Oceans Exam 2
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
131 Terms
The Coriolis effect in the atmosphere is due to:
The atmosphere rotating faster at the equator than at the poles
What is the role of condensation nuclei in the formation of precipitation?
They are necessary for the formation of water droplets in the atmosphere
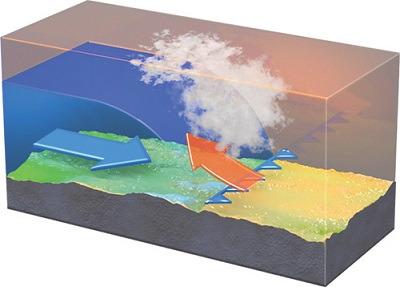
In this cross section of a cold front, which of the following is most likely occurring?
Cold air is moving to the right, lifting and cooling warm air, causing clouds and rain
Low-pressure systems are associated with ___ air and ___ weather
Rising, stormy
What helps cause hurricanes to grow and be sustained?
Warm surface water evaporates into warm rising water vapor, which condenses
What is the difference between a hurricane, typhoon, and cyclone?
They are all different names for tropical cyclones dependent upon location
Supercell thunderstorms are characterized by what
Downward-moving winds (called microbursts) along the front of the storm, a strong central updraft that may produce tornadoes, and an anvil shape
Which process of feature would be most responsible for the greatest incremental growth in a water droplet?
Collision-coalescence
How do hailstones form?
Particles of ice are moved vertically by downdrafts and updrafts, alternately thawing and freezing
What weather phenomena occurs when the polar jet stream wanders southward?
Polar vortex
What is the ultimate source of food for animals living around deep-sea hydrothermal vents?
Bacteria that break down hydrogen sulfide
The deepest parts of the seafloor are:
Oceanic trenches
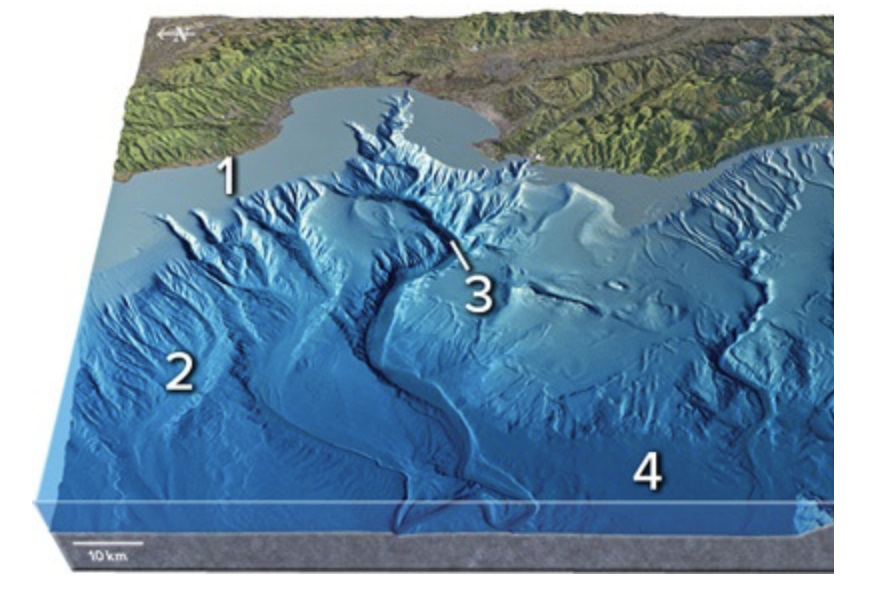
Which of the numbered feature on this figure is a continental shelf?
1
What rock type forms oceanic plateaus?
Basalt
What is a popular model for the formation of an atoll?
A volcanic island forms and subsides
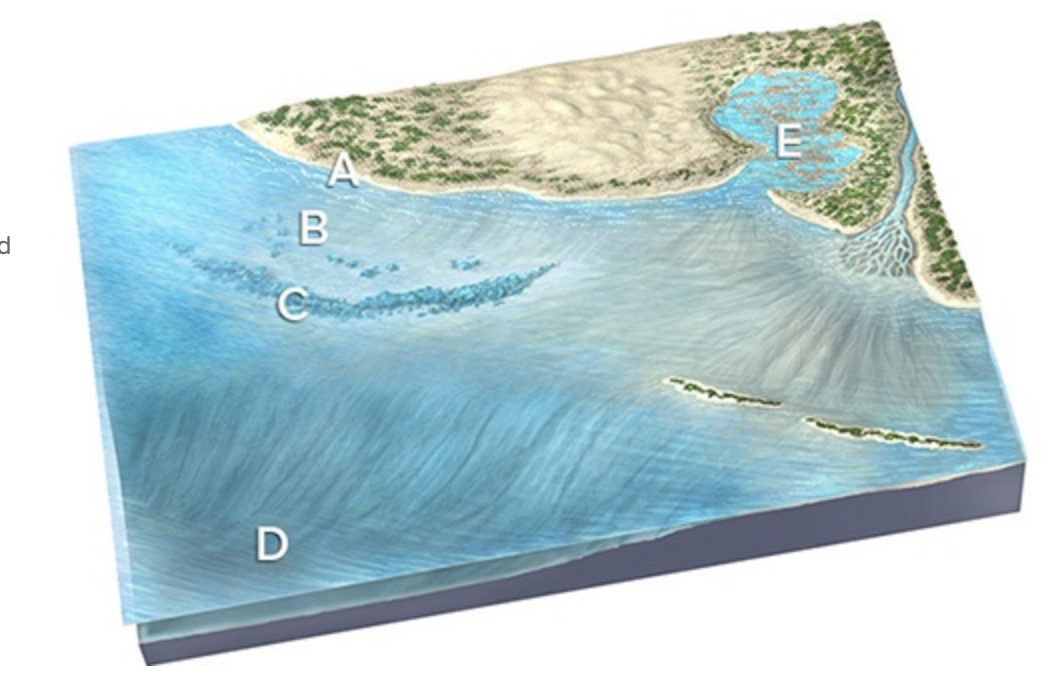
Fine-grained sediment like mud and dust would most likely be present at
The lagoon at B and deep seafloor at D
Which of the following is a characteristic of transgression?
The seas move in, with marine facies moving toward the land
The deep sea floor is characterized by sediment dominated by:
Fine dust and the remains of single-celled organisms
Which os the following parts of the seafloor are the shallowest?
Continental shelves
Most oceanic plateaus are:
Constructed by volcanic eruptions probably over mantle plumes
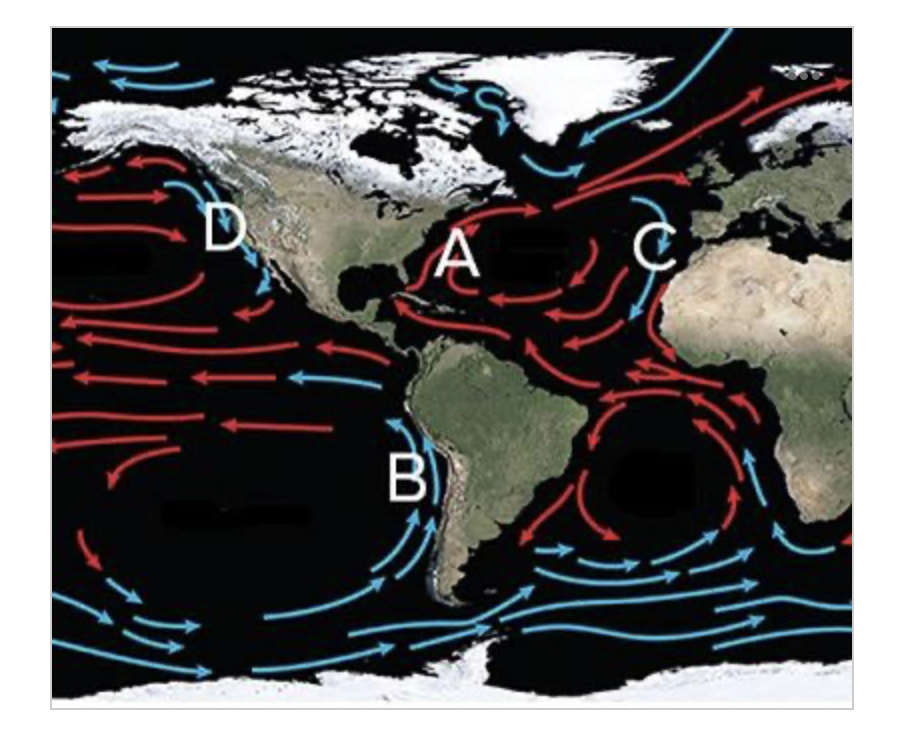
Which of the following shows the location of the Gulf Stream?
A
Surface ocean currents circulate in ocean basins:
Clockwise in the Northern hemisphere
Surface temperatures (SST’s) are typically warmest:
On the western sides of oceans
The thermohaline conveyor is important in the North Pacific because:
It warms the coast of Alaska, allowing longer growing seasons
The climate of Western Europe is moderated by:
The warm water of the Gulf Stream
A thermohaline current is driven by what?
Density differences caused by temperature and salt content
A gyre is ___
A circular current of water
What is geostrophic flow?
Water movement caused by Eckman transport and gravity
What is Eckman transport?
Water movement 90 degrees to the direction of the wind caused by the Coriolis effect
Ocean currents transport ___
Heat, nutrients, and carbon
What is nitrogen fixation
When nitrogen gas is converted to ammonia by bacteria
What is nitrification?
Ammonia is converted to nitrite and then nitrate by bacteria
What is primary production?
Phytoplankton use nitrate during photosynthesis
What is the nitrogen cycle?
Nitrogen gas → ammonia, ammonia → nitrite → nitrate, phytoplankton use nitrate during photosynthesis, consumers eat phytoplankton and consumers eat other consumers, organisms die → decomposition breaks down complex organic compounds into simple compounds, Bacteria breaks down simple nitrogenous compounds back into nitrogen gas
What is denitrification?
When bacteria breaks down simple nitrogenous compounds back into nitrgoen gas
Earth’s 5 major oceans
Atlantic, Pacific, Arctic, Southern, Indian
What is a passive continental margin?
Places where land meets sea and there is no active plate boundary, lacks earthquakes and volcanoes
Where are passive continental margins found?
Right side of South America, left side of Africa, and East Coast of US
What are active continental margins?
Places where land meets sea and there is an active plate boundary, typically see earthquakes and volcanoes are likely
Where are active continental margins found?
West Coast of US, left side of South America
What are continental margin features?
Continental shelf, shelf break, continental slope, continental rise, continental margin, and abyssal plain
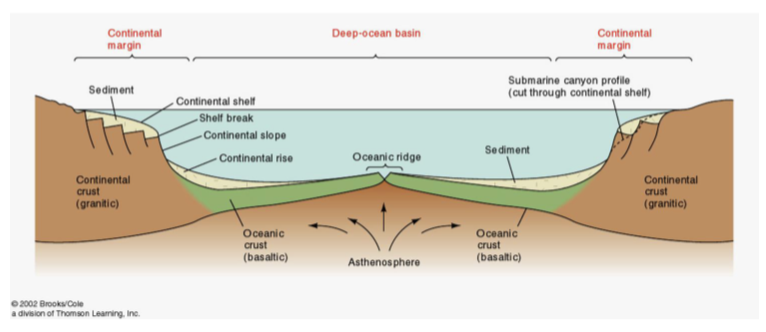
What process does this image represent?
Continental margins
What is an ocean trench?
Deepest portions of the ocean
How deep is the Mariana Trench?
11,000 meters or 7 miles deep
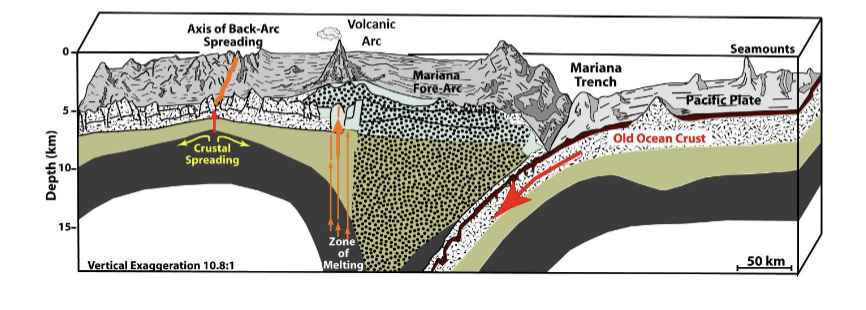
What process does this image represent?
Ocean trenches
How do seamounts form?
Eruptions of lava onto seafloor → volcano rises above the sea as an island → top of the mountain is leveled by the sea, crust cools and the island subsides below the sea
What is nitrogen fixation? (Nitrogen Cycle)
When nitrogen is converted into amonia by bacteria
What is nitrification? (nitrogen Cycle)
When amonia is converted into nitrite, and then into nitrate by bacteria
What is primary production? (Nitrogen Cycle)
When phytoplankton uses nitrate for photosynthesis
What is the nitrogen cycle?
Nitrogen is converted into amonia by bacteria
Amonia is converted into nitrite, and then nitrate
Phytoplankton use nitrate during photosynthesis
Consumers eat phytoplankton, consumers eat consumers
Organisms die - decomposition breaks down complex organic compounds into simple compounds
Bacteria breaks down simple nitrogenous compounds back into nitrogen gas
What is denitrification? (Nitrogen Cycle)
When bacteria breaks down simple nitrogenous compounds back into nitrogen gas
What are earth’s 5 major oceans
Pacific, Atlantic, Arctic, Southern, and Indian
What is a passive continental margin?
Places where land meets sea and there is no active plate boundary, lacks earthquakes and volcanoes
Where are passive continental margins found?
Along the right side of South America, left side of Africa, and the East Coast (US)
What is an active continental margin?
Places where land meets sea and there is an active plate boundary, typically see earthquakes, and volcanoes are likely
Where are active continental margins found?
Along the left side of South America, and the West Coast (US)
What is the deepest part of the ocean?
Trenches
How deep is the Mariana Trench?
11,000 meters, or 7 miles deep
How do seamounts form?
Lava erupts onto seafloor
Volcano rises above the sea as an island
Top of the mountain is leveled by waves, curst cools and the island subsides below sea
Are seamounts islands?
No
What are flat-topped seamounts called?
Guyots
Life cycle of a guyot and atoll
Volcanic island
Sinking island
Guyot
Barrier reef
Atoll
Seamount
2 Types of rocks
Detrital (terrigenous), and chemical (biogenous)
How are detrital and chemical rocks formed?
Originate as solid particles from weathered rocks
Forms into detritus form
Forms into detrital or classic sedimentary rocks
Examples of detrital rocks
Conglomerate, breccia, sandstone, arkose, siltstone, and shale
Examples of chemical rocks
Crystalline limestone, microcrystalline limestone, fossilfeous limestone, coquina, chalk, tavertine, rock salt, rock gypsum, chert, flint, agate, and bituminous coal
Where are rock-based sediments found?
Gravel (coarsest), sand, and mud (finest)
Where are life-based sediments found?
Where there is little to no sand or mud
Most sediments are composed of:
Quartz, calcite, clay, and rock or shell fragments
What are turbidity currents?
Underwater avalanches, gravity and water flow carries sediment from shallow to deep water
What is graded bedding?
As the energy in an environment changes over time, the size of material deposited will change
Decreasing energy = (graded bedding)
Smaller sediment towards the top, graded bedding
Increasing energy = (graded bedding)
Larger sediment towards the top, reverse graded bedding
Is transgression graded bedding or reverse graded bedding?
Graded bedding
What is an example of a transgression?
The sea moving in
Is regression an example of graded bedding or reverse graded bedding?
Reverse graded bedding
What is an example of regression?
The seam moving out
For every ___ depth, pressure increases by ___
10 m, 1 atm
How many atm is at 60m?
7 atm
Ocean surface temperature laws
Lower latitudes = warmer ocean temps
Higher latitudes = colder ocean temps
Ocean temperature with depth laws
Warmest at the surface because of sunlight
Colder at depth
Density formula
Density = mass/volume
What is mass?
The amount of matter in an object (grams)
What is volume?
How much space is occupied by the matter (cm³)
What 3 things affect the density of seawater?
Temperature
Pressure
Salinity
What range of the EMF spectrum is visible light?
400 - 700 nm
What EMF objects are safe to living organisms?
AM, FM, TV, radar, TV remote, light bulb
What EMF objects are not safe to living organisms?
The sun, X-ray machines, and radioactive elements
Why does blue light go deeper in the ocean?
As light enters the water, the red wavelength is absorbed by water molecules leaving only shorter, blue wavelengths
What is sound?
A wave of pressure that moves through a media
Is there sound and space? Why or why not?
No because there is no air, sound travels through air
Why does sound get weaker as it travels?
Spreading - loudness decreases as sound waves spread out, same energy over a bigger area
Absorption - sound energy is absorbed by the molecules in the media it travels through (heat)
How does sound travel?
Reflection - sound can reflect off of different medias
Refraction - sound will “bend” when it travels from one media into another
Scattering - sound waves can bounce off of objects in the media
Reverberation - the sum of reflection & scattering, basically “noise” created when sound waves interact with a media
In the ocean, where does sound travel faster and why?
Sound travels faster at the surface because the temperature is higher
What does SONAR stand for?
SOund Navigation And Ranging
What is passive SONAR?
Listening
What is active SONAR?
Making a noise and then listening
What is SONAR used for?
Detecting and mapping things like the seafloor, objects, organisms, layers of sediment, and rock
What is thermal convection?
Thermals are rising pockets of warm air
Which is more dense, humid air, or dry air?
Dry air