APES MIDTERM
1/323
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
324 Terms
Tragedy of the Commons
situation in which people acting individually and in their own interest use up commonly available but limited resources, creating disaster for the entire community
overusing public/shared resources since they don't experience the negative consequences of doing so (acting in self interest)
Clean Water Act
(CWA, 1972) set maximum permissible amounts of water pollutants that can be discharged into waterways; aims to make surface waters swimmable and fishable
Clean Air act
(CAA, 1970) set emission standards for cars and limits for release of air pollutants
6 Air pollutants
- SO2
- NOx
- CO
- Pb
- PM
- O3
air pollutants
specific chemicals, compounds, or particles harmful to air
air pollution
the introduction of harmful pollutants into atmosphere
SO2 (Sulfur Dioxide)
a pollutant from coal combustion
a respiratory irritant
causes acid rain
Reducing SOx and NOx
Reducing ______ and _____ (air pollutants)
- crushed limestone
- fluidized bed combustion
Crushed limestone
used to reduce SO2 from coal power plants
calcium carbonate + SO2 = calcium sulfate (rather than SO2)
Fluidized bed combustion
a clean-coal technology in which crushed coal is mixed with limestone to neutralize the acidic sulfur compounds produced during combustion
fluidized jets of air are pumped into the combustion "bed"
efficient combustion
brings SO2 into more contact with limestone
less NOx
NOx (Nitrogen Oxides)
pollutant occurs from fossil fuel combustion (gas)
causes smog and acid rain by creating O3
health impact:
- causes ozone formation
- respiratory irritant
- can form nitric acid and acid rain when combined with water and O2
CO (Carbon monoxide)
pollutant from incomplete combustion of fuel source (either from a lack of O2 or lack of temperature)
displaces O2 in the blood -- lethal
impacts:
causes suffocation
binds with hemoglobin in red blood cells
lethal in high concentration
oderless, colorless, and hard to detect
Pb (Lead)
a pollutant from metal plants and waste incineration
in 1978 the EPA prohibited its use in paint
impacts:
nuerotoxicant
damages nervous system
O3 (ozone)
a pollutant that causes photochemical oxidation and photochemical smog
respiratory irritant
causes plant damage
PM (particulate matter)
a pollutant from suspended particles -- common indoors
occurs from combustion, fire, construction, smoke
impacts:
respiratory irritant
causes smog
Electrostatic Precipitator
A device used for removing particulates from smokestack emissions. The charged particles are attracted to an oppositely charged metal plate, where they are precipitated out of the air.
Reduces PM
baghouse filter
Dirty air enters, combustion exhaust stream moes through and dust particles are trapped in a series of filter bags, cleaner and filtered air moves out of unit, shaker mechanism activated periodically to dislodge trapped particles which can then be collected from below unit.
reduces PM
VOCs (Volatile Organic Compounds)
chemical pollutants used in home
products that easily vaporize
ex. adhesives, formaldehydes
carcinogens
ex. plastics and fabrics
impacts:
irritate the eyes and lungs
asbestos
A long, thin, fibrous silicate mineral with insulating properties (no longer used but may be present in older architecture), which can cause cancer when inhaled.
can enter the air and the respiratory track
mesothelioma
lung cancer
Radon Gas
Radioactive gas from uranium decay
can leak into houses through cracks in the ground
impacts:
2nd leading cause of cancer
Primary air pollutant
a pollutant emitted directly from the source
NOx, SOx, CO2, VOCs, CO, hydrocarbons
secondary air pollutant
primary pollutants transformed by sun, 02, H2O
O3
H2SO4, SO42-, HNO3, NO3-
indoor air pollutants in developing nations
the source of the air pollution is from subsistence fuels that are combusted indoors with little ventilation
(these cause NOx, PM, and CO -- toxic)
causes millions of deaths
indoor air pollutants in developed nations
the source of the air pollution is from industrial chemicals (chemicals in products (adhesives, cleaning supplies, lead paints)
Vapor recovery nozzle
an air pollution control device on a gasoline pump that prevents fumes from escaping into the atmosphere when fueling a motor vehicle
VOCS are captured and held in a storage tank under the gas station
Reduces benzene
catalytic converter
a platinum, coated device that oxidizes most of the VOCs and some of the CO that would otherwise be emitted in exhaust, converting them to CO2 rather than toxic pollutants
Dry Scrubbers
Large column/tube/pipe filled with chemicals that absorb or neutralize oxides (NOx, SOx, VOCs) from exhaust streams (emissions)
Wet Scrubbers
fine mists of water vapor trap air particulates and the SO2 passing through a limestone mixture is converted to calcium sulfite sludge that is disposed of in landfills
Ecological footprint
measures of how much a group/person consumes expressed in an area of land
Maximum Sustainable Yeild
the maximum amount of renewable resource that can be used without reducing or depleting the resource for the future
--> roughly half of the carrying capacity is the max sustainable yield (max yield while regenerating the population)
Environmental indicators of sustainability
Biodiversity — greater diversity is healthier
Food Production — indicates soil, water, climate health - less agricultural yield is an indicator of less health
global temperature —
CO2 levels —
Population — increased population leads to less resources
Renewable Resource
a resource that is replenished naturally at/near the rate it is consumed and reused
Nonrenewable resources
a resource that cannot be replaced and exist in fixed amounts
Depletable renewable resources
renewable resources that can run out if overused
nondepletable renewable resources
renewable resources that do not run out
nuclear power
energy from uranium or radioactive fuels
subsistence fuels
Biomass fuel sources that are easily accessible (can be cheaply found and gathered by hand); often used in developing countries as a home heating or cooking fuel
fossil fuels
fossilized remains of ancient biomass and takes millions of years to form (coal, natural gas, oil)
coal formation
Pressure from overlying rock & sediment layers compacts peat into coal over time
the longer a coal deposit is pressurized, the more energy dense
Top Coal Producers
Top _______ Producers
1. US
2. Russia
3. China
4. Australia
types of coal
lignite (least energy dense), bituminous, anthracite (most energy dense)
environmental consequences of coal
consequence of ___________:
mining this fossil fuel causes habitat destruction, releases the most CO2 and greenhouse gasses of the fossil fuels, releases many air pollutants (soot, toxic ash from combustion contains lead/mercury/arsenic, sulfur, NOx), and ash ponds can leak
natural gas
pressure on the decaying remains of plants and animals (marine life) underneath layers of rock turns material into gas and oil
the cleanest fossil fuel (less CO2 and pollutants released)
methane is trapped in the oil deposits
Top natural gas Producers
Top ________ Producers
1. Russia
2. Iran
3. Qatar
4. US
5. Saudi Arabia
50-60 years of reserves left
hydraulic fracturing (fracking)
in order to extract natural gas, a vertical well is drilled, and water is injected into the well. Pressure from water fractures rock layers containing gas and creates fissures
environmental consequences of fracking
consequences of ____________:
well leaking releases salt and acidic fracking fluids, water pollution and depletion, can cause seismic activity such as earthquakes
crude oil (petroleum)
fossilized remains of organic matter are extracted through drilling in the rock layers
Top oil producers
Top _________ producers
1. Venezuela
2. Saudi Arabia
3. Iran
4. Canada
5. Iraq
50 years of reserves left
petroleum uses
gasoline, petroleum gas, jet fuel, diesel fuel, motor oil, bitumen (asphalt), naphtha (plastic)
environmental consequences of crude oil
consequences of ___________:
always possibility of oil spills, toxic chemicals, habitat loss
tar sands
used to extract crude oil
mix of sands, clay, water, and bitumen
bitumen needs to be heated in order to flow through pipes
tailing ponds
where tar sand waste water is stored
environmental consequences of tar sands
consequences of ___________:
equipment and land cause habitat destruction, biodiversity loss, group and surface water depletion through extraction processes, tailing ponds cause water contamination, CO2 release
fractional distillation of crude oil
the separation of crude oil into individual hydrocarbons by boiling point (low boiling point gathers at the top, and high boiling point gathers at the bottom of the column where it is separated)
generating electricity
always:
heat —> water steam —> turns turbine —> powers generator —> produces electricity
cogeneration
using waste heat (heat lost in energy production) to make electricity
fossil fuel combustion reaction
a step in the carbon cycle where fossil fuels react with O2 to form energy
reaction where fossil fuels react with oxygen to produce H2O and CO2
FF + O2 --> H20 + CO2
Ex. Methane, gasoline, and butane all react with O2 in this way
Small scale energy conservation methods
lowering the thermostat, planting native vegetation, energy efficient appliances, more insulation
large scale energy conservation methods
improving fuel economy standard, subsidizing electric vehicles, public transport
CAFE standards
fuel efficiency standards (stands for Corporate Average Fuel Economy)
Average MPG that that vehicles use
Less gasoline/diesel to travel the same distance
reduces energy use and air pollution
Pollution credits
Credits that can be earned and then sold by companies that emit pollutants below established standards.
Deciduous shade trees
trees used in landscaping to conserve energy by blocking the sun in the summer and letting the suns heat in in the winter
Green roof
roof covered in vegetation that helps combat heat-island effect
Decreases runoff, increases air quality, absorbs the sun's heat, and cools the area
Peak electricity demand
the time of the year/day where electricity demand is the highest
Rolling Blackouts
A series of intentional electrical blackouts affecting small areas in succession as a means of conserving electricity when supply is low.
Occurs when the demand of electricity exceeds the supply
Variable Price model
- Users pay a higher rate for energy during peak demand hours or events, to discourage energy use
- Users pay a lower rate/kWh when using a lower amount of energy (incentivizes lower overall use)
Smart Grid
an efficient, self-regulating electricity distribution network that accepts any source of electricity and distributes it automatically to end users
Different integrated power producers
2 way electricity flow
Water conservation methods
planting native vegetation (less water use), low flow water heads/appliances, rain barrels
Atmospheric gases
nitrogen makes up 78%, 21% oxygen, and remaining 1% is carbon dioxide, water vapor and other gases (ex. argon)
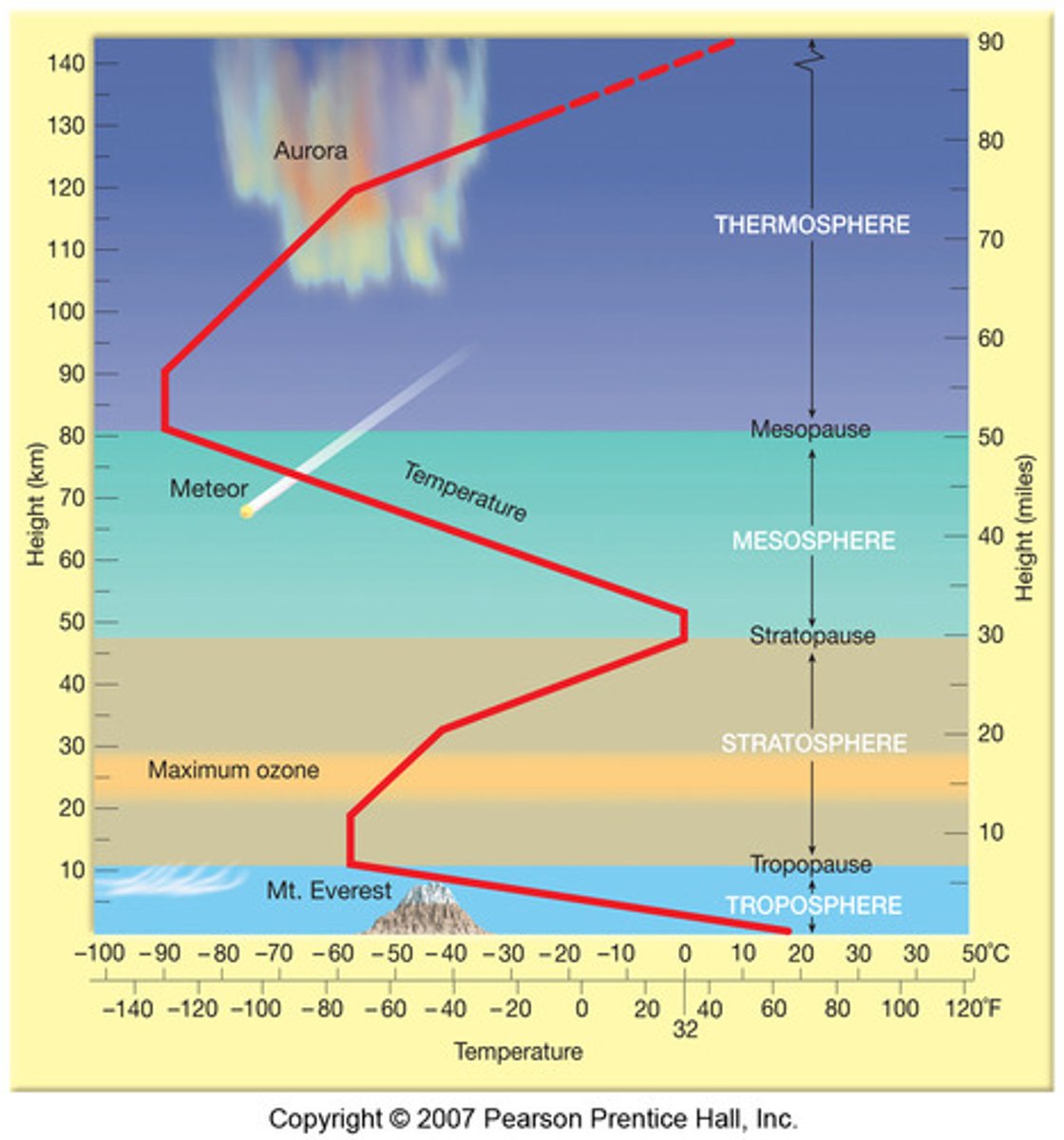
Layers of the atmosphere
1. Troposphere
2. Stratosphere
3. Mesosphere
4. Thermosphere
5. Exosphere
Troposphere
The lowest layer of Earth's atmosphere
- weather changes
- dense
Gets colder farther from earth's warmth
Stratosphere
The second-lowest layer of Earth's atmosphere
- dense ozone layer (tropospheric ozone on the other hand is BAD)
- absorbs UV-B rays and UV-C rays (cancerous rays)
Gets warmer by UV rays
Mesosphere
3rd layer of the atmosphere
Gets colder as density decreases
Thermosphere
The 4th layer of Earth's atmosphere.
- absorbs harmful x-rays
- northern lights are caused by charged gas molecules
Gets warmer due to solar radiation
Exosphere
The outer layer of the atmosphere merging with space
Atmospheric Temperature Gradient
Photochemical Smog
An atmospheric condition formed through a combination of weather conditions and pollution, especially from motor vehicle emissions. (increases with increased temperature, sunlight, VOC emissions, traffic, urban areas)
NO2 is broken down by the sun and combines
Ozone forms and the reaction can't be reversed with the presence of VOCs
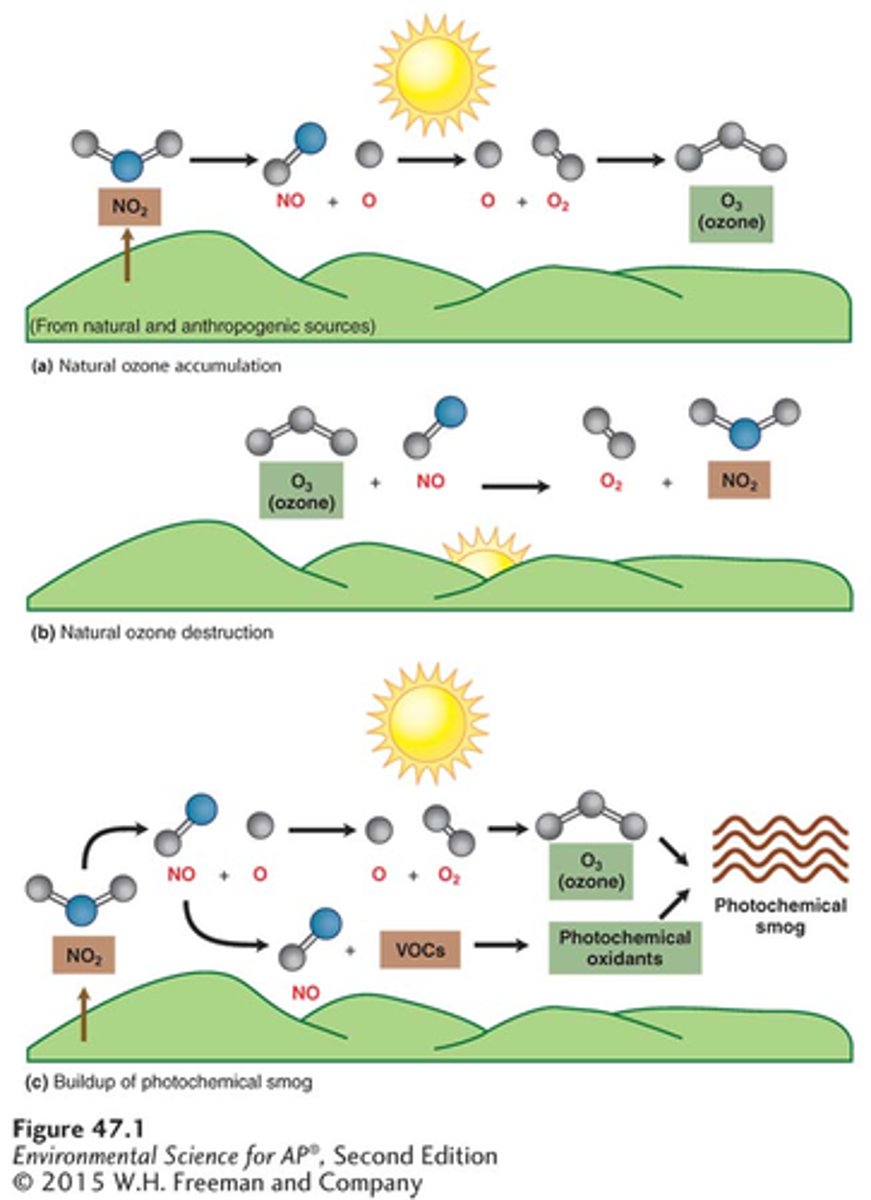
Photochemical smog impacts
__________________ impacts
- blocks sunlight
- less photosynthesis, less plant growth
- respiratory irritant
- increased healthcare costs
- less productivity
- less agricultural yield
can be reduced with less vehicle use and less NOx
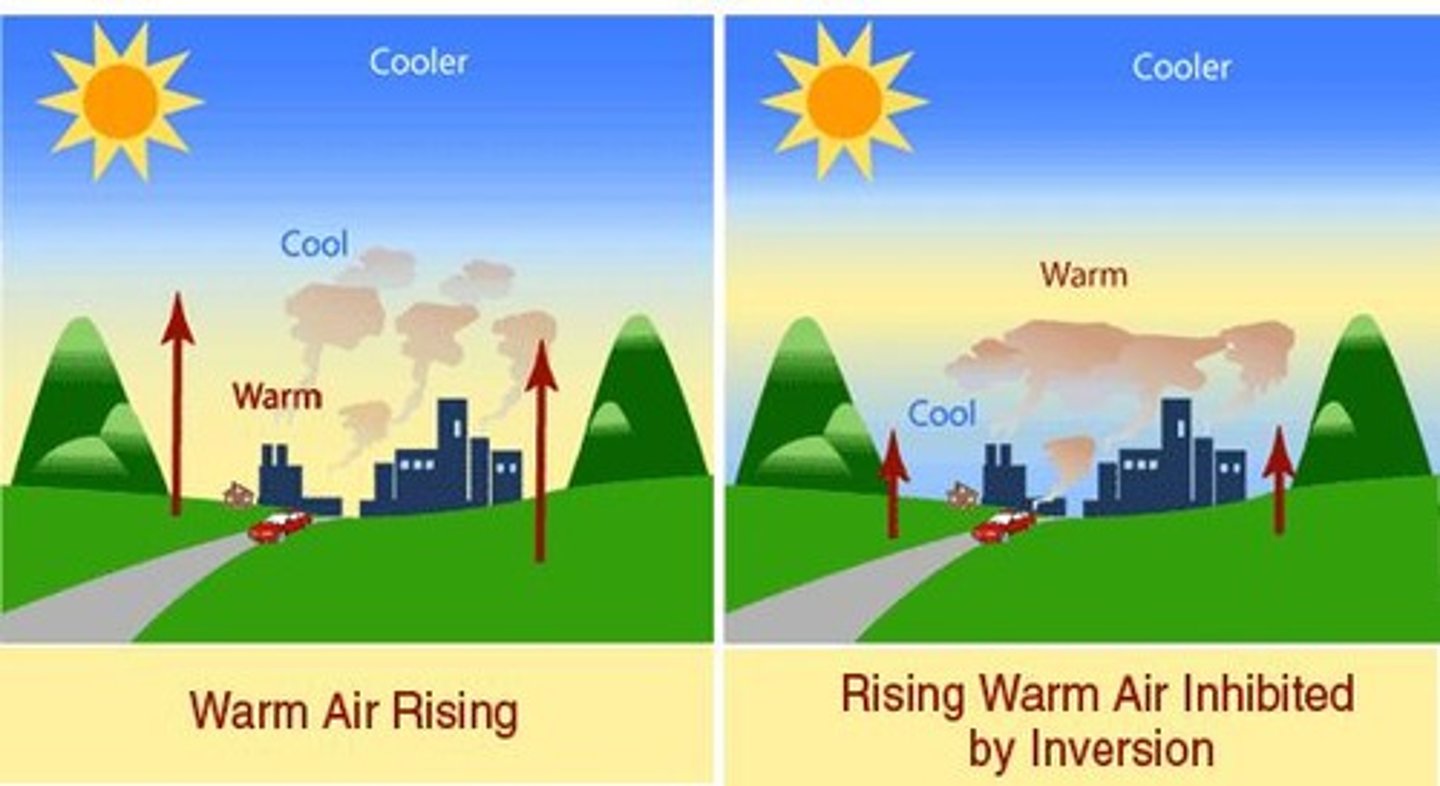
Thermal Inversion
A situation in which a relatively warm layer of air at mid-altitude covers a layer of cold, dense air below (caused naturally - more common in basins and cities surrounded by mountains).
Impacts:
- air pollutants can't be carried away and are trapped at earth's surface
- respiratory irritation
- decreased revenue
- less photosynthesis
Urban Heat Island Effect
The idea that urban areas are hotter than suburban. The heat that cities generate as a result of having many buildings and few trees or other vegetation
Does not have as much evapotranspiration
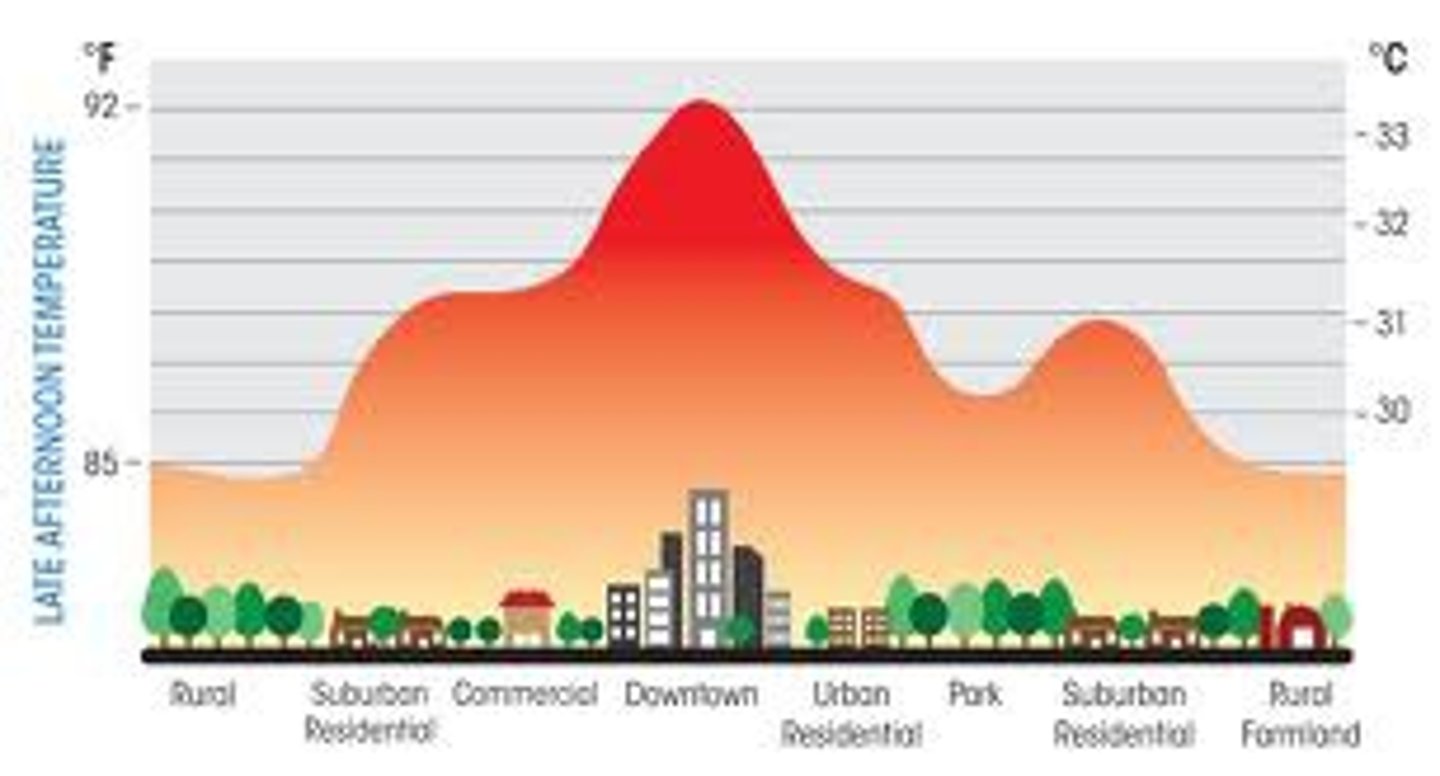
Evapotranspiration
The combined amount of H2O evaporation and transpiration -- carries heat from surface into atmosphere
A cooling process
Natural sources of air pollutants
lightning strikes (NOx), forest fires (PM, CO, NOx), plants (VOCs), volcanoes (SO2, PM, CO, NOx)
natural sources of CO2
respiration, decomposition, and volcanic eruptions
natural sources of PM
Sea salt, pollen, ash from forest fires and volcanoes dust (windborne soil)
PM10
chemical symbol for particular matter smaller than 10 micrometers
dust, pollen, ash, mold
to small to be filtered out when breathing through the nose
causes inflammation
PM2.5
chemical symbol for particulate matter smaller than 2.5 micrometers
travel deep into the lungs
so small
lung cancer and chronic bronchitus
haze
atmospheric moisture or dust or smoke that causes reduced visibility
aerobic decomposition
organic material is broken down and recycled in the presence of air
releases CO2
Anaerobic decomposition
decomposition that occurs without using, or in the absence of, oxygen
produces methane
Acid Deposition
Sulfur oxides and nitrogen oxides, emitted by burning fossil fuels, enter the atmosphere-where they combine with oxygen and water to form sulfuric acid and nitric acid-and return to Earth's surface
can be limited through less NOx and SOx emissions
impacts:
- soil and water acidity
- lowers pH
- Al toxicity
Acid Rain formation
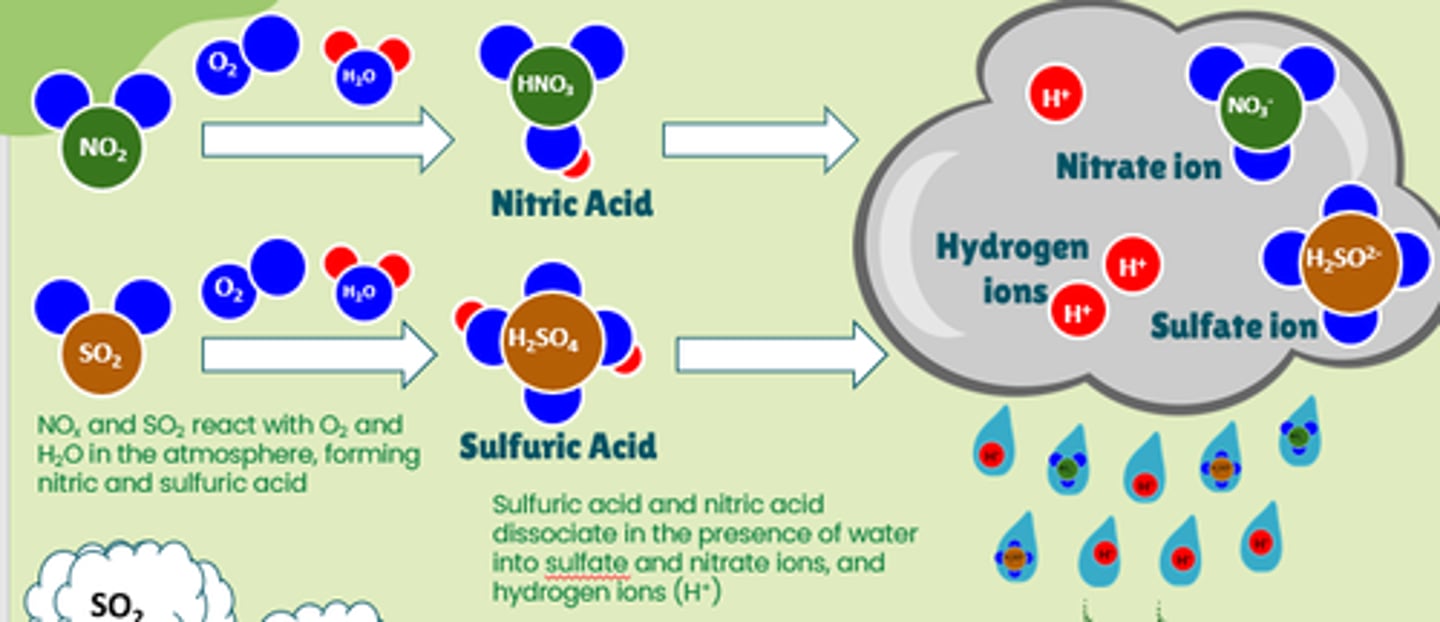
soil and water acidification
H+ ions displace or leech other pos. charged nutrients (Ca2+, K+) from soil. H+ ions also make toxic metals like aluminum and mercury more soluble in soil and water
(slow growth or kill plants and animals)
Acid Rain mitigation
Mitigating ___________
areas with low pH can be neutralized by adding a buffer such as limestone, lime, or calcium carbonate
burning less coal/fossil fuel
Aluminum toxicity
due to acid rain or low pH that causes rapid inhibition of root growth and disruption of root morphology
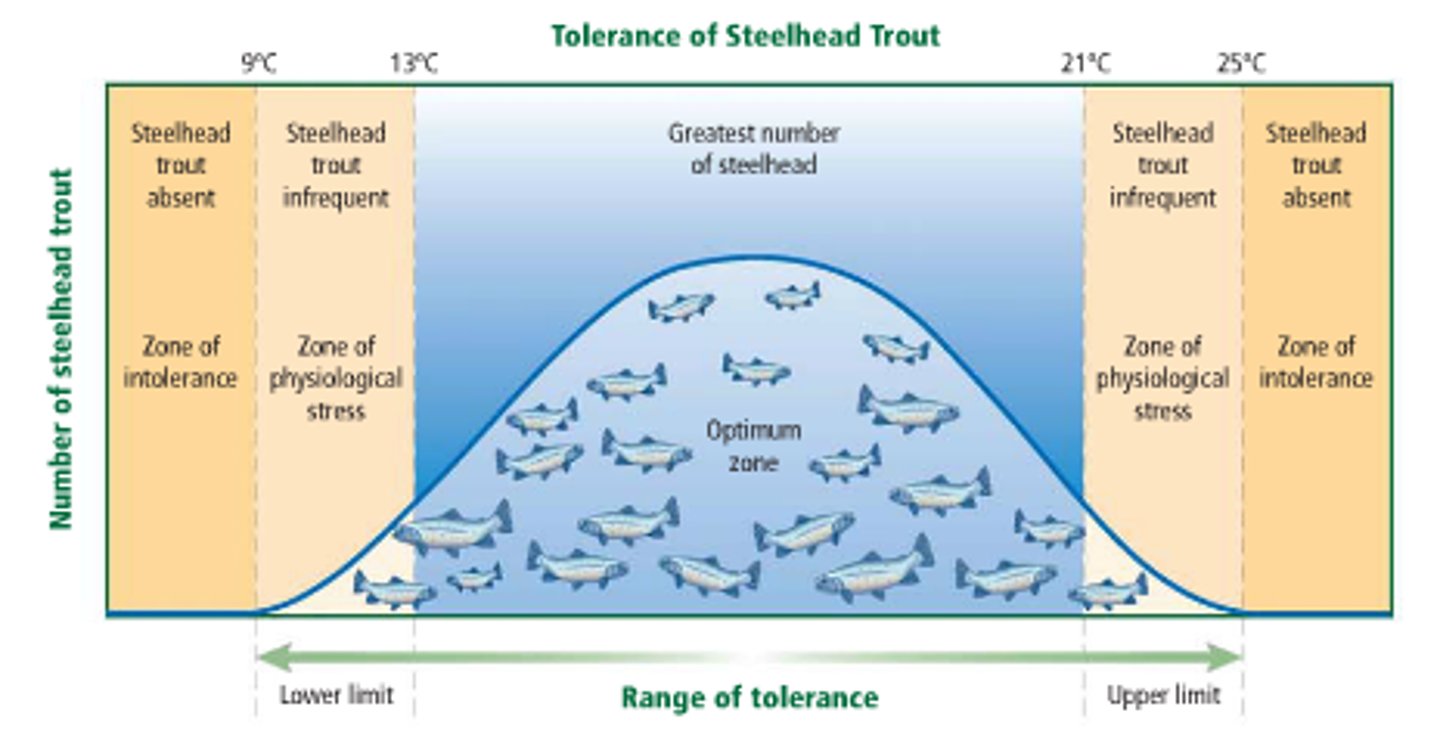
Range of Tolerance
the limits to the abiotic conditions that a species can tolerate
apply to all organisms
Indicator species
Species that serve as early warnings that a community or ecosystem is being degraded or impacted by environmental change.
Overfishing
capturing fish faster than they can reproduce
impacts:
reduced coral health
Bottom trawling
a fishing technique in which the ocean floor is literally scraped by heavy nets that smash everything in their path.
impacts:
- breaking coral
- sediment pick up
Urban Runoff
Surface runoff of rainwater created by urbanization. Hard, non-permeable surfaces, such as concrete and asphalt, replace soil, preventing water from entering aquifers. Rainwater instead flows over the hard surfaces, gathering pollutants and chemicals until it eventually rejoins a water source.
Sediment Pollution
Excessive amounts of soil particles or solid matter that enter the water.
A water pollutant
impacts:
- hurts producers due to limited sunlight and clouding