Mass Spectrometry
1/47
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
What is the challenge with ion sources in mass spectrometry?
Creating gaseous ions
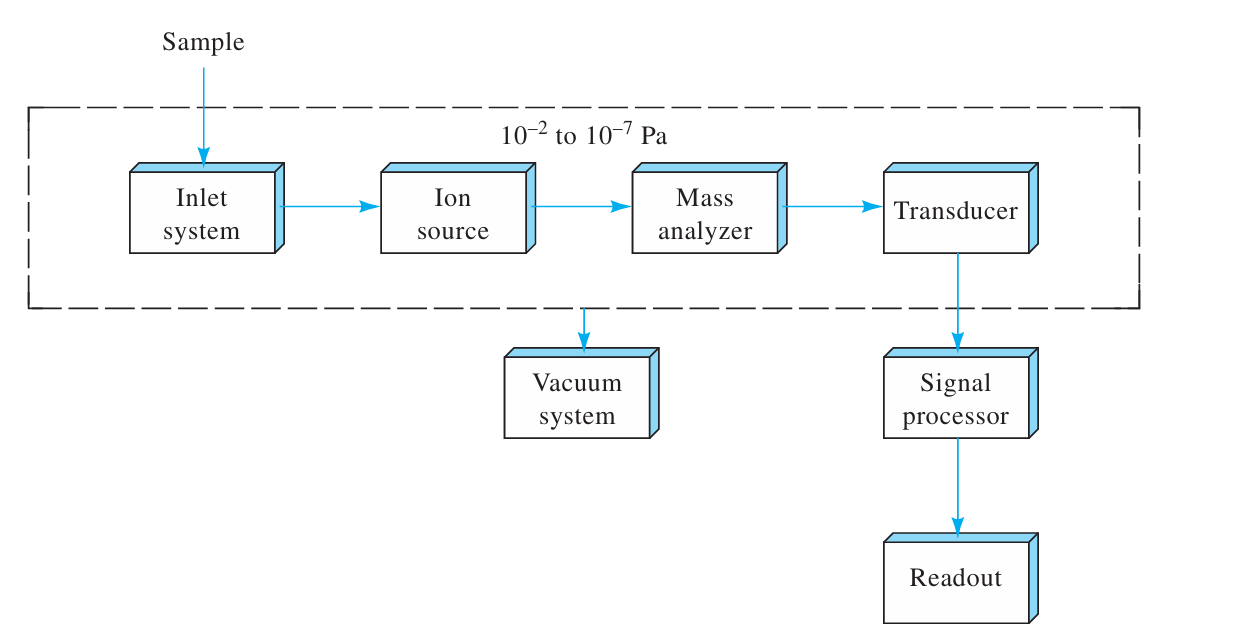
Draw a diagram of the parts of a basic molecular mass spectrometer
Hard vs. Soft Ion Sources
Hard sources: impart high energy (apply a force over a period of time resulting in a change in momentum of the ion) causing fragmentation and producing ions with lower mass-to-charge ratios
Soft Sources: produce minimal fragmentation, resulting in spectra primarily featuring the molecular ion peak
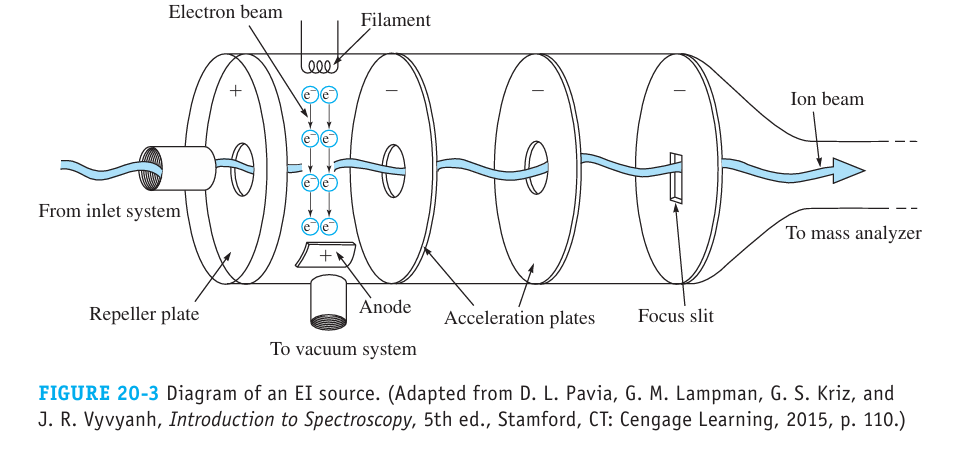
What is Electron Ionization (EI)?
An electron beam is emitted by a hot filament and accelerated to ~ 70 eV (by applying approximately 20 V between the filament and the anode)
The beam intersect the gaseous sample molecules and ionizes them
m + e- → m+ + 2e-
Where m represents an analyte molecule and m+ is the analyte’s molecular ion
low efficiency, very extensive fragmentation since 70 eV >> band energy, but pattern is characteristic of molecule
Fragmentations reduce the intensity of the M+ peak and make the quantification difficult, but the pattern is specific to a molecule and can be compared to databases for identification
What does the 'M+' represent in mass spectrometry?
The analyte's molecular ion
Where is low pressure required in the mass spectrometer and why is it necessary?
Low pressure is required in all of the components of the mass spectrometer except the signal processor and readout
Low pressure (high vacuum) ensures infrequent collisions with atmospheric components in the mass spectrometer and allow the production and manipulation of free ions and electrons
What is the purpose of the Inlet System in MS?
To introduce a very small amount of sample into the MS, where its components are converted to gaseous ions
What is the purpose of the Ion Source in MS?
To convert the components of a sample into gas-phase ions. The output is a stream of + or - ions (more commonly +) that are then accelerated into the mass analyzer
In many cases, the inlet system and the ion source are combined into a single component
What is the purpose of the Mass Analyzer in MS?
To disperse ions according to their mass-to-charge ratios
Analogous to how a grating in an optical spectrometer disperses light
What does the Ion Transducer do in MS?
To convert the beam of ions into an electrical signal that can be processed and stored in the memory of a computer
most common transducer is the Electron Multiplier
Resolution in Mass Spectrometry
The capability of mass spectrometers to differentiate between masses

What is Chemical Ionization and its purpose?
A technique that adds reagent gas to EI to create additional ions that can react with the analyte, reducing fragmentation
Can be selective toward certain analytes
Give chemical equations showing how Chemical Ionization creates many reagent molecules:
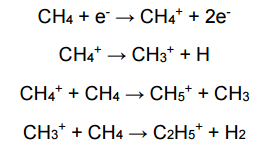
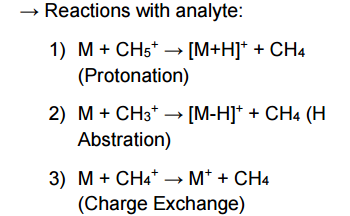
Give the chemical equations showing the reaction of reagent molecules with the analyte in Chemical Ionization:
Electrospray ionization
A solution of the charged analytes are pumped through a sharp tip held at 1-3 [kV] (to create the charged particles)
This produces small, charged droplets in the desolvating capillary (where evaporation of the solvent and attachment of charge to the analyte molecules take place) and yield mostly intact ions
![<ul><li><p>A solution of the charged analytes are pumped through a sharp tip held at 1-3 [kV] (to create the charged particles)</p></li><li><p>This produces small, charged droplets in the desolvating capillary (where evaporation of the solvent and attachment of charge to the analyte molecules take place) and yield mostly intact ions </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/98c62642-e8a2-4951-833c-55b73eb20566.png)
What type of molecules is Electrospray Ionization used for?
Soluble molecules that can be charged in solution
For example, amino acids, peptides, and proteins.
What is the basic principle of Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization (MALDI)?
The analyte is mixed with a radiation absorbing matrix and evaporated with a laser (commonly a nitrogen laser ~ 337 [nm])
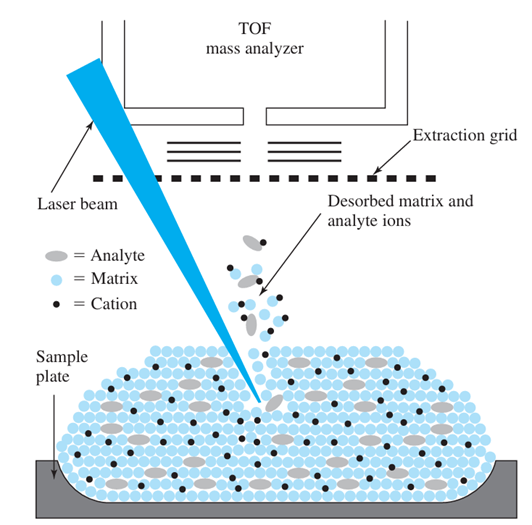
What type of molecules is Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization (MALDI) used for?
Insoluble molecules like proteins or polymers
What does Time-of-flight Analyzer do in mass spectrometry?
Accelerates ions using an electric field (Vs), measuring their different arrival times based on mass.
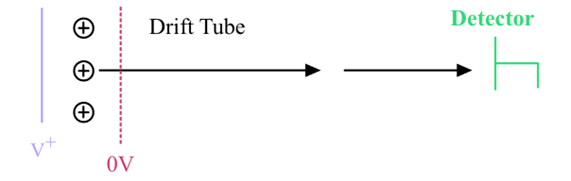
Calculation of arrival times at the detector for different masses in a Time-of-Flight Analyzer:
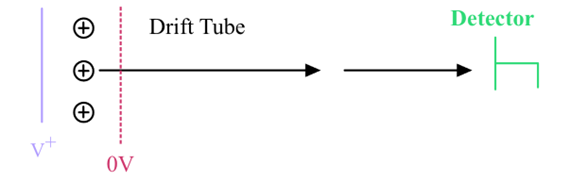
» Note: Vs = ½ V+ if the ions start in the middle of the plate and grid
Potential Energy from E field = kinetic energy in the drift tube
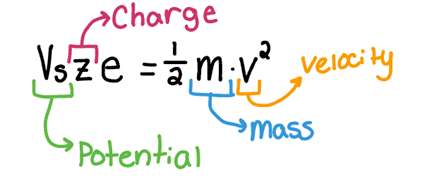
All masses will have the same kinetic energy but different velocities
Different masses will have different arrival times at the detector
v=\sqrt{\frac{\left(2Vs\cdot z\cdot e\right)}{m}}
tA=L/V where L is the length of the drift tube
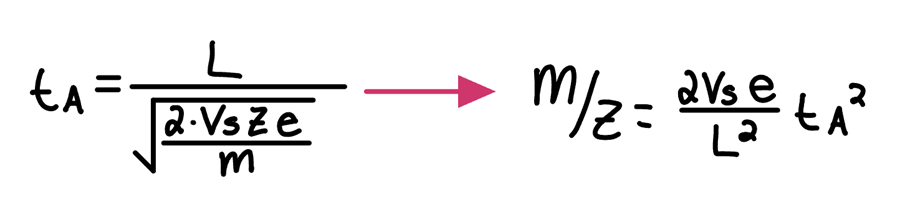
What are the pros and cons of Time-of-Flight analyzers?
Pros: Simple design, cheap.
Cons:
Requires large footprint for drift tube
Fast detector (~ns)
Limited resolution
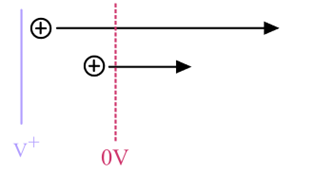
What are the limiting factors for resolution in Time of Flight Analyzers?
i) Different initial positions lead to different kinetic energy
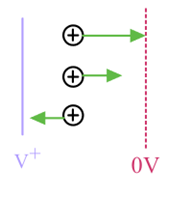
ii) Spread in initial kinetic energy from thermal velocity leads to spread in arrival times
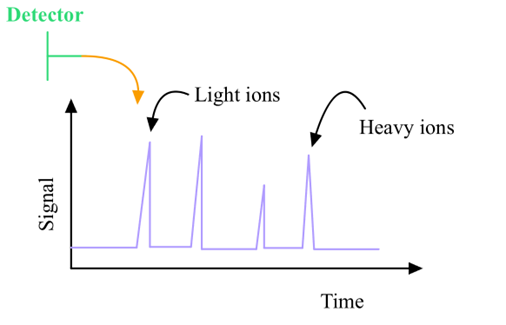
Time-of-Flight Analyzer signal vs. time graph:
What is the purpose of a Reflection (ion mirror) in mass spectrometry?
To increase travel length of ions with more kinetic energy such that they have the same arrival time as the slowest ions (R>10,000)
Requires a very fast response time to separate small differences in arrival time
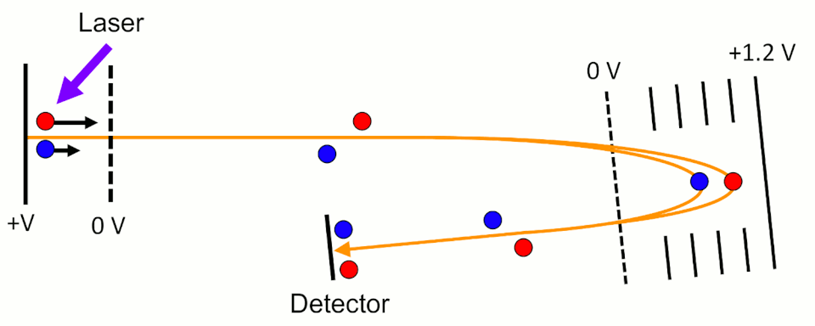
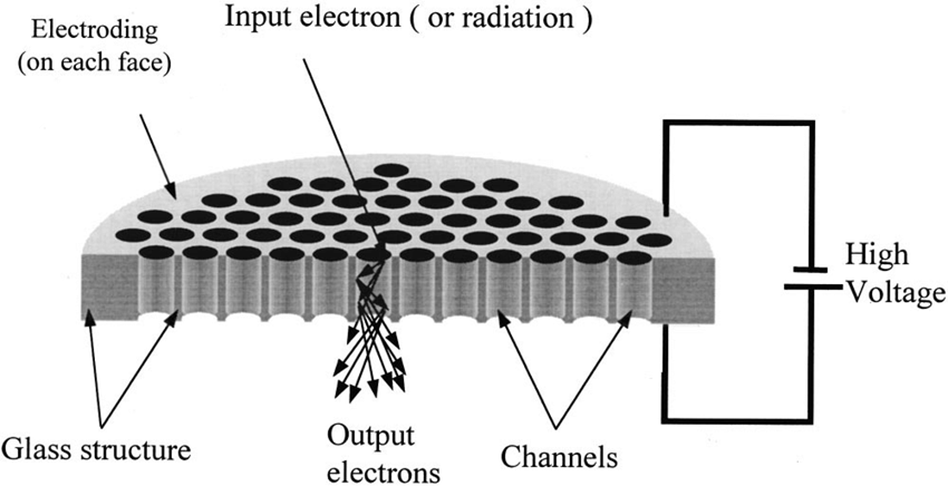
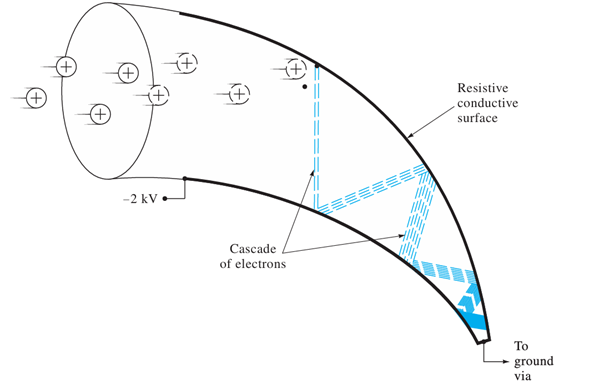
What is the role of Multichannel Plates (MCP) in detection?
Creates an electron cascade per ion, offering high gain and fast response time.
Gain ~ 106 e- per ion
Response time ~ 0.5 ns
Requires ADC with sampling > 1 GHz
What does a Quadrupole Mass Filter do?
Filters ions based on their m/z ratio using AC and DC fields created by four parallel rods
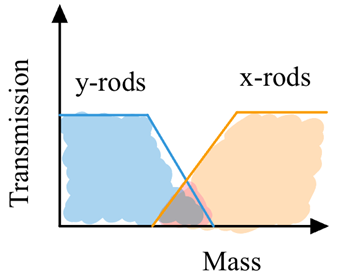
only a narrow range of m/z can pass through
Band pass filter for ions
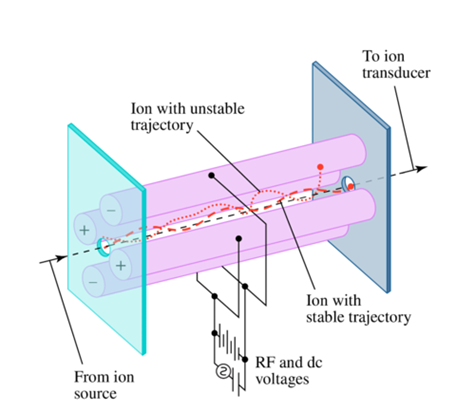
How does the Quadruple Mass Filter work?
AC voltage is applied to pairs of rods
The alternating AC voltage attracts and repels ions between the rods; ions that react too much will oscillate and hit the rod.
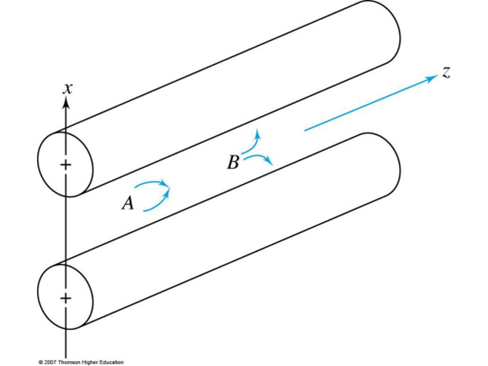
In addition to the AC Voltage, a DC voltage is applied between each pair
x-rods: + V DC voltage = high mass pass filter
y-rods: -V DC voltage = low mass pass filter
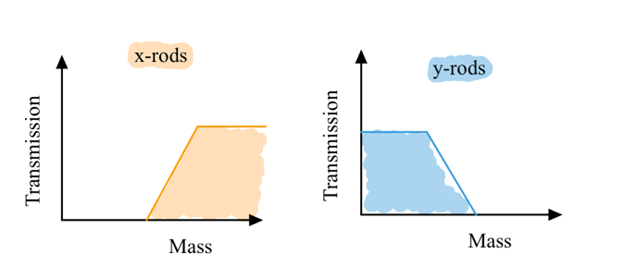
Only a small range of m/z are stable in both axis
Motion in QMF:
Motion is described in terms of (unitless) a and q
r0 and ω are fixed parameters
U and V are adjustable
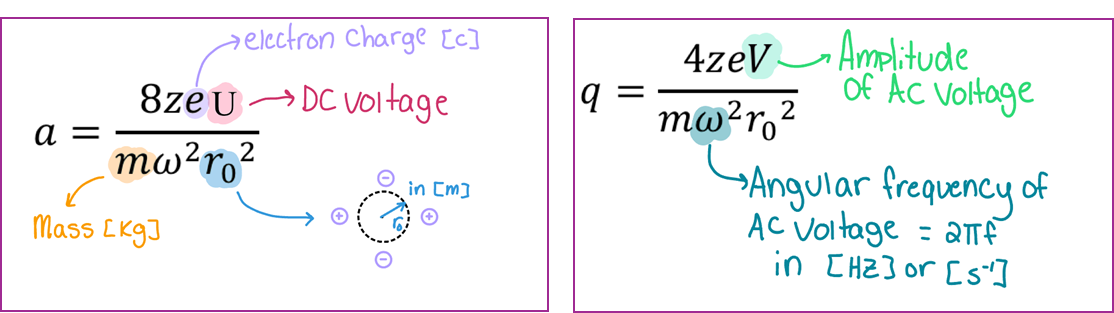
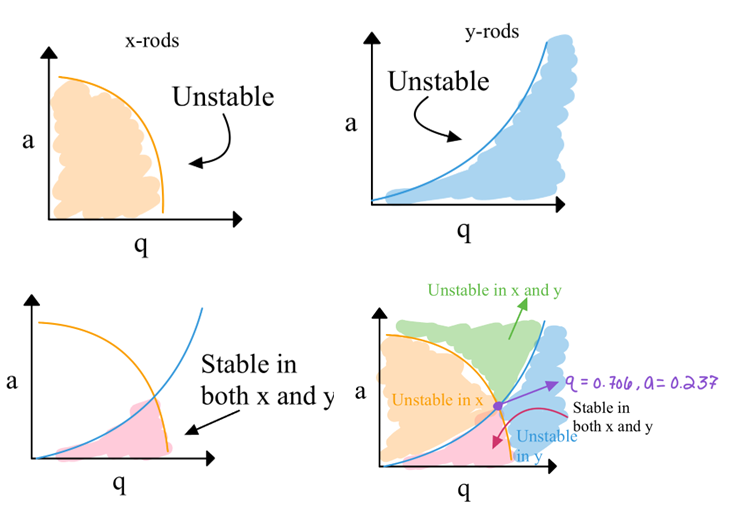
Stability diagrams in terms of a and q for QMF
Stability diagrams in terms of U and V for QMF
We can plot the stability diagram in terms of U and V for different m/z:
Each mass has a slightly different stable region in U and V
The apex of the stability diagram is the most specific region for a given mass
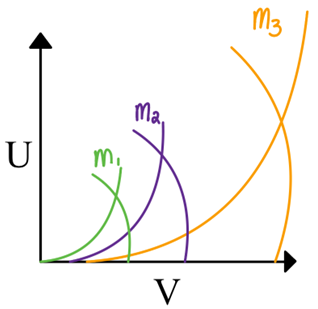
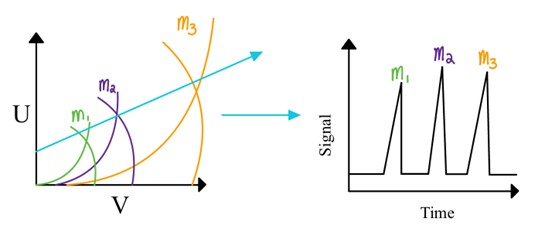
How do we get a mass spectrum from a QMF?
Scan U and V together through the apex of multiple m/z regions
Scanning a broad range of mass in small increments can be slow (several seconds
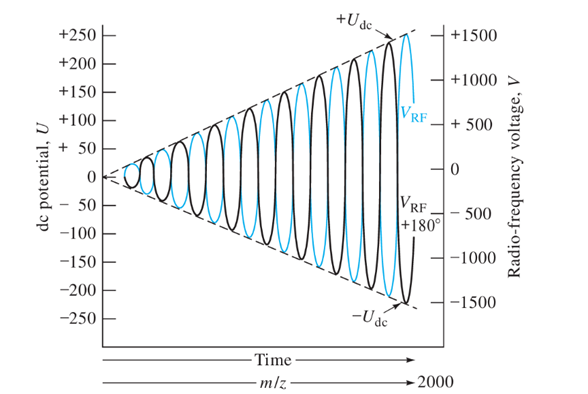
Resolution in QMF
Resolution depends on how close to the apex the scan line is
Higher resolution = lower transmission and signal; meaning a large m/z requires a large DC and high amplitude AC voltage
Small mass range limits resolution
What are the limitations of a Quadrupole Mass Filter?
One mass can be processed at a time (limited resolution, R<100) and limited mass range
Detector for QMF:
Dynode Electron Multiplier
Same electron cascade multiplication as MCP
Cons: Slower response time than MCP (not critical for QMF)
Pros: Simple design and can operate at higher pressure, cheaper instrument
How does Tandem Mass Spectrometry enhance analysis?
Uses multiple QMFs to analyze ion fragments, providing information about molecular structure
QMF 1 — Selects particular m/z
QMF 2 — Collision cell to fragment the ions
QMF 3 — Scan to get the mass of all the fragments
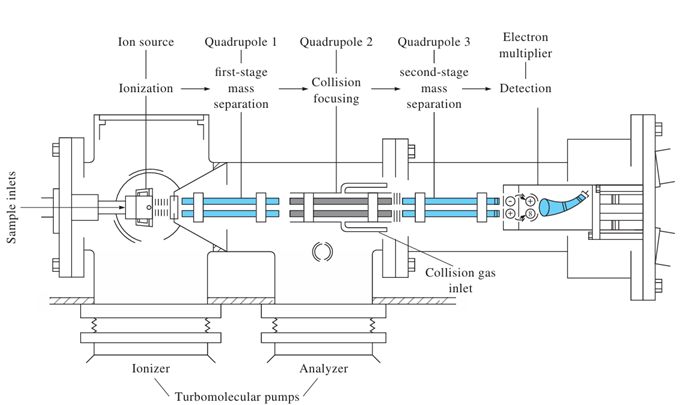
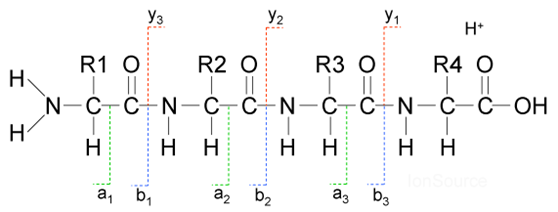
What are the steps for protein sequencing in Tandem Mass Spectrometry?
Trypsin digestion to cut protein at the lysine/arginine site
Use LC-MS to separate the resulting peptides
In the MS, isolate the mass corresponding to the intact peptide
Perform CID, and measure the mass of all the fragments
Mass of fragment yields the amino acid composition. Sequence can be determined if enough fragments are measured.
Advantages and disadvantages of FT-ICR
Advantages:
1) Longer acquisition time = higher resolution in frequency and m/z
2) Higher magnetic field (B) = higher frequency and therefore shorter time is necessary to achieve high resolution
R >1,000,000
Disadvantages:
1) Complex and expensive instrument
What does Ion Cyclotron Resonance MS (FT-ICR) utilize for operation?
Utilizes ion motion in a strong magnetic field to measure frequency of rotation.
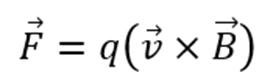
Ions have circular motion in a magnetic field
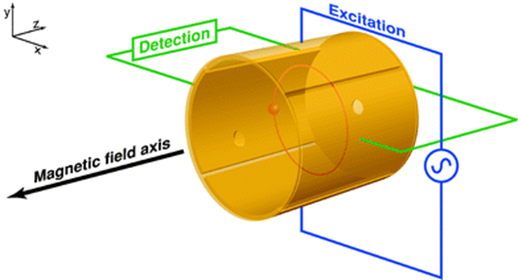
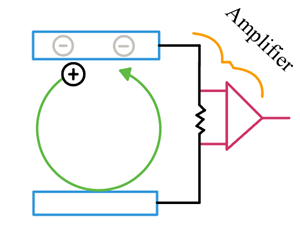
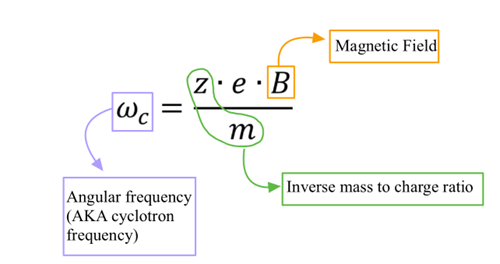
Equation for Angular Frequency (AKA Cyclotron frequency) in FT-ICR
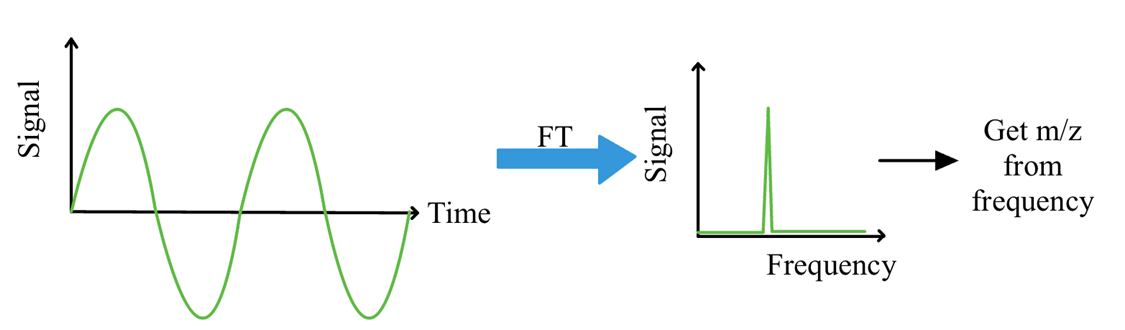
Detection in FT-ICR
Need a non-destructive detection method to measure the frequency of rotation
Image charge in opposite plate is detected with sensitive amplifier → gives signal as a function of time then Fourier Transform it and it will give you a frequency that you can get a m/z
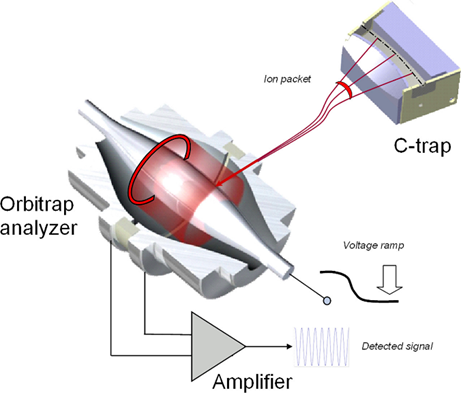
What is the key feature of FTMS-Orbitrap?
Achieves FT-MS without a large, expensive magnet; instead precise machine electrodes create rotation without an electric field
Recent advancement
R ≈ 100,000-1,000,000 (cost vs. resolution choice)
Why do different masses have different arrival times in Time-of-Flight analysis?
Because they have different velocities when accelerated in the electric field.
What is the purpose of applying both AC and DC voltages in a Quadrupole Mass Filter?
To create a band-pass filter for specific m/z ratios.
What is a critical limitation when scanning for high resolution in QMF?
Higher resolution leads to lower transmission and signal.
What role does the electron cascade play in Multichannel Plates?
Provides amplification of the ion signal by creating multiple electrons per hit.
What is a defining feature of reflection in a mass spectrometer?
Increases the effective travel path to enhance resolution.
What are the detector requirements for efficient mass spectrometry?
Fast response time and capable of handling high-pressure operations.