Chromosomal Abnormalities / Genetics & Disease / Cancer Genetics
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Single gene disorders examples
cystic fibrosis, albinism, sickle cell disease, galactosemia, etc (100% genetic)
familial aggregration
if disease has genetic component, then may cluster in families
higher the relative risk for disease
the stronger the genetic component
multifactoral diseases
genetics + environment…diabetes, schizophrenia, cancer, etc.
Chromosomal abnormalities
changes in # of chromosomes…missing or extra
OR rearrangements (# doesn’t change, PIECES change)…duplication, deletion, inversion, translocation
Aneuploidy
2n +- x chromosomes…gain or loss of 1 or more chromosome but not a complete set…can be monosomy, disomy, trisomy, tetrasomy, pentasomy, etc.

Euploidy
multiples of (n)…change in # of haploid chromosome sets…entire SET of chromosomes change, excess or lack of entire set of chromosomes…Diploidy (2n), polyploidy, triploidy, tetraploidy, pentaploidy

Causes of aneuploidy
random error during production of gametes called non-disjunction
Non-disjunction
paired homologs fail to ‘disjoin’ during segregation…can occur in both Anaphase 1 or 2 with different final results
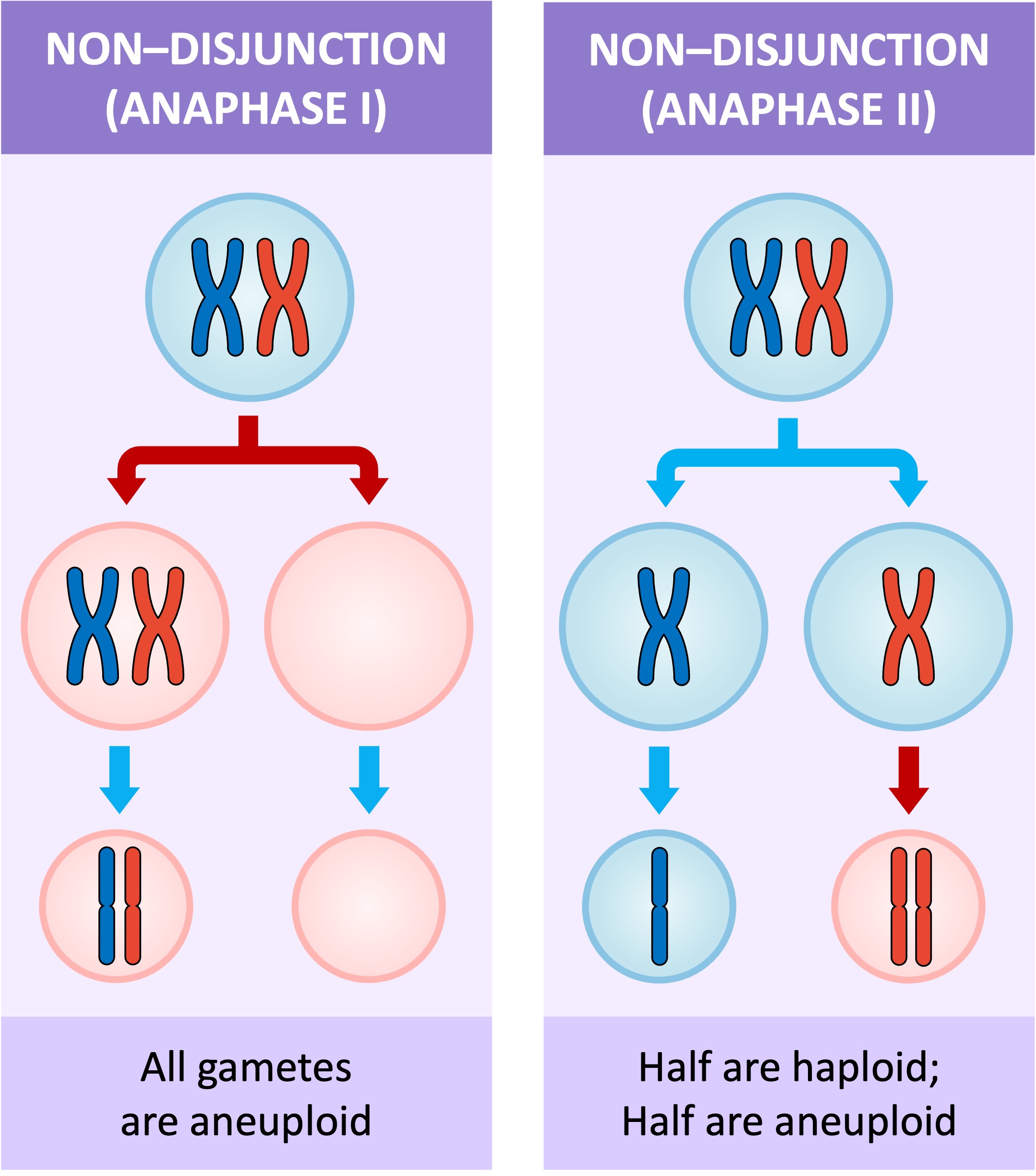
Monosomy
Lack of 1 chromosome (2n-1)…NOT tolerated in humans b/c only 1 copy of gene (instead of 2)…haploinsufiency= inadequate function, exposes hidden defects…potential lethal recessive alleles
Y Chromosome
determines maleness, void of essential genes…older men losing Y chromosome = it’s okay!!
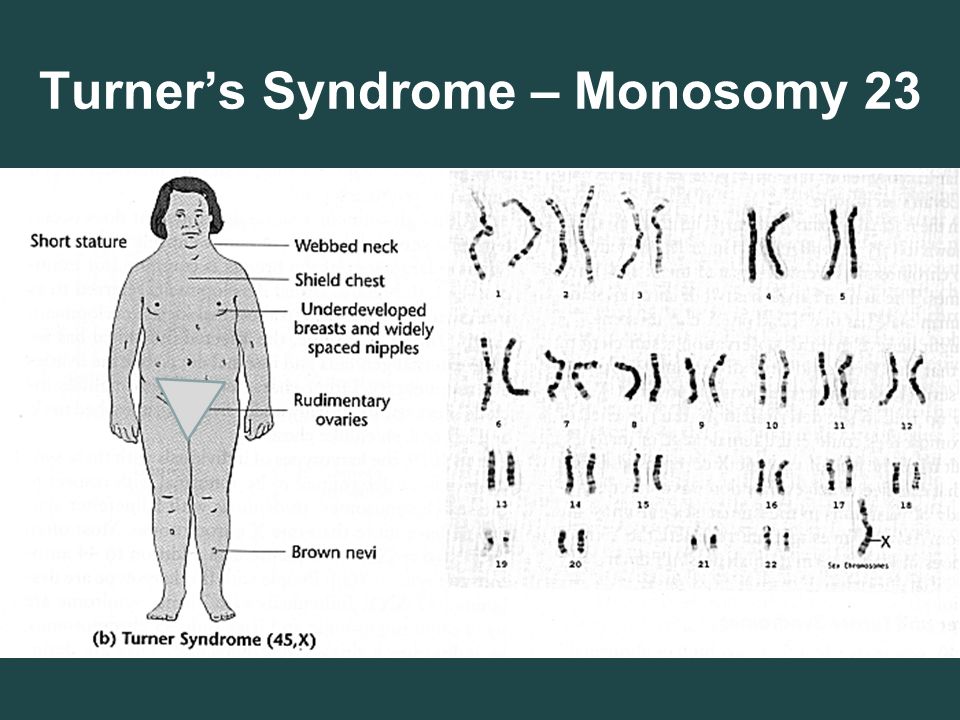
Syndromes associated with monosomy
Turner Syndrome…1 X…underdeveloped ovaries…females
Trisomy
Extra chromosome (2n+1)
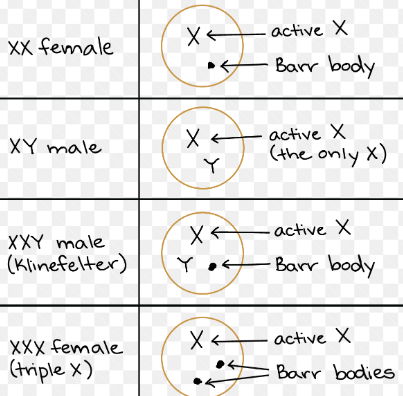
X inactivation
genes in 1 X adapted to function as 1 copy…1 X is inactivated —> Barr Body (if females had 2 active Xs, then 2x genes than males…no)
Chromosomal Rearrangements
spontaneous or environmental DNA breaks occur constantly…sometimes not repaired = rearrangements —> Duplication, deletion, inversion, translocation
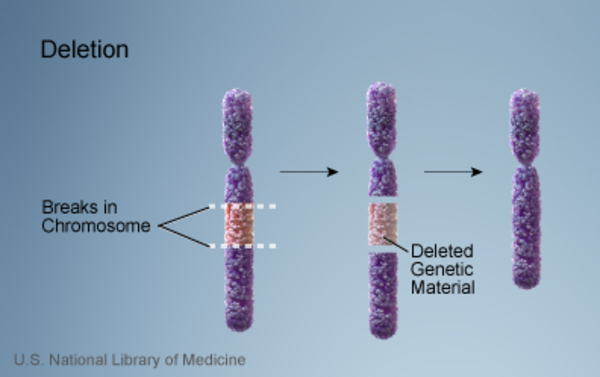
Deletions
missing region in chromosome…only tolerated when small…Ex. Cri-du-chat syndrome
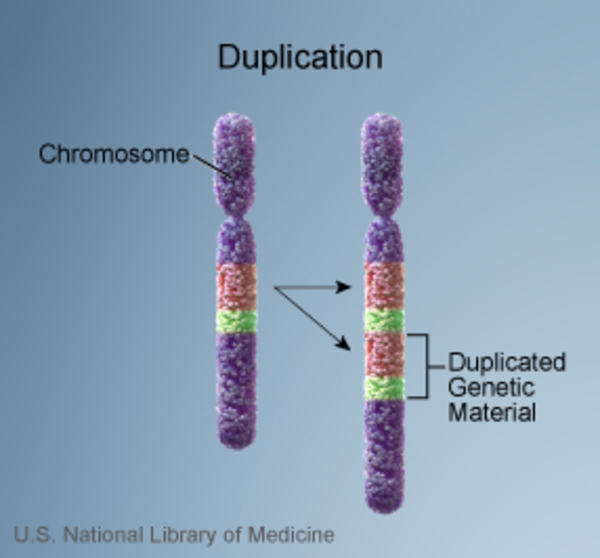
Duplications
repeated region in chromosome…Ex. Charcot-Marie Tooth
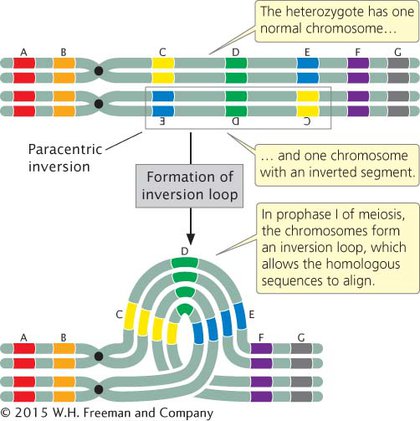
Inversions
segment of chromosome turned 180 degrees…no loss of genetic material :)
pericentric
inverted segment contains centromere
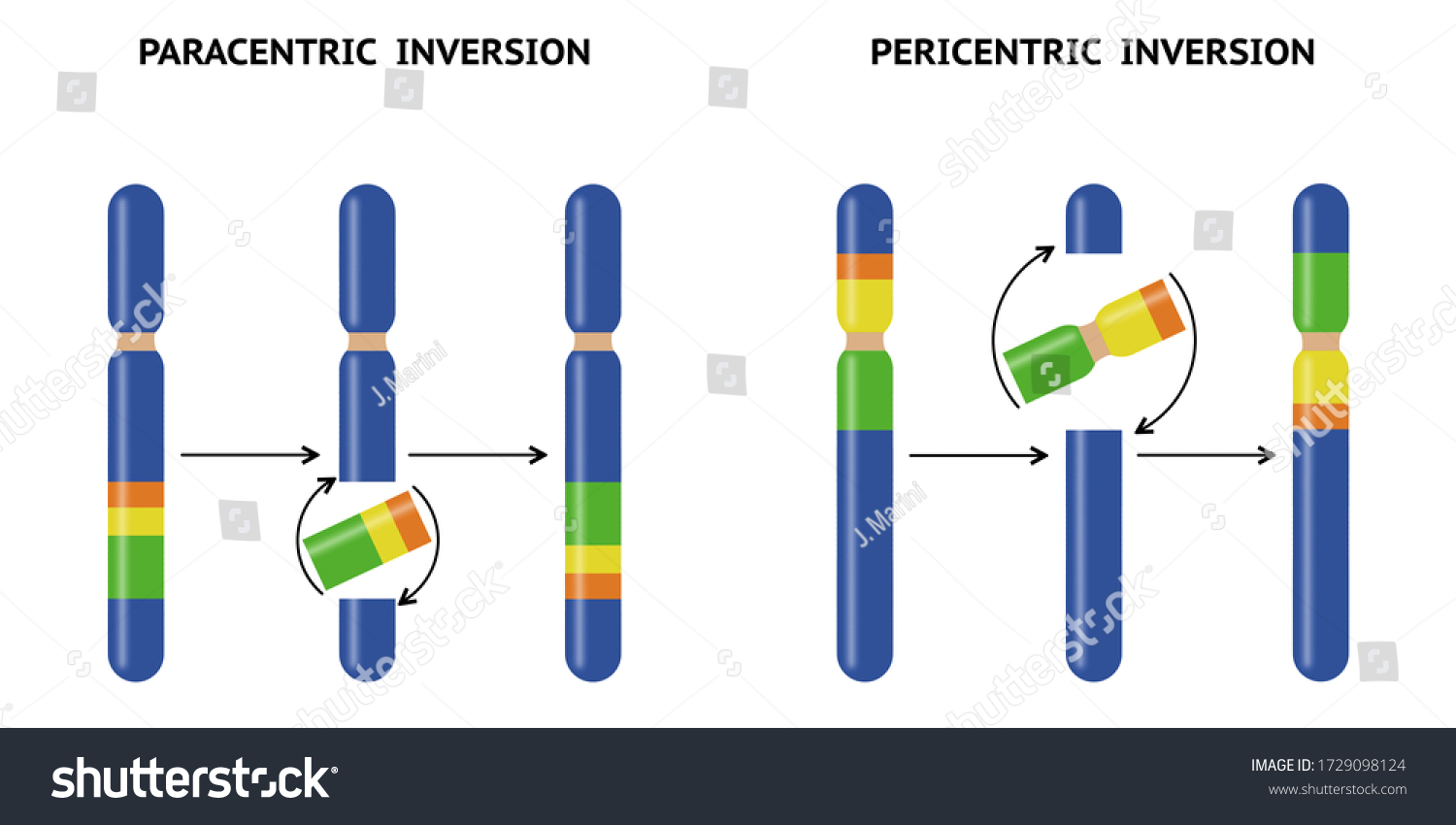
paracentric
segment does not contain centromere
Risk of inversions
reduced fertility…non-viable offspring
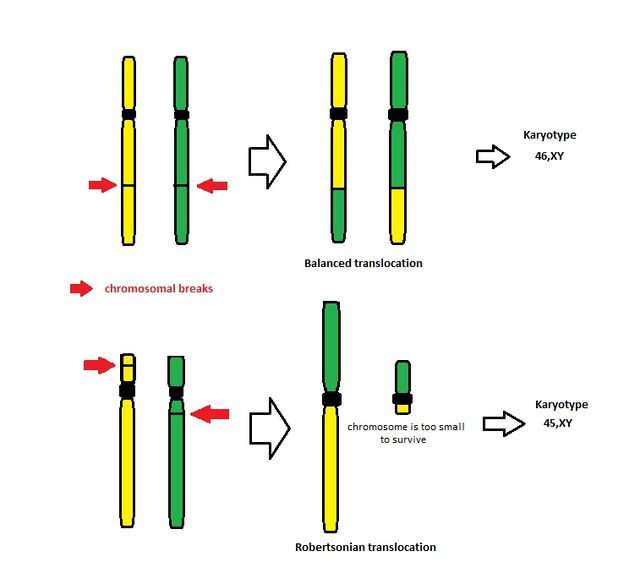
Translocations
relocation of chromosome fragments…reciprocal & robertsonian
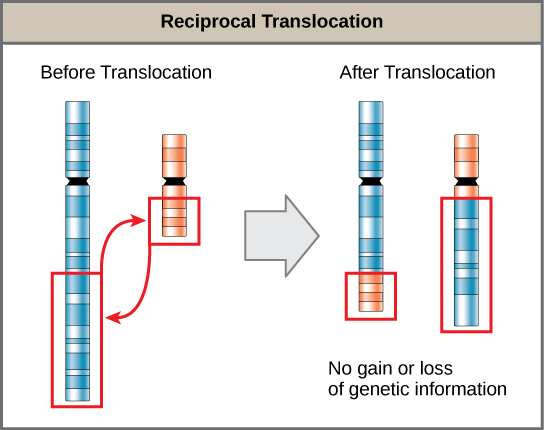
reciprocal translocation
exchange of genetic material between 2 chromosomes…if genetic info not lost = balanced translocation
Risk of translocation
EVEN IF BALANCED!!! break can disrupt important genes/create gene fusions…fertility issues, gametes with loss/duplication of genetic info —> non-viable offspring even if no loss of genetic info (Ex. two centromeres on 1 chromosome)
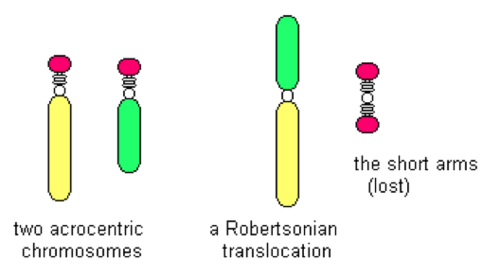
Robertsonian translocations
genetic exchange between acrocentric chromosomes (long arm & tiny arm)…loses genetic material but not important info
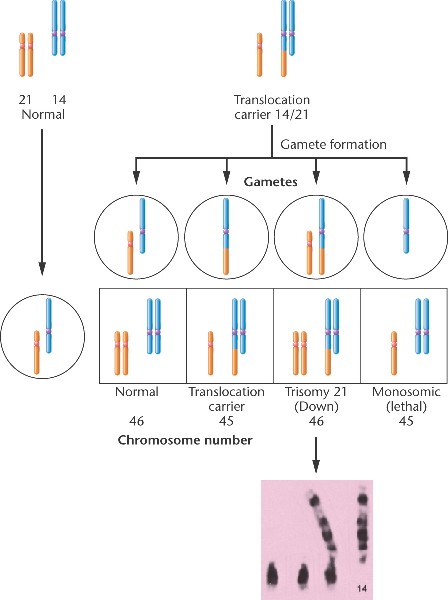
Familial down syndrome
caused by robertsonian translocation between 14 and 21…family passes down translocation…5% of down syndrome…
Non-familial down syndrome
caused by an extra copy of chromosome 21 due to nondisjunction during meiosis in mom…95% of Down syndrome
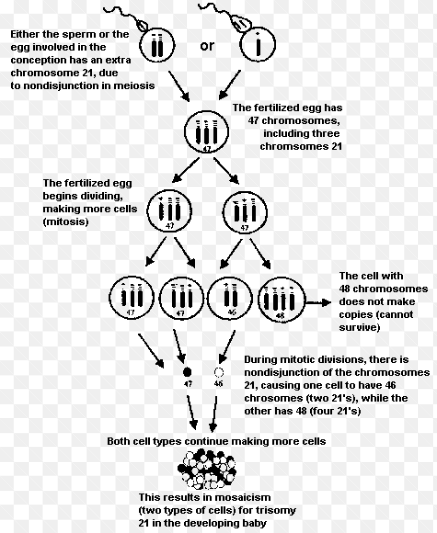
triplet expansion
multiple repeats of triplet nucleotide leading to genetic disorders…Ex. Huntington's disease
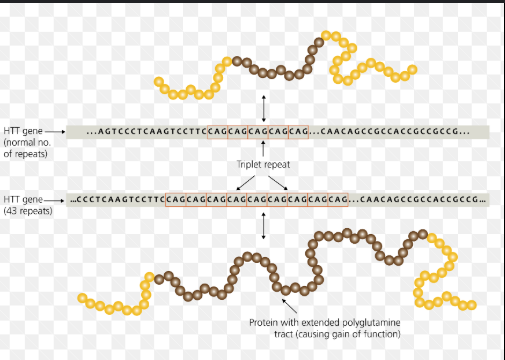
triplet expansion: anticipation
symptoms of genetic disorders appear at an earlier age and with increased severity in successive generations due to the increase in the number of triplet repeats.
How do we know diseases have genetic component?
relatives of affected individuals will have a higher probability of developing the disease than general population…aggregation & twin studies
Aggregation studies
relative risk= probability of disease in relatives/ general population…if it concentrates in family = genetic
concordance in twin studies
if both twins have disease (Ex. diabetes), they are said to be concordant for that disease…If MZ have a much higher concordance rate than DZ, it suggests that the trait has a strong genetic basis (more genes you share the more likely)…If concordance similar b/t MZ and DZ twins, likely influenced by environment
Twin studies
compare concordance in monozygous twins with dizygote twins
single trait diseases have what % concordance in MZ
100%…Ex. cystic fibrosis
common mutated genes that cause cancer
Tumor suppressor genes, proto-oncogenes, oncogenes
Tumor suppressor example
p53: DNA damage checkpoint
proto-oncogenes
normal genes, make proteins and contribute to cell growth/survival
oncogenes
mutated proto-oncogenes that drive cancer progression
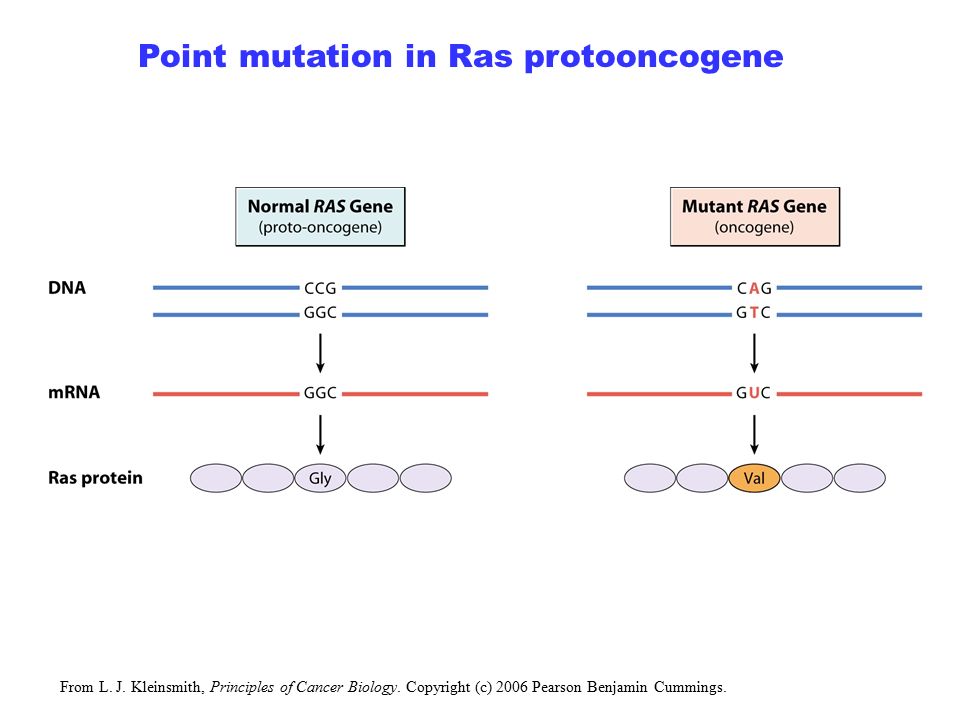
Oncogene example
RAS oncogene…differs from RAS proto-oncogene by point mutation
what causes oncogenes
viruses, point mutations , gene amplifications, chromosomal translocations, DNA rearrangements (insertion, deletion, inversion), insertional mutagenesis
Loss of which genes promotes cancer
tumor suppressor genes
Gain of which genes promotes cancer
oncogenes
Multiple hit hypothesis
takes an accumulation of mutations (hits) over time to develop cancer…why cancer seen more in older people…if cancer shown early —> expected familial predisposition to cancer