BIO260 Unit 4 Resource 3 - Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
29, 32
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Relevant info on ATP (?)
NOT transported from cell to cell
ea cell must make its own ATP supply
NOT stored by cell
a cell uses energy from carbo, lipids, and other things to add inorg phos to ADP to make ATP
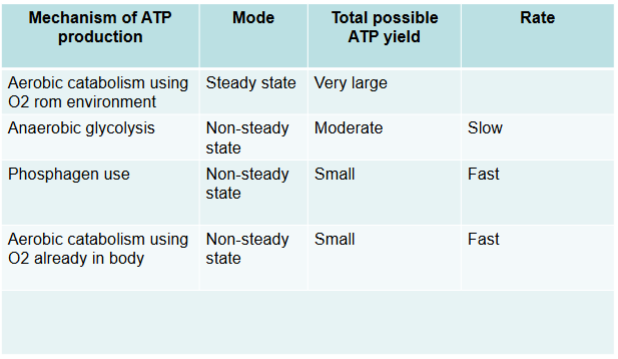
What are the 3 mechanisms of ATP production?
anaerobic glycolysis
phosphagen use
aerobic catabolism
from env
from preexisting sources in the body
Anaerobic Respiration
energy-making chem pathway, functions w/o oxygen
glycolysis and phasphagens (in animals) are major pathways
fast rate of accel
non-steady state, not always active
ATP yield is moderate
(says rate is slow on slide 5 but says diff on slide 7)
Glycolysis
occurs in cytoplasm
directly makes ATP by substrate lvl phosphorylation
syn of ATP by direct transfer of phosphate group from high energy intermed to molec of ADP
animals: glucose is the most common starting point for glycolysis
plants: sucrose is starting point for glycolysis
chloroplastic glycolysis: makes ATP in the dark & makes precursors for syn of primary metabolites
How much molec of ATP is produced per molec of surcorse?
60
Gluconeogenesis
important in plants, specifically in seeds that store C in forms of oil
oil is converted by gluconeogenesis into sucrose that can be transported to other sites in the germinating plant
req add enzymes not found in animals
in animals, it occurs primarily in liver
Glycolysis in plants and animals
can be div into 2 general steps: energy consuming, energy generating
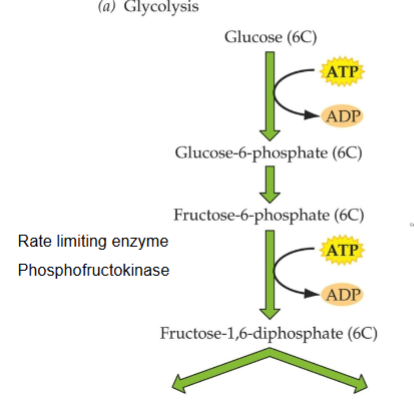
What is phosphofructokinase?
rate limiting enzyme
controls rate of glycolysis for plants and animals
4 ID monomers
binds substrates: ATP and Fructose-6-phosphateat catalytic sites
F-6 + ATP → F-1,6-P + ADP
General Process of Glycolysis (?)
binds AMP at allosteric activation site to promote ATP-F6 binding
when at high lvls, ATP binds at allosteric inhibition site ,lowering the affinity of the enzyme for F-6-P
high levels of citrate bind at allosteric inhibition site, lowering the affinity of the enzyme for F-6-P
What happens in the energy producing steps of glycolysis?
electrons move thru protein complexes in bio systems via special molec that pick up electrons at one place and deliver them to another (NAD)
What is nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD)?
coenzymes syn from vit niacin
exists in 2 forms
oxidized (NAD+/oxidizing agent): accepts electrons and becomes reduced
reduced (NADH/reducing agent): donates electrons and becomes oxidized
involved in redox rxns
Oxidative rxn in glycolysis
doesn’t req O2
occurs at the same time of oxidation of G3P → release of 2H atoms → red of NAD when the 2H+ are transferred to NAD
the only net redox step
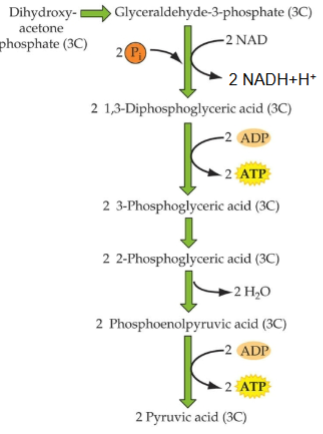
General process of energy extraction steps of glycolysis
ea Glyceraldehyde 3-Phosphate is then phosphorylated → yielding 1, 3-diphosphoglycerate
then 1 phosphate is transferred to ADP, water is given off then final phosphate is transferred to ADP
Glycolysis alt end product in plants
alt end product is malate
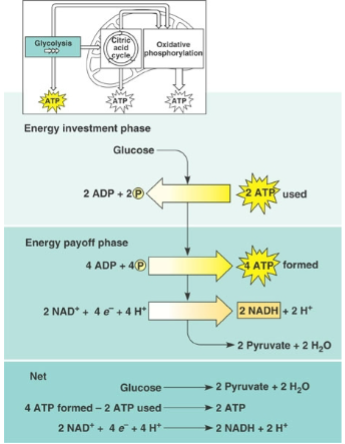
What are 2 pathways after glycolysis?
fermentation: process of making ATP w/o oxygen
aerobic respiration: process of making ATP w/ oxygen
Process of making ATP w/o oxygen (fermentation)
cytochromes and other parts of the electron transport chain become fully red-electrons, cannot be discharged
ox-phos cannot take place
NADH+H+ and FADH2 cannot become oxidized by electron transport chain so glycolysis stops
only certain tissues have alt mechanisms to make ATP w/o O2
human brain cannot
Aerobic respiration in plants
oxygenated air in soil is alr present
oxygen present among soil particles diffuses into root hairs
from root hairs, oxygen is transported to all parts of the roots for respiration
also used to syn other org matter such as citric acid, oxalic acid, lactic acid
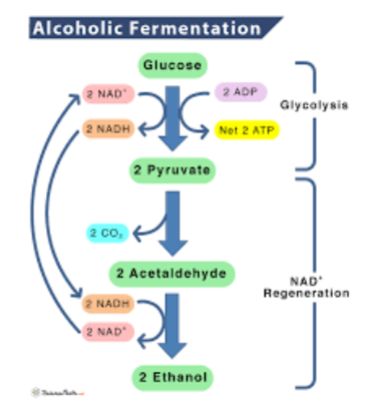
plants use alcohol fermentation and most animals use lactic acid fermentation
Glucose → Alc + CO2 + 2ATP
Glucose → Lactic acid + 2ATP
Similarities b/w Anaerobic respiration in plants and animals
both take place in absence of molec oxygen
in both, 2 ATPs are made
both involve the incomplete breakdown of respiratory substrate
the NADH made in both glycolysis processes is often used
electron transport chain is absent in both processes
both are enzyme-catalyzed rxns
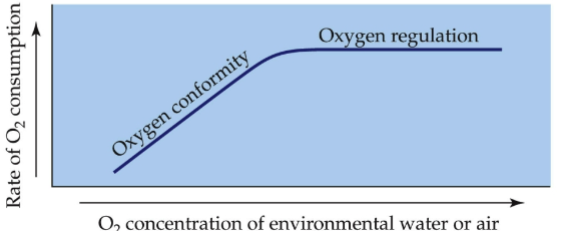
Oxygen regulators vs Oxygen conformers
animals faced w/ red O2 avail show conformity
oxygen regulators display steady state of aerobic respiration regardless of O2 lvls
conformer’s aerobic respiration rate will more closely correlate w/ O2 lvls
Anaerobic respiration: Phosphagens
provide additional mechanisms of ATP production w/o ocygen by
substrate lvl phosphorylation
non-steady state
small yield
peak rate is very fast
serve as temp stores of high energy intermed
creatine phosphate (phosphagen of vertebrate muscle)
doesn’t exist in plants
arginine phosphate (phosphagen of invertebrates)
What are the rxns in aerobic catabolism?
glycolysis
krebs cycle
electron transport
oxidative phosphorylation
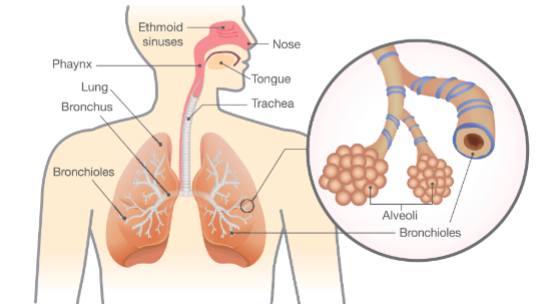
Vertebrates breath
use ventilation to deliver oxygen to the lungs
oxygen diffuses the lung spaces (alveoli) and into the blood where it is circulated to cells
Plant respiration in lenticels
plants respire with the help of lenticels and stomata
lenticels
pores in fruits, petiole, roots, and the stem of a woody plants that allow gas exchange b/w atmosphere and the internal tissues
always open
don’t contain chlorophyll
active at night
have no guard cells
Plant respiration in stomata
stomata
exist in stems non-woody plants and leaves
carry out the function of gaseous exchange in those organs
they can open and close-reg
contain chlorophyll and can carry out photosyn
active during the day
have guard cells
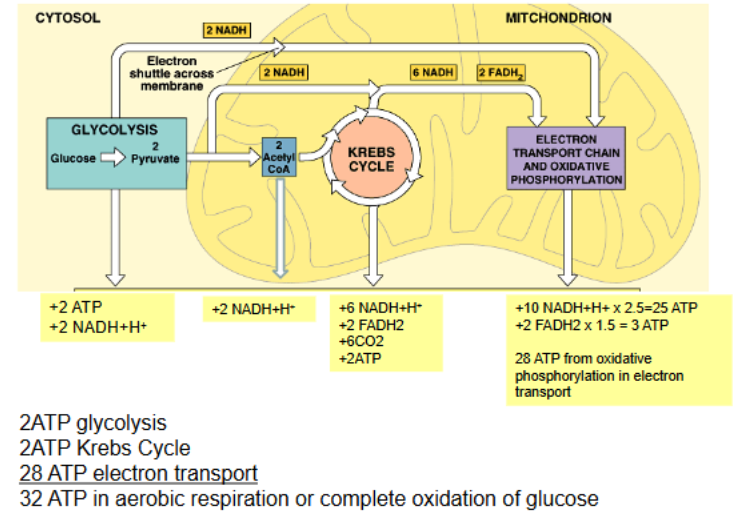
Where is pyruvate transported if oxygen is present?
mitochondria
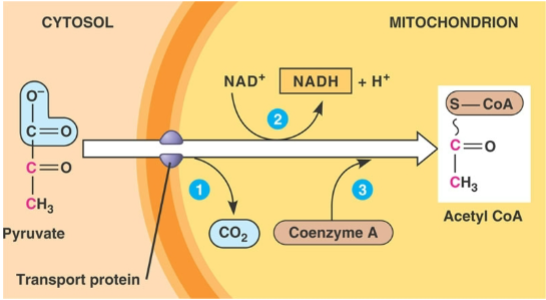
What happens in the cystol?
pyruvate is oxidized into an acetyl group and CO2
acetyl group is them transferred to CoA by pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
acetyl CoA serves as the starting compound for the Kreb cycle
In the Kreb Cycle
pyruvate to acetyl CoA
2NADH
2CO2
Krebs cycle
6NADH
2FADH2
2ATP
6CO2
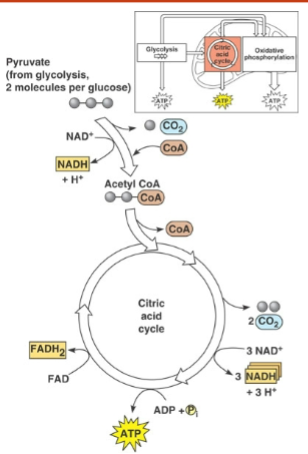
Unique features of the Kreb Cycle
the step that catalyzed by succinyl-CoA synthetase makes ATP in plants and GTP in animals
plants have malic enzymes in mitochondrial matrix of plants that catalyzes the rxn: Malate + NAD+ → pyruvate + CO2 + NADH
allows plants to operate alternative pathways for the metabolism of pyruvate derived from glycolysis
Oxidative phosphorylation
uses oxygen to oxidize the electron carriers NADH and FADH2 in order to generate ATP
ATP is made thru a mechanical process
The general process of Aerobic respiration