B1.1 Carbohydrates and lipids
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
Do carbon-carbon bonds stabilize chains?
The more carbon-carbon bonds, the more stable a chain, as the covalent bonds are strong
What structure is glycogen made of
It is made up of glucose rings. Because glucose is a sugar, glycogen is a branched polysaccharide made up of many monosaccharides
3 main polysaccharides
Cellulose, glycogen and starch
What are macromolecules
Large molecules made up of many monomers
How are macromolecules formed
Macromolecules are formed in condensation reactions between monomers, covalently bonded.
What is a condensation reaction?
A polymerisation reaction, which occurs between two or more monomers, where one loses the hydroxyl (-OH) group and the other loses a hydrogen (H) group. These form water
What is the bond between sugar molecules called
glycosidic bond
What is it called when 2 monosaccharides are bonded together
It makes a polysaccharide called a disaccharide
What is it called when 3 monosaccharides bond together
It makes a polysaccharide called a trisaccharide
What are the 4 main macromolecules
Carbohydrates, Lipids, proteins and nucleic acids
How and why does the body break down macromolecules into monomers?
The body does this by hydrolysis (reverse reaction to condensation reaction), needing to break down macromolecules because they are too large to be absorbed. This requires water to do so
what do hydrolysis and condensation reactions do
they are reversible reactions that break down or bond polymers and monomers
what are carbohydrates
they are one of the 4 main macromolecules (they are sugars)
what are monosaccharides
the simplest form of a carbohydrate (a single sugar unit), that cannot be broken down any further by hydrolysis
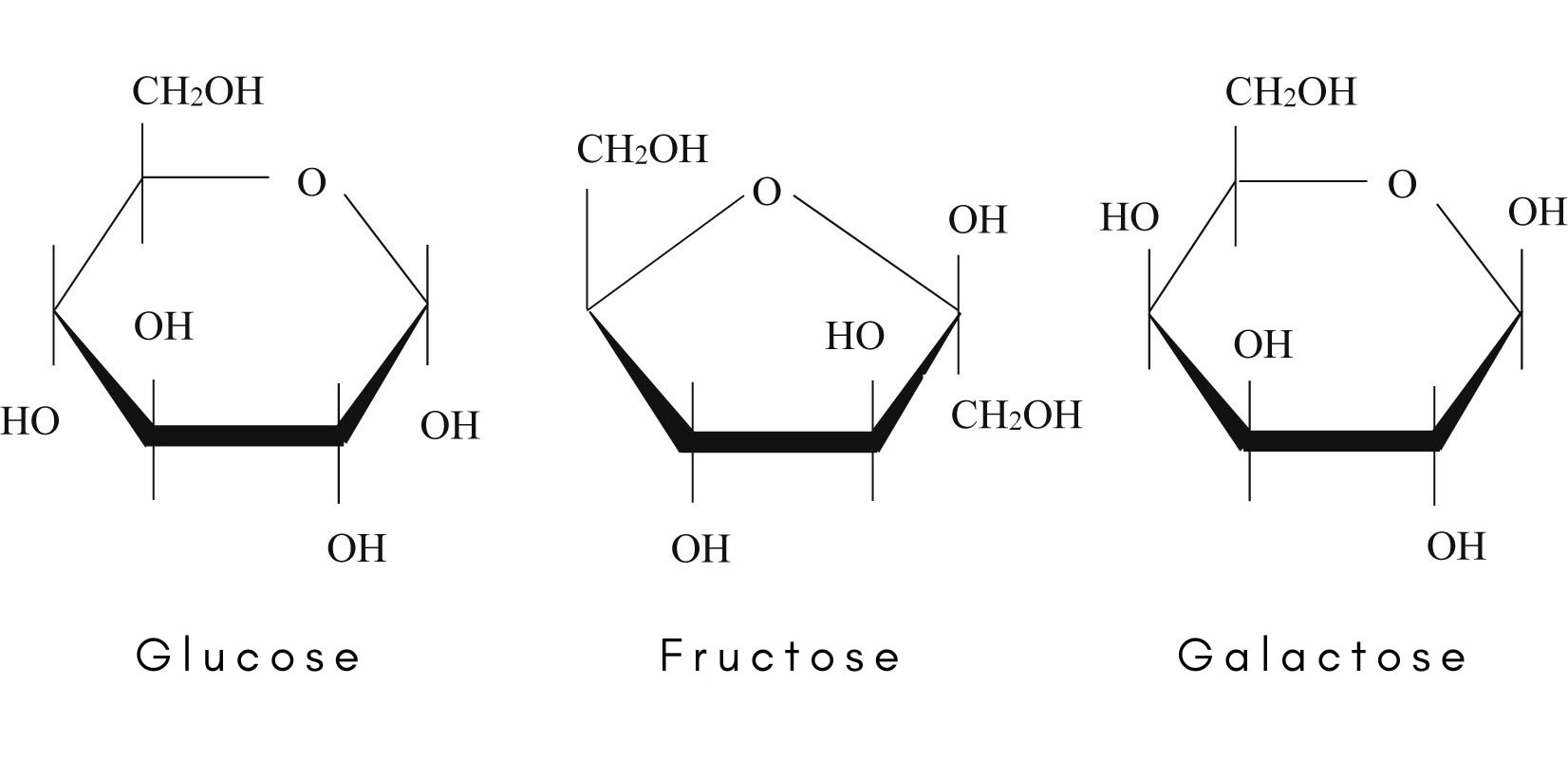
what are the most common monosaccharides
glucose, fructose and galactose - these are hexoses as they have 6 carbon atoms. Glucose is the most common monosaccharide as it is found in nature and used as a source of energy
2 isomers of glucose
Alpha and Beta
they vary in the location of their hydroxyl (-OH) groups
What is alpha glucose?
It is one of the 2 isomers of glucose, where the hydroxyl (-OH) group is oriented downwards

What is beta glucose?
It is one of the 2 isomers of glucose, where the hydroxyl (-OH) group is oriented upwards

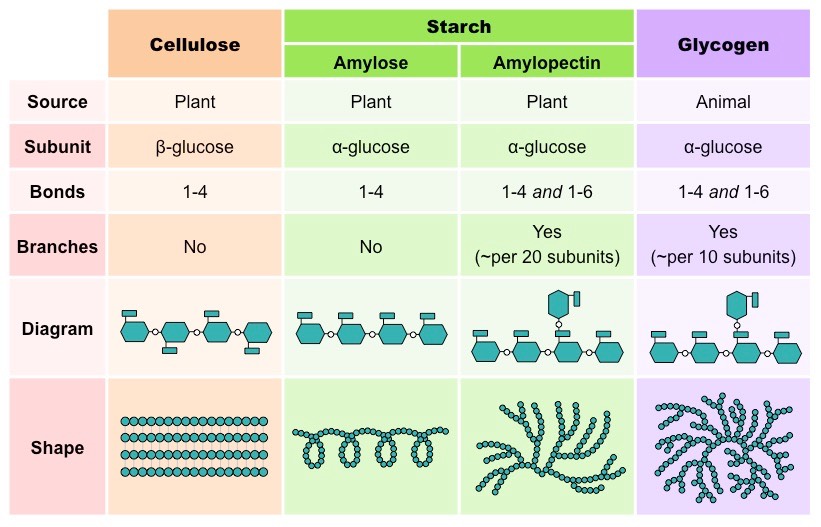
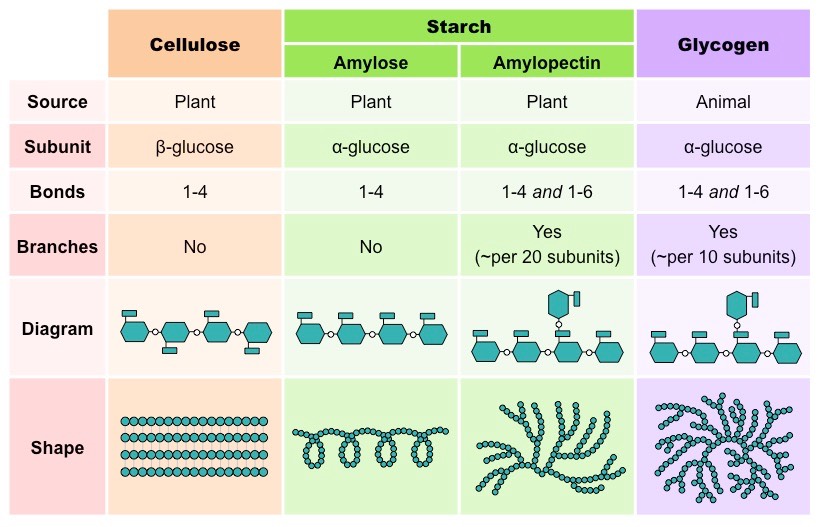
What monosaccharides are cellulose, glycogen and starch made up of?
Cellulose - beta glucose
Glycogen - alpha glucose
Starch - alpha glucose
What are the properties of glucose?
-it has 2 isomers (alpha and beta)
-it is soluble
-it is stable (cyclic ring structure)
-it is a good energy source
why is glucose soluble?
It is polar, so it attracts water molecules, making hydrogen bonds with them
why can glucose easily travel in the blood
Because it is soluble, it can be transported in the blood plasma (made up of 95% water)
Which polysaccharides are used as an energy storage
Glycogen is used as an energy storage in animals and starch is used as an energy storage in plants
(Cellulose is not, as animals don’t have cellulase to break this down)
Why is glycogen used as an energy storage in animals?
Because of its highly branched and compact shape, a large amount of glucose can be stored in small volume. It has a quick energy release due to its rapid breakdown, allowing for quick short-term energy
What are the 2 types of starch
amylose and amylopectin
What is the difference between the polysaccharides of starch: Amylose and Amylopectin
Amylose is a linear chain (1,4 alpha glycosidic bonds) but it is coiled
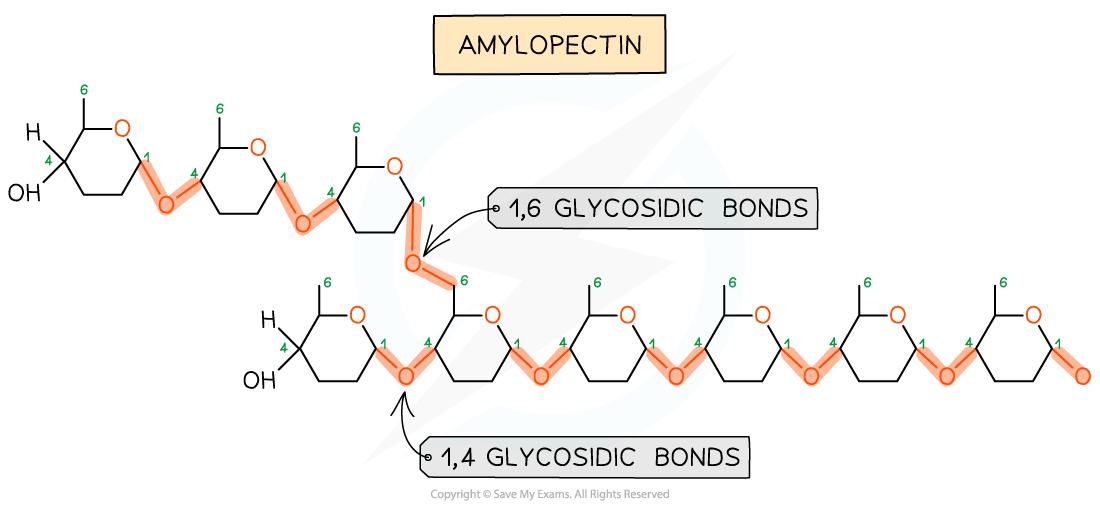
Amylopectin is a branched chain (1,4 and 1,6 alpha glycosidic bonds)
What do 1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds mean?
It shows which of the 6 carbon atoms between two monosaccharides are bonded together. E.g, in the bond “1,4” it is the first carbon atom of one monosaccharide, bonded with the fourth carbon atom of another monosaccharide
Why is it good that starch and glycogen are insoluble?
Then they won’t dissolve in the cell cytoplasm and cause differences in water potential
What are the structures of cellulose, glycogen and starch?
Cellulose → linear
Glycogen → highly branched
Starch → amylose is linear but coiled, amylopectin is branched
What is the structure of cellulose and why?
Cellulose is a linear chain, as unlike starch and glycogen, it is made up of beta-glucose molecules, which alternate in orientation.
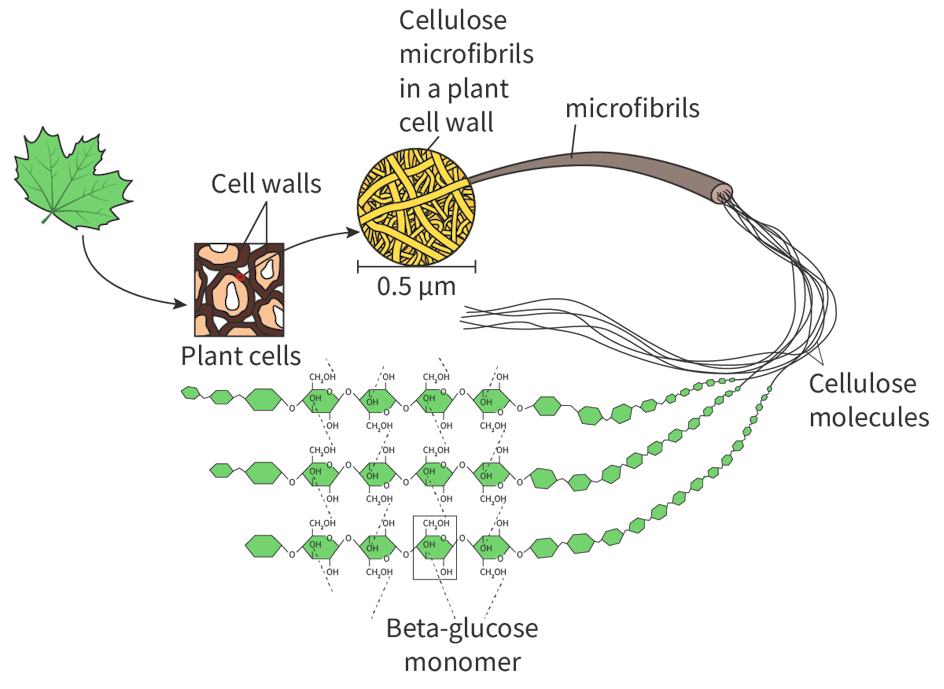
How does cellulose support plant cell walls?
Cellulose linear chains bundle into microfibrils which strengthen cell walls. These help the plant stay rigid and firm, helping it to withstand forces such as osmosis
Summary of everything

What are glycoproteins?
Proteins that have one or more carbohydrates attached to them in branched or linear chains. The short carbohydrate chain can also be called an Ogliosaccharide. These can be made up of any monosaccharides (not only glucose)
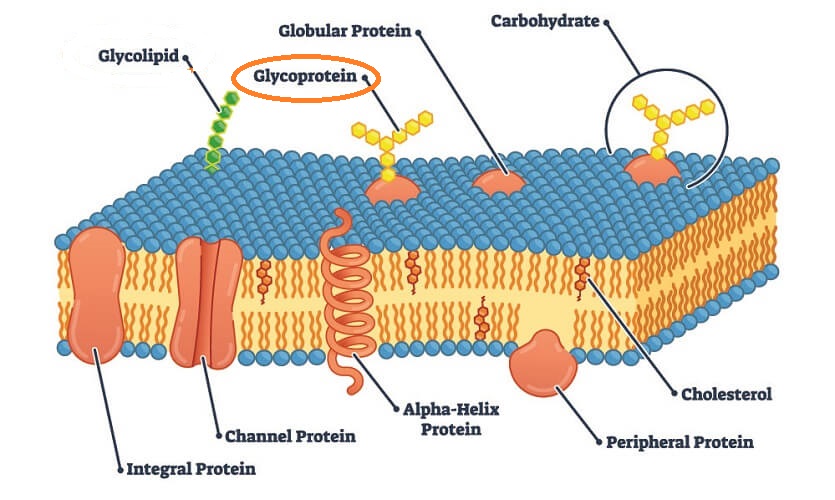
Where are glycoproteins found?
On the cell surface membrane
What do glycoproteins do?
Glycoproteins act as receptors receiving signals from other cells and cell-cell recognition by identifying other cells
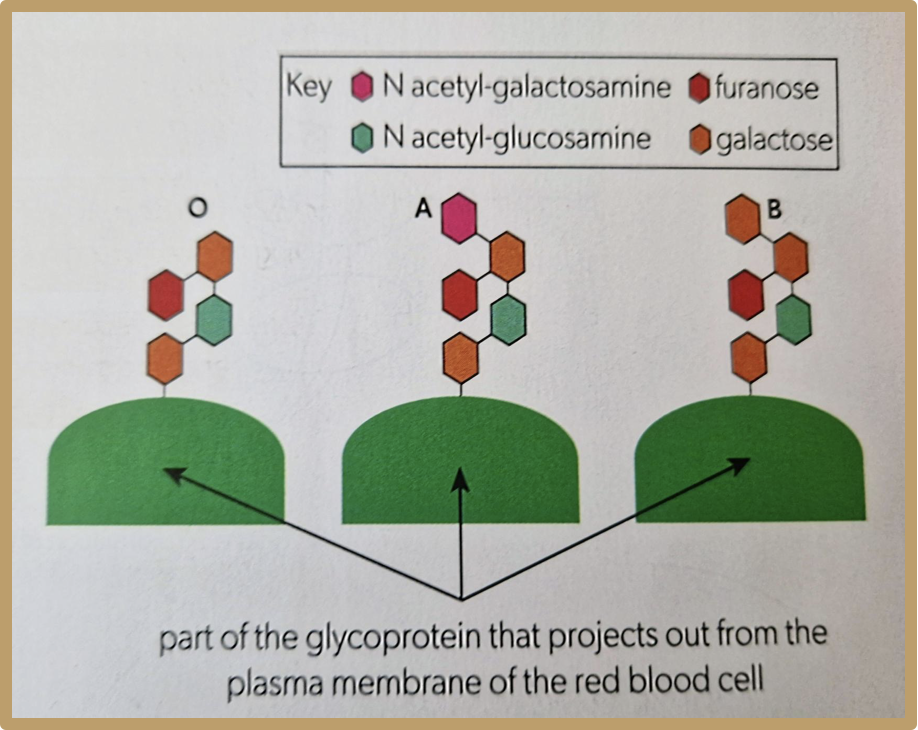
What is the ABO blood group system
Red blood cells also have glycoproteins on their cell surface membrane, which are called A and B antigens. These give individuals their blood group, and one can have both or neither of these as well. Having neither is called group O
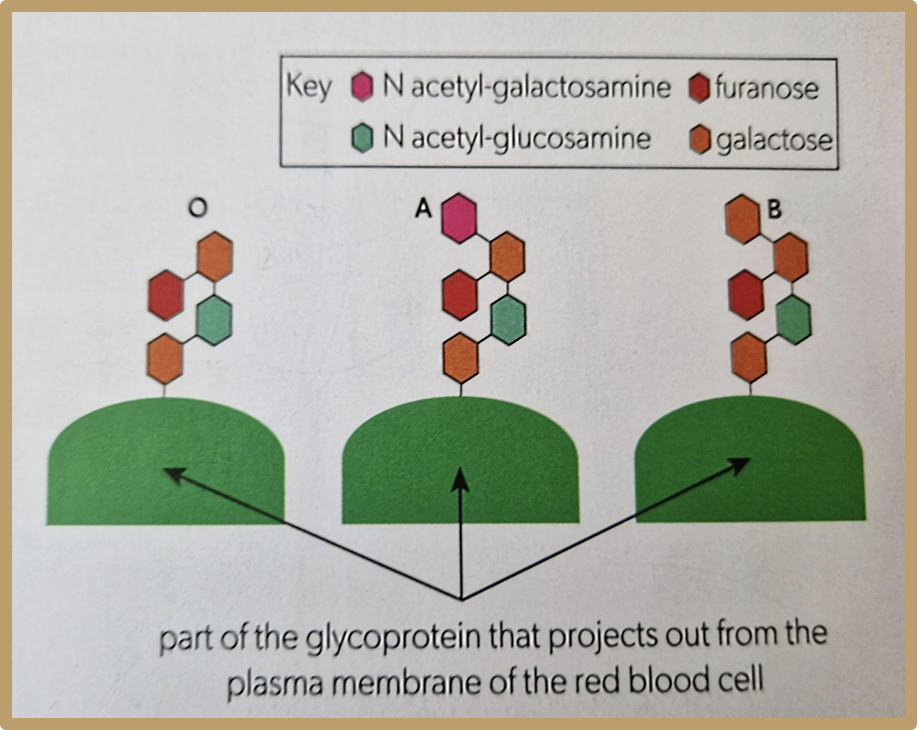
What is the blood group called that doesn’t have A or B antigen in glycoprotein?
Blood group O
Why would blood group A be rejected by blood group B, but blood group O wouldn’t?
Blood group A has a monosaccharide which makes it different to blood group B, so it would be rejected, however blood group O has the same structure, just one less monosaccharide
What are lipids
Lipids are one of the 4 main macromolecules, made up of glycerol and fatty acids. They are non-polar, meaning they are hydrophobic
Why are lipids typically insoluble in water?
Lipids are non-polar, so they repel water. They are hydrophobic.
What solution are lipids soluble in?
Lipids are non-polar, so they are soluble in other non-polar solutions
What is the structure of lipids?
A glycerol covalently bonded with 1-3 fatty acids. These are ester bonds
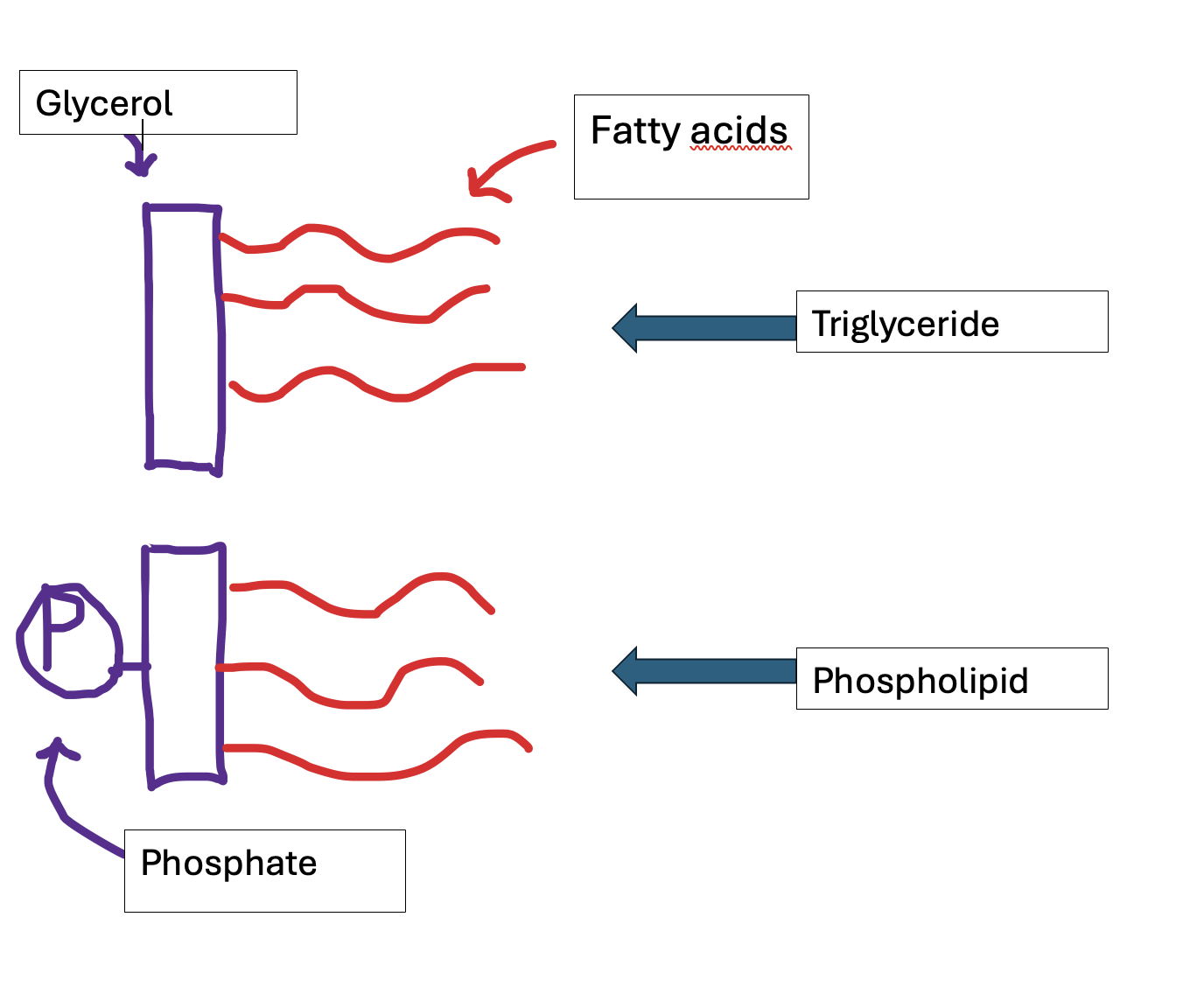
What are the most common lipids?
Steroids, phospholipids, waxes and triglycerides
How are triglycerides formed?
Triglycerides are a common type of lipid, consisting of glycerol covalently bonded by a condensation reaction to 3 fatty acids. This means that each time a fatty acid bonds to the glycerol, a water molecule is formed. These bonds are ester bonds
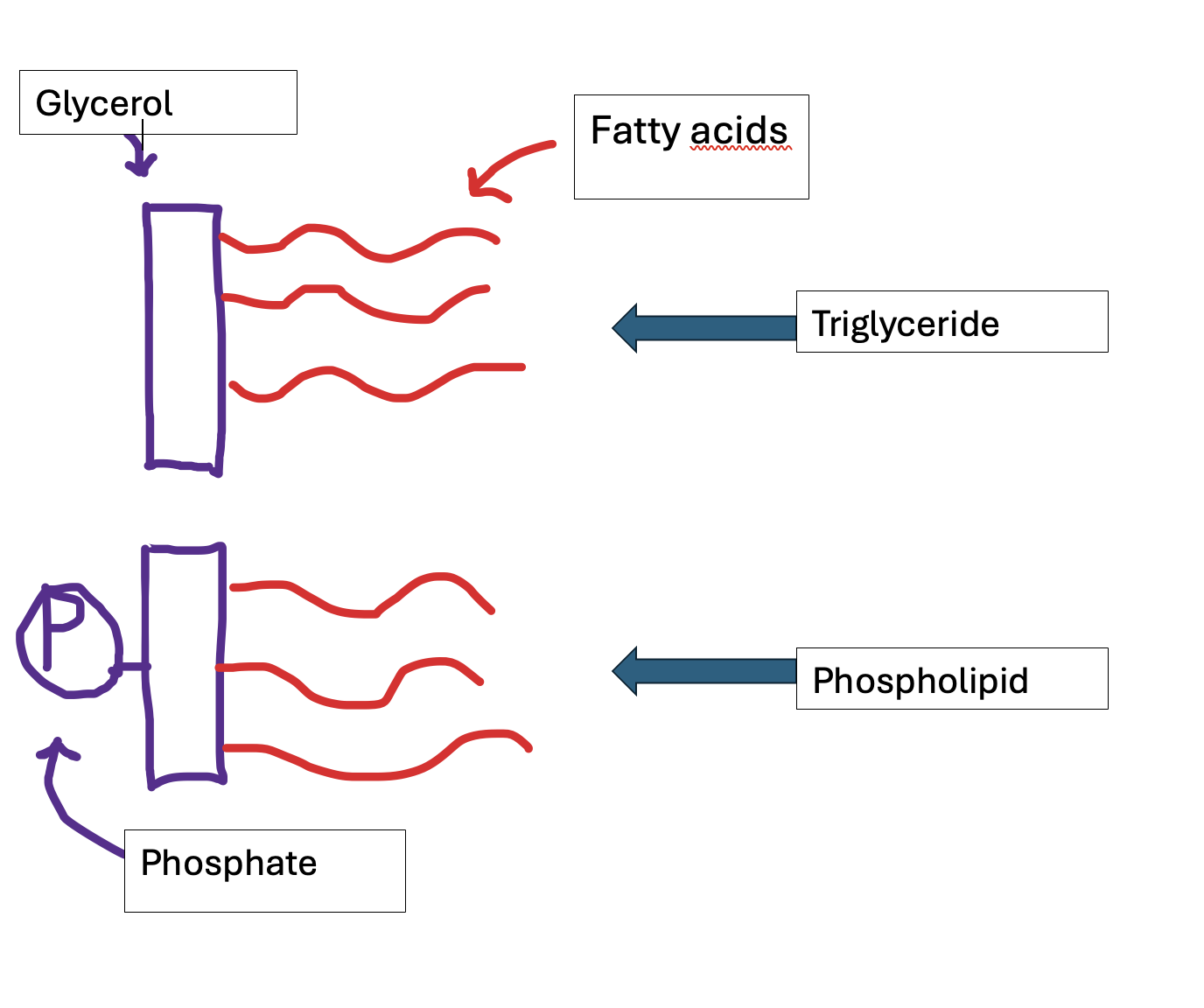
How are phospholipids formed?
Phospholipids are a common type of lipid, consisting of glycerol covalently bonded by a condensation reaction to 2 fatty acids and a phosphate molecule.
What are the classifications of fatty acids
Monounsaturated, saturated and polyunsaturated
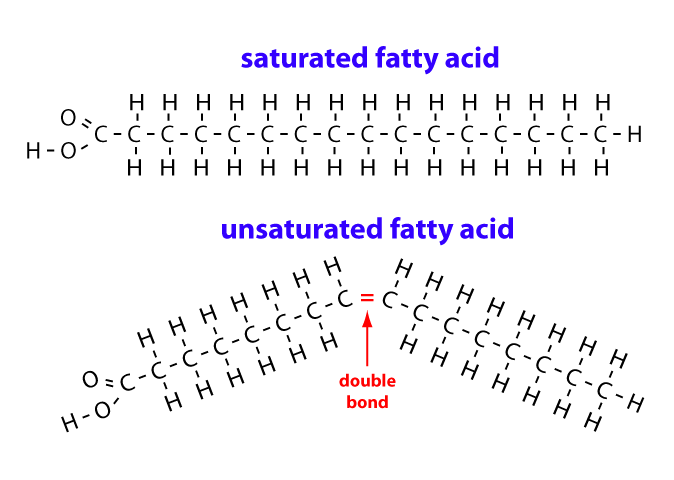
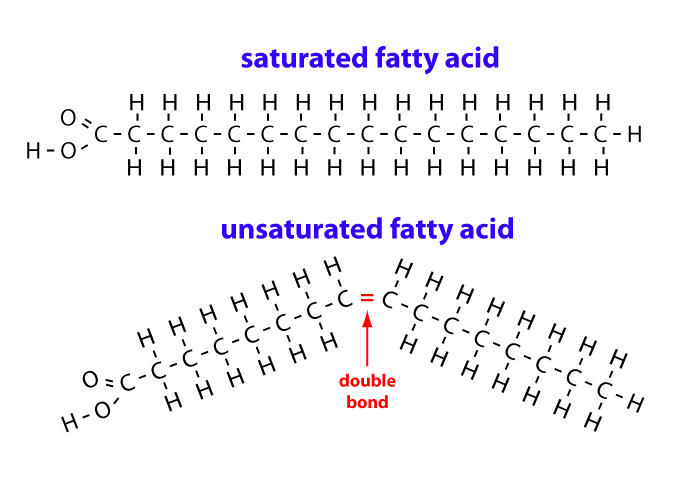
What is a monounsaturated fatty acid
A fatty acid that has one double bond in its hydrocarbon chain, causing a bend. These double bonds can be cis-isomers or trans-isomers
what is a polyunsaturated fatty acid
A fatty acid that has two or more double bonds in its hydrocarbon chain, causing bends in the chain. These double bonds can be cis-isomers or trans-isomers (trans-isomers do not cause a bend in the chain)
what is a saturated fatty acid
A fatty acid that doesn’t have any double bonds in its structure, resulting in a linear hydrocarbon chain. This allows the molecules to be tightly packed together, so it is a solid
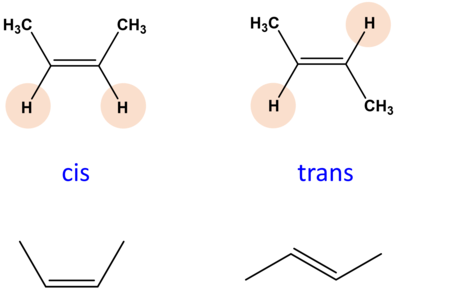
What are cis- and trans- isomers
These are used to describe the hydrogen arrangement around the carbon double bond in a fatty acid.
Cis-isomers →the hydrogen atoms are on the same side, causing a bend in the chain. Fatty acid is then liquid, cannot be tightly packed.
Trans-isomers →the hydrogen atoms are on opposite sides, do not cause bend in chain. Fatty acid is solid as it can be tightly packed
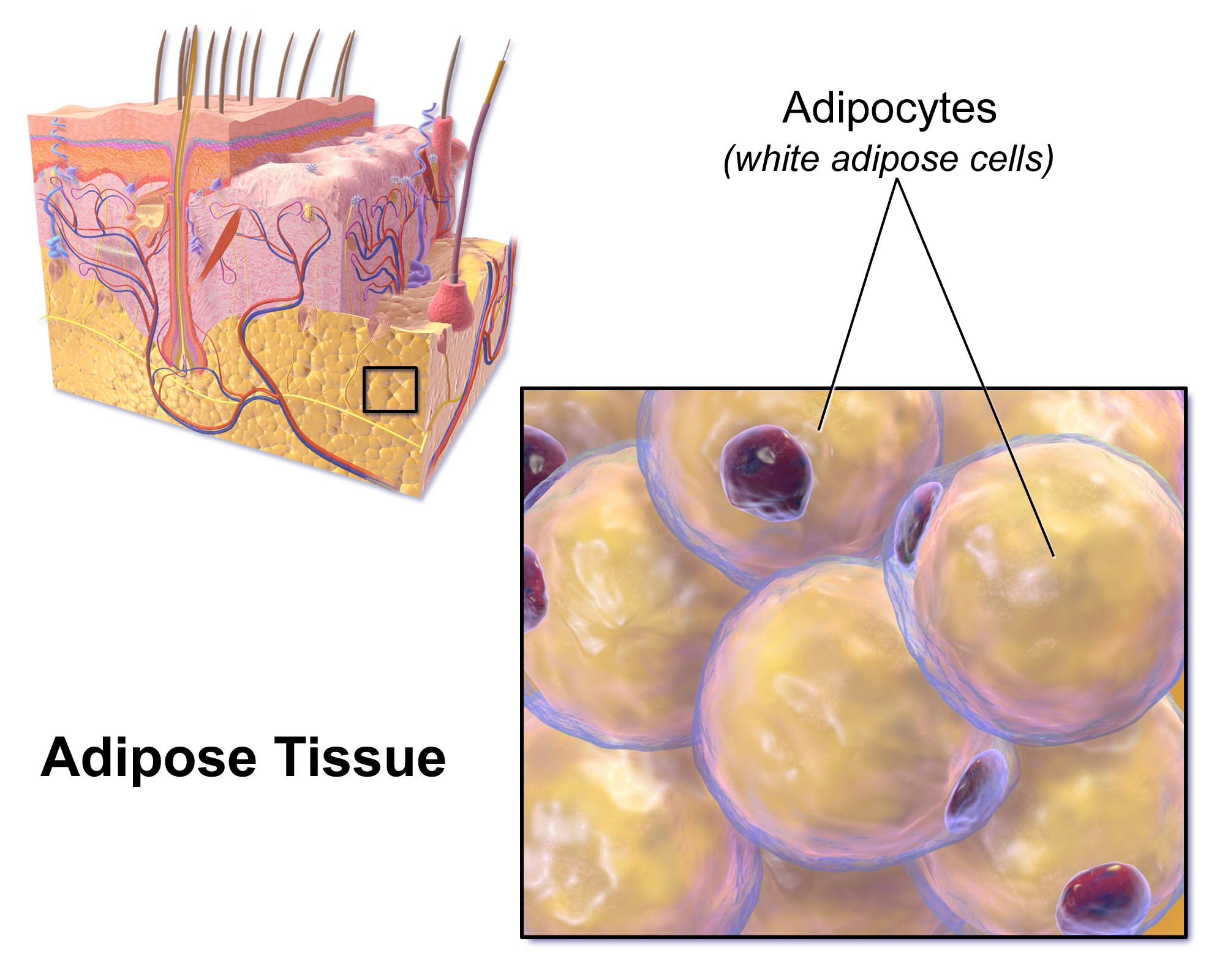
Where are triglycerides stored as energy in animals?
In adipose tissues
What are triglycerides useful for?
As an energy storage in animals, and as a thermal insulator (e.g., stored in blubber in whales, protecting them from cold ocean)
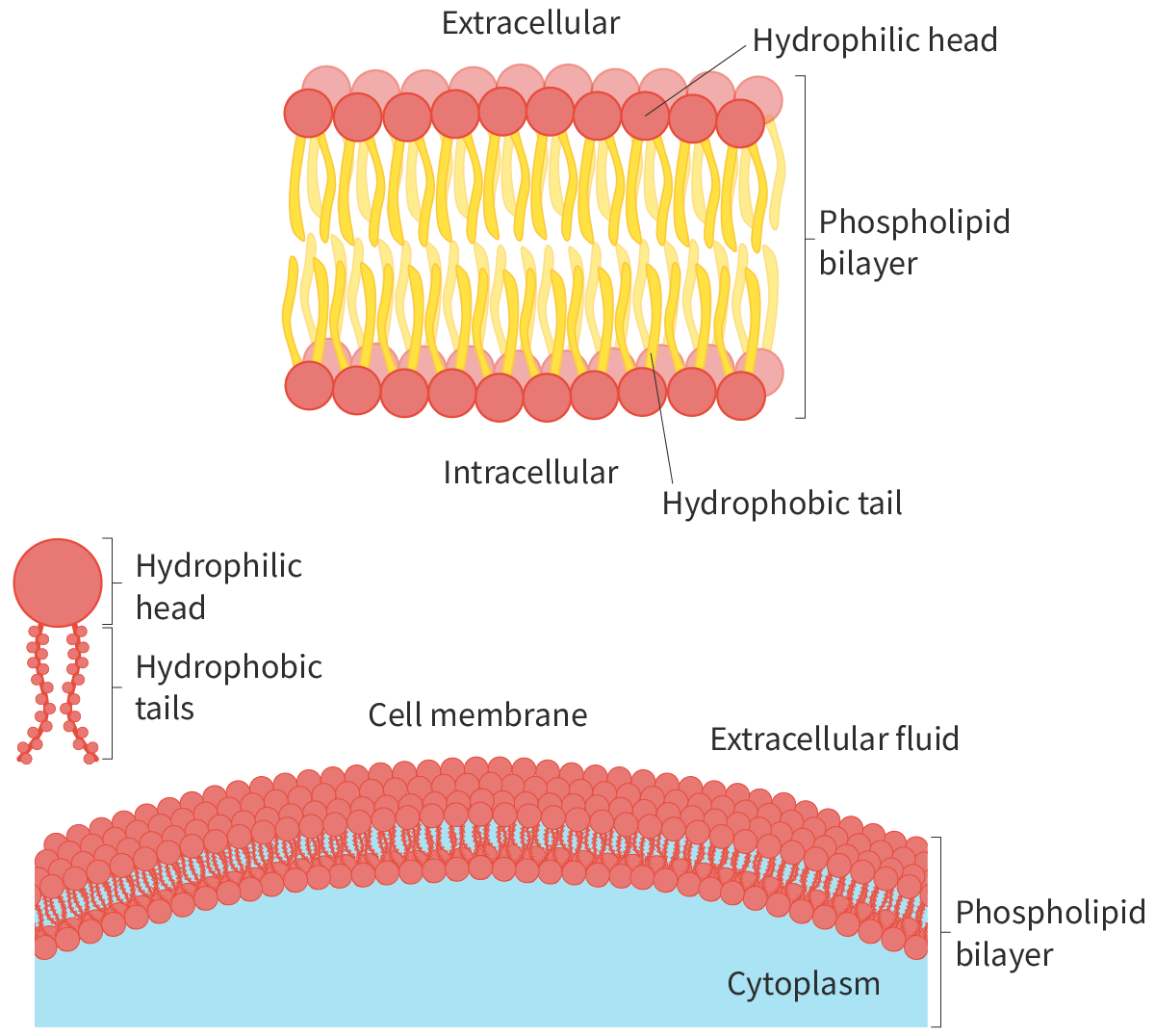
What are cell membranes primary composed of?
A phospholipid bilayer
Is a phospholipid hydrophobic or hydrophillic?
Both. The phosphate and glycerol backbone is hydrophillic (attracted to water) and the fatty acid chain is hydrophobic. This is because the phosphate is polar, and the fatty acid non-polar
How is the phospholipid bilayer in the cell membrane arranged and why?
Because the head is hydrophillic and the tail is hydrophobic, the head faces the aqueous solution, and the tail faces inwards
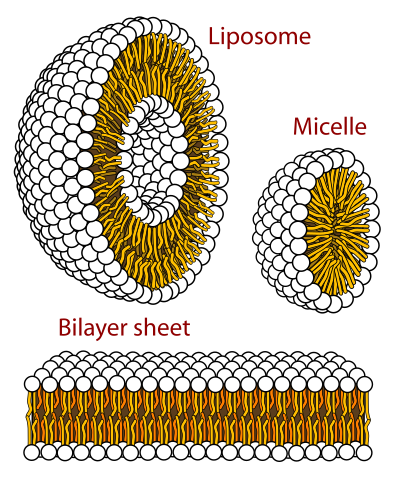
Which ways can phospholipids arrange themselves in an aqueous solution?
Why can steroids pass through the phospholipid bilayer?
Steroids are lipids, and are therefore hydrophobic