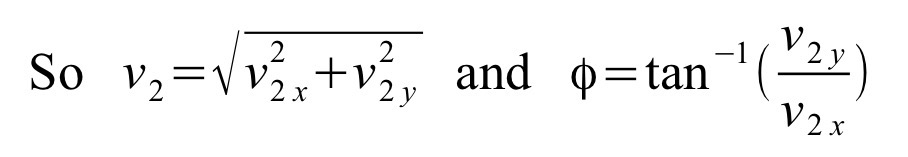Projectile Motion (U3) - Physics
1/5
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Suffer
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
Formulas for impact velocity
Solving for v2 using time and distance, acceleration in y-axis is g, vertical velocity will change.
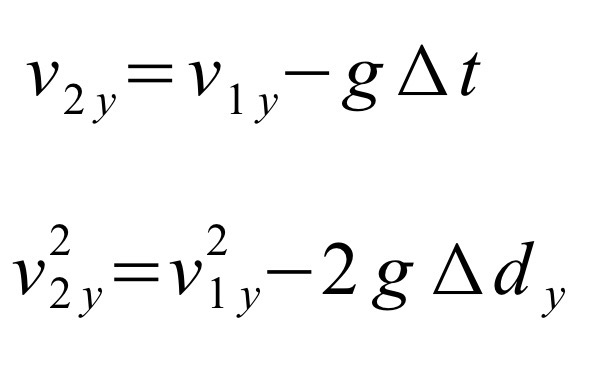
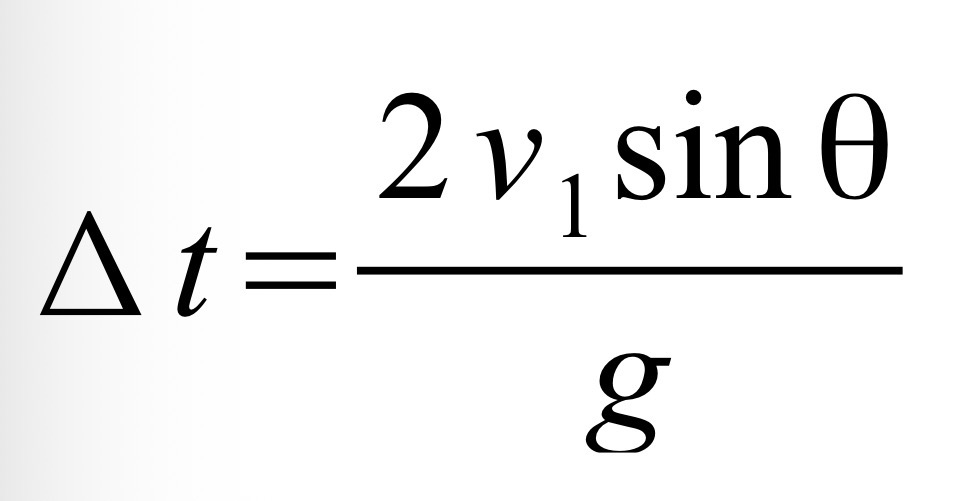
2v1sin(theta)/g
If the range (dx) is unknown, use this formula for hang time.
Find formula for hang time
V1x is the horizontal component of V1 found with cosine. Displacement in the x direction / v1cos(theta) = hang time
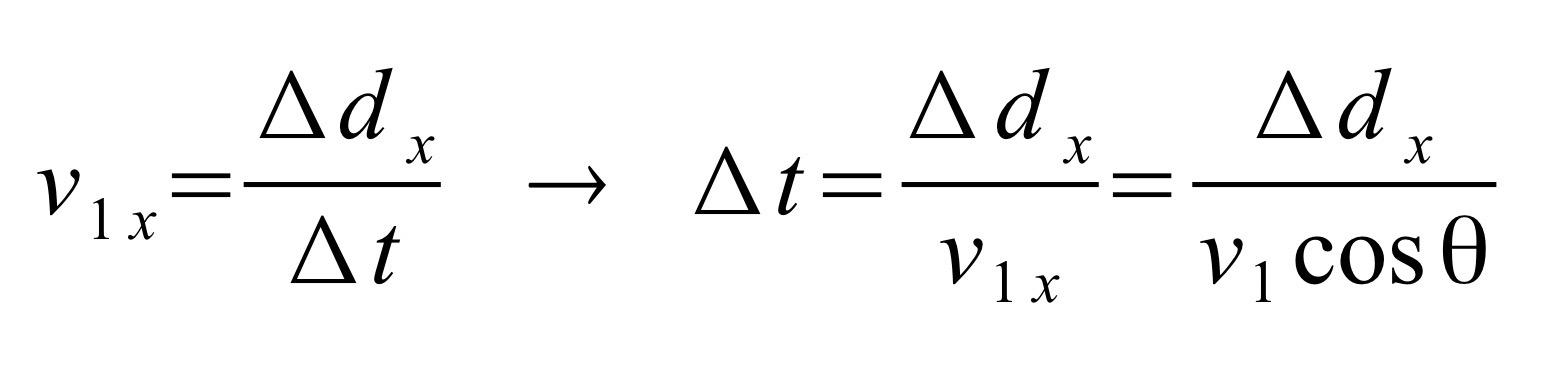
Symmetric trajectory
When a projectile is launched and lands at the ground level, vertical displacement is 0. This means that the maximum height of the projectile is half of its trajectory.
Formula for time at halfway point of a projectile with symmetric trajectory
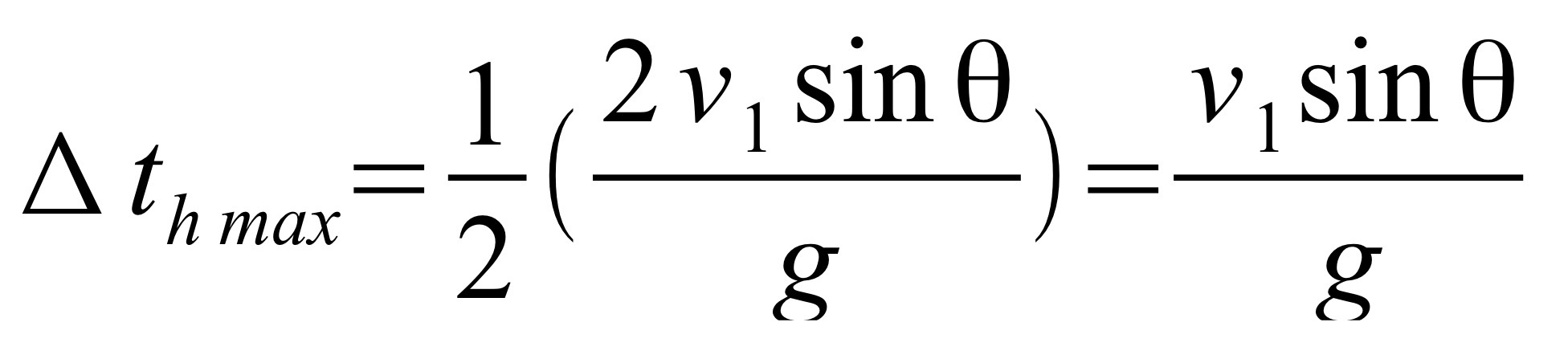
Impact velocity
Impact velocity refers to the velocity of the projectile before the ground exerts a force on it to stop it (or cause it to bounce). The impact velocity is therefore not zero but can be calculated (as can any velocity after launch) from its components.