S3.2.2 Esters
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 10:09 PM on 5/5/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
1
New cards
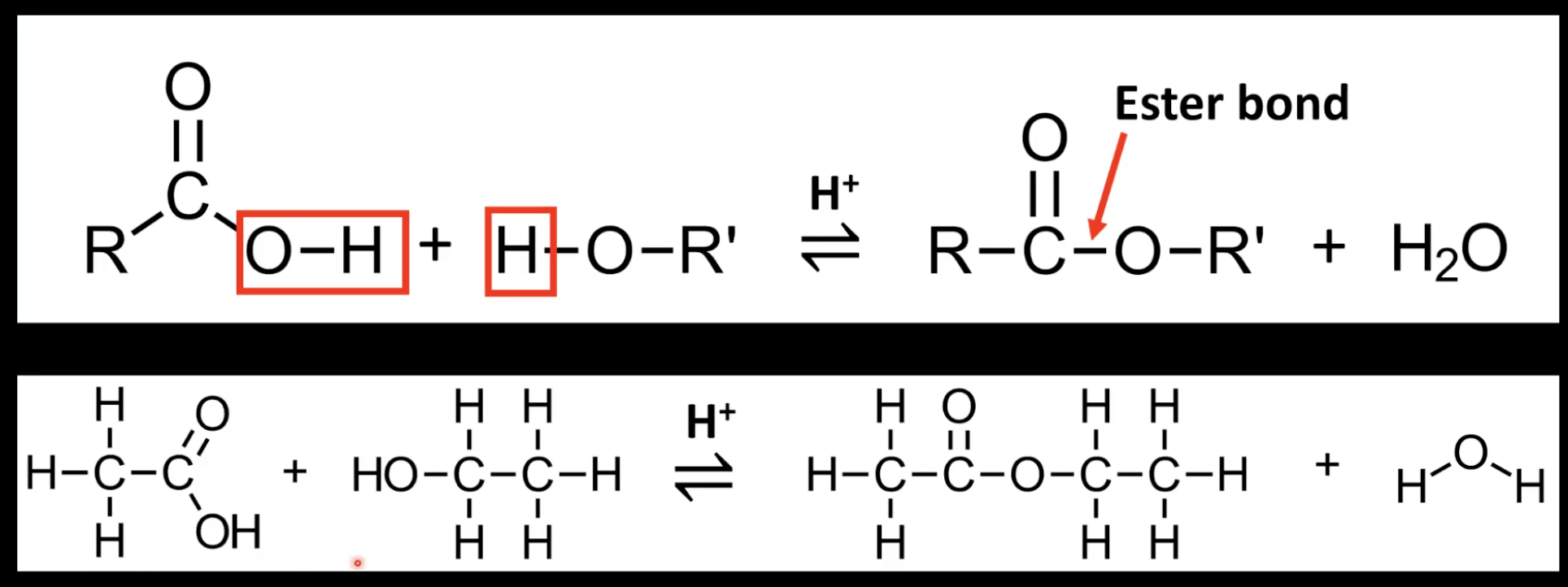
How are esters formed?
Carboxylic acid + alcohol → ester + water.
Reaction is condensation (or esterification), catalyzed by H₂SO₄.

2
New cards
What type of reaction forms esters?
Nucleophilic substitution/condensation.
Water is formed.
Reversible reaction.
3
New cards
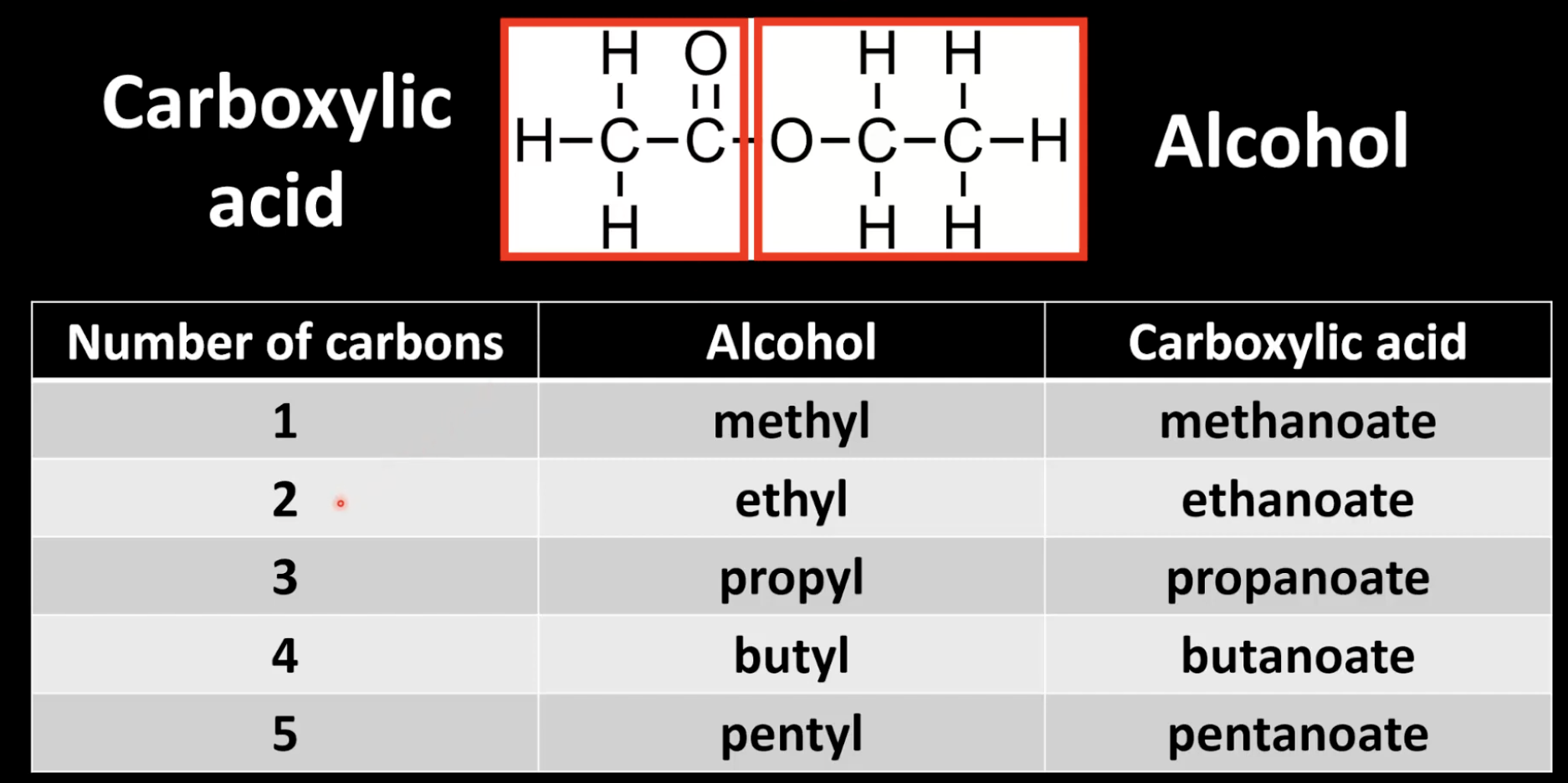
Naming esters
Alcohol part first (e.g. ethyl), acid part second (e.g. ethanoate).
Example: ethyl ethanoate.
4
New cards
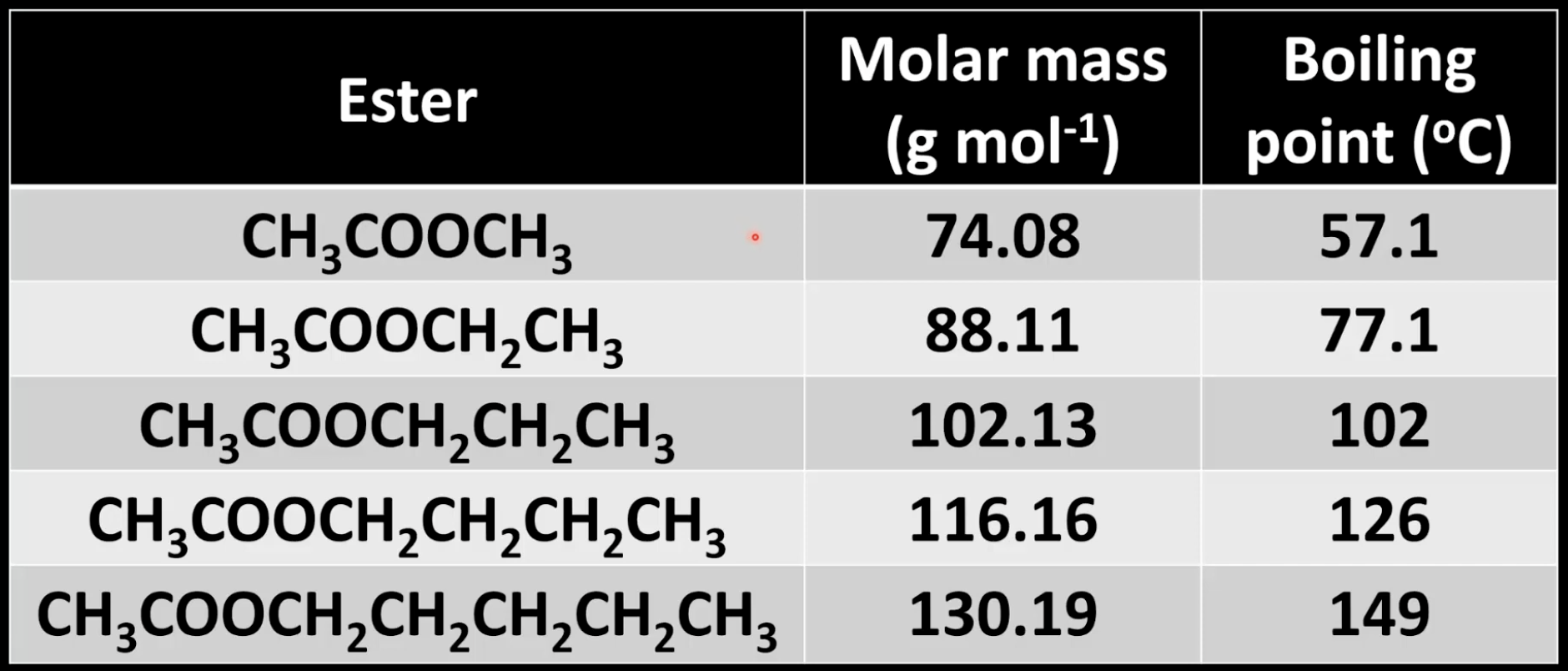
Boiling point trend in esters
Increases with molar mass due to stronger London dispersion forces.
Example: methyl ethanoate < pentyl ethanoate.
5
New cards
Solubility of esters
Decreases with molar mass.
Larger hydrocarbon chains reduce solubility in water.
6
New cards
Uses of esters
Used as food flavorings, solvents, and plasticizers.
Fruity smells make them ideal for fragrances.