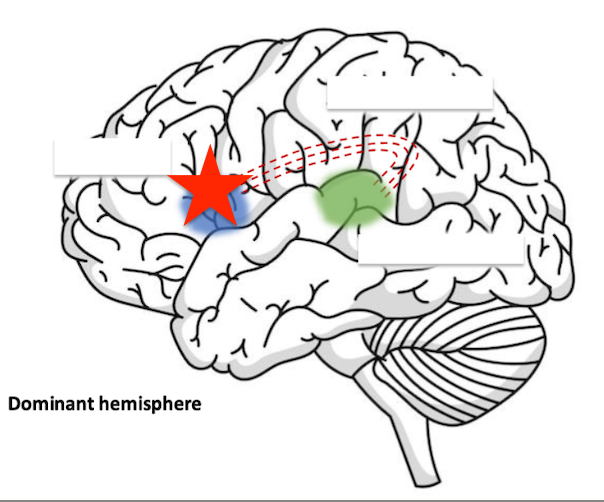
impaired speech (brocas aphasia)
damage to this area would cause?
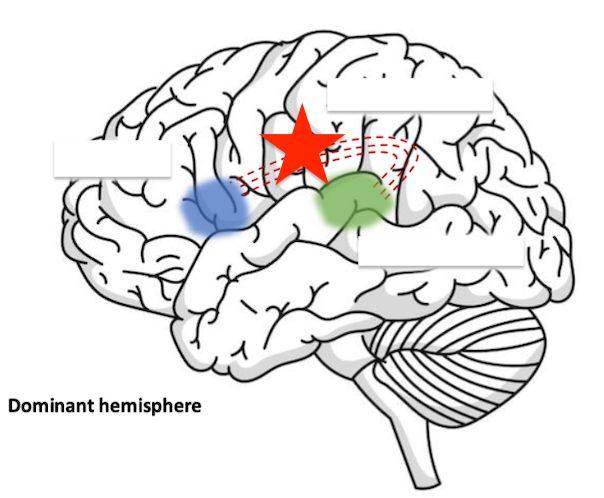
impaired repetition (conduction apahsia)
damage to this area would cause? (arcuate fasciculus)
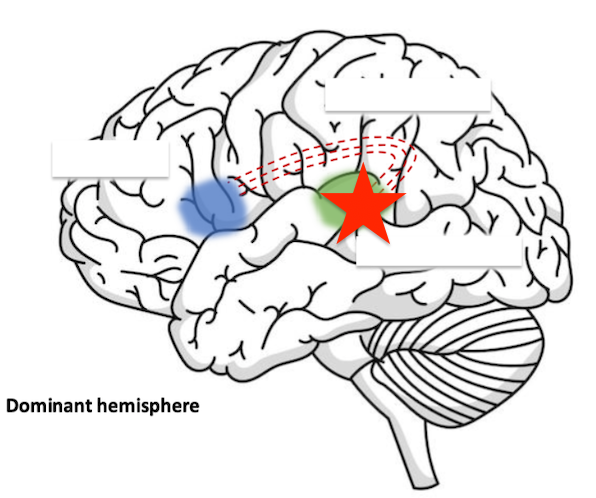
impaired comprehension (wernickes aphasia)
damage to this area would cause?
prefrontal cortex
controls executive planning such as: concentration, judgment, reasoning, PLANNING
limbic
What system in the brain is responsible for EMOTION and MEMORY PROCESSING?
hippocampus
region of LIMBIC system responsible for MEMORY
amygdala
region of LIMBIC system responsible for EMOTIONS
agnosia
inability to recognize or interpret sensory information despite intact primary sensory modalities (ex: recognition of objects, faces, or sounds)
astereognosis
form of agnosia where a person cannot identify objects by touch, despite having intact tactile sensation
Hypokinetic
Too little movement (bradykinesia, rigidity, akinesia)
parkinsons disease, drug-induced parkisonism
examples of HYPOkinetic movement disorders
bradykinesia (slowness of movement)
Defining feature of Parkinson's
Drug-induced Parkinsonism
decreased dopamine due to blocking of dopamine receptors by antipsychotic drugs (1st gen)
Hyperkinetic
too much involuntary movement
essential tremor, Huntington's disease, dystonia, tourettes syndrome
examples of HYPERkinetic movement disorders
Rest tumor/Pill rolling tremor
tremor occurs when muscles are not voluntarily activated (classic for Parkinson's)
Action tremor
What type of tremor is characteristic of essential tremor?
Rest tremor
What type of tremor is characteristic of Parkinson's?
Action tremor
tremor occurs during voluntary muscle contraction
Essential tremor
neurological disorder characterized by rhythmic tremors during voluntary movements (ACTION TREMORS), often affecting the hands
Propranolol (beta-blocker), primidone (barbiturate anticonvulsant
First-line pharmacological treatment options for essential tremor
Blocks beta-adrenergic receptors (reduces activity in muscle and possibly GABA modulation)
Propranolol MOA
Blocks voltage-gated Na channels (enhances GABAergic inhibition)
Primidone MOA
Fatigue, bradycardia, low blood pressure
Propranolol side effects
Sedation, dizziness, nausea
Primidone side effects
Motor (chorea), cognitive (decline), behavioral (mood changes)
clinical triad of Huntington's Disease
30–50 years
Usual age of onset of huntingtons disease
Chorea
involuntary, irregular, dance-like movements, often seen in HUNTINGTONS disease
antipsychotics (block dop receptors) and VMAT2 inhibitors (reduce dop release)
Treatments for chorea
Huntington gene on short arm of chromosome 4
What genetic mutation is related to Huntington's disease
autosomal dominant
inheritance pattern of huntingtons disease
Dystonia
SUSTAINED muscle contractions, abnormal postures, or twisting movements
Writer's dystonia
task-specific focal dystonia that causes involuntary muscle contractions in the hand and forearm, primarily during writing
Tics
Sudden, brief, repetitive movements or vocalizations
Tourette's syndrome
BOTH multiple motor and at least one vocal tic for >1 year, onset before age 18
tics bother patient
When should toureettes be treated?
benzodiazepines, alpha-adrenergic receptor agonist, VMAT2 inhibitors, dopamine blockers
Drugs used to treat tourettes
botox
cleaves SNARE proteins, preventing release of acetylcholine
focal dystonia
When might botox be used as a medical treatment?
Dyskinesia
variety of involuntary motor movements (ex: chorea, dystonia, tic tremor ext)
Tardive dyskinesia
HYPERkinetic movement disorder caused by exposure to dopamine-BLOCKING agents
discontinue offending drug (if possible), avoid 1st gen antipsychotics, VMAT2 inhibitors
Treatment for tardive dyskinenia
lesodopa -induce dyskinesia
side effect of drug used to treat PARKINSONS
Hypokinetic movement disorders
decreased dopamine signaling the basal ganglia