Antivirals and viruses pharmacology
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
What is a virus?
Sub microscopic entity consisting of a single nucleic acid surrounded by a protein coat and capable of replication only within living cells
What can viruses infect?
Bacteria, fungi, Protozoa, plants or animals
What type of parasite are viruses commonly referred as?
Obligate intracellular parasite
What do viruses consist of?
DNA or RNA genome
Protein coat/capsid made of protein subunits - capsomers
Envelope derived from plasma-membrane of host but not always present
Surface proteins/glycoproteins that bind to receptors of host cells
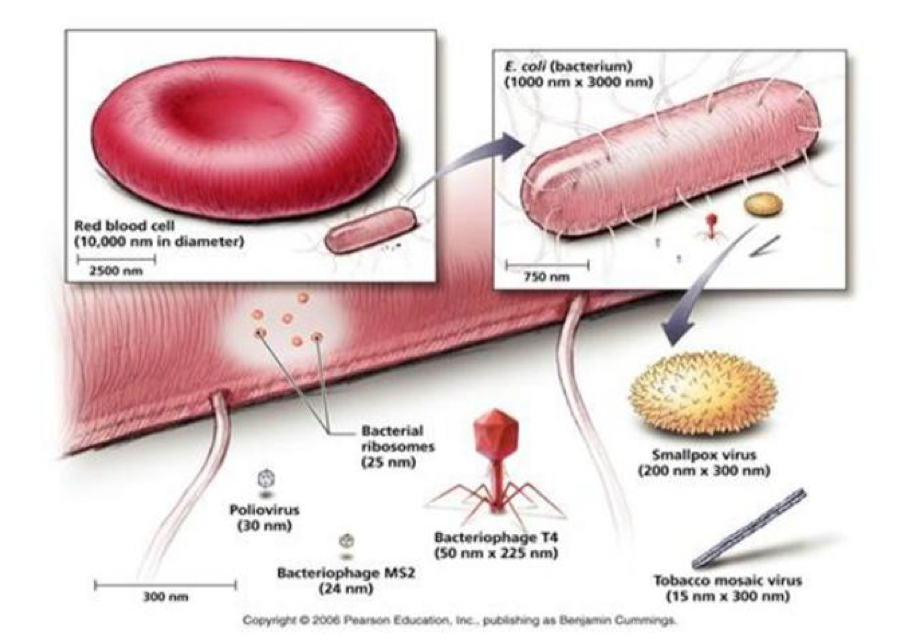
What is a diagram comparing sizes of cells, bacterial, viral and eukaryotes?
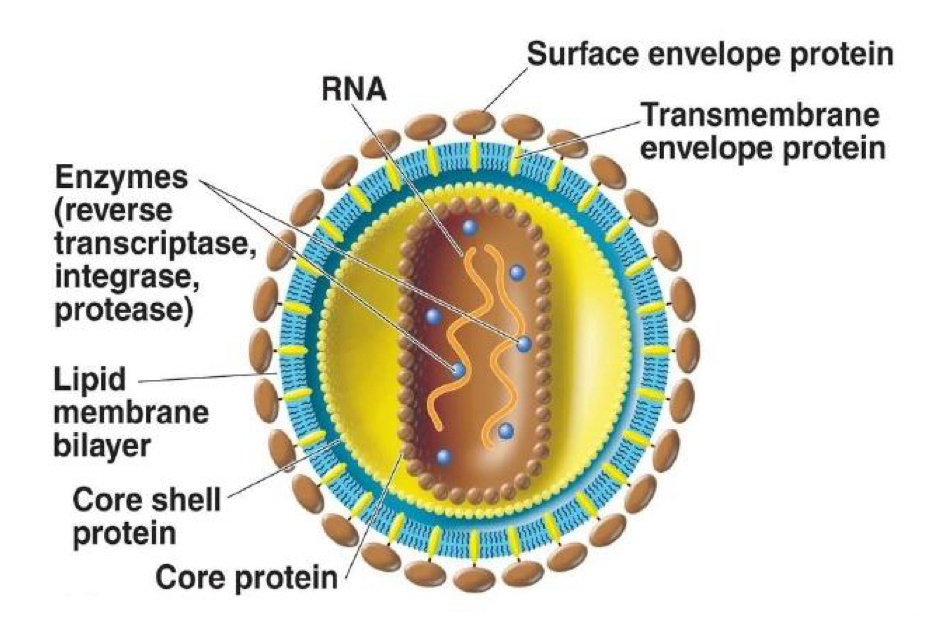
What is a diagram showing virion structure?
What are the main way viruses are classified? (DO NOT LEARN THE TABLE)
DNA based or RNA based, or RNA to DNA viruses

What are DNA based viruses split into?
ssDNA and dsDNA
What are RNA viruses split into?
ssRNA and dsRNA
What are RNA to DNA viruses classified into?
ssRNA - retroviruses - and dsDNA - hepadnaviruses (single stranded RNA and double stranded DNA)
What is a diagram showing how different DNA, RNA and RNA to DNA viruses act on mRNA?

How does dsDNA viruses work to become MRNA?
Transcribed into mRNA+ sense
How is ssRNA + viruses made into mRNA +sense?
Can be used directly
How can ssRNA- viruses be made into mRNA?
Transcription of - strand
How can dsRNA viruses be made into mRNA+ strand?
Transcription of - strand as if it is DNA
How is ssRNA + retrovirus made into mRNA+?
Reverse transcription into dsDNA intermediate which is then transcribed by the host cell
How is ssDNA virus made into mRNA+ strand?
Synthesis of other strand into dsDNA intermediate, then transcribed into mRNA + sense
What are some examples of DNA viruses?
Herpesviruses family e.g., Herpes simples virus 1 and 2 and Varicella zoster, hepatitisviruses like hepatitis B
What are some examples of RNA viruses?
Myxoviruses - influenza, rhabdoviruses - rabies, filoviruses - Ebola
How many nucleotides do small viruses hold?
Max 5000 - not enough for all capsids if made
What proteins must viruses use in order to made capsids?
Many copies of 1 or a few proteins so leads to high symmetry
Why is the use of many copies of 1 or a few proteins advantageous?
Simpler proteins and self assembly can happen
What is the viral geometry based around?
Single helical axis
What does the helix axis of viruses allow?
Flexibility and evolved alongside other helical structures e.g., DNA
What property does all helical viruses have?
All enveloped unlike phage and plant viruses
How are most helixes formed in viruses?
Single major protein arranged with constant relationship to each other
What symmetry is found in viruses?
Icosahedral symmetry
What are the 3 types of cubic symmetry that is very energetically favourable?
Tetrahedral - 12 identical subunits (2:3)
Octahedral - 24 identical subunits (4:3:2)
Icosahedral - 60 identical subunits (5:3:2)
What type of symmetry will only lead to isometric particles?
Cubic symmetry
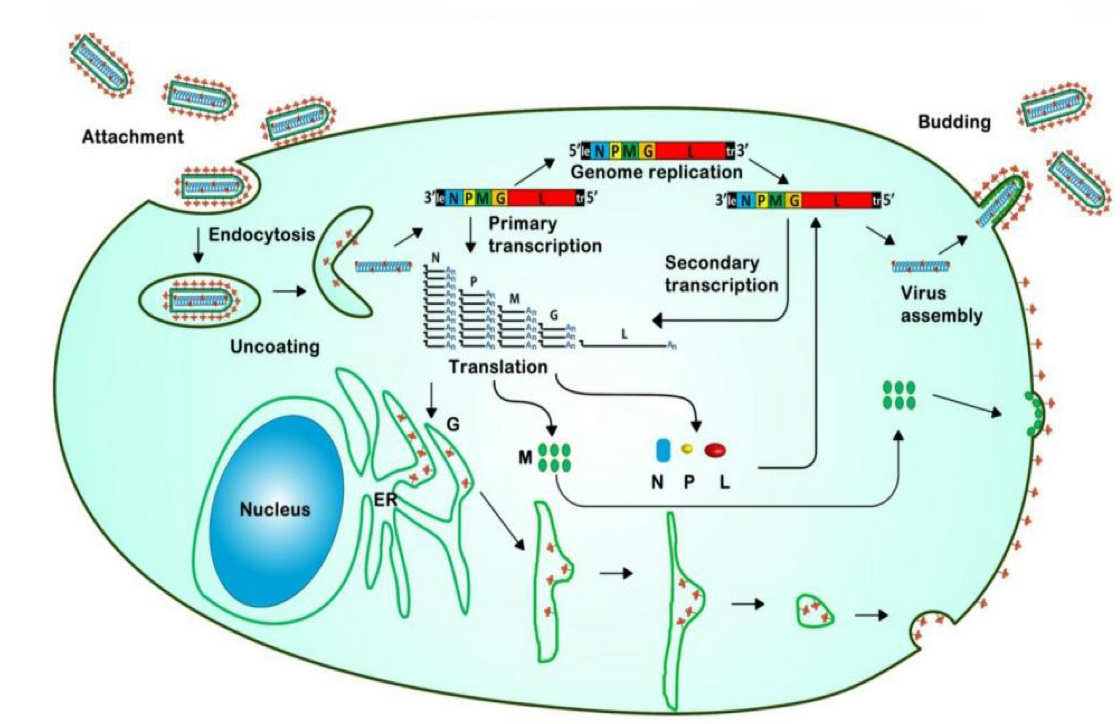
What diagram shows the lifecycle of a virus in an animal cell?
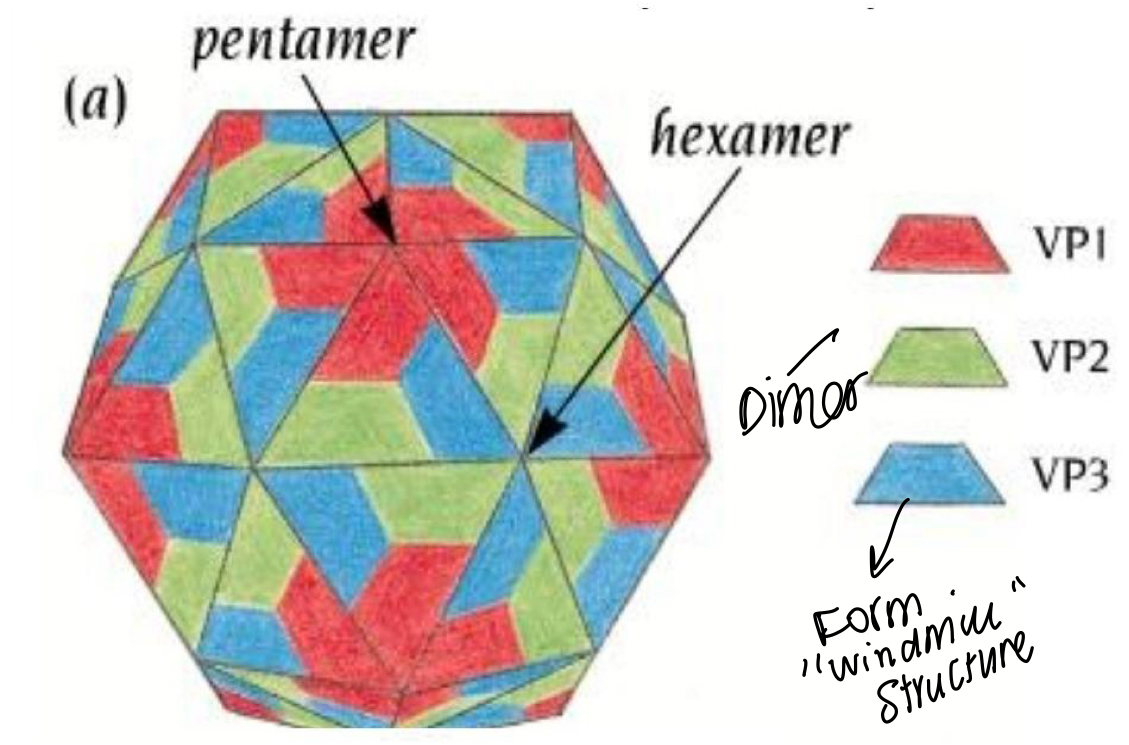
What diagram shows the structure of a viral protein?
Energetically stable, has pentamer structure, dimer in green and blue forms a windmill like structure
What do non-enveloped viruses do?
Lyse cells
What viruses are included in herpes viruses?
Herpes simplex viruses, varicella zoster, shingles, cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr virus
What conditions are caused by herpes simplex virus?
Genital herpes, cold sores
How is HSV transmitted?
Cutaneous
What are the symptoms of HSV?
Cutaneous - localised e.g., oral, genital. CNS effects
Where is the latency site for HSV and VSV?
Neurons
How are HSV and VSV diagnosed?
Clinical, PCR, culture/DFA
What is the antiviral of choice in HSV and VSV?
Aciclovir
Is there a vaccine for HSV, cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr virus?
No
How is VSV transmitted?
Respiratory
What are the symptoms of VSV?
Cutaneous - disseminated and localised
Is there a vaccine for VSV/shingles?
Yes
How is cytomegalovirus transmitted?
Secretions - oral, urogenital
What are the symptoms of cytomegalovirus?
Systemic, ocular, GI, haematopoietic, respiratory
What is the latency site for cytomegalovirus?
Monocytes, macrophages
How is cytomegalovirus diagnosed?
Serology, PCR, culture/DFA
What is the antiviral of choice in cytomegalovirus?
Ganciclovir
How is Epstein-Barr virus transmitted?
Oral secretions
What are the clinical syndromes of Epstein-Barr virus/glandular fever?
Systemic lymphoma
Where is the latency site for EBV?
B cells
How is EBV diagnosed?
Serology, PCR, Culture/DFA
What is the antiviral of choice for EBV?
None
What are the main properties of herpes viruses?
Large, enveloped virus, double-stranded DNA genome of 100-150 proteins, family is herpesviridae
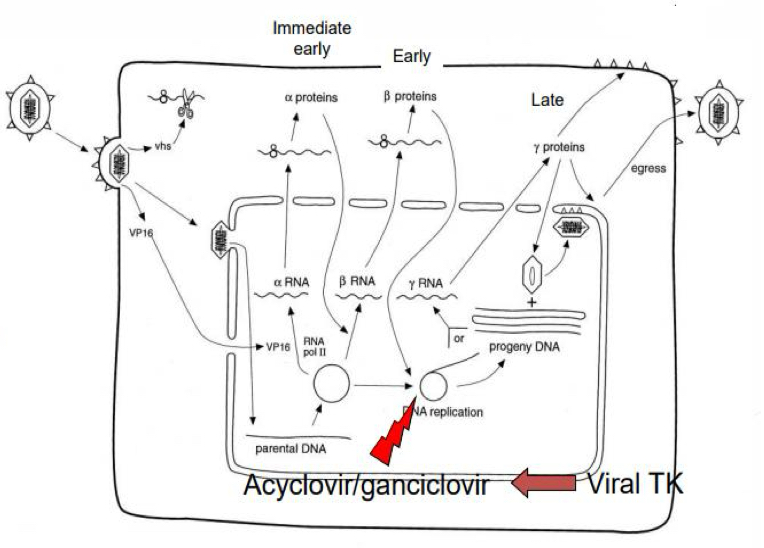
What is the lytic herpesvirus life cycle?
Nuclear dependence, temporal gene expression, viral thymidine kinase key, direct cell lysis
What is the latent herpesvirus life cycle?
Main site of infection - productive infection of epithelial cells, infects secondary site by retrograde transport
Sensory ganglion - no integration, minimal gene expression, prevents immune recognition
Secondary site of infection/site of latent infection - sensory neuron
Site of recurrent infection - productive infection of epithelial cells
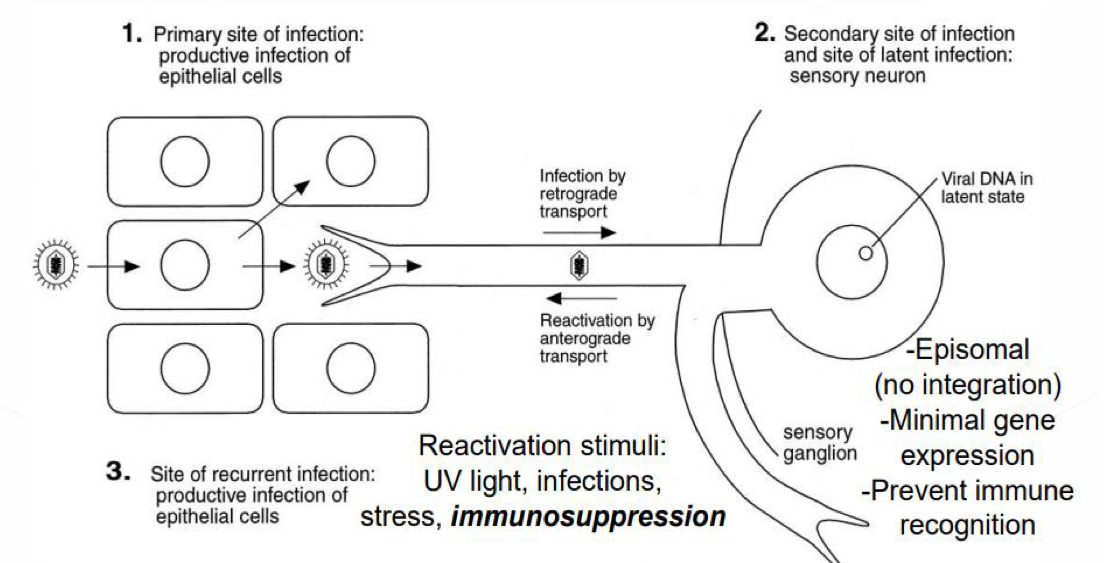
What is the reactivation stimulus for herpesvirus?
UV light, infections, stress, immunosuppresion
What are the most commonly used antiviral medicines?
Aciclovir, penciclovir, ganciclovir
What are aciclovir, penciclovir and ganciclovir used to treat?
Herpes virus infections - HSV and cytomegalovirus
When is cytomegalovirus usually treated?
Only in immunocompromised patients
What is the MOA of aciclovir?
Activated by viral thymidine kinases to become inhibitors of viral DNA polymerases and block viral DNA synthesis - allows intracellular phosphorylation to monophosphate derivative, converted to triphosphate which is then incorporated into viral DNA and is an irreversible inactivator of DNA polymerase
What is the PK of aciclovir?
Oral bioavailability 15-21%, 20% protein bond, half life 2.5-3 hours, renally excreted, safe in pregnancy
What are the side effects of aciclovir administered IV?
Lethargy, confusion, tremor and reversible renal dysfunction but all not very common
What are the side effect of aciclovir orally?
Nausea, vomiting, rash, headache
What are some common drug interactions with aciclovir?
Cyclosporin increases renal toxicity and aciclovir can decrease renal clearance of other drugs
What drug is a prodrug of aciclovir?
Valaciclovir
What are the properties of penciclovir?
Similar spectrum of antiviral cover, topical cream, oral treatment with prodrug - famciclovir
What are the properties of ganciclovir?
Predominantly used to cytomegalovirus, more toxic than aciclovir, severe interaction with zibovudine
What are the properties of the influenza virus?
Enveloped negative strand RNA, part of orthomyxoviridae
How many types of flu are there?
3 - A, B, C
What flu types are responsible for seasonal flu?
A and B
Where does synthesis of influenza mRNA/genome replication occur?
Nucleus - unusual for an RNA virus
Where do most RNA viruses synthesise usually?
Cytoplasm
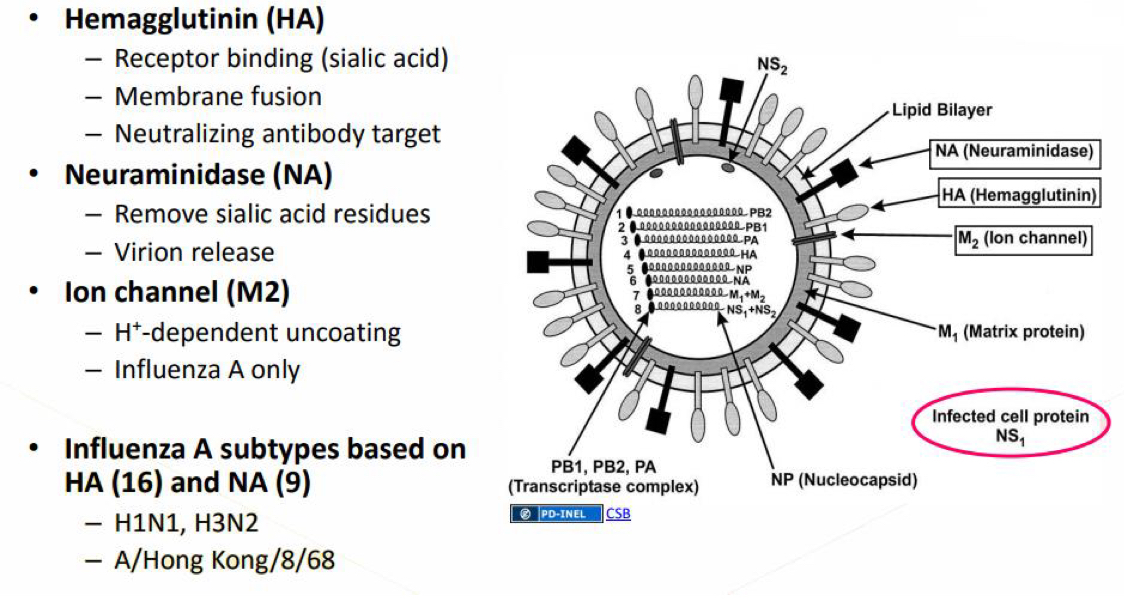
What are the influenza A subtypes divided into?
Presence of haemagglutinin and neuraminidase - 18 H subtypes, 11 N subtypes
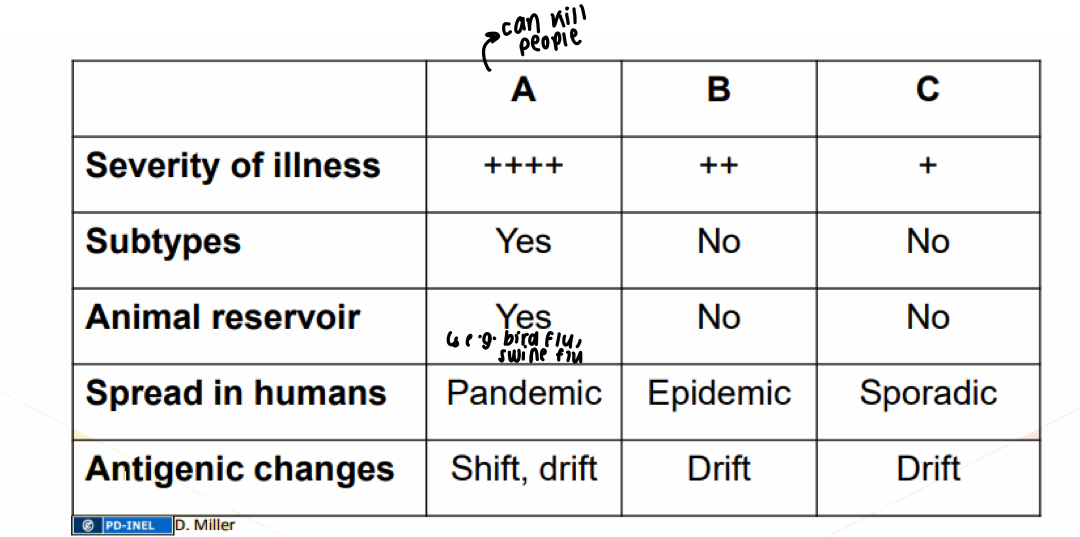
What is a table comparing flu A, B and C?
Flu A is most severe - has subtypes and animal reservoirs and pandemic when in humans, shift/drift antigenic changes
B is still severe, no subtypes, no animal reservoirs, epidemic and drift antigenic changes
C is least severe, no subtypes or animal reservoirs, sporadic spread in humans, drift antigenic changes
What is a diagram showing influenza A virus structure?
Hemagglutinin - receptor binding, membrane fusion and neutralising antibody target
Neuraminidase - removes sialic acid residues, virion release
Ion channel - H+ dependant, influenza A
What is a diagram showing influenza life cycle?
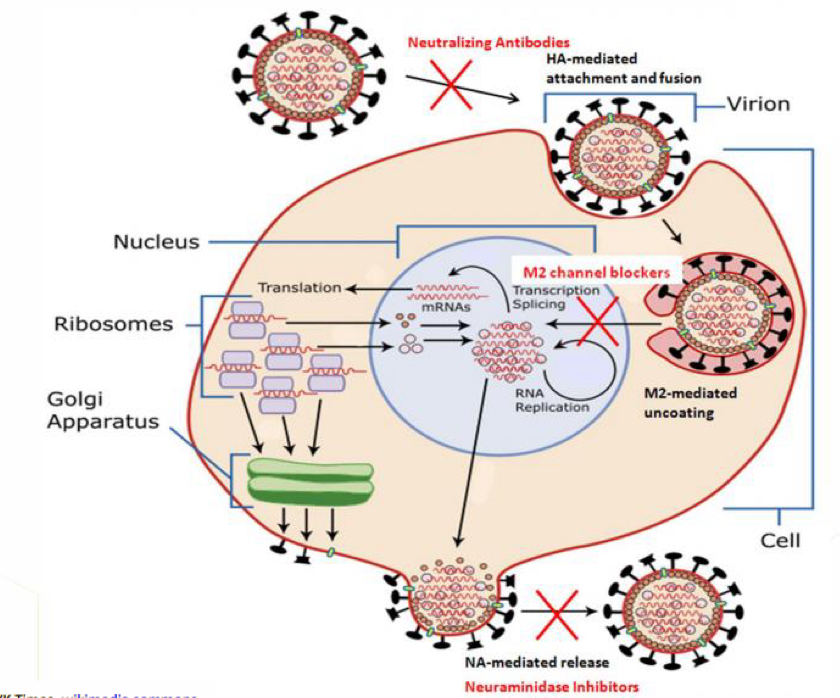
What is the pathogenesis for influenza?
Direct cell lysis in upper/lower respiratory tracts
What is the role of the immune response for influenza?
Protective rather than pathogenic, induces virus and type-specific immunity, virus mediated suppression
What drugs can be used to reduce symptom duration of flu and as prophylaxis?
Tamiflu and Rilenza
When are tamiflu/rilenza most effective for flu?
Taken within 48 hours of first symptoms and can reduce duration by 1-1.5 days as well as reducing complication risk
What drugs class are Tamiflu and Relenza?
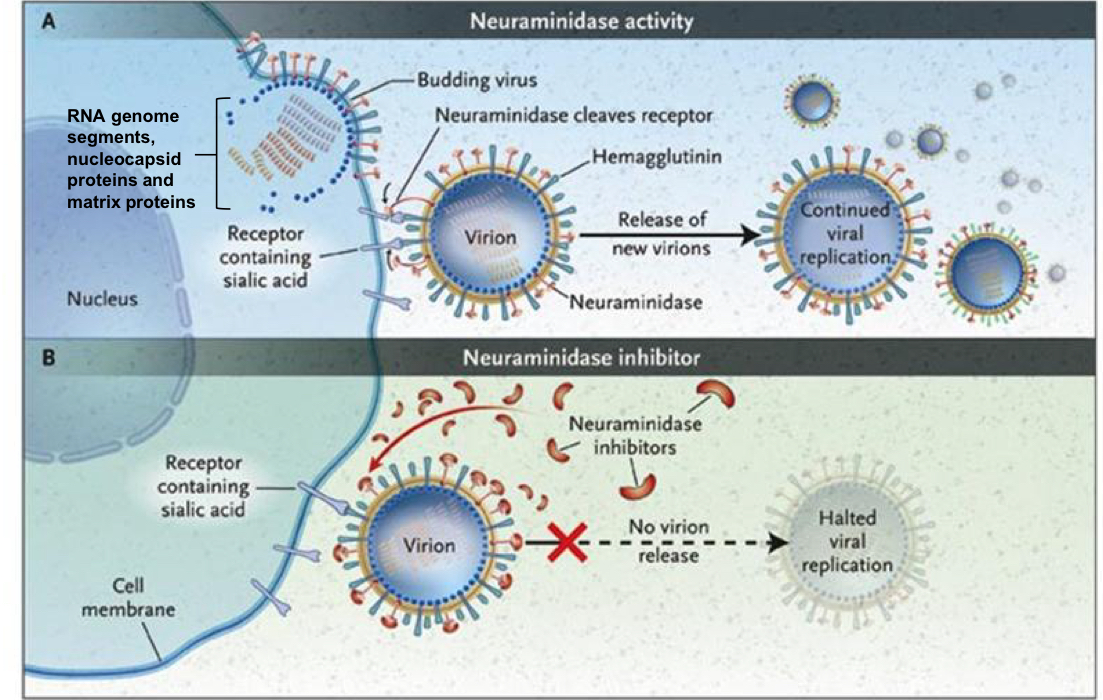
Neuraminidase inhibitors
What is the API of Tamiflu?
Oseltamivir
What is the API of relenza?
Zanamivir
How do neuraminidase inhibitors work?
Prevents virion release and halters viral replication
What is the PK of tamiflu?
100% bioavailability, renally eliminated
What are the ADRs of oseltamivir/tamiflu?
Nausea and vomiting, headache, cough, blocked nose
What is the medicinal form of zanamivir?
Dry powder inhaler - 2x a day for prophylaxis
What is the PK for zanamivir/relenza?
10-20% inhalation, renally eliminated
What are the ADRs of zanamivir/relenza?
Rash
What is the caution of zanamivir/relenza?
Risk of bronchospasm - care taken in COPD/asthma patients
What is the coronavidae subfamily?
Subfamily of around 40 single stranded RNA viruses that have a high ability to recombine, mutate and infect multiple species/cell types
What is the hosts response to the SARs-COV-2 virus?
Hyperactive - excessive inflammatory reaction e.g, cytokine storm
What part of SARS-COV-2 catalyses the synthesis of IL6?
Structural part of the virion - nucleocapsid protein
What interleukin causes the cytokine storm?
IL-6
What are the challenges for Covid-19?
Lung injury and cardiovascular complications, generalised hyperinflammation, multi-organ damage
What steroid has recently been shown to have a decreaing effect on mortality?
Dexamethasone