Hematology and Endocrinology
1/276
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
277 Terms
List ddx for macrocytic, normochromic, non-regenerative anemia:
breed-related: mini and toy poodles
dysplasia or leukemia (+/- FeLV)
folate (+/- B12) deficiency
PK deficiency hemolysis
List ddx for normocytic, normochromic, non-regenerative anemia:
extramedullary dz
endocrinopathy (eg. hypoadrenocorticism, hypothyroidism)
inflam. dz
CKD = ↓ EPO
aplasia (eg. estrogen)
neoplasia (eg. acute leukemia, primary myelodysplasia)
ineffective hematopoiesis (eg. IM, histiocytic sarcoma, drugs, infxn, eg. Ehrlichia canis)
pure red cell aplasia
List ddx for microcytic, normochromic/hypochromic. non-regenerative anemia:
breed-associated: Shar-Pei, Japanese breeds, Siberian Husky
Fe deficiency
PSVA - fxnal Fe deficiency
Medullary causes of non-regenerative anemia:
primary medullary (eg. aplastic anemia, myelodysplastic syndromes)
infxs
dugs
toxins
neoplasia
congenital
immune
Extramedullary causes of non-regenerative anemia:
renal
endocrine
Addison’s
hypothyroidism
GI (cobalamin deficiency)
hepatic
pancreatitis
neoplasia
Fe deficiency
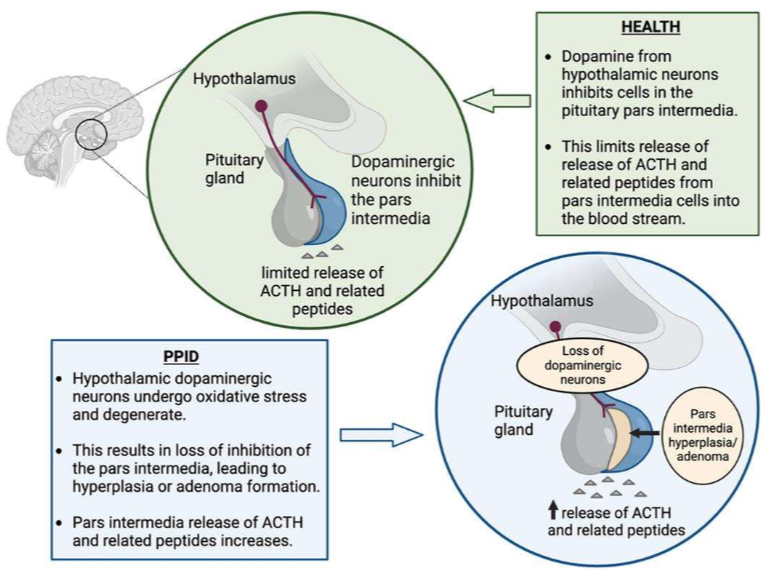
Pathophysiology of PPID:
oxidative stress dopaminergic neurons
pars intermedia hyperplasia and adenoma
loss of inhibition
↑ POMC, ACTH, glucocorticoids
Pathophysiology of EMS:
genetic predisposition
easy keepers, breed
excessive carbs
grain, grass
inadequate exercise
↓
insulin dyregulation
hyperinsulinemia-associated laminitis (HAL)
Clinical signs of PPID:
hypertrichosis
loss of muscle mass
abnormal sweating
lethargy & poor performance
chronic laminitis
secondary infxns
PUPD
hyperlipidemia
Clinical signs of EMS:
obesity or regional adiposity
INSULIN DYSREGULATION (ID)
HAL
chronic low-grade inflammation
Lab findings of PPID:
↑ glucose
↑ insulin
↑ triglycerides
↑ Phos
stress leukogram
↑ neutrophils
↓ lymphocytes
Lab findings of EMS:
↑ or normal glucose
↑ or normal insulin
↑ triglycerides
↓ adiponectin
Diagnostic tests for EMS:
insulin conc.
glucose conc.
adiponectin conc. (↓)
oral sugar test (OST)
Diagnostic tests for PPID:
baseline ACTH conc.
TRH stim. (NOT licenses by FDA in horses)
insulin conc.
α-MSH (research only)
dexamethasone suppression test NOT recommended
Treatment for PPID:
medications FOR LIFE
pergolide - dopamine agonist
cyproheptadine - serotonin antagonist
trilostane - 3β-HSD inhibitor
Treatment and management for EMS:
diet
limit carbs and fat
avoid grass
mineral supplements
weight loss
exercise
medications
levothyroxine - thyroid supplement
SGLT2 inhibitors
Why are so many horses incorrectly diagnosed and treated for hypothyroidism?
rely solely on tT3 and tT4
if both low:
seek plausible explanation
check fT4 conc.
perform TRH stim.
Signs of regenerative anemia in horses:
NO reticulocytes
↑ MCV
anisocytosis
↑ RDW
hx of blood loss
hyperplasia on BM aspirate
Signs of regenerative anemia in ruminants and camelids:
reticulocytes
↑ MCV
cows:
basophilic stippling
Understand why the PCV and TP does not drop immediately in cases of acute hemorrhage (<2-6 hours)
RBC and plasma lost in equal proportions
fluids need to re-equilibrate before ↓ PCV and TP detectable
Major LA disorders under regenerative anemia due to RBC loss:
loss
external
GI parasites (Haemonchus, coccidia)
ulcerative dz
internal
thorax, peritoneum
Major categories of LA disorders under regenerative anemia due to RBC lysis:
infectious
immune-mediated
toxic
Major LA infectious disorders under regenerative anemia due to RBC lysis:
parasites
cows:
babesiosis
Eperythroon wenyonii
bacterial
cows:
anaplasmosis
leptospirosis
alpacas:
Mycoplasma haemolamae
viral
horses:
EIA
Major LA immune-mediated disorders under regenerative anemia due to RBC lysis:
immune-mediated
secondary to drugs, toxins, infxns, etc.
horses:
autoimmune
IMHA
viral (EIA)
bacterial (Clostridia)
neoplastic (lymphoma, lymphosarcoma)
drug (penicillin, phenylbutazone)
foal neonatal isoerythrolysis
Major LA toxic disorders under regenerative anemia due to RBC lysis:
Heinz body anemia (oxidative damage, IV + EV hemolysis)
onion, rape, kale
equine: red maple leaves
ovine: copper toxicity
bovine: selenium deficiency, post-parturient hemoglobinuria
Major LA disorders under non-regenerative anemia:
anemia of chronic disease
BM suppression
lymphoma
other aplastic anemia
chemotherapy drugs
toxicity
EPO deficiency
recombinant human EPO administration
CKD
nutritional deficiency
Ddx of hypoglycemia due to decreased intake:
juvenile hypoglycemia
starvation
Ddx of hypoglycemia due to excess insulin activity:
beta cell neoplasia
insulin overdose
xylitol toxicity
extrapancreatic neoplasia
Ddx of hypoglycemia due to decreased glucose production:
juvenile hypoglycemia
severe hepatic dysfunction
extrapancreatic neoplasia
hypoadrenocorticism
Ddx of hypoglycemia due to increased utilization:
sepsis
hunting dog hypoglycemia
polycythemia vera or massive leukocytosis
treatments for PDH:
surgical
bilateral adrenalectomy
hypophysectomy
medical
mitotane
trilostane
radiotherapy
Signs of hypocortisolemia:
hyporexia
weakmess
lethargy
vomiting
diarrhea
Clinical signs associated with thrombocytopenia (<250,000 platelets/uL):
petechiae/ecchymoses
bleeding tendencies
Clinical signs associated with vasculitis:
warm and painful edema
dependent; limbs and ventral abdomen
Clinical signs associated with coagulation disorders:
epistaxis
hyphema
melena
prolonged bleeding from venipuncture
List the 4 classifications of thrombocytopenia:
regenerative
non-regenerative
undetermined
pseudothrombocytopenia
List diagnostic tests for thrombocytopenia:
CBC
orange thiazole staining (research only)
platelet surface associated antibody test (flow cytometry)
BM biopsy
List mechanisms of regenerative thrombocytopenia and give examples:
increased destruction
immune-mediated (primary, secondary)
increased consumption
DIC, hemorrhage
sequestration
in the spleen
List mechanisms of non-regenerative thrombocytopenia and give examples:
decreased production
BM disease
aplastic anemia
myeloproliferative disease
neoplasia
drug or toxin → myelosuppression
List drugs or toxins that cause myelosuppression and thrombocytopenia:
bracken fern
furazolidone
mycotoxins
List mechanisms of undetermined thrombocytopenia and give examples:
viral infections
EIA
BVDV type II
EVA
bacterial infections
sepsis
Anaplasma phagocytophilum
neoplasia
Define pseudothrombocytopenia:
artificial platelet activation and agglutination outside of the body
LA diseases with clinical signs of vasculitis + petechiae/ecchymosis WITH thrombocytopenia:
Anaplasma phagocytophilum
endotoxemia?
Potomac Horse Fever
LA diseases with clinical signs of vasculitis + petechiae/ecchymosis WITHOUT thrombocytopenia:
EVA
purpura hemorrhagica
Anaplasma phagocytophilum clinical signs:
vasculitis + petechia/ecchymosis
thrombocytopenia
Anaplasma phagocytophilum dx:
morula in neutrophils
serology +/- PCR
Anaplasma phagocytophilum tx:
oxytetracycline
Anaplasma phagocytophilum prevention:
tick control
no vaccine
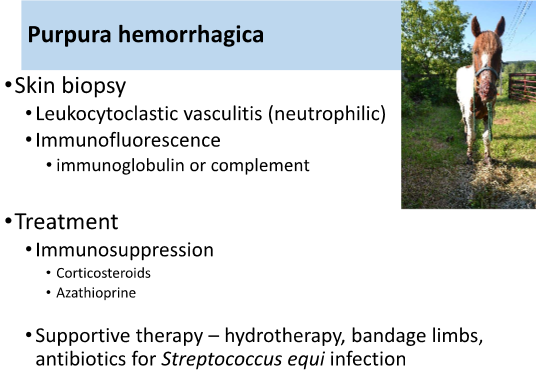
Purpura hemorrhagica (associated with Strangles infection) clinical signs:
vasculitis + petechia/ecchymosis
Purpura hemorrhagica (associated with Strangles infection) dx:
skin biopsy
neutrophilia
IF staining
Purpura hemorrhagica (associated with Strangles infection) treatment:
immunosuppression
corticosteroids
azathioprine
supportive therapy
Equine viral arteritis (EVA) clinical signs:
vasculitis + petechia/ecchymosis
leukopenia
fever, depression, anorexia
abortion
rhinorrhea, epiphora, conjunctivitis, hives
Equine viral arteritis (EVA) diagnosis:
PCR, VI, serology
post-mortem
Equine viral arteritis (EVA) treatment:
supportive care
Equine viral arteritis (EVA) prevention:
vaccination
castrate males, no breeding
DIC occurs in horses secondary to:
sepsis
acute GIT disease
endotoxin
DIC treatment in horses:
treat underlying disease
treat endotoxemia
flunixin meglumine
polymyxin B (nephrotoxic)
pentoxifylline
replace clotting factors and anti-thrombin III by administering fresh frozen plasma
if blood loss, use whole blood
heparin therapy (controversial)
Functions of cortisol:
maintains arterial tone via alpha adrenergic receptors
maintains normal GI mucosal integrity and function
stimulates gluconeogenesis and glycogenesis
mobilizes protein and fat from tissues
many more!
Functions of aldosterone:
save sodium
pee potassium
pee H+
Protracted hyperglycemia from DM due to:
loss or dysfunction of insulin secretion by pancreatic beta cells
diminished insulin sensitivity (i.e. insulin resistance)
both
Insulin suspensions vs. solutions

IMHA signalment:
dogs
young to middle-aged adults (2-8 years)
female > male
cats
wide age range (1-10 years)
female = male
often with concurrent disease
List life stages involved in IMHA, regenerative or non-regenerative, and if hemolysis is observed:
regenerative
mature RBCs
IV or EV hemolysis
non-regenerative
precursor
NO hemolysis
mixed
+/- hemolysis
IMHA clinical signs:
rapid onset (1-3d hx)
anemia + systemic inflammation
pallor
lethargy, weakness
fever
GI upset (anorexia, vomiting)
hepatomegaly
peripheral lymphadenopathy
+/- (hemolysis rate-dependent)
icterus
dark urine (bilirubinuria)
dark orange feces (bilirubin pigment)
hemoglobinuria/hemoglobinemia (rare)
complications
PTE
Benefits of basal insulins:
mimic basal phase of endogenous insulin secretion
formulated as solutions so do not require resuspension
less within- and between-day variability in absorption
lower potency and longer duration
can be given once daily in many dogs
do not need to be administered around meals
available as pen
easier for owners to administer
IMHA dx:
blood smear and CBC
severe ↓ PCV/HCT
spherocytes
ghost cells
polychromasia/reticulocytes
+/- nRBCs
agglutination
neutrophilia w/ L shift
agglutination tests
gross autoagglutination
microscopic autoagglutination
direct agglutination test (DAT) / Coomb’s test
chem + UA
imaging
US
AXR
infectious disease testing
BM aspirate for non-regen.
Describe non-associative IMHA:
previously called primary IMHA
idiopathic
immune-mediated destruction of RBCs without identifiable cause
Describe associative IMHA:
previously called secondary IMHA
presumptive underlying cause/trigger ID’d
drugs (penicillin’s, cephalosporins, sulfa drugs)
vaccines
infectious (Rickettsia, Babesia, FeLV, fungal)
neoplasia
drugs or vaccines may be associated if given ~4 weeks prior
Acute stabilization in IMHA tx:
blood transfusion
indicated for life-threatening anemia or rapid declining PCV
avoid transfusion to “normal” PCV
goal is clinical improvement and stabilization
Immunosuppressive therapy in IMHA tx:
glucocorticoids (taper after PCV stabilizes)
prednisone/prednisolone
dexamethasone
Adjunctive therapy in IMHA tx:
secondary immunomodulatory drugs
azathioprine
mycophenolate (pIMHA)
cyclosporine (pIMHA)
uncommon rescue therapies
hIVIG
splenectomy
plasmapheresis
rescue drugs
antithrombotic therapy
clopidogrel
rivaroxaban
LMW heparin
Monitoring plan for IMHA tx:
PCV
blood smear
agglutination
Coomb’s
Give examples of physiologic thrombocytopenia:
CKCS
thrombocytopenia w/ macroplatelets
normal plateletcrit/mass
no clinical problems
greyhound
borderline low
normal coags
Mechanisms of IMTP:
Ab against hapten-platelet membrane complex
specific anti-platelet Ab
passive absorption of preformed Ag-Ab on platelet
Etiologies of thrombocytopenia:
decreased production
BM disease
destruction (IMTP)
sequestration
spleen
consumption/loss
bleeding
DIC
physiologic
Signalment of IMTP in dogs and cats:
dogs
adult, ~6 yo
females > males
cocker, sheepdog, poodle, German shepherd
cats
less common
often associated with FeLV or myeloproliferative diseases
Diagnostic plan for patients with thrombocytopenia:
CBC
often <10,000 platelets/uL, typically <30,000
secondary anemia
platelet morphology:
large platelets
fragmented platelets: ITP = ↓MPV
Coomb’s test
if anemic and IMHA suspect
coagulation testing
infectious disease testing
FeLV/FIV, rickettsial diseases, fungal infections
List advanced diagnostics to dx ITP:
BM aspirate
megakaryocyte hyperplasia if ITP
flow cytometry
anti-platelet Ab’s (IgG)
Acute management of ITP:
whole blood transfusions
crystalloid therapy
platelet products
PRP
platelet concentrate
Immunosuppressive and adjunctive therapies for IMTP:
immunosuppressive
glucocorticoids
adjunctive
enteric protection
omeprazole or famotidine
sucralfate
secondary immunomodulatory drug
mycophenolate
azathioprine
vincristine or hIVIG break up megakaryocytes
splenectomy
Hyperthyroidism pathophysiology:
normal thyroid (with few thyrocytes predestined for growth)
thyroid hyperplasia (susceptible thymocytes proliferating)
thyroid adenoma (hyperplastic nodules coalescing into adenomas)
Methimazole side effects:
vomiting
anorexia
lethargy
hepatotoxicity (icterus)
facial swelling/excoriations
thrombocytopenia
neutropenia
decompensation of azotemic CKD
Functions of thyroid hormone:
increase basal metabolic rate
stimulate lipolysis
stimulate gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis
increase protein and enzyme synthesis
increase # and affinity of beta-adrenergic receptors
marked chronotropic and inotropic effects on heart
fetal development
stimulate erythropoiesis and bone turnover
Primary hypothyroidism thyroid panel results:
tT4: ↓
fT4: ↓
TSH: ↑
thyroglobulin autoAb’s: +/-
Secondary hypothyroidism thyroid panel results:
tT4: ↓
fT4: ↓
TSH: ↓
thyroglobulin autoAb’s: -
Non-thyroidal illness (NTI) thyroid panel results:
tT4: ↓
fT4: normal (unless SEVERE NTI)
TSH: normal
thyroglobulin autoAb’s: -
thyroglobulin autoAb’s thyroid panel results:
tT4: ↑ (falsely)
fT4: ↓
TSH: ↑
thyroglobulin autoAb’s: +
DKA clinical signs:
anorexia, lethargy
vomiting, decreased appetite
hx of PUPD, weight loss, other signs associated with DM
DKA PE findings:
dehydration
hypovolemia
tachycardia
poor PQ, pale MM, increased CRT
mental dullness
ketone breath
signs of chronicity
poor BCS
unkempt haircoat
Glucocorticoid MOA:
inhibit phospholipase A2 (PLA2) to:
inhibit production of pro-inflammatory mediators
↓ leukotrienes, prostanoids
Azathioprine MOA:
inhibit GPAT
interferes with de novo purine synthesis
Mycophenolate MOA:
inhibit IMPDH
interferes with de novo purine synthesis
Leflunomide MOA:
inhibit DHODH
interferes with de novo pyrimidine synthesis
Cyclosporine MOA:
inhibits calcineurin
inhibits NF-AT activation
regulates gene transcription of IL-2
prevents T-cell proliferation
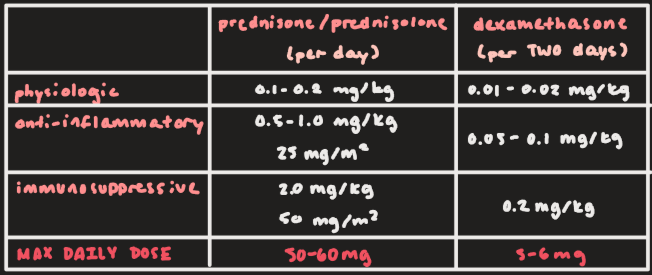
Prednisone/prednisolone and dexamethasone dose range for physiologic effect:
Prednisone/prednisolone: 0.1-0.2 mg/kg
Dexamethasone: 0.01-0.02 mg/kg
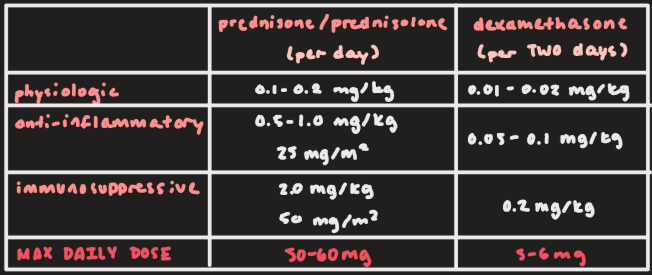
Prednisone/prednisolone and dexamethasone dose range for anti-inflammatory effect:
Prednisone/prednisolone: 0.5-1.0 mg/kg or 25 mg/m2
Dexamethasone: 0.05-0.1 mg/kg
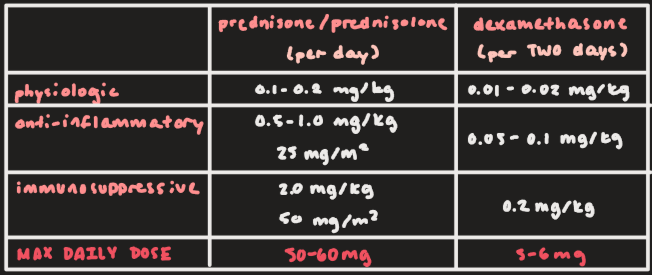
Prednisone/prednisolone and dexamethasone dose range for immunosuppressive effect:
Prednisone/prednisolone: 2.0 mg/kg or 50 mg/m2
Dexamethasone: 0.2 mg/kg
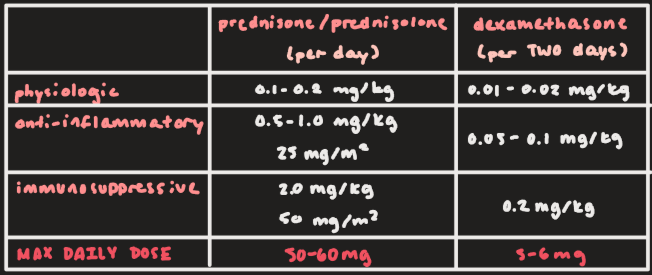
Max daily dose for prednisone/prednisolone and dexamethasone:
Prednisone/prednisolone: 50-60 mg
Dexamethasone: 5-6 mg
Azathioprine should NOT be given to:
Giant Schnauzers
cats
What drug class that includes azathioprine, mycophenolate, and leflunomide should NOT be given to cats? What drug IS okay to give to cats and small dogs for immunomodulation?
cell cycle inhibitors (CCIs), cyclosporine
List second drugs for IMHA in (large) dogs or secondary immunosuppresive drugs:
azathioprine
mycophenolate
leflunomide
cyclosporine (modified if using as secondary immunosuppressive)