2 - Scientific Measurement
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Measurement
a number that shows the size or amount of something usually in reference to a standard measurement
Measurement
a process of determining how large or small a physical quantity is as compared to a basic reference quantity of the same kind
Number
Unit
A measurement is consist of:
Number
which tells the amount (how many or how much)
Unit
which tells the scale of measurement
Metric system
is the standard system based on decimal values. It has unit conversions based on the powers of 10.
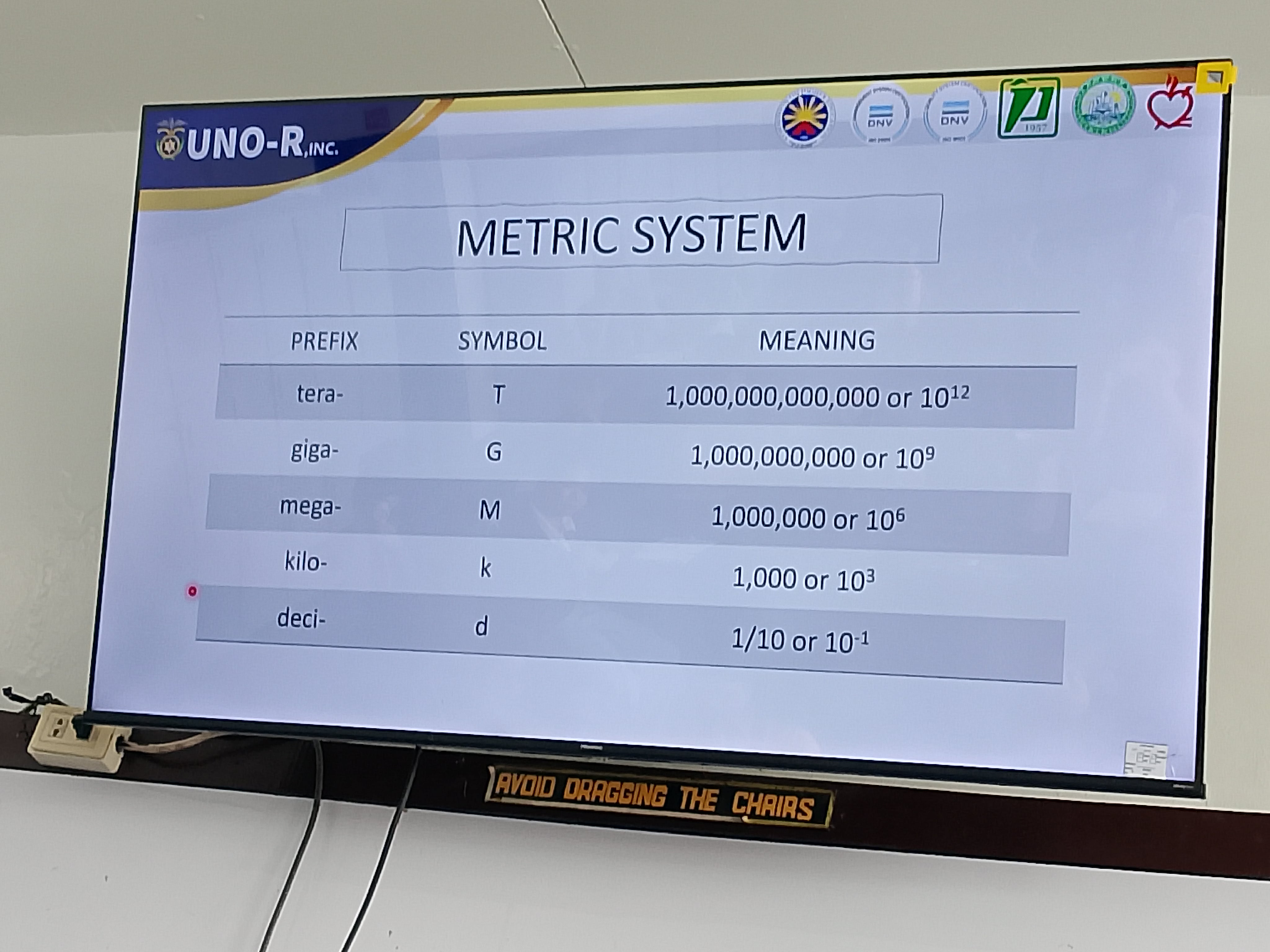
tera
giga
mega
kilo
deci
centi
milli
micro
nano
pico
Metric System prefixes:
English system
a system of measurement based on foot, pound, and seconds (fps)
English system
helps to measure the bigger units without the need for external measuring tools
International System of Units (SI)
is the system that is used as universal standard for measurements
Système International
SI - abbreviation for ___________
Fundamental
Derived
Quantities of Measurement:
Fundamental quantities
independent on other quantities for their measurement
Derived quantities
dependent upon other fundamental quantities for their measurement
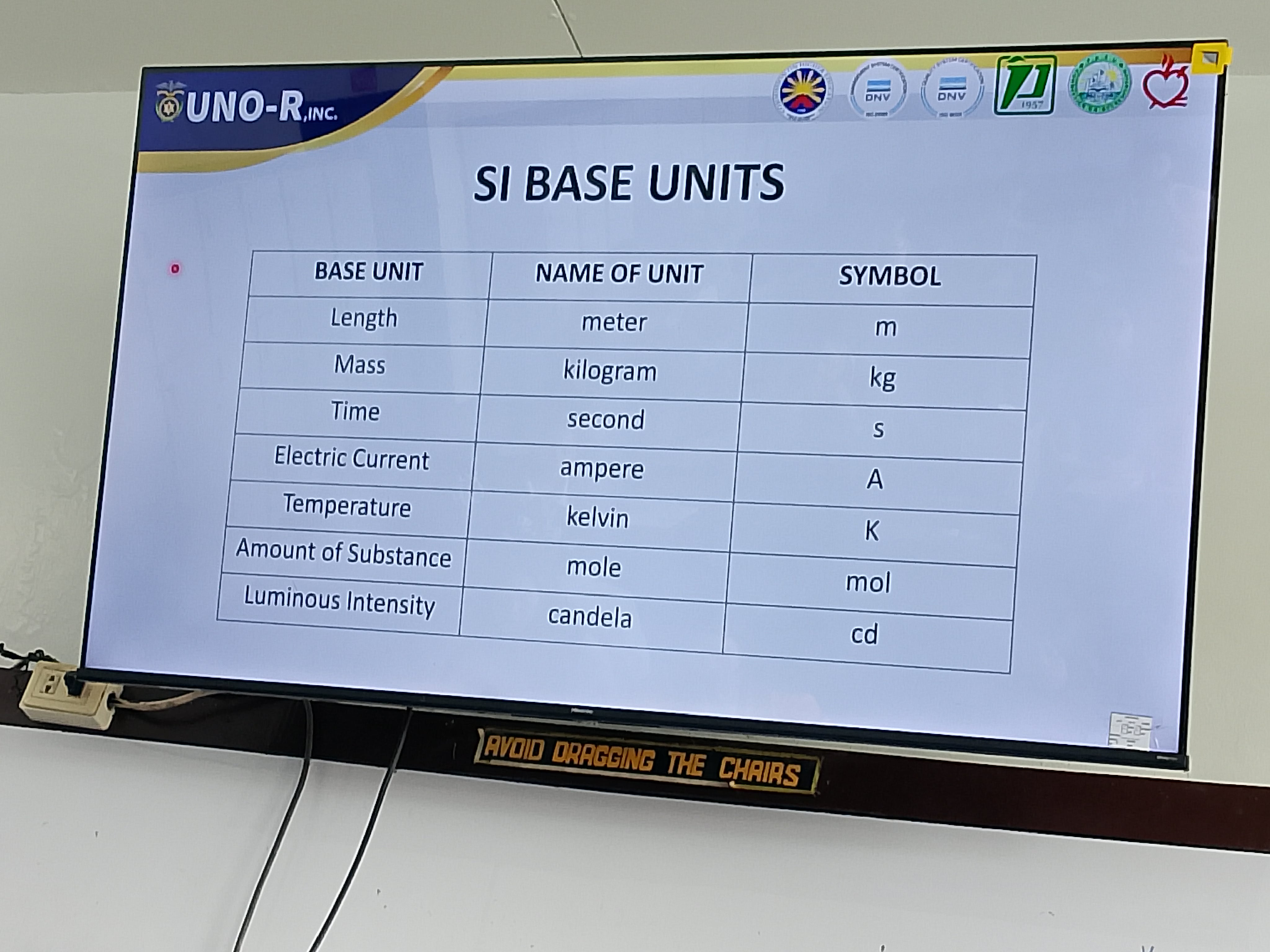
Length
Mass
Time
Electric Current
Temperature
Amount of substance
Luminous intensity
SI Base units: (7)
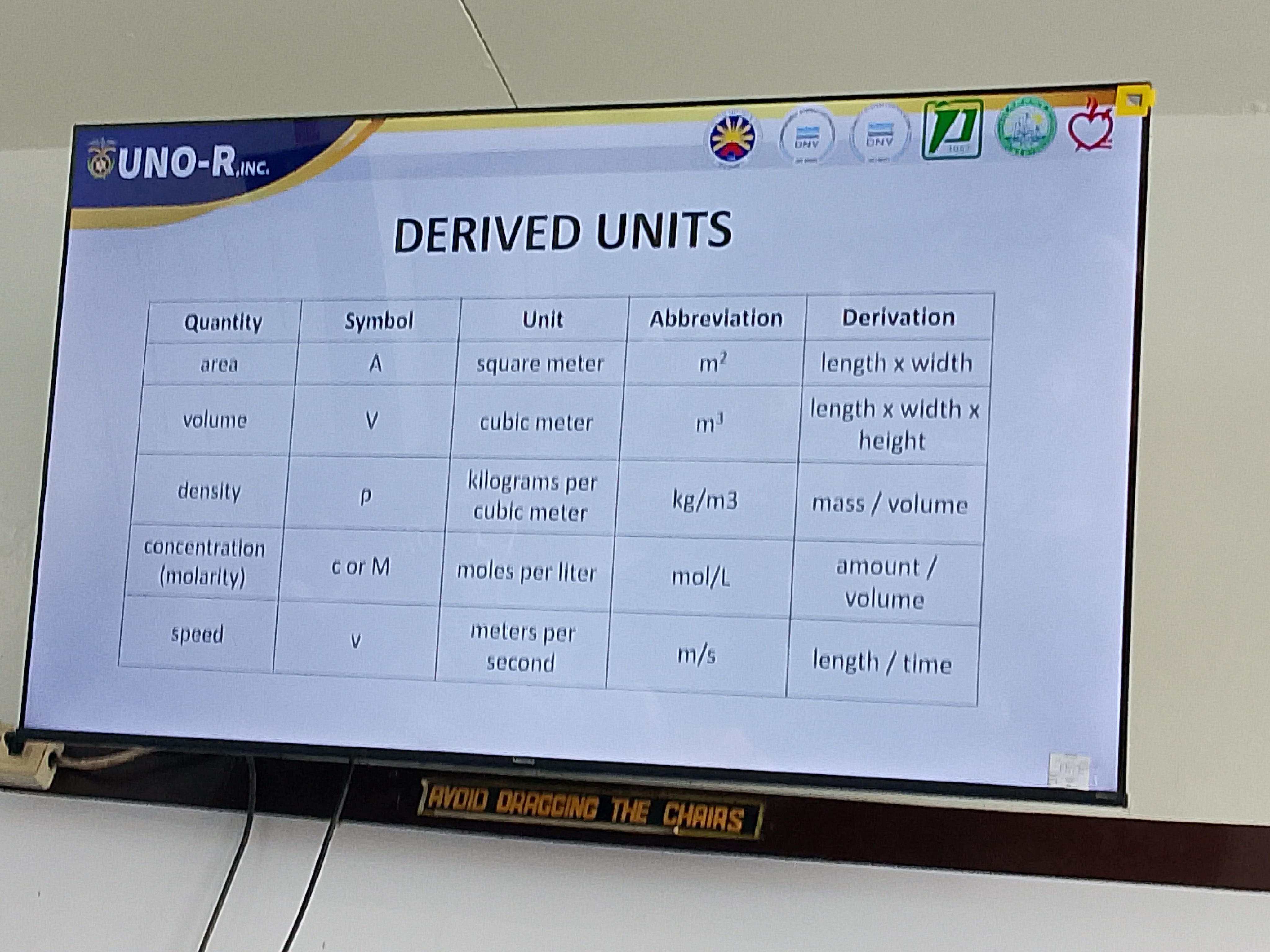
Area
Volume
Density
Concentration (molarity)
Speed
Derived units:
Significant figures
are the number of digits in a value, often a measurement, that contribute to the degree of accuracy of the value.
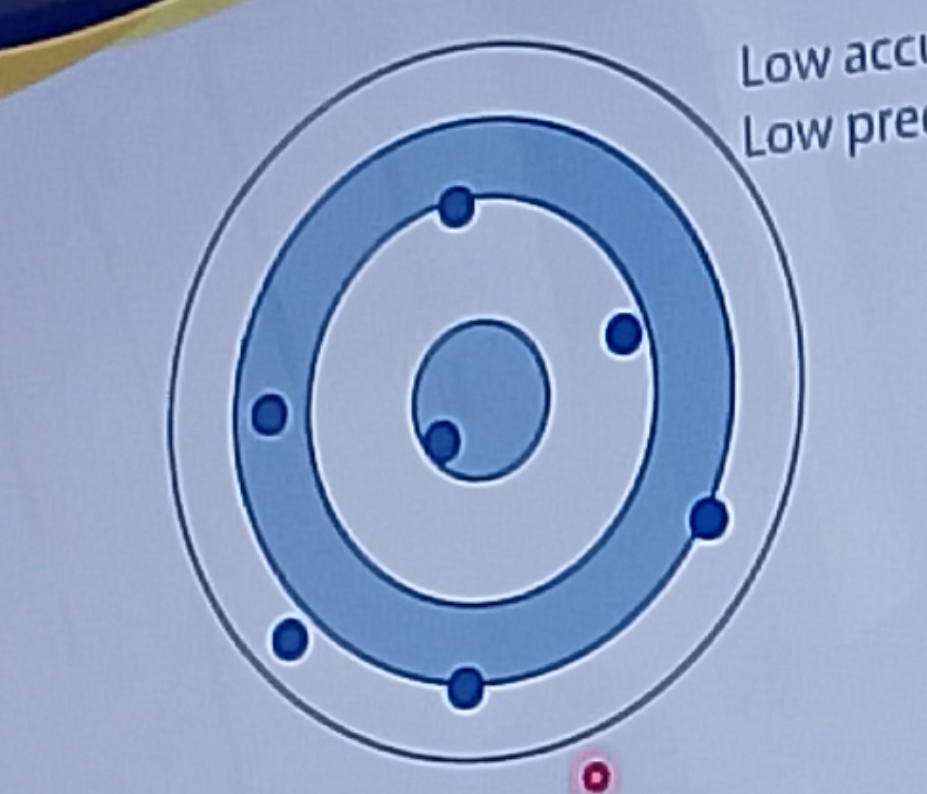
Accuracy
refers to how close a determined value is to the true value
Precision
refers to the closeness by which values agree within a series of measurements of the same parameter
Low accuracy, Low precision
High accuracy, Low precision
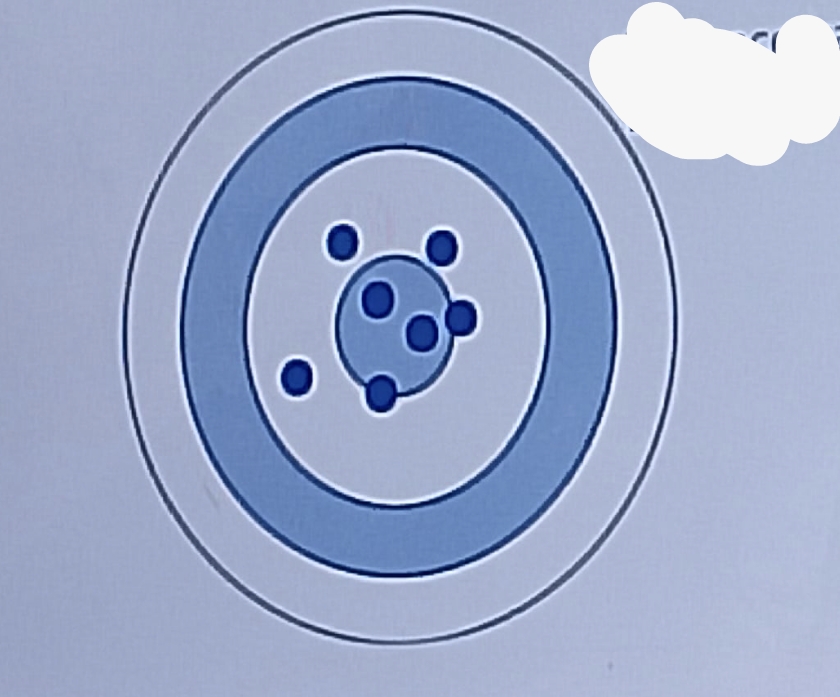
Low accuracy, High precision
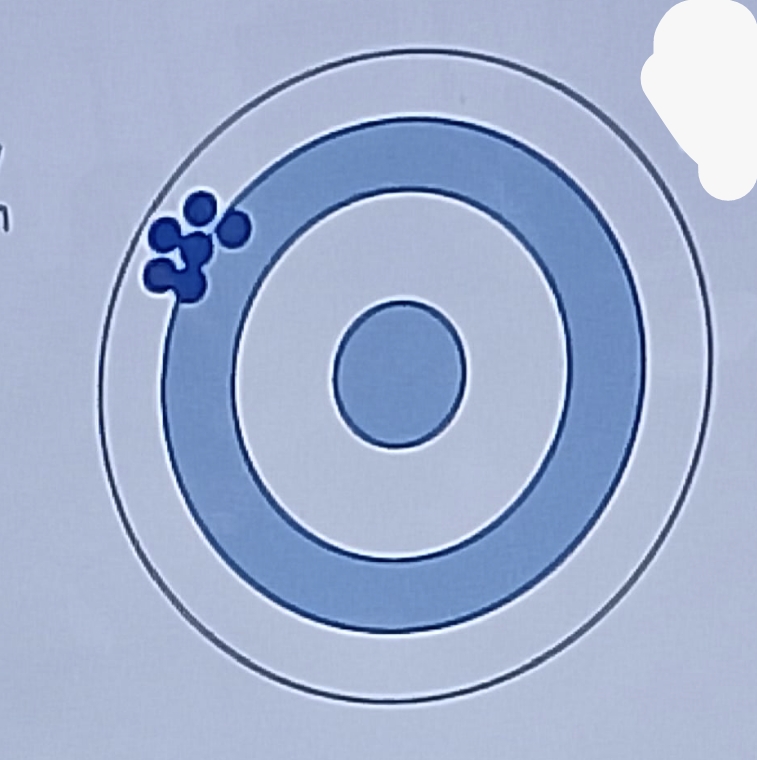
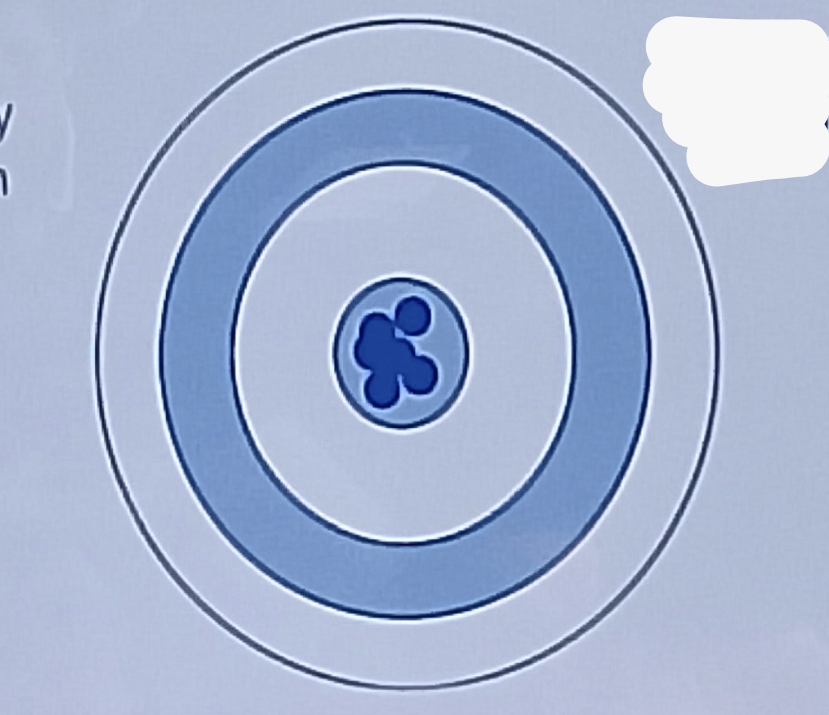
High accuracy, High precision

significant
Zeros between nonzero digits are ________.
not significant
Leading zeros are _______.
significant
Trailing zeros to the right of the decimal point are ______.
significant
Trailing zeros in a whole number with decimal shown are ______.
not significant
Trailing zeros in a whole number without decimal shown are ______.
Dimension analysis
a problem-solving method that uses the fact that any number or expression can be multiplied by one without changing its value.
F = (1.8)(°C)+32
How to get °F
C = F - 32 / 1.8
How to get °C
K = C + 273.15
How to get °K
R = F + 460
How to get °R