3.6.2 Nervous Coordination
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
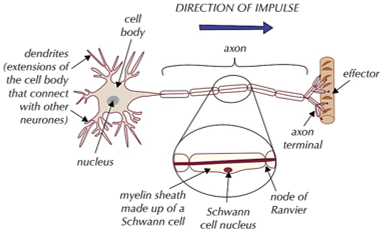
structure of neurone
-dendrons = collect electrical signals/impulses
-cell body = contains organelles + lots of rER
-axon = passes electrical impulses from cell body to dendrites of other cell
-axon terminals = forms synapse with other neurone
resting potential
potential difference across membrane of neurone when not stimulated
-around -70mV
how resting potential is established
-membrane is more permeable to K+ ions more than Na+ ions due to more potassium channels so K+ ions can diffuse out of cell
-however in sodium-potassium pump, 3 Na+ ions pumped out while 2 K+ ions pumped in through active transport
-also few Na+ ions move in through channels by facilitated diffusion
-so establishes electrochemical gradient as there is a higher concentration of K+ ions inside and higher concentration of Na+ ions outside
threshold potential
-triggers action potential → increases membrane potential
-need to have enough Na+ ions inside cells to have positive potential
action potential
-is positive potential
-around +40mV
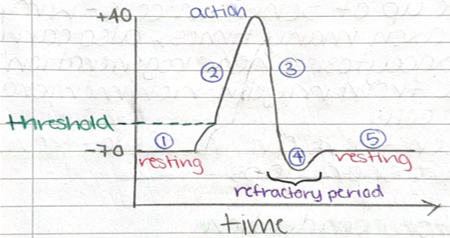
stages in generating action potential
1) stimulus + 2) depolarisation
-causes sodium channels to open so membrane becomes more permeable to Na+ so they move in more so potential becomes more positive
-if membrane reaches threshold, the voltage-gated Na+ channels open so more Na+ ions move in
stages in generating action potential 3) repolarisation
voltage-gated Na+ channels close and voltage-gated K+ channels open so K+ ions diffuse out down gradient so potential becomes more negative
stages in generating action potential
4) hyperpolarisation + 5) resting potential returned
-lots of K+ ions moving through channels quickly causing an ‘overshoot’ so potential becomes more negative than resting potential
-ions channels reset and conc gradients maintained through active transport of sodium out
refractory period + importance of it
the ion channels are recovering and cannot be forced open - no stimulus is large enough to reach action potential
-ensures unidirectional action potential
-ensures discrete impulses
-limits frequency of impulse transmission
‘all-or-nothing’ principle
any stimulus that causes the membrane to reach threshold potential will generate an action potential
-all action potentials have the same magnitude → but a larger stimulus reaches threshold more quickly so greater frequency of impulses
FACTORS that affect speed of conductance -myelination
myelin sheath = electrical insulator, made from myelin-rich membranes
-made of Schwann cells = wrap around axon, carry out phagocytosis + nerve regeneration
-between each, there are nodes of Ranvier which are short gaps
saltatory conduction
-in myelinated neurones = does happen, impulse jumps from node to node so does not travel the whole axon length - depolarisation only occurs at nodes
-in non-myelinated neurones = does not happen, impulse travels as a wave of depolarisation along whole length of membrane
FACTORS that affect speed of conductance -axon diameter
greater diameter = faster
-less resistance to flow of ions = allows local currents to flow faster along axon, quicker depolarisation
-less ‘leakage’ of ions = maintains membrane potential
FACTORS that affect speed of conductance -temperature
higher temperature = faster
-faster rate of diffusion of ions
-faster rate of respiration = more ATP for active transport for pump
-temp too high = denatured membrane proteins
structure of synapse
-presynaptic neurone → postsynaptic neurone
cholinergic synapses STAGES 1) arrival of action potential
-action potential arrives at synaptic knob
-this stimulates voltage-gated Ca2+ channels to open in presynaptic neurone
-Ca2+ ions diffuse into synaptic knob
cholinergic synapses STAGES 2) fusion of vesicles
-influx of Ca2+ ions causes synaptic vesicles to fuse with presynaptic membrane
-causes the release of the neurotransmitter ACh into synaptic cleft by exocytosis
cholinergic synapses STAGES 3) diffusion of ACh
-ACh diffuses across synaptic cleft and binds to receptors on post synaptic membrane
-this causes ligand-gated Na+ channels to open leading to depolarisation of membrane
-this increases potential so will eventually meet threshold + generate action potential
-then ACh is hydrolysed by the enzyme acetylcholinerase (AChE) + is reabsorbed into presynaptic neurone so ligand-gated Na+ channel closes
-Ca2+ also released by ER
why is the process unidirectional?
only the presynaptic neurone contains synaptic vesicles + only the postsynaptic neurone has complementary receptors
different neurotransmitters
-excitatory = depolarise the membrane so will generate potential
-inhibitory = hyperpolarise the membrane by opening Cl- channels so Cl- ions move in and K+ ions move out by facilitated diffusion
spatial summation
multiple neurones release enough neurotransmitters together at the same time onto the same postsynaptic neurone so trigger action potential
temporal summation
multiple impulses arrive in quick succession from one presynaptic neurone so lots of transmitters released will trigger action potential
neuromuscular junction
-specialised cholinergic synapse between motor neurone and muscle cell
-also used ACh which binds to nicotinic receptors
-differences between = always excitatory, postsynaptic membrane has more receptors, end of neural pathway
effects of drugs on synapses -increase synaptic transmission
-have same shape as neurotransmitters so mimic action at receptors
-inhibit AChE so more neurotransmitters in synaptic cleft left to bind
-stimulate release of neurotransmitters
effects of drugs on synapses -decrease synaptic transmission
-block receptors
-inhibit release of neurotransmitters
-hyperpolarise presynaptic membrane