IB Economics Review (Microeconomics)
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Factors of Production
1) Land / Natural Resources
2) Labor
3) Entrepreneurship / Businesses
4) Capital / Tools & Machinery
What causes a change in supply?
The Factors of Production
Scarcity
Limited / Costly Resources
Major conflict creator in economics
Sustainability
Meeting the needs of present generation without compromising the future
Opportunity Cost
Giving something up in order to gain something
Next best alternative
Free Market System
Laissez-faire
Hands free economy
Resources allocated freely
Founder of Free Market System
Adam Smith
Planned Economy
Government controls all
Centrally planned economy
Founder of Planned Economy / Criticized Free Market System
Karl Marx
Mixed Economy
Free market ideas with some governmental control
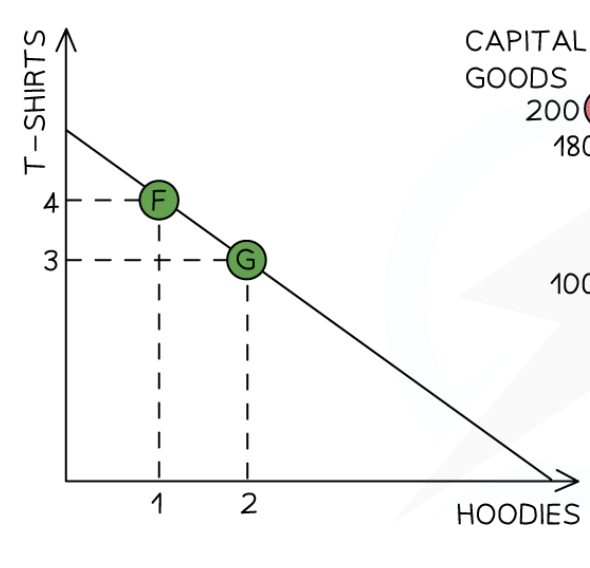
Production Possibilities Curve (PPC)
Graph that shows opportunity cost
Circular Flow of Income Model
Households spend money on firms
Firms give income to households
Related to GDP measurement
Laissez-Faire
No governmental intervention
Keynesian Revolution
More governmental management
Post Great Depression
John Keynes
Circular Economy
Waste becomes resource
Sustainable economy
Law of Demand
Price goes up, quantity goes down
Demand Curve
Graph showing change in quantity’s affect on price
Affects consumers
Change in Demand
Change in quantity bought
Shift of demand curve
Non-price determinants of demand
1) Income
2) Taste
3) Preferences
4) Future price expectations
5) Price of related goods
Law of Supply
Quantity goes up, price goes up
Supply Curve
Graph showing change of price’s affect on quantity
Represents producers
Change in Supply
Changes in price of good
Shift of supply
Non-price of determinants of supply
1) Changes in F.O.P
2) Indirect tax/subsidies
3) Change in technology
4) Future price expectations
Market equilibrium
Price and quantity of where supply and demand meet
Price Mechanism
Changes in supply and demand led to changes in price and quantity
Community Surplus
Benefits resulting from a market
Consumers save, producers make profit
Resource Allocation
Choice of what gets made and who gets it
Allocative Efficiency
At equilibirum, quantity demanded = quantity supplied
Marginal Benefit
The gain of producing one more product
Marginal Cost
The cost of producing one more product
Total Revenue
NOT profit
Total money collected from a sale
Profit - spendings = revenue
Elasticity
The degree of responsiveness to price changes
Price elasticity of demand (PED)
percent change of quantity / percent change of price
Determinants of PED
Necessity
Lack of substitutes
Proportion of income
Time to response
Income elasticity of demand (YED)
How consumers react to change in income
Engel curve
YED Diagram, quantity of goods consumed v. income
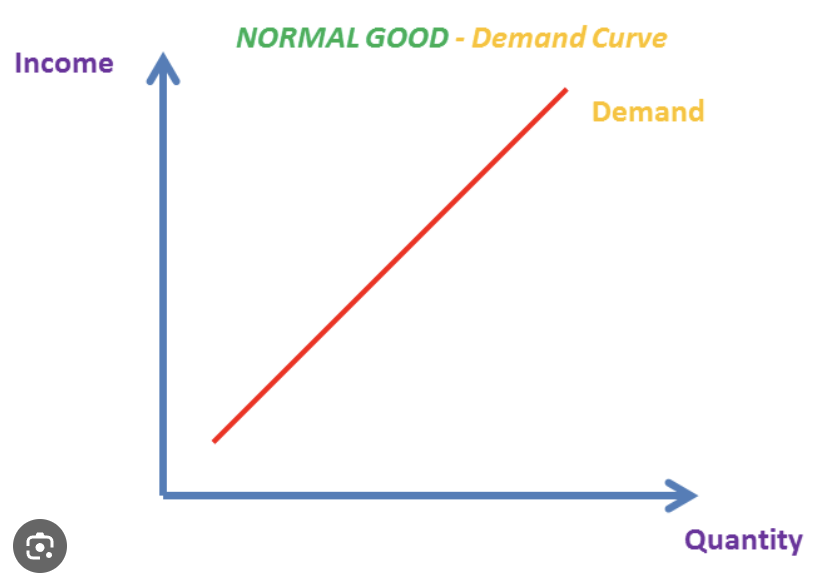
Normal goods
People buy more when income increases
Inferior goods
People buy less when income increases
Price elasticity of supply (PES)
How much more/less firms produce in response to a change of price
Determinants of PES
Mobility of factors of production
Unused capacity
Ability to store
Time to respond
Price ceiling
The maximum price on a good
E.g. rent, gas, drugs
Price floor
The minimum price on a good
E.g. minimum wage
Indirect tax
Taxes included in the price
ad valorem = percentage and
specific = set amount per unit
Subsidy
Money provided by government to a firm
Encourage production
Direct provision
Government produces a product instead/ in addition to private goods
Regulation
Rules and limitations placed on a product/ production by government
Shortage
Price below equilibrium
Lower quantity supplied than demanded
Oversupply
Price above equilibrium
Lower quantity demanded than supplied
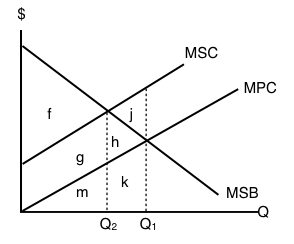
Socially optimal output
Equilibrium price and quantity when social costs and benefits are taken into account
Marginal social benefit
Level of demand when social costs and benefit are taken into account
Marginal social cost (MSC)
Total cost to society of producing one additional unit of a good or service
Positive externalities of production
Unaccounted positive outcomes from production
Benefits gained by a third party
E.g. Bee Keeping
Negative externalities of production
Unaccounted negative outcomes from production
Costs that affect a third party
E.g. Pollution
Positive externalities of consumption
Benefits gained by non producers when a good/service is consumed
e.g vaccinations, education, and using public transportation
Negative externalities of consumption
Consequences faced by consumers and non producers when a good or service is consumed
e.g secondhand smoke, noise pollution, and traffic congestion
Merit Goods
Gives long term benefits to consumer
Creates positive externalities
Demerit Goods
Causes harm to the consumer
Welfare loss / Deadweight loss
Lost benefits or harm resulting from a market not in equilibrium
Common pool resources
Non-excludable, causes rivalry
Tradegy of the commons
Exhausting common pool resources
Self interest undermines a better outcome for society
Pigouvian Tax
An indirect tax on a demerit good to discourage its use
Carbon Tax
Tax per unit of carbon emission by producer
Tradable Permits
Method of regulating emissions
Issue a permit to sellers and they can buy or sell them
Collective self-governance
When regulations are placed on the industry itself
Public Goods
Non-rivalrous, non-excludable
E.g. town road, park, or school
Free-rider problem
Tendency to avoid paying for a product when everybody else could have it for free