Lab #2: Microscope and Sponges
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
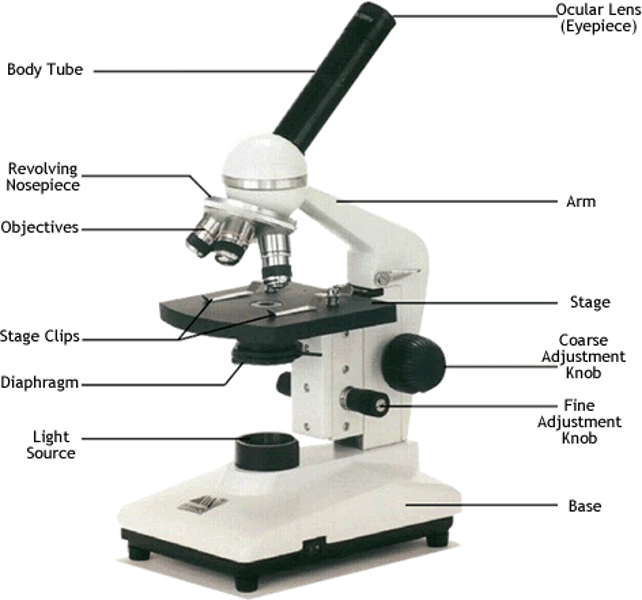
compound light microscope
higher total magnification
able to see more detail
able to see very small objects
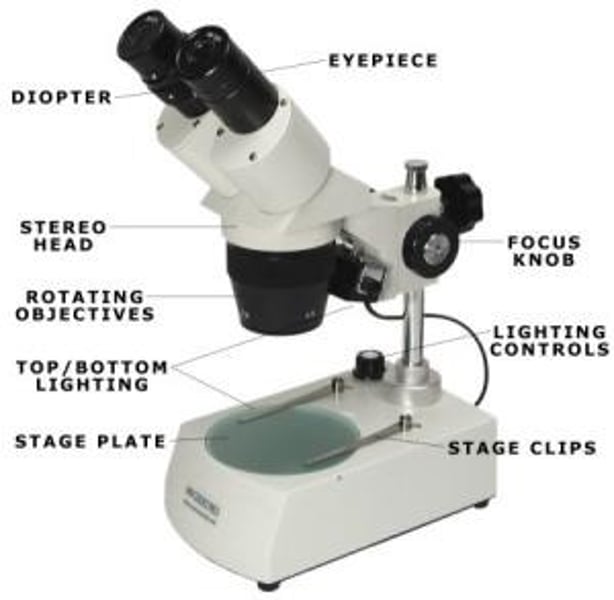
dissecting microscope
able to see objects in 3D
larger view (larger field of vision)
able to look at live specimens (that are not microscopic)
able to place light anywhere to view specimen
Phylum Porifera (sponges)
most primitive animal phylum
no true tissues, no organization
aquatic, mostly marine, some freshwater
no mouth nor anus
asymmetrical
Three classes under Phylum Porifera
Class Calcarea
Class Hexactinellida
Class Demonspongia
classes of sponges are based on ____________
characteristic structures and body organization
mesohyl
gelatinous matrix with scattered cells
pinacocytes
flattened epithelial (outer) cells
choanocytes
collar cells
create water currents in canals and chambers
spicules
made of calcium carbonate, silica, or fibers of spongin
provide structural support
gemmules
internal asexual buds in freshwater
produced during period of cold or drought and can survive to produce a new sponge body when conditions improve
syncytial
having many nuclei contained within a single plasma membrane
can be the outer tissue layer in some sponges
amoebocyte
within the body wall of a sponge, a specialized cell that crawls about and delivers nutrients from the choanocytes to the rest of the body cells
ostium/ostia
small incurrent pores where water enters the body of the sponge
oscula
one or more large excurrent pores where water leaves the body of a sponge
spongocoel
large central cavity of the sponge
the three type of sponge canal systems
asconoid
syconoid
leuconoid
asconoid sponge
incurrent pores
spongocoel lined with choanocytes
osculum
one large flagellated chamber
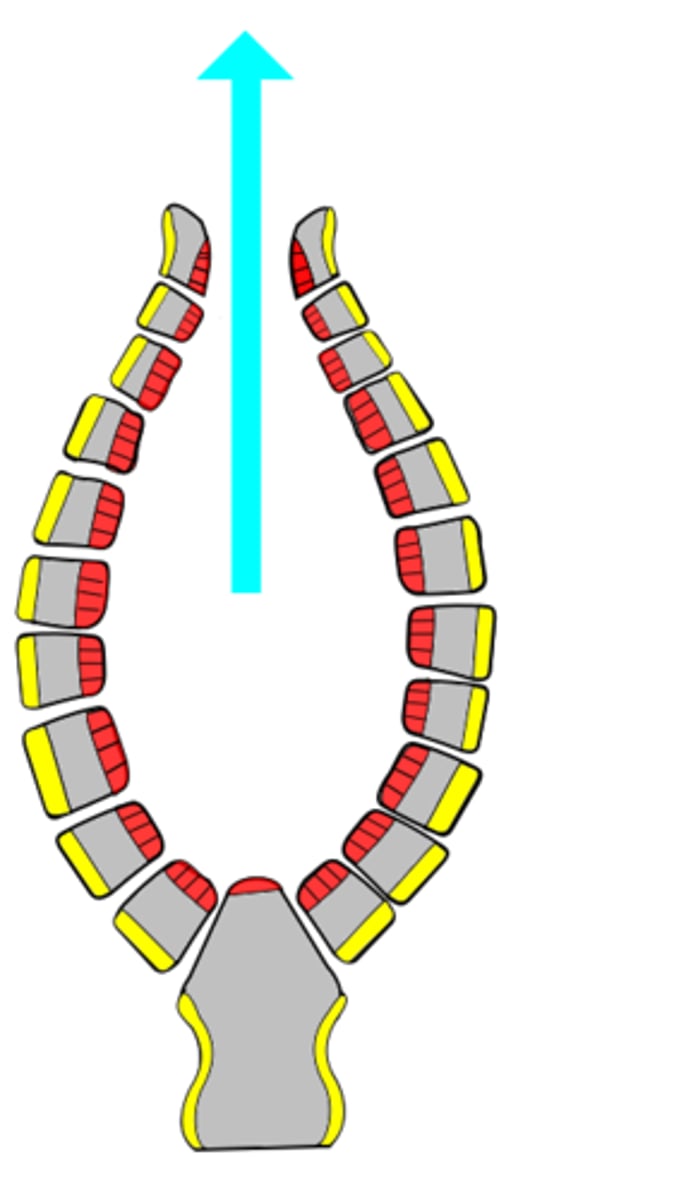
syconoid sponge
ostium
incurrent canals
radial canals lined with choanocytes
spongocoel
osculum
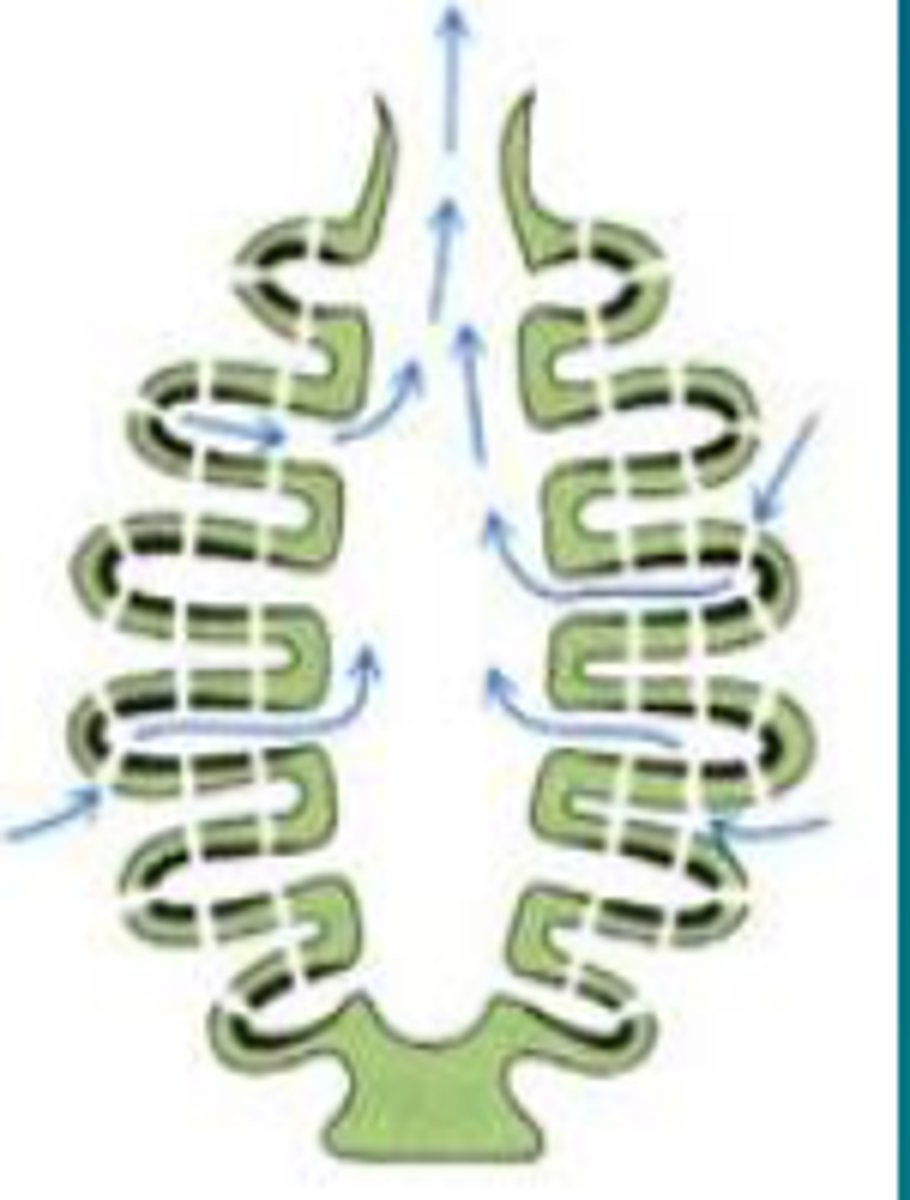
leuconoid sponge
pores
incurrent canals
radial cannals
flagellated chambers with choanocytes
osculum
much thicker body wall
is found in all of the larger sponges
class Calcarea
calcareous sponges
spicules make of calcium carbonate (CacCO3)
all marine
all canal systems are found in this class
class Hexactinellida
glass sponges
spicules are siliceous (SiO2) and are 6-rayed
all marine
syconoid and leuconoid canal system
unique trabecular (porous material of hard and soft tissue) network
class Demospongiae
commercial sponges
siliceous spicules, but not 6-rayed
AND/OR
fibers of spongin
all leuconoid
most marine; some freshwater
the importance of sponges
- break down material into food for other animals in coral reef systems
- food for hawksbill sea turtles (and other turtles)
- filters bacteria and contaminants in water
shelter for other animals