ALL TRANSITION METALS
1/122
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
123 Terms
Transition Metal
Metal that can form one or more stable ions with a partially filled d sub-level.
Scandium isn't a TM because...
Has an empty d-shell when Sc3+
Zinc isn't a TM because...
Has a full d-shell when Zn2+
Which 2 TM have 1 electron in 4s sub-level to give stability?
Chromium and Copper
Which sub levels electrons fill up first and empty first?
4s
What physical properties do they have?
High density
High melting and boiling points
Similar ionic radii
What chemical properties do they have?
Form complex ions
Form coloured ions
Are good catalysts
Can exist in variable oxidation states
Complex ion
Central metal atom/ion surrounded by co-ordinately bonded ligands.
Co-ordinate bond (Dative covalent)
Covalent bond in which both electrons in the shared pair come from the same atom.
Ligand
Is an atom/ion/molecule that donates a pair of electrons to a central metal ion to form a transition metal.
Co-ordination number
Number of co-ordinate bonds that are formed with the central metal ion.
Lewis Base
Lone pair donor.
Lewis Acid
Lone pair acceptor.
How many small ligands like H20/NH3 can fit around the central metal ion?
6
How many larger ligands like Cl- can fit around the central metal ion?
4
Shape and bond angle of 6 Co-ordinate bonds
Octahedral, 90 degrees.
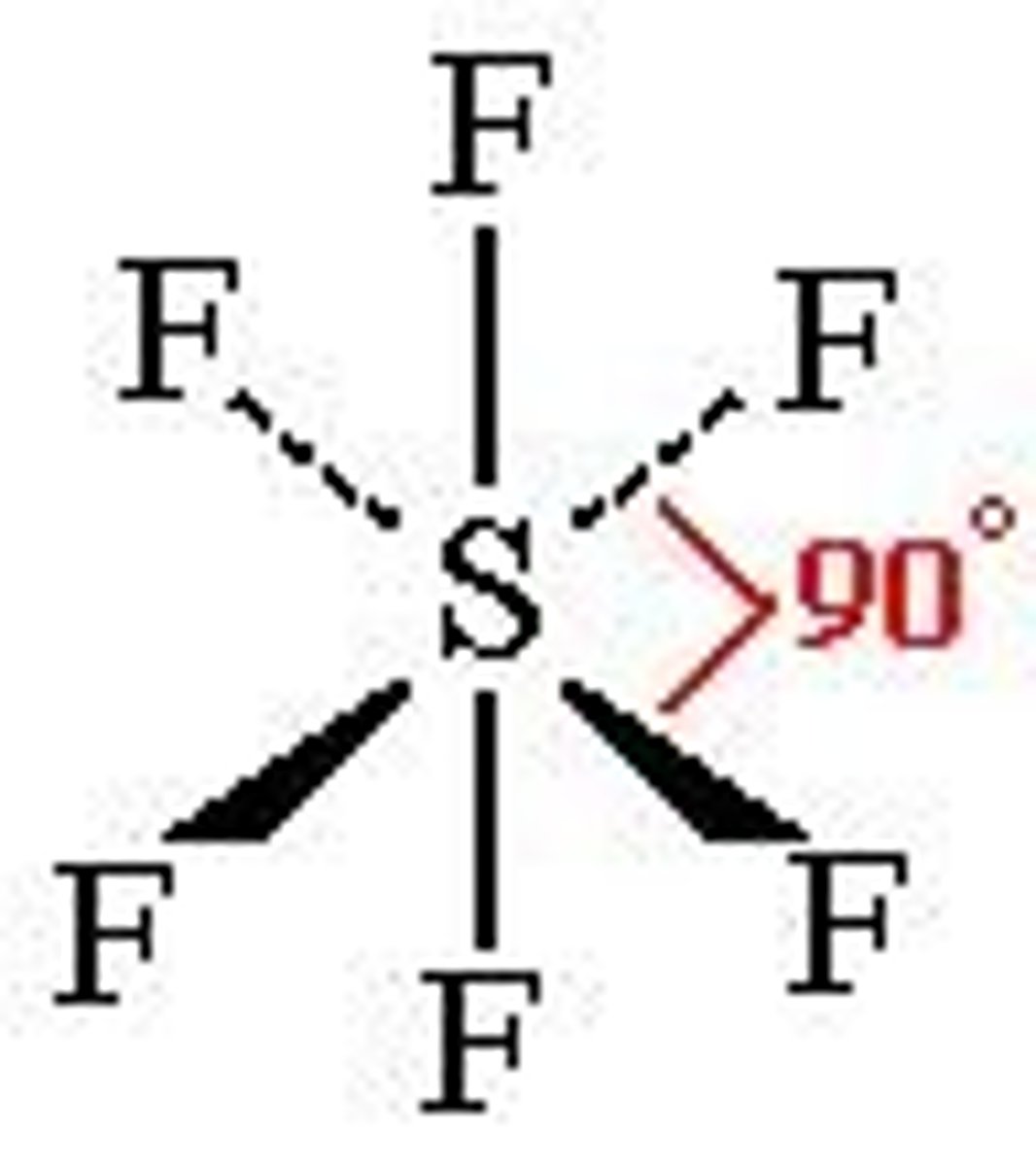
Example of 6 Co-ordinate bond complex
[Fe(H20)6]2+ (hexaaquairon(ii))
Shape and bond angle of 4 Co-ordinate bonds
Tethrahedral, 109.5 degrees.
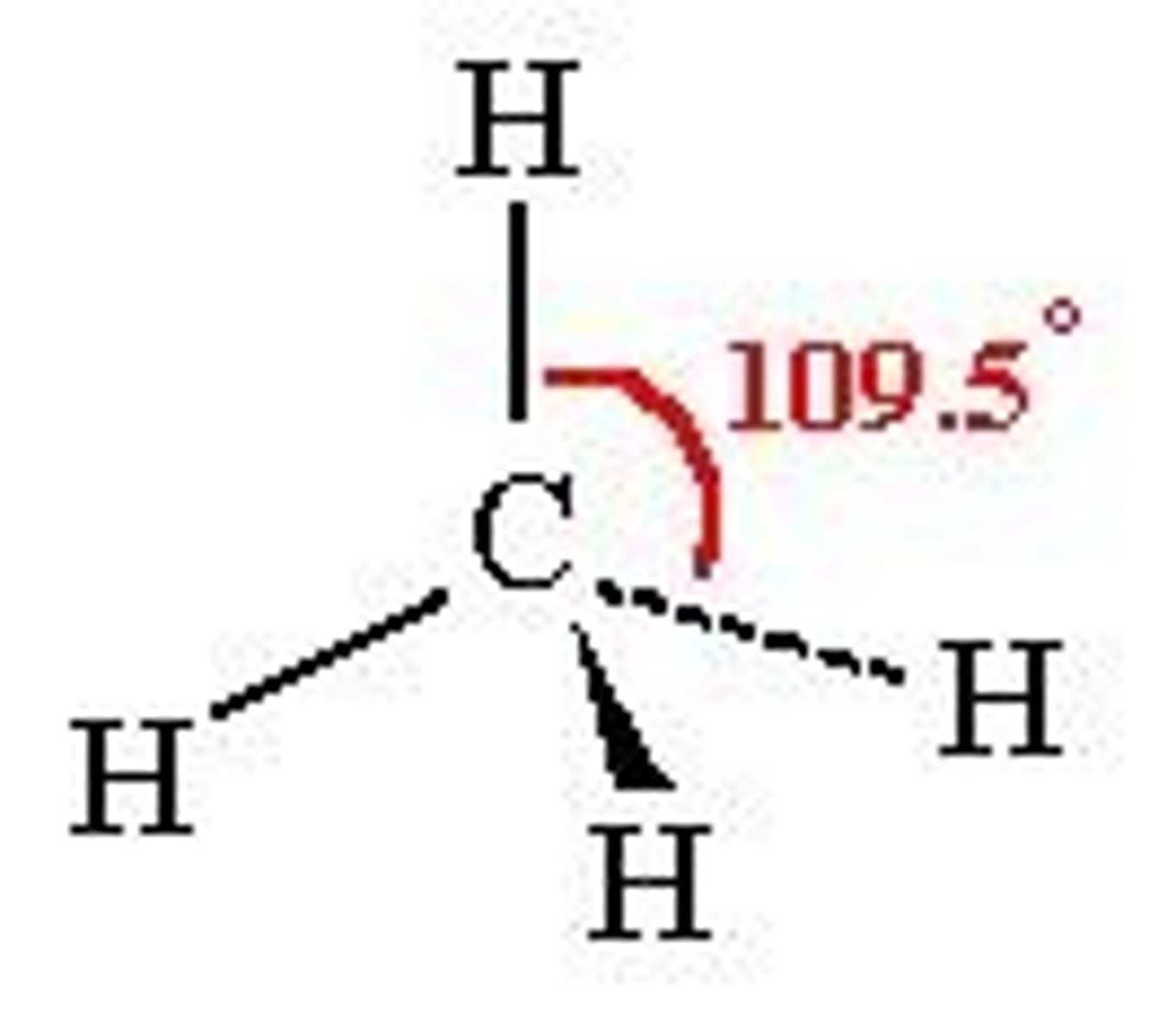
Examples of 4 Co-ordinate bond complex
[CuCl4]2- and [CoCl4]2-
Colour of [CuCl4]2-
Yellow
Colour of [CoCl4]2-
Blue
Ni 2+ and Pt 2+ complexes have 4 co-ordinate bonds with what shape and angle?
Square planar, 90 degrees.
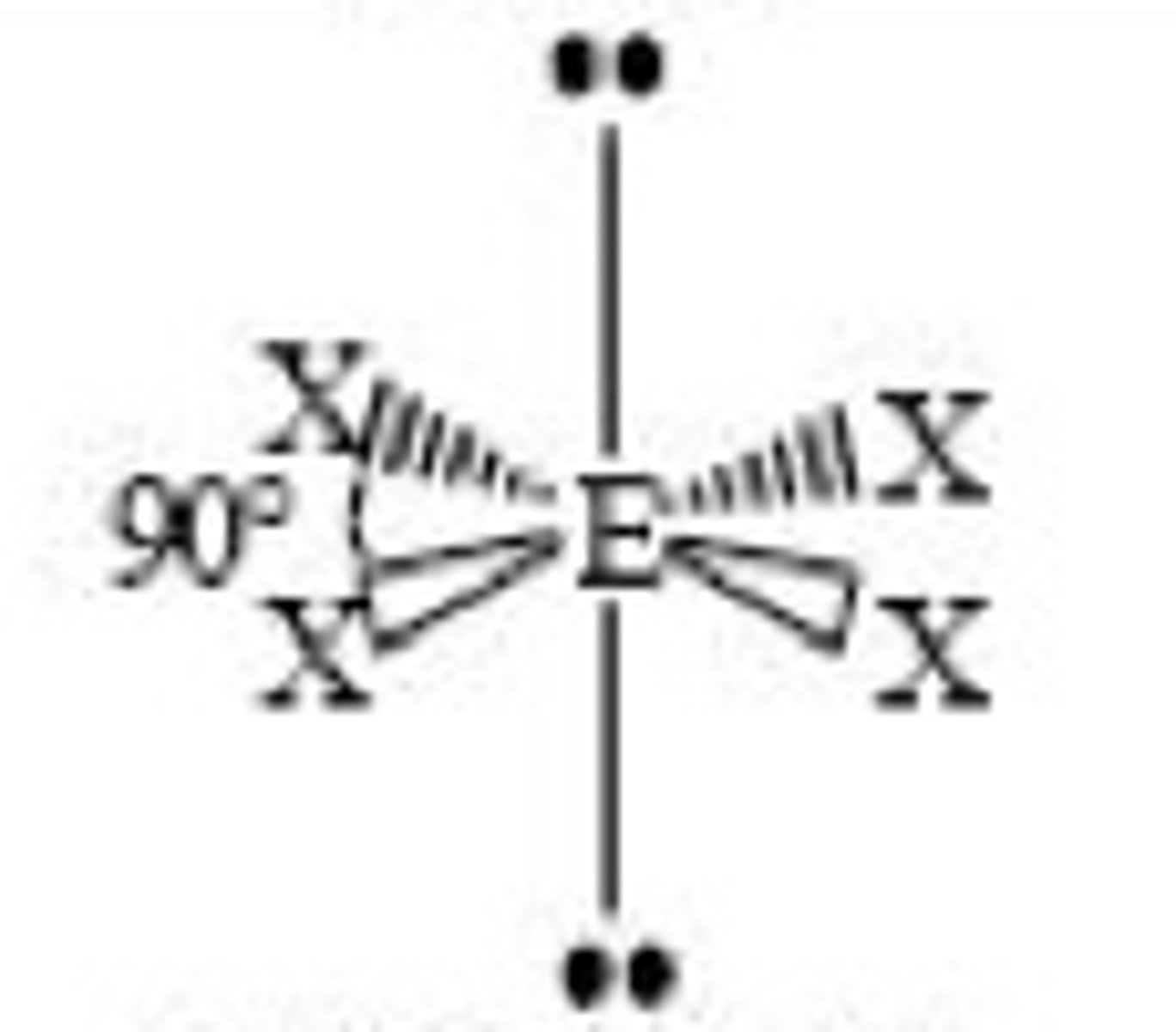
Shape and bond angle of 2 Co-ordinate bonds
Linear, 180 degrees
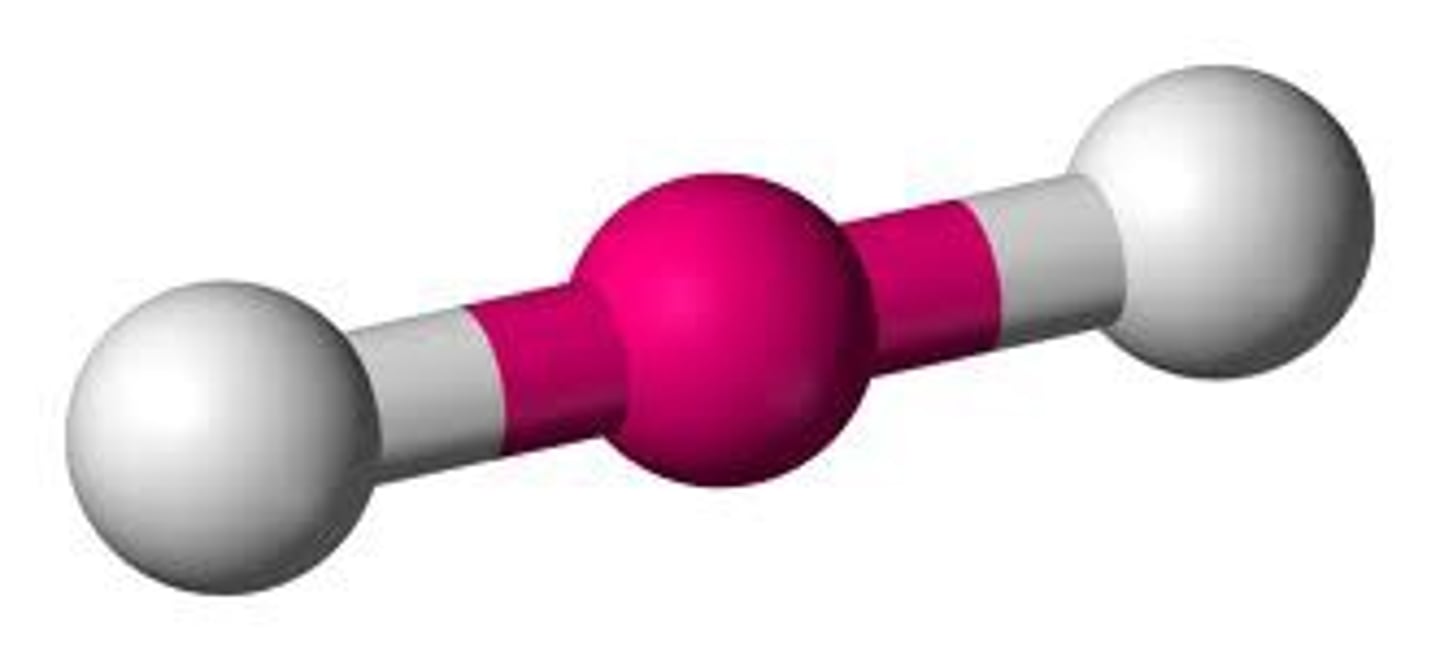
Which complexes have a linear shape?
Ag+ complexes
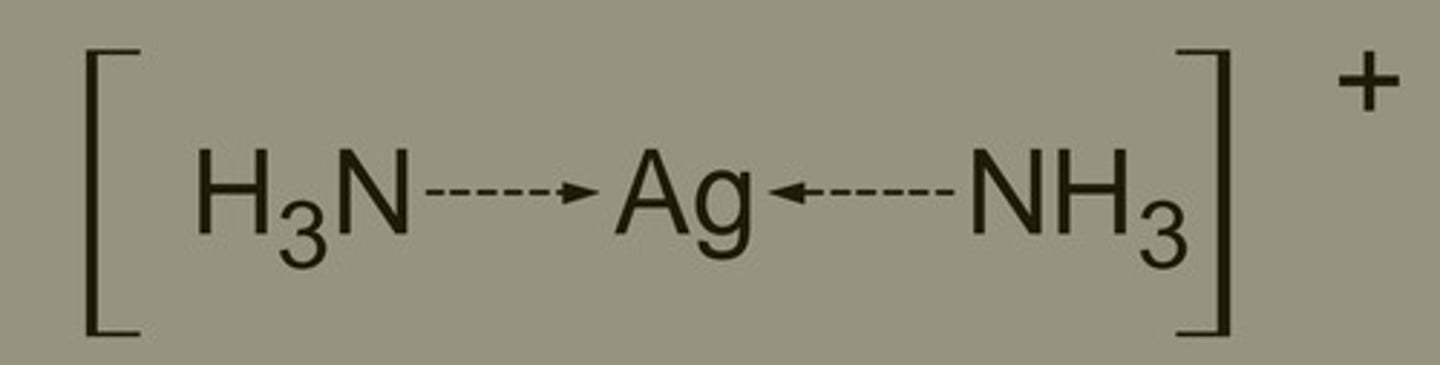
What linear Ag complex is used in Tollens Reagent?
[Ag(NH3)2]+
Working out Oxidation state of metal ion
Total oxidation state - sum of oxidation state of ligands
Monondentate Ligand
Can form 1 Co-ordinate bond
Examples of monodentate ligands
Cl-
OH-
CN-
H2O
NH3
Bidentate ligands
Can form 2 co-ordinate bonds.
Examples of bidentate ligands
NH2CH2CH2NH3 (ethane-1,2-diamine)
[OOCCOO]2- or C2O4 2- (ethanedioate)
3 bidentate ligands showing optical isomerism can form what shape?
Octahedral
Multidentate ligands
More than 2 co-ordinate bonds.
Examples of multidentate ligands
EDTA4-
Haemoglobin
How is oxygen able to travel in the blood with haem?
Oxygen forms co-ordinate bond to Fe(ii) in haemoglobin.
Why is carbon monoxide toxic?
Replaces oxygen that's co-ordinately bonded to fe(ii) in haemoglobin.
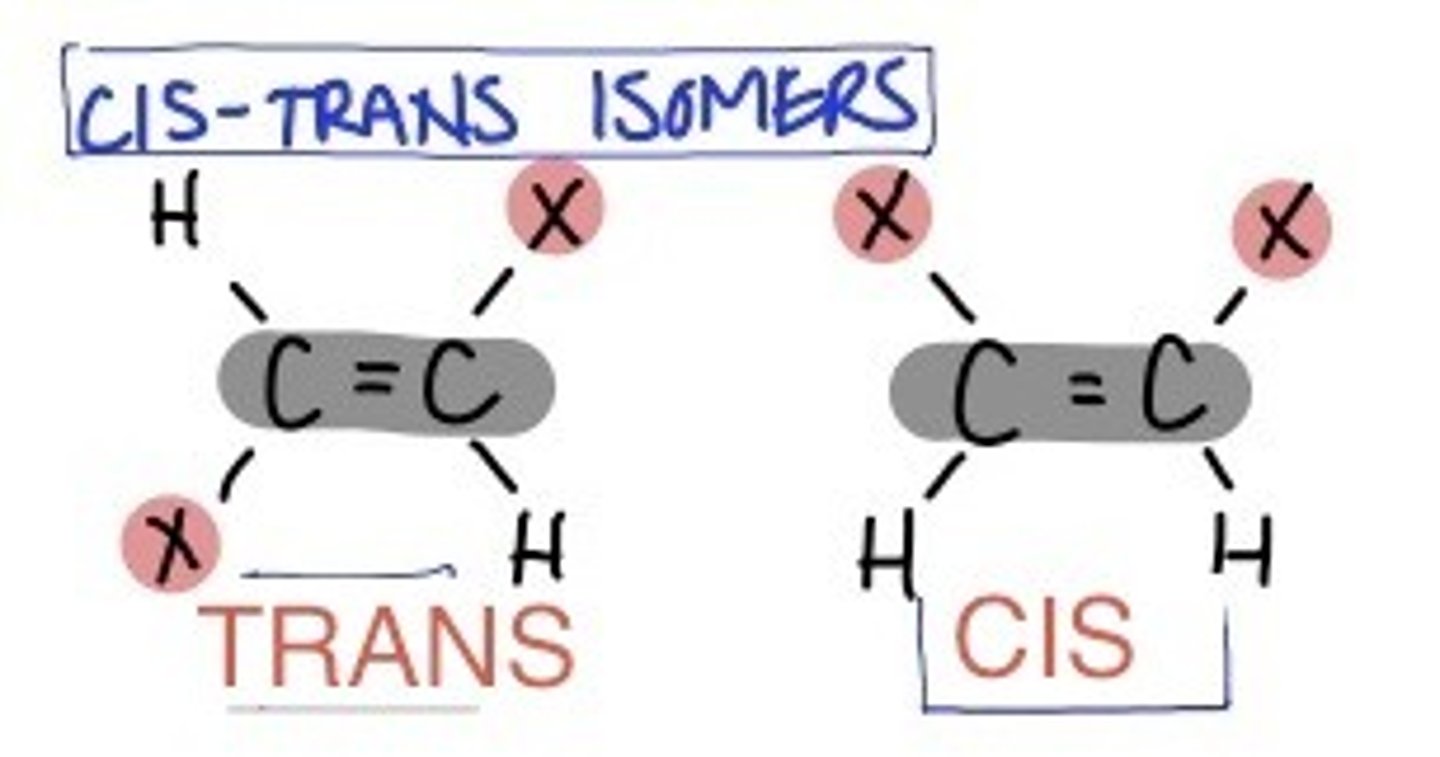
What type of isomerism can octahedral display with monodentate ligands?
Cis/Trans
What type of isomerism can octahedral display with bidentate ligands?
Optical

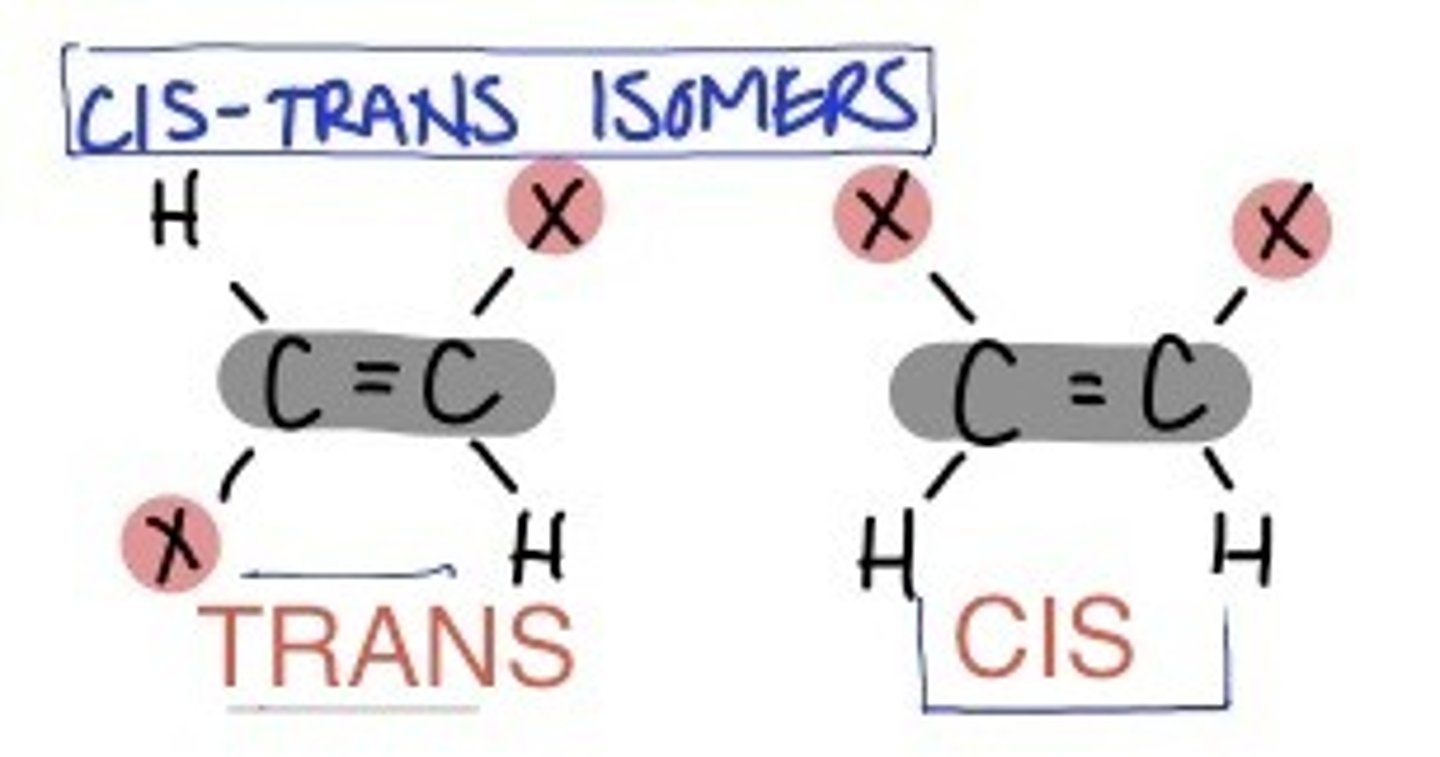
What type of isomerism can square planar complexes display?
Cis/Trans
How does colour arise?
Wavelengths of visible light are absorbed, remaining wavelengths are transmitted/reflected which is the colour we see.
What happens to the 3d orbitals when ligands bond to ions and some orbitals get energy?
3d orbitals split into 2 different energy levels, ground state and excited states.
Which orbitals do electrons tend to occupy, ground or excited?
Ground (lower)
What happens when visible light is absorbed in terms of the d electrons?
D electrons move from ground state to excited state.
How can the energy difference between ground state and excited state of d electrons be given?
ΔE = hv = hc/λ
(difference = Planck's constant 6.63x10-34 J s X frequency of light absorbed Hz = Plancks X speed of light 3.00x10 to the 8 m s-1/wavelength of light absorbed)
The amount of energy needed to make electrons jump depends on what? and why?
Central Metal ion
oxidation state
ligands
co-ordination number as these affect the size of energy gap (or energy difference)
Calibration Curves
Measuring absorbance of known concentrations of solutions and plotting on graph.
What does spectroscopy do?
Determine concentration of solution measuring how much light is absorbed.
Steps of Spectroscopy
1) White light shone through filter that lets through colour absorbed by sample
2) Light passes through sample to colorimeter (calculates absorption of light)
3) More concentrated, more light it will absorb.
Ligand Substitution
One ligand can be swapped for another causing colour change.
Ligands of similar size and same charge like H2O and NH3 means...
Co-ordination number and shape doesn't change (co2+ and cu2+)
Why does Partial/Incomplete Substitution like [Cu(NH3)4(H2O)2] 2+ occur?
Excess of ligand, here ammonia is in excess.
Ligands of different sizes like Cl- means...
Co-ordination number and shape change. (Co2+, Cu2+ and Fe3+)
Ligand substitution reactions can be reversed unless...
New complex ion is much more stable than old one.
Examples of new ligands forming stronger bonds
CN- is stronger than H2O
[Fe(H2O)6]3+ + 6CN- -> [Fe(CN)6]3- + 6H2O
Which form more stable complexes, Multidentate or Monodentate>?
Multidentate
What is the enthalpy change for a ligand substitution reaction; big or small?
Small as strength of co-ordinate bonds forming and breaking is similar.
Chelate Effect
Bidentate and Multidentate ligands replace monodentate ligands increasing number of particles, and entropy and increasing stability.
Why is it difficult to reverse these reactions?
Reversing would cause a decrease in entropy.
What is it called when you switch between oxidation states?
Redox reaction.
How many oxidation states does Vanadium exist in?
4 oxidation states
What are the different oxidation states of vanadium?
+2, +3, +4, +5
V2+
Oxidation State: +2
Colour: Violet
V3+
Oxidation State: +3
Colour: Green
VO^2+
Oxidation State: +4
Colour: Blue
VO 2 ^+
Oxidation State: +5
Colour: Yellow
How is the variable oxidation states of Vanadium from Vanadium(V) to Vanadium(II) formed?
Reducing Vanadium(V) ions or (VO 2 ^+) by zinc in ACIDIC SOLUTION.
Equations showing reduction of Vanadium(V) to Vanadium(II)
2VO2 ^+ + Zn + 4H+ -> 2VO^2+ + Zn2+ + 2H2O
(yellow -> blue)
2VO ^2+ + Zn + 4H+ -> 2V ^3+ + Zn2+ + 2H2O
(blue -> green)
2V^3+ + Zn -> 2V^2+ + Zn2+
(green -> violet)
Redox Potential
How easily an atom/ion is reduced to a lower oxidation state.
What 2 things is redox potential influenced by?
Ligands and pH
How ligands affect redox potential
Aqueous ions will be surrounded by water ligands, different ligands may increase/decrease redox potential depending on how well they bind to metal ion in particular ox state.
How pH affects redox potential
Some ions need H+ in order to be reduced (vanadium(V) to vanadium(II)), others release OH- when reduced. pH affects size of redox potential.
What will redox potentials be in acidic conditions? Large or Small
Larger, making the ion more easily reduced.
Silver being reduced to Silver metal equation
Ag+ + e- -> Ag (s)
(Electrode Potential = +0.80V it is large so can easily be reduced).
What is Tollens Reagent used for?
Distinguish between aldehydes and ketones.
What makes Tollens Reagent?
Ammonia solution and Silver nitrate.
What is the complex ion of Tollens?
[Ag(Nh3)2]+
What happens when it's added to aldehydes?
Reacts to give a silver mirror, aldehyde is oxidised to carboxylic acid, Ag+ reduced to silver metal.
RCHO + 2[Ag(Nh3)2]+ -> RCOO- + 2AG + 4NH3 + 2H2O
Titration equation for Fe2+ and MnO4-
MnO4- + 8H+ + 5Fe ^2+ -> Mn2+ +4H2O + 5Fe3+
Titration equation for C2O4 ^2- and MnO4-
2MnO4- + 16H+ + 5C2O4 ^2- -> Mn2+ + 8H2O + 10CO2
Heterogeneous Catalyst
Is in a different phase (physical state) from the reactants.
Where does the reaction happen on the Heterogeneous Catalyst?
Occurs at the active sites on surface of it.
What do Support Mediums do?
Maximises the surface area of heterogeneous catalyst and minimises cost of reaction (small coating of catalyst needed to give big SA)
Examples of a Heterogeneous Catalyst
- V2O5 in Contact Process to make Sulfuric Acid
- Fe in Haber Process to make Ammonia
Equations of V2O5 in Contact Process
V2O5 + SO2 -> V2O4
V2O4 + 1/2 O2 -> V2O5
Equation of Fe in Haber Process
N2 + 3H2 (Fe->) 2NH3
How do Heterogeneous catalysts work?
They adsorb reactants onto active sites on their surface.
What is catalyst poisoning?
Impurities in the reaction bind to catalyst's surface and block reactants being adsorbed.
What does Catalyst poisoning do to the Surface area and reaction?
Reduces SA and slows reaction.
What does Catalyst poisoning do to the cost?
Increases cost as less product is made in certain time. Catalyst may need regenerating or replacing increasing cost.
Homogeneous Catalyst
Is in the same phase (state) as the reactants.
How do homogeneous catalysts work?
Combine with reactants to form an intermediate species. This then reacts forming products and reforms the catalyst.
Why is variable oxidation states in catalysis important?
Provides an alternative pathway for the reaction lowering activation energy, as Transition Metals can gain/lose electrons within their d orbitals so can transfer electrons to speed up reactions.
Why is the reaction between I- and S2O8 2- slow?
Both ions are negatively charged which means they repel and so has a high activation energy.
What is the overall equation between I- and S2O8 2-?
S2O8 2- + 2I- -> I2 + 2SO4 2- (all aq)
What homogeneous catalyst is used in the I- and S2O8 2- reaction?
Fe 2+
Why does Fe2+ speed up the reaction between I- and S2O8 2-?
There is a positive and negative ion at each stage of the reaction so no repulsion.
Using equations explain how Fe2+ ions catalyses the reaction of I- and S2O8 2
# S2O8 2- + 2Fe 2+ -> 2Fe 3+ + 2SO4 2- (all aq) (the fe2+ ions are oxidised to fe3+ by S2O8 2-)
# 2Fe 3+ + 2I- -> I2 + 2Fe 2+ (all aq)
(the intermediate fe3+ easily oxidise I- to I2, and regenerate the catalyst)
Autocatalysis
It's when a product catalyses the reaction.
Why is the homogeneous catalyst Mn2+ in the reaction between C2O4 2- and MnO4- an autocatalysis reaction?
Mn2+ is the product and acts as a catalyst, so as reaction progresses and amount of product increases, reaction speeds up.
What is the overall equation for the reaction of C2O4 2- and MnO4- with Mn2+ catalyst?
2MnO4 - + 16H+ + 5C2O4 2- -> 2Mn 2+ + 8H20 + 10CO2
Using equations explain how Mn2+ ions catalyses the reaction of C2O4 2- and MnO4-
# MnO4- + 4Mn2+ + 8H+ -> 5Mn3+ + 4H2O
(Mn2+ catalyses by reacting with MnO4-)
# 2Mn3+ + C2O4 2- -> 2Mn 2+ + 2CO2 (Mn3+ reacts with C2O4 2- to form CO2 and Mn2+ catalyst)