2023-2024 Periodic Table 낱말 카드 | Quizlet
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
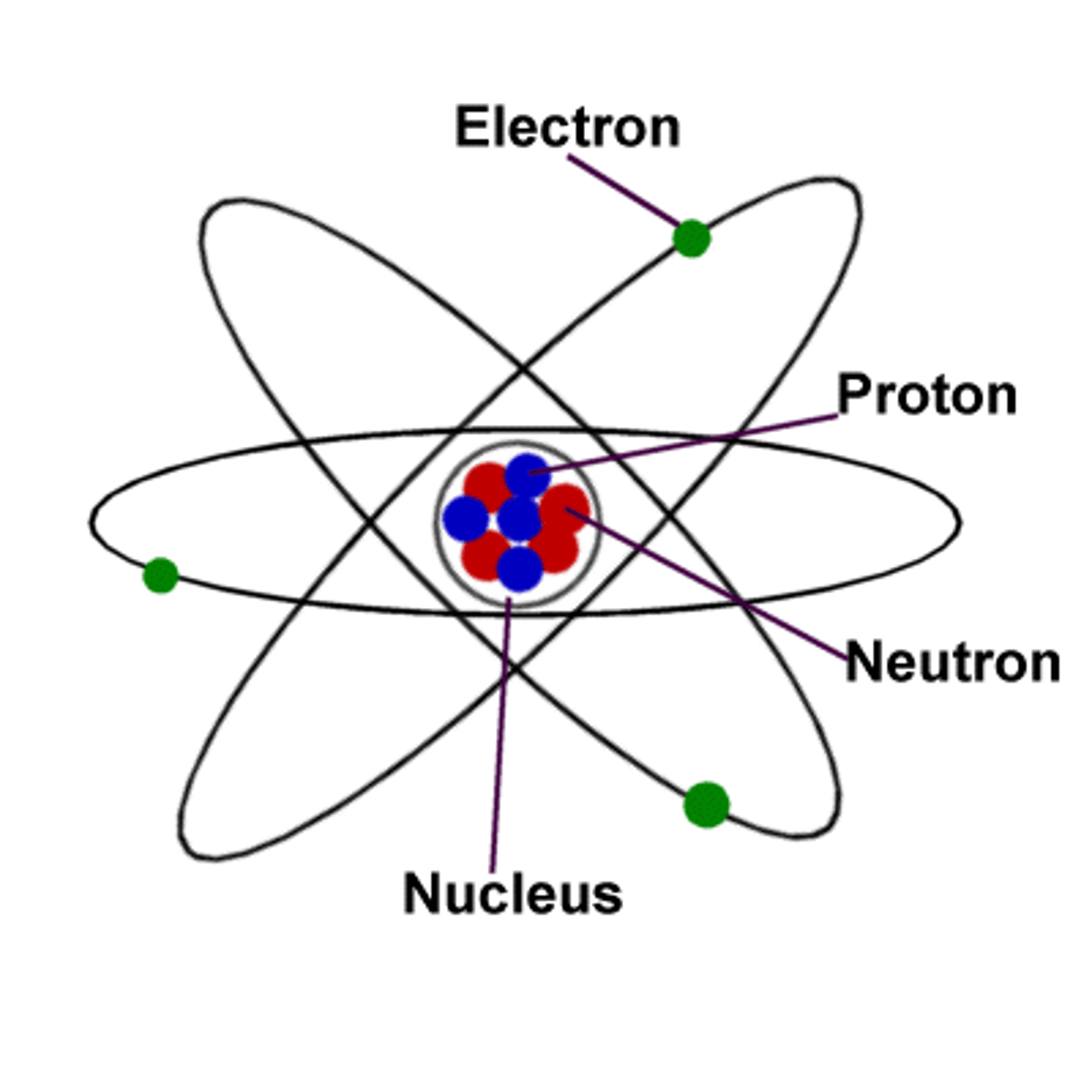
center of an atom, contains most of the atoms mass
Nucleus
the average mass of the atoms of an element
Atomic mass
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
Atomic number
A one or two letter representation of an element
Chemical symbol
A subatomic particle that has a negative charge, located outside an atom nucleus
Electron
a region around the nucleus of an atom where electrons are likely to be found
Electron cloud
a substance that cannot be separated or broken down into simpler substances by chemical changes
Element
Vertical column in the periodic table, elements have similar properties
Group
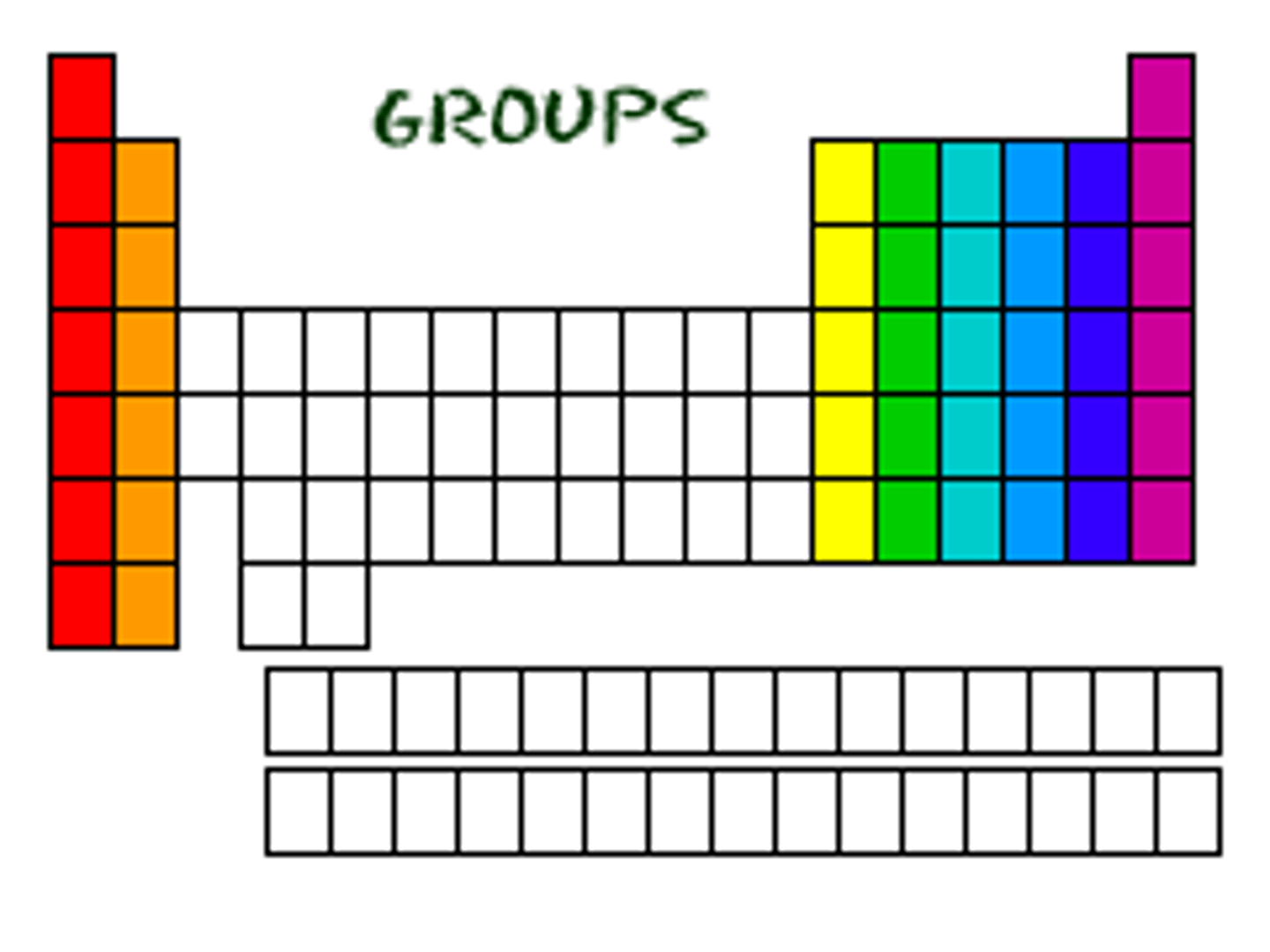
an element that is shiny and that conducts heat and electricity well. Located on the left of the periodic table.
Metal
an element that has properties of both metals and nonmetals
Metalloid
the particles of the nucleus that have no charge, located in an atom's nucleus
Neutrons
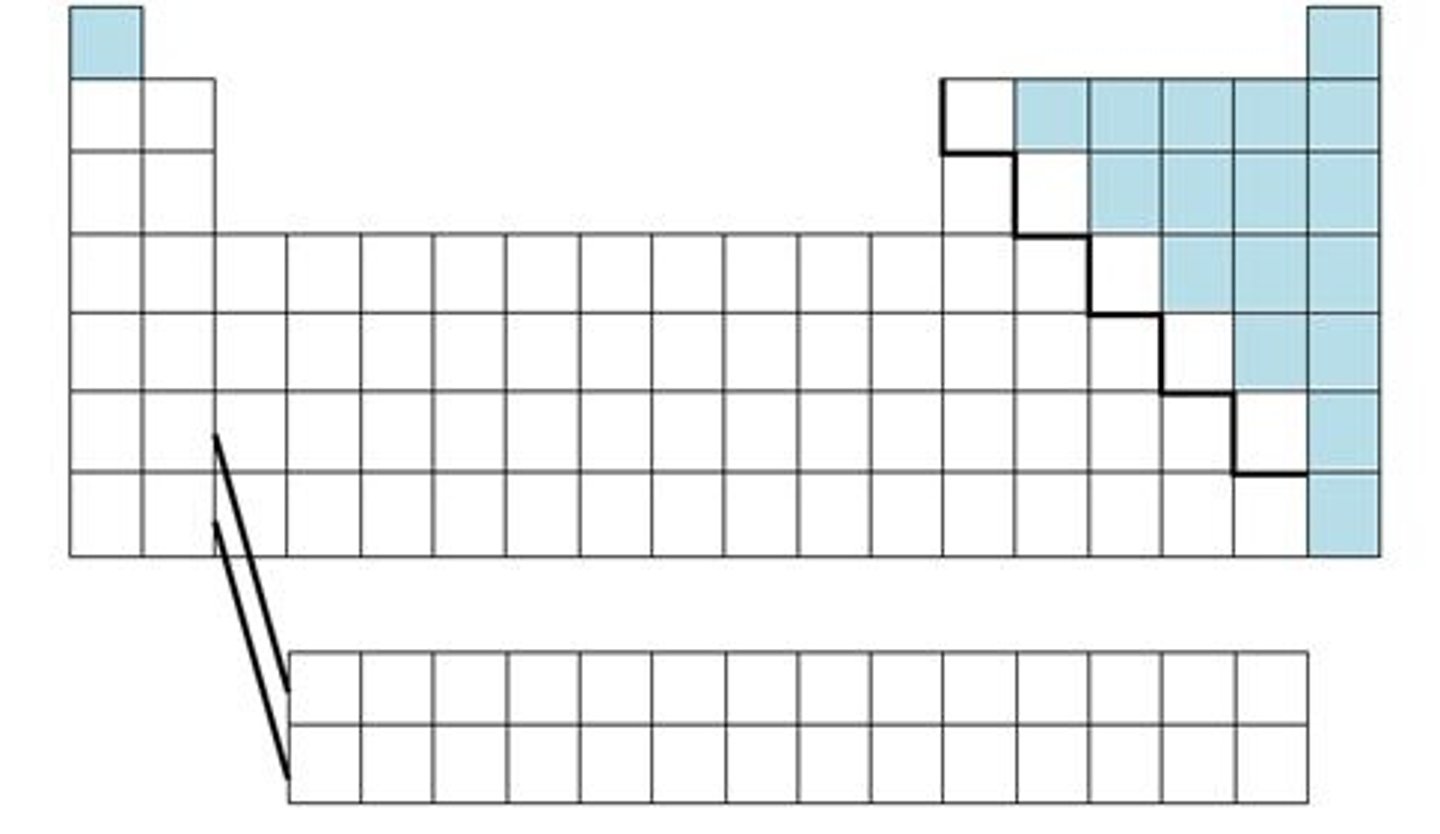
Elements that are poor conductors of heat and electric current. Located on the right of the periodic table.
Nonmetals
A chart of the elements showing the repeating pattern of their properties
periodic table
A subatomic particle that has a positive charge and that is found in the nucleus of an atom
Proton
protons, neutrons, and electrons that make up an atom.
subatomic particles
Electrons on the outermost energy level of an atom
valence electrons
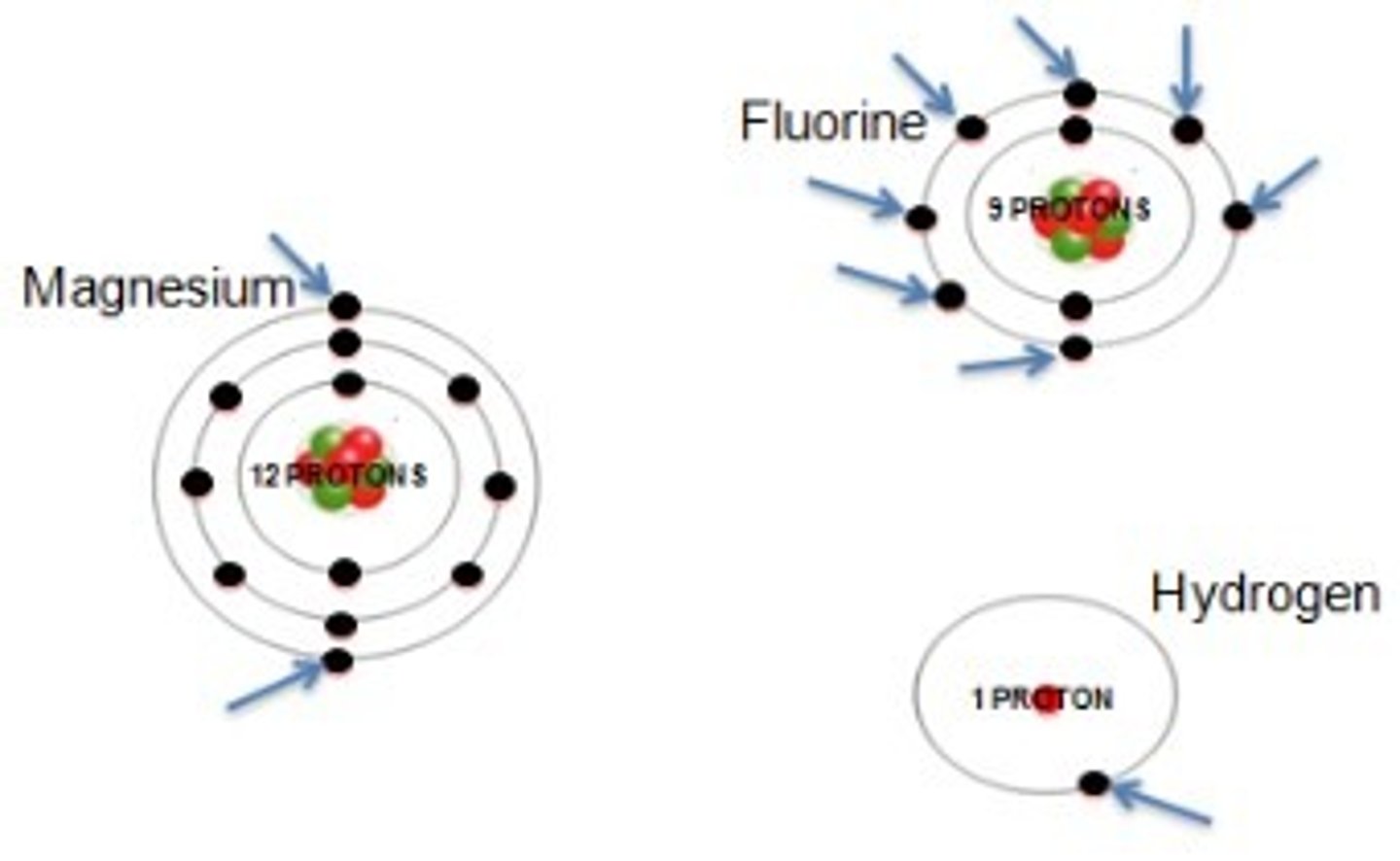
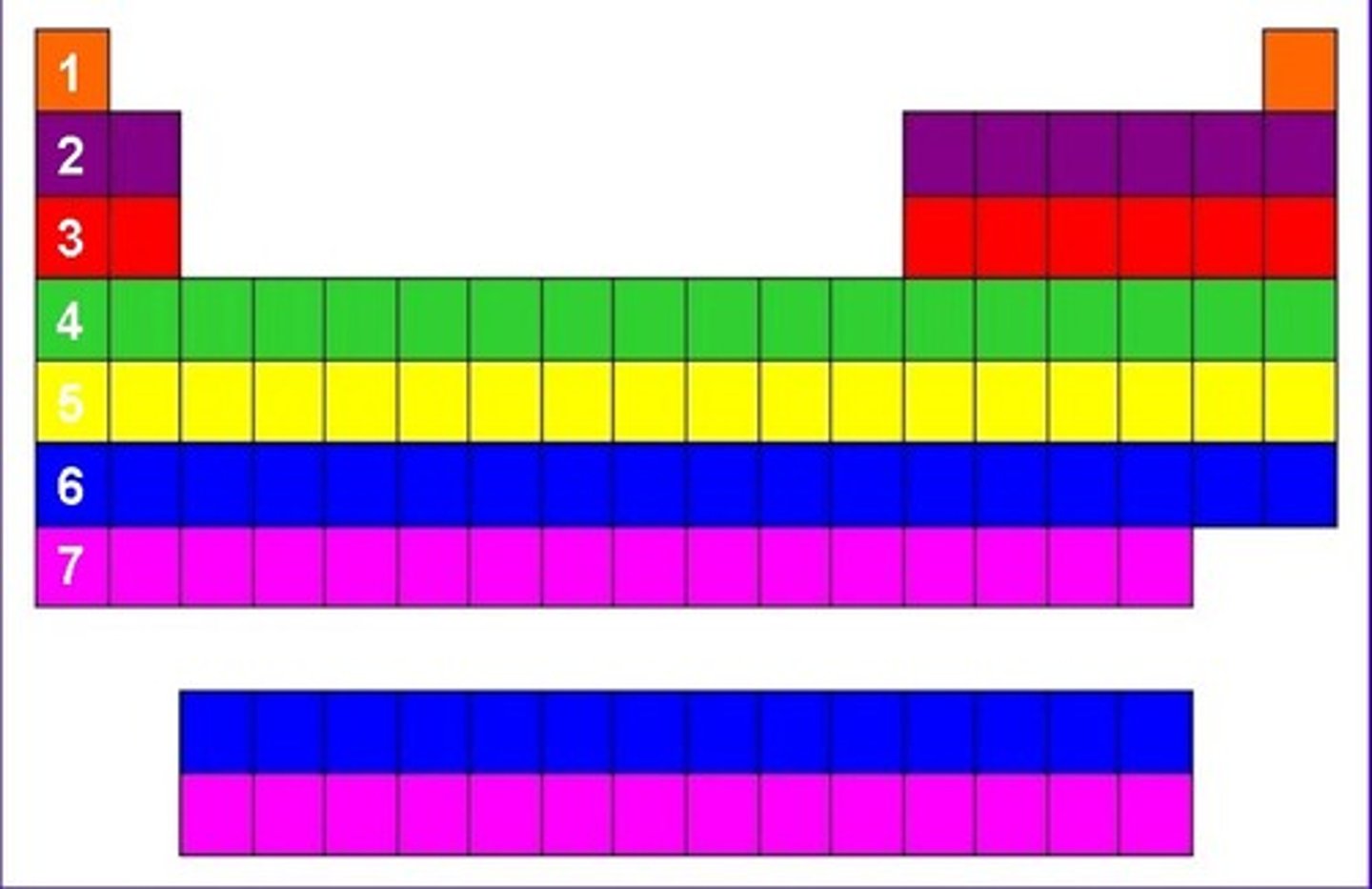
18
number of groups on the periodic table
7
Number of periods on the periodic table
A horizontal row of elements in the periodic table
period
protons
atomic number is based on an atom's
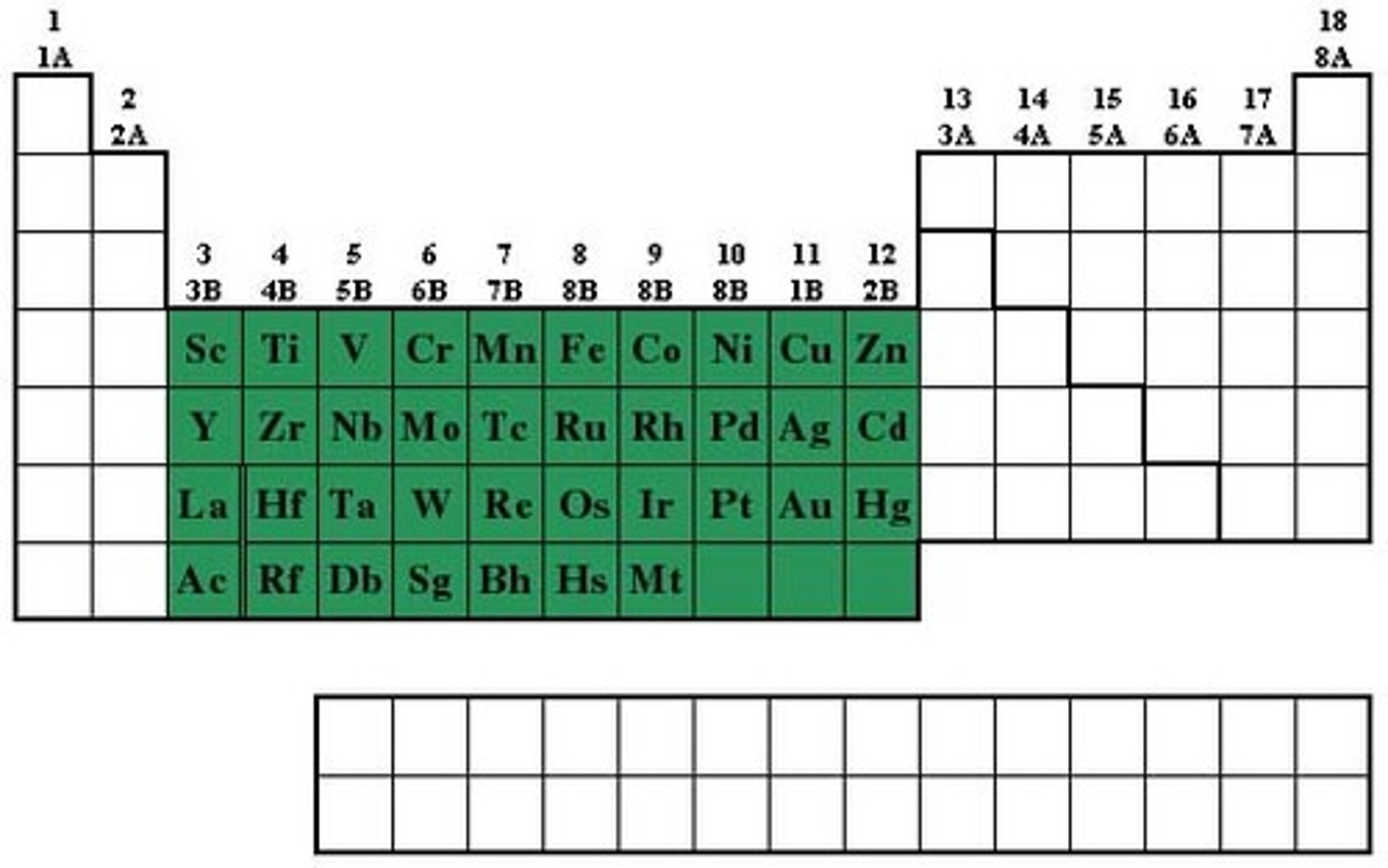
Groups 3-12 elements
transition metal group
group 17 on the periodic table
Halogens
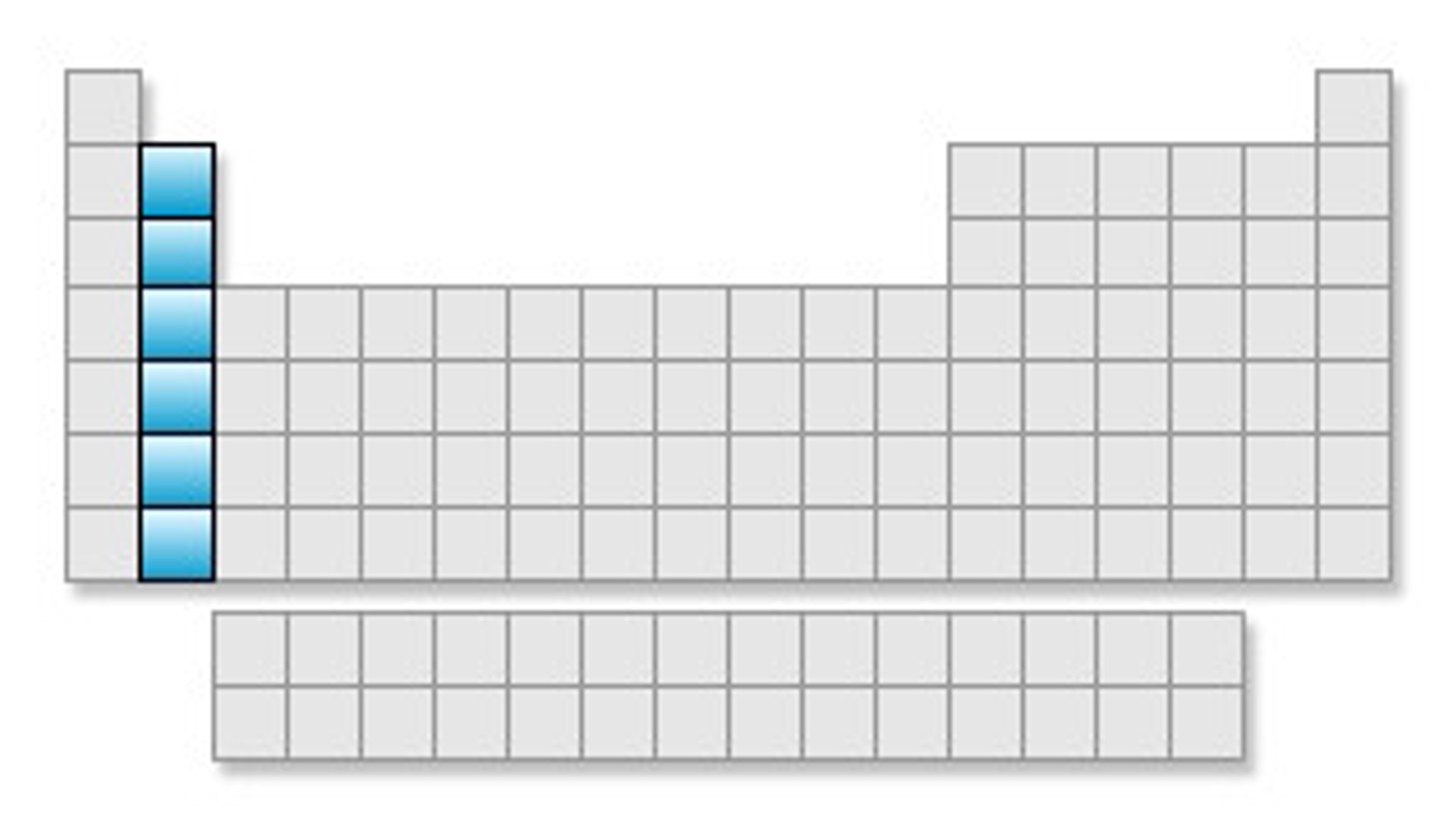
Group 1 of the periodic table
alkali metals group
Group 2 of the periodic table
alkaline earth metals group
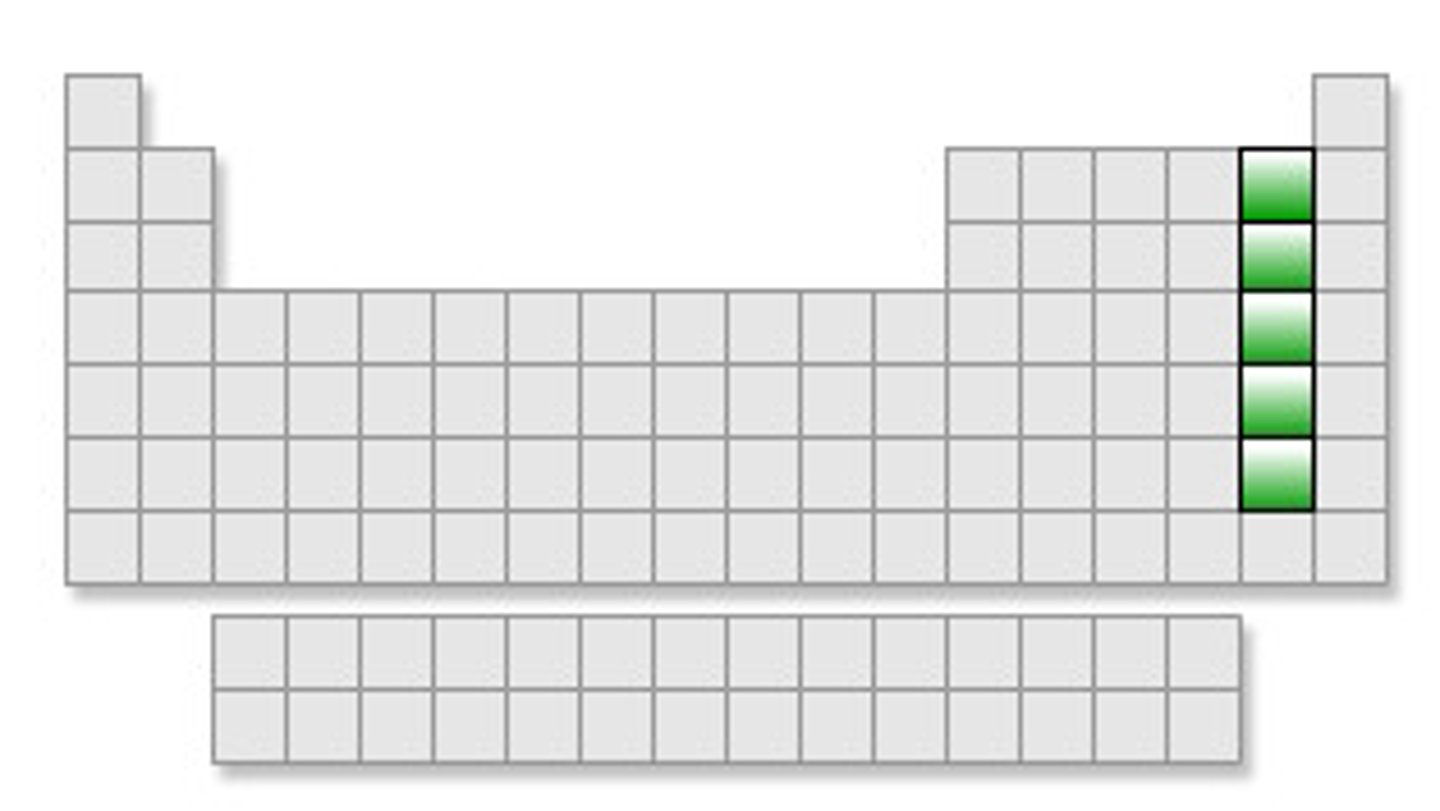
Group 18
noble gases group
2 electrons
1st energy level can hold
chemical properties, like number of valence electrons
elements in a group have similar
8 VE
How many valence electrons does Neon have?
4 VE
How many valence electrons does carbon have?
3 VE
How many valence electrons does Boron have?
7 neutrons
How many neutrons does Nitrogen have?
4 neutrons
How many neutrons does Lithium have?
Mo/ Molybdenum
Which element is located in group 6, period 5(use periodic table)
O/Oxygen
Which element is located in group 16, period 2 (use periodic table)
K/ potassium
Which element is located in group 1, period 4 (use periodic table)
Ni/Nickel
Which element is located in group 10, period 4 (use periodic table)
B/ Boron
Which element is located in group 13, period 2 (use periodic table)
alkali metals
the most reactive metals in the periodic table
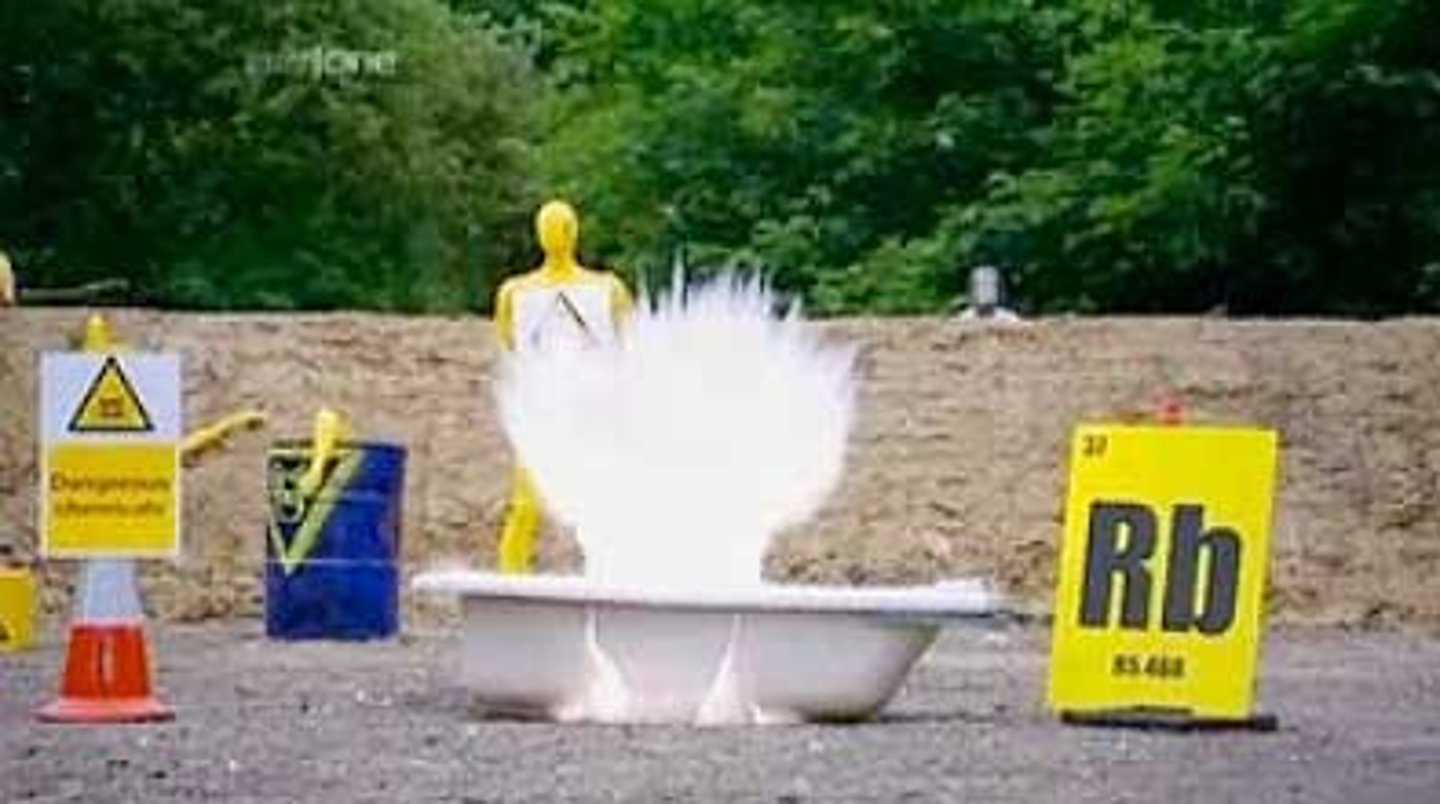

Halogens
Most reactive nonmetals
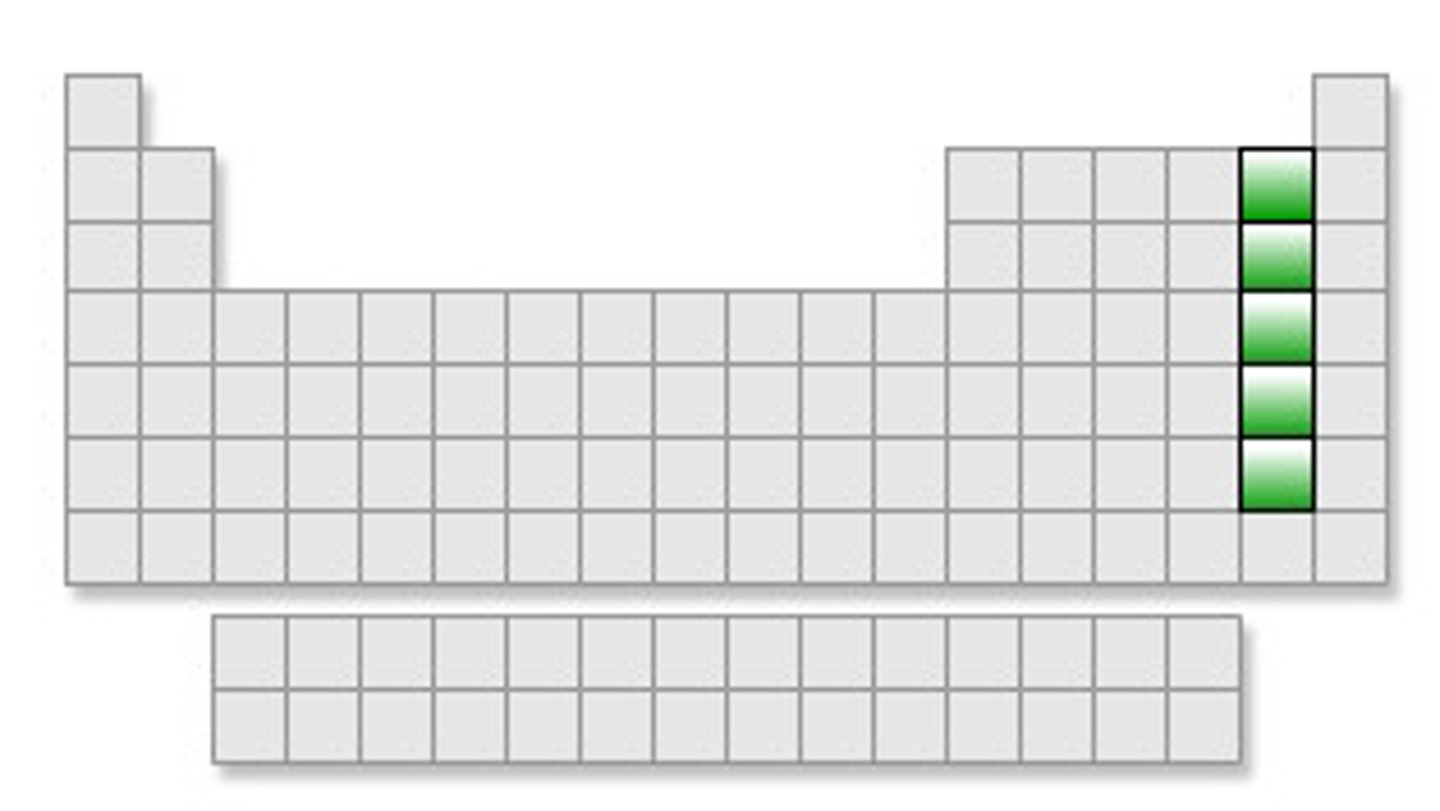
noble gases
The most stable group on the periodic table
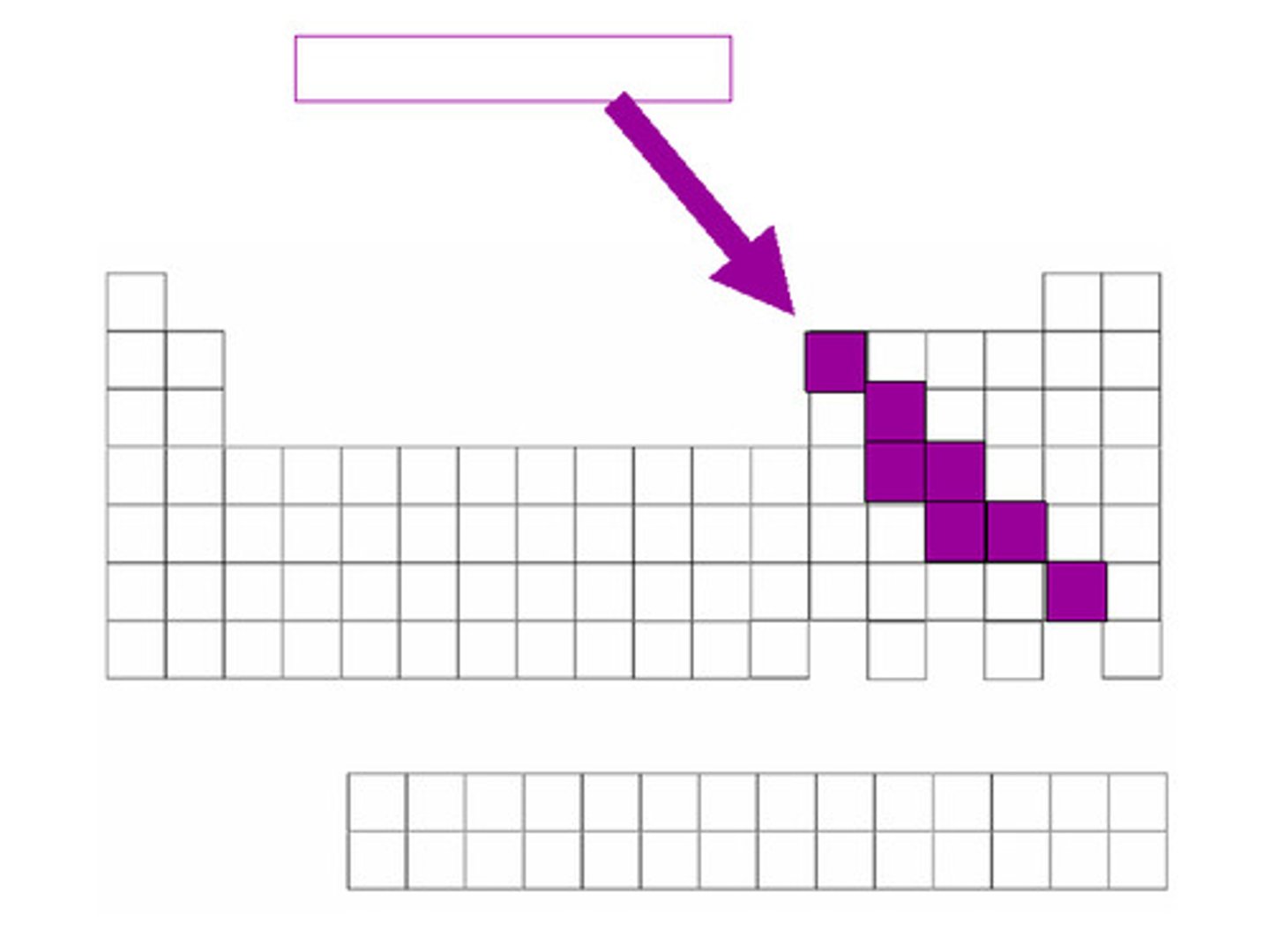
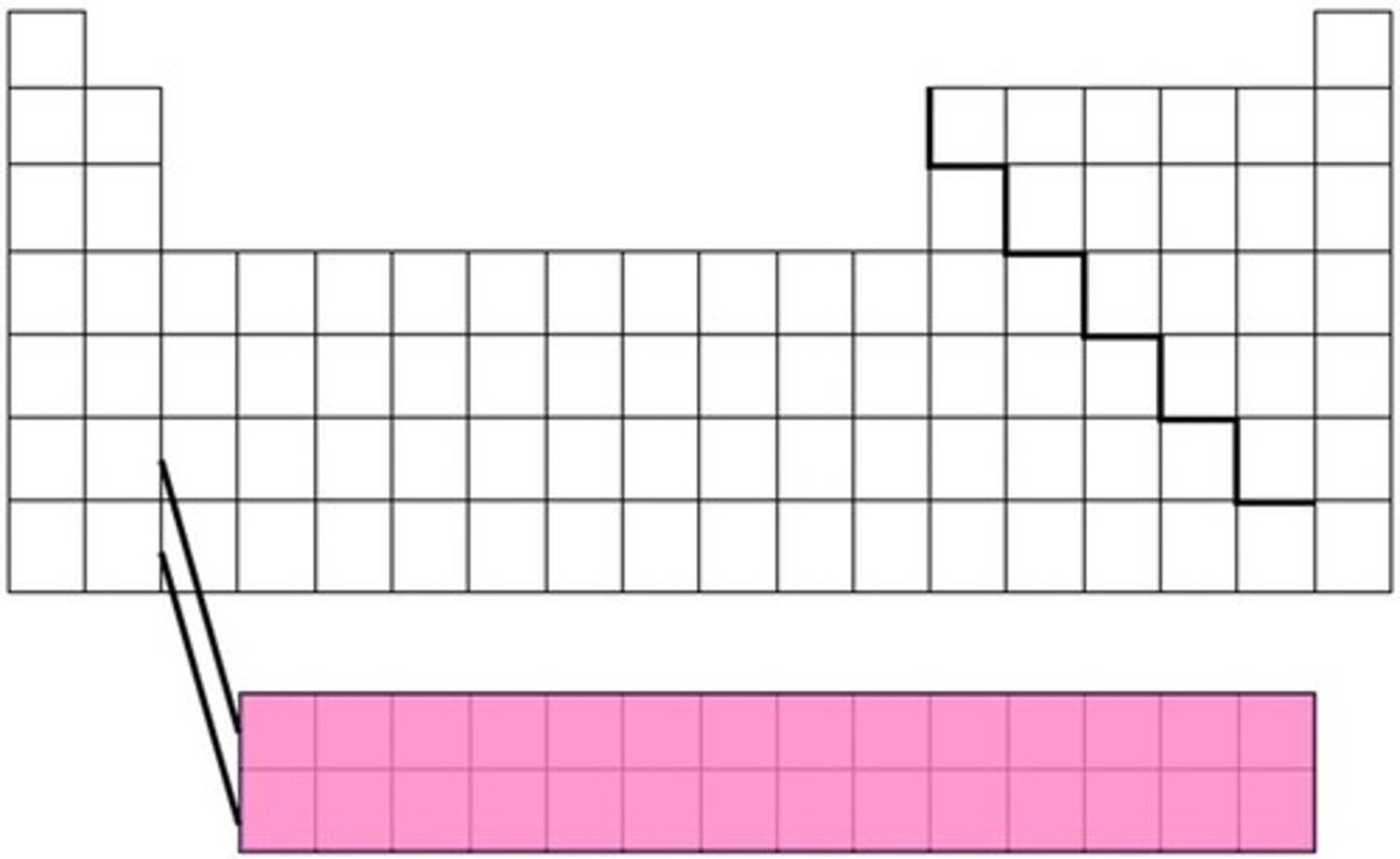
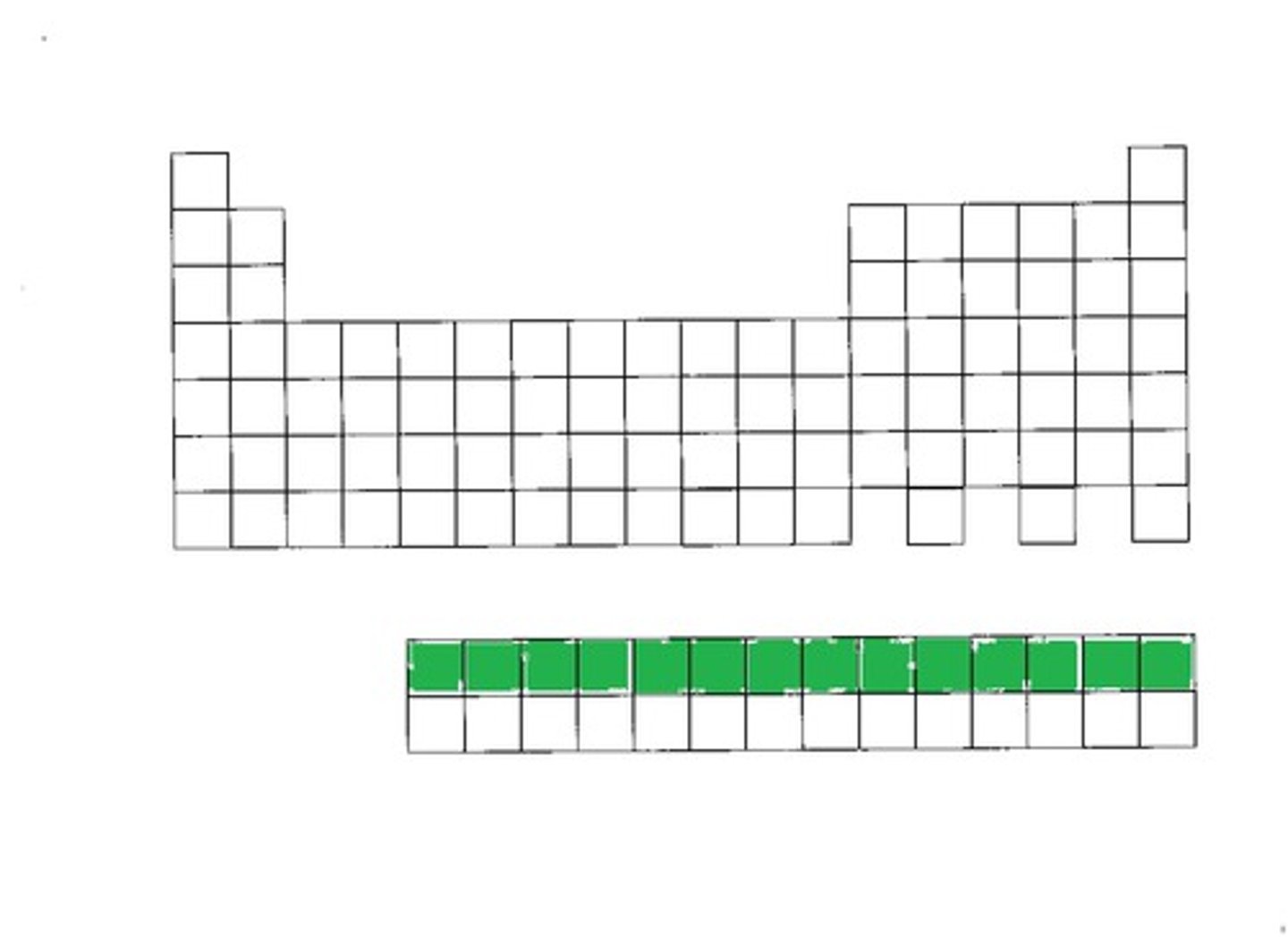
inner transition metals
elements that appear below the main body of the periodic table. Also referred to as the f block
Lanthanides
the 14 elements with atomic numbers from 58 (cerium, Ce) to 71 (lutetium, Lu)
Actinides
the 14 elements with atomic numbers from 90 (thorium, Th) to 103 (lawrencium, Lr)
sublevels
Refers to electron orbitals designated s, p, d or f. These have characteristic shapes which can be used to explain and predict the chemical bonds that atoms can form.
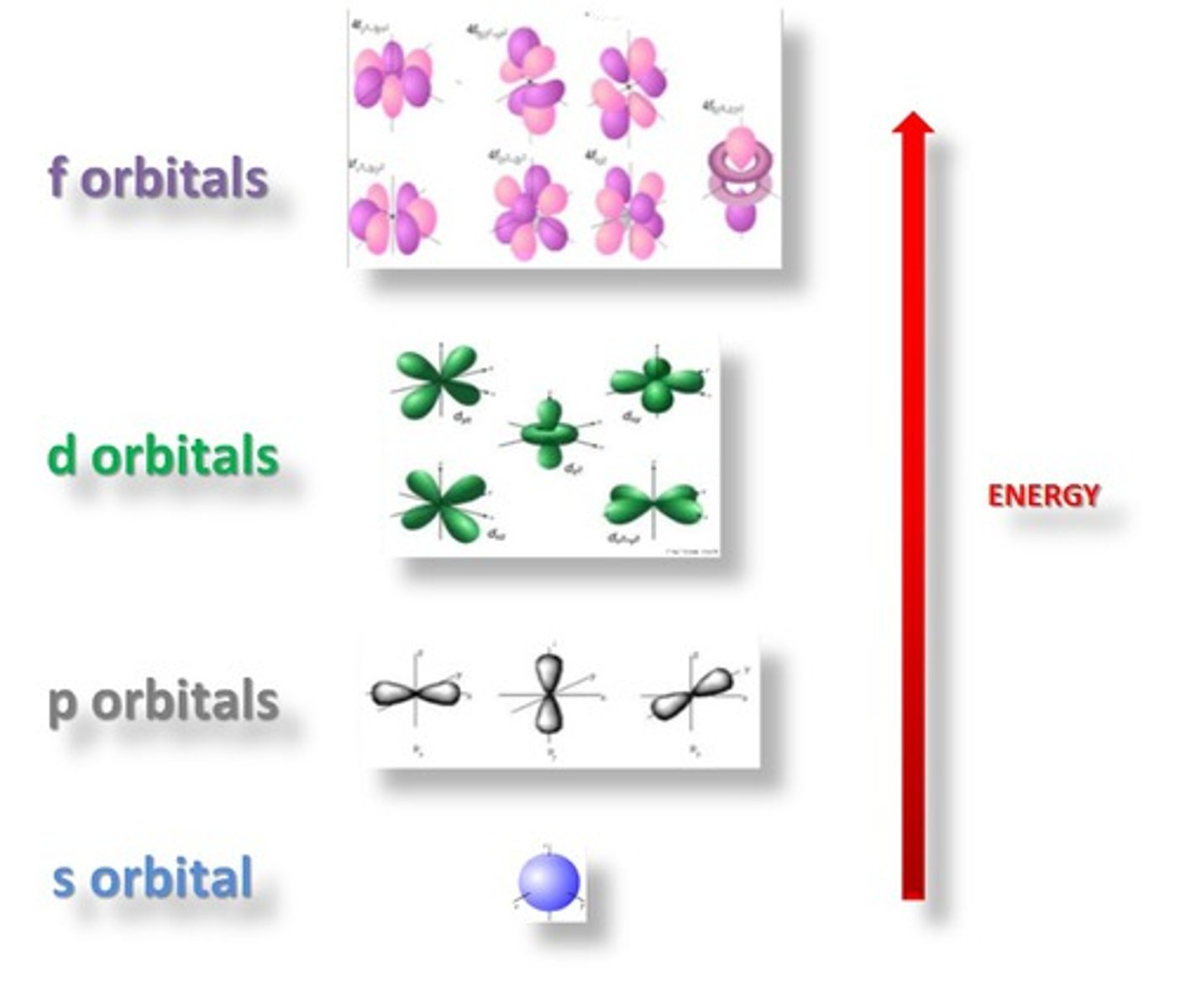
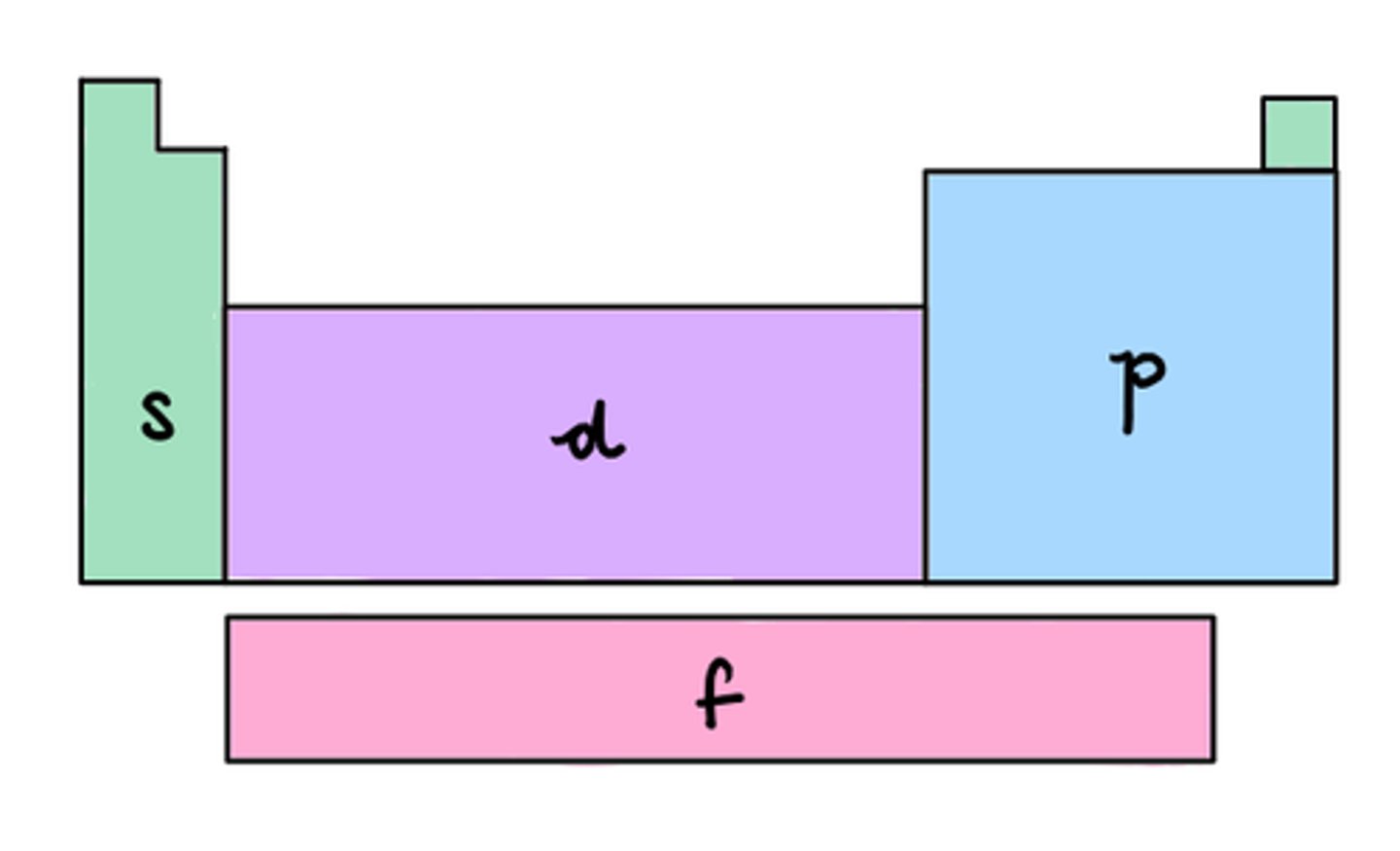
s,p,d,f blocks
S block: Groups 1&2
P block: Groups 13-18
D block: 3-12
F block: Lanthanide & Actinide series
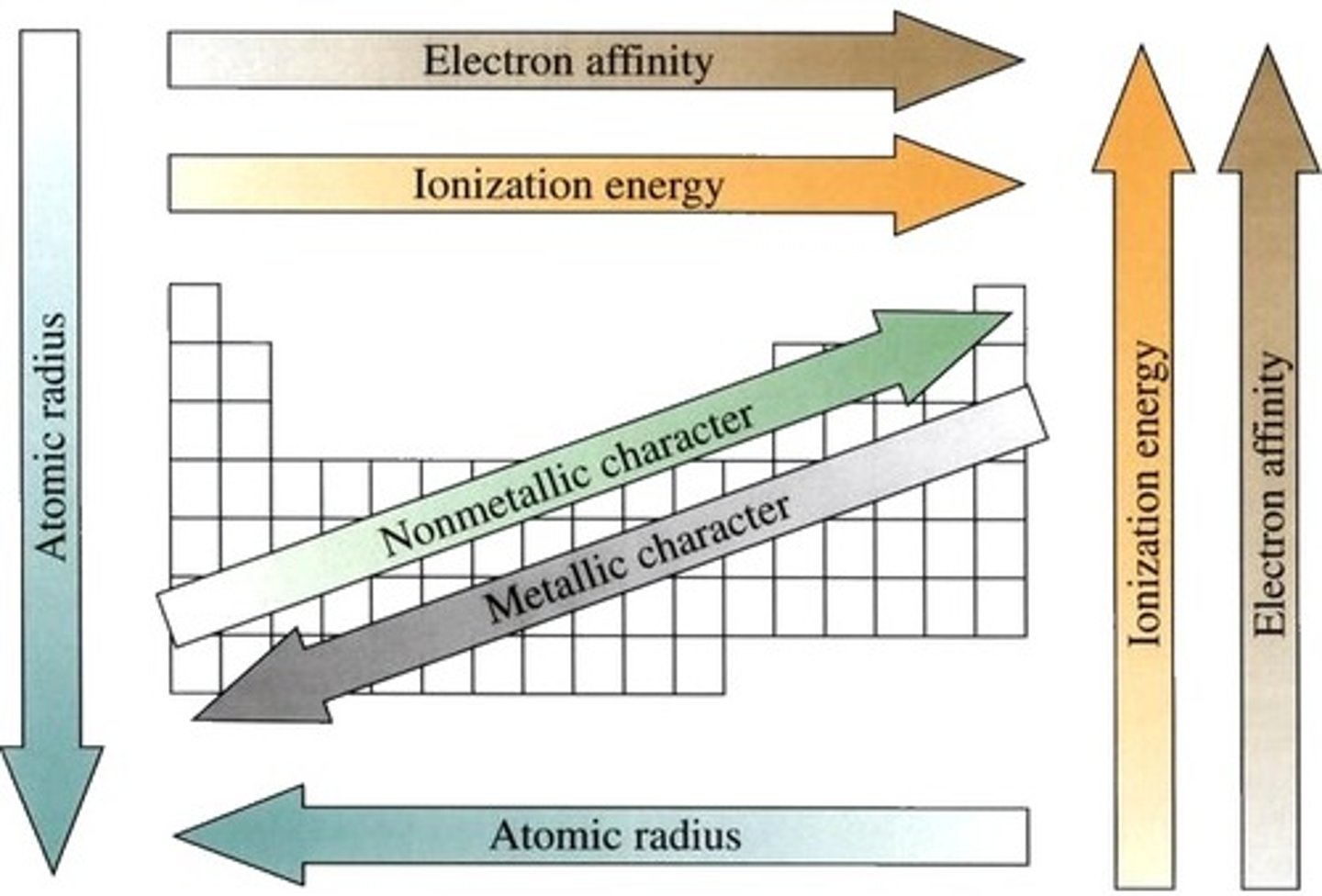
Periodic Trends
specific patterns that are present in the periodic table that illustrate different aspects of a certain element, including its size and its electronic properties
ionization energy
The amount of energy required to remove an electron from an atom
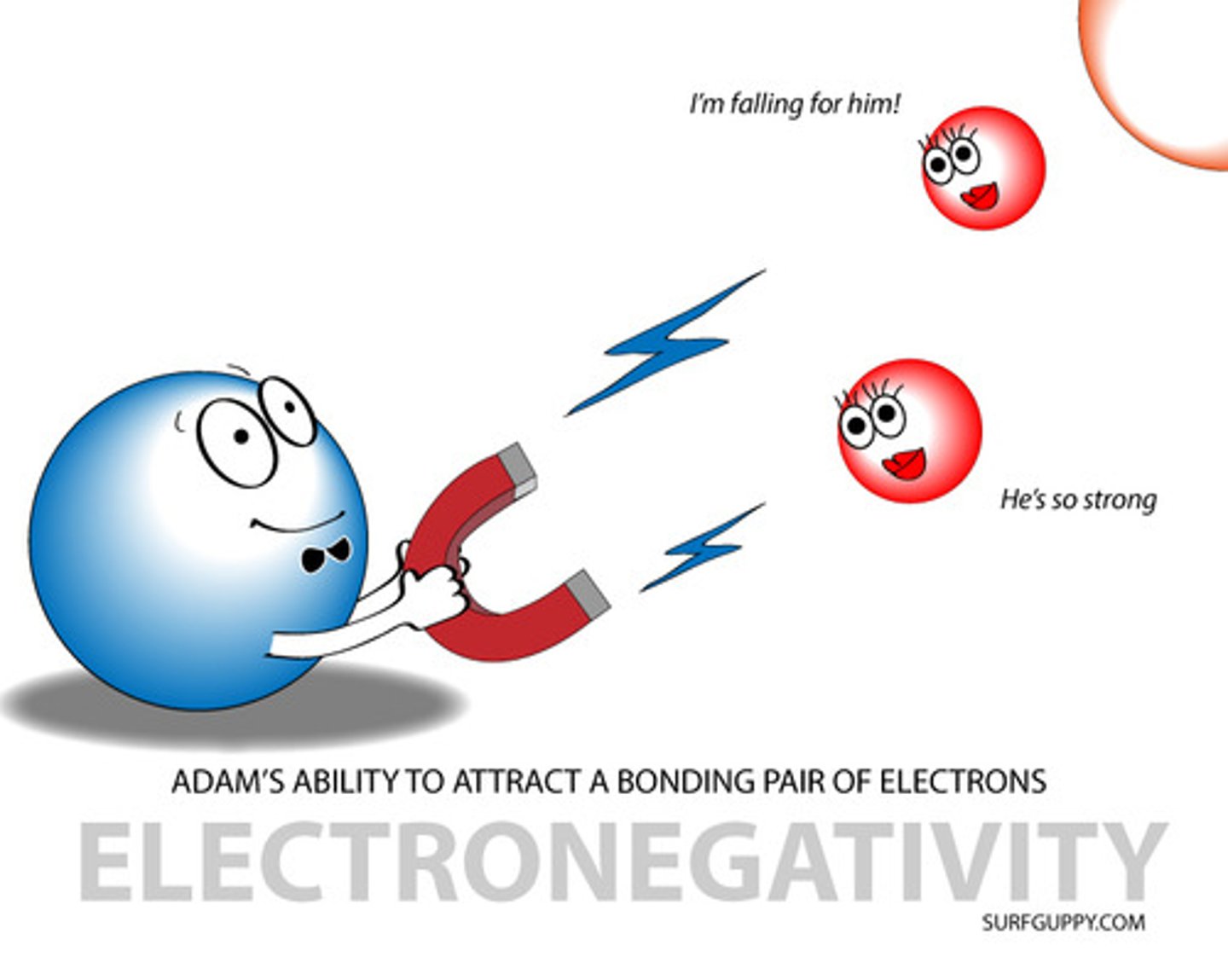
electronegativity
A measure of the ability of an atom in a chemical compound to attract electrons
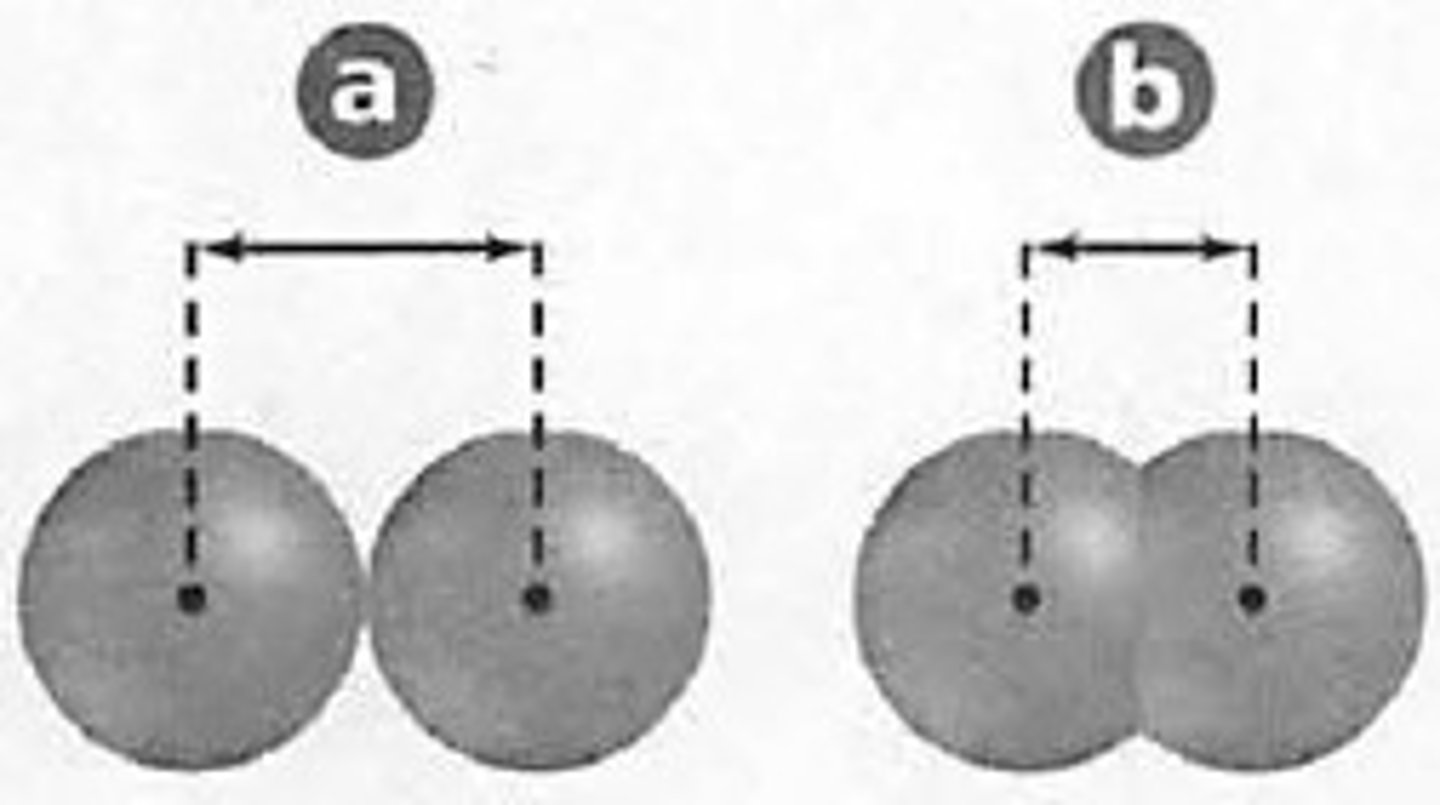
atomic radius
Size of an atom; Specifically: one-half the distance between the nuclei of two atoms of the same element when the atoms are joined
metallic character trend
based on ionization energy; increases down a group; decreases across a period
ionization energy trend
decreases down a group, increases across a period
electronegativity trend
increases across a period, decreases down a group
atomic radius trend
increases down a group, decreases across a period
periodic law
the law that states that the repeating chemical and physical properties of elements change periodically with the atomic numbers of the elements
bohr model
model of an atom that shows electrons in circular orbits around the nucleus
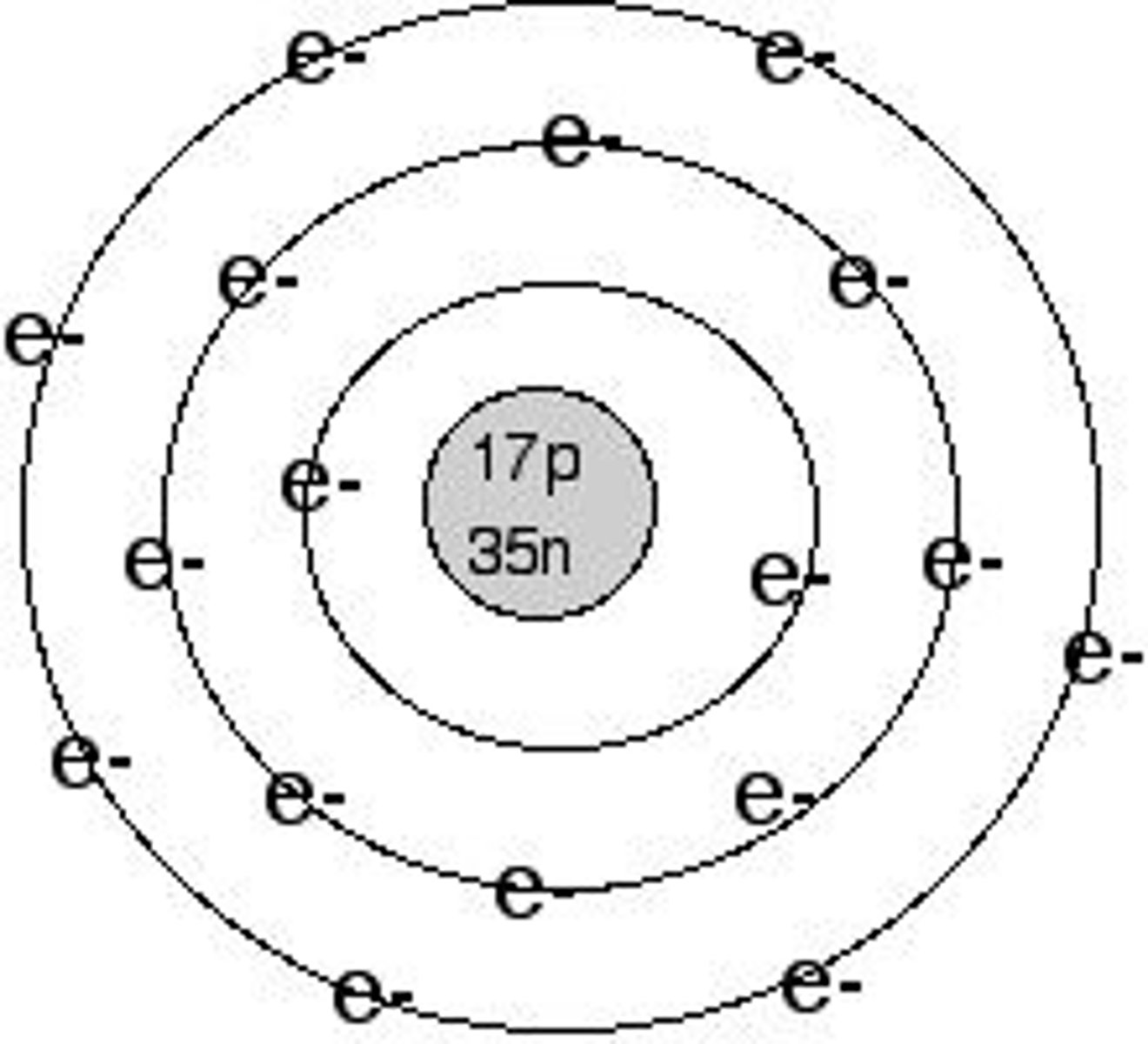
ion
An atom or group of atoms that has a positive or negative charge.
cation
A positively charged ion

anion
A negatively charged ion

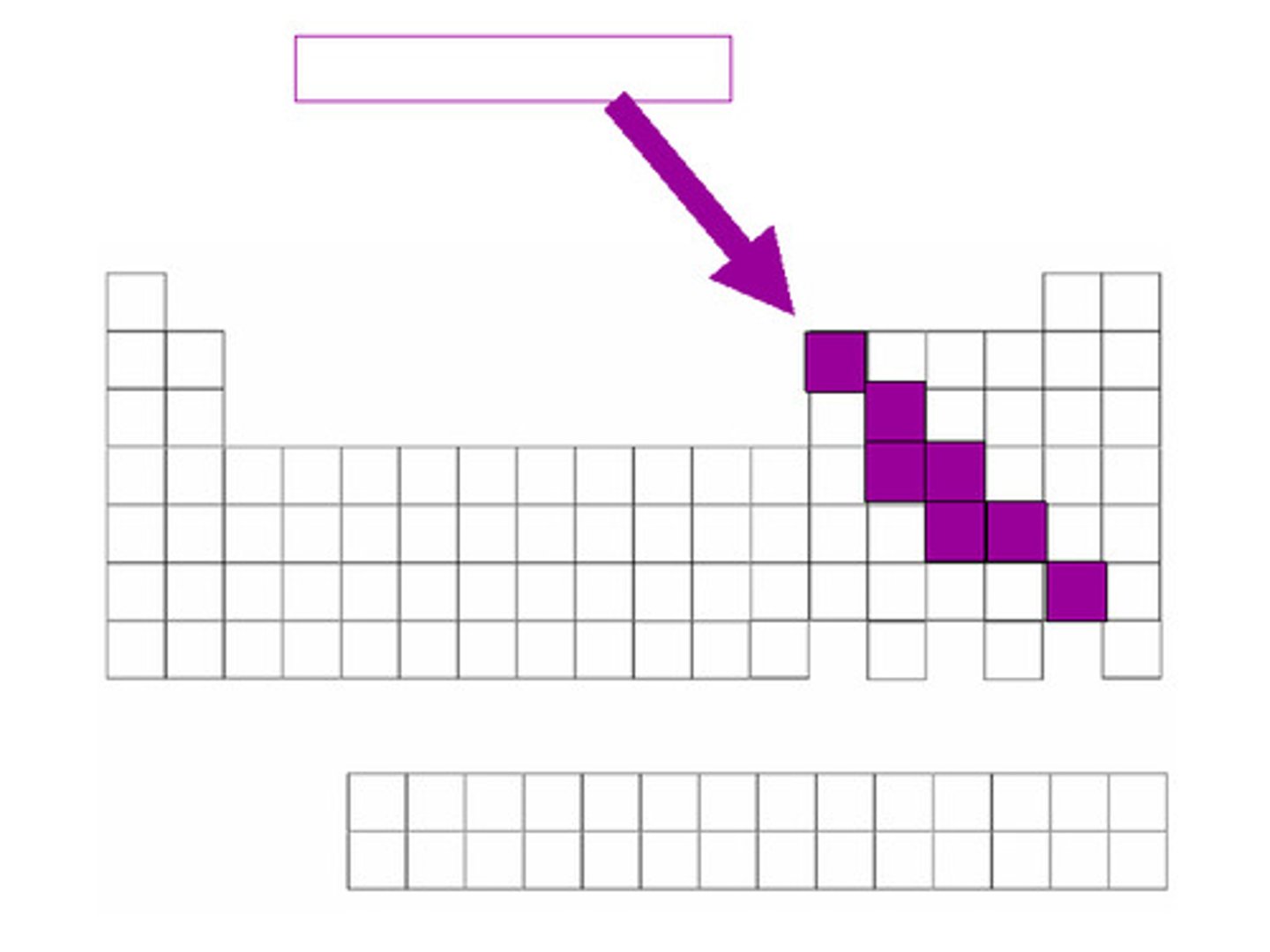
semi-conductor
Another name for metalloid
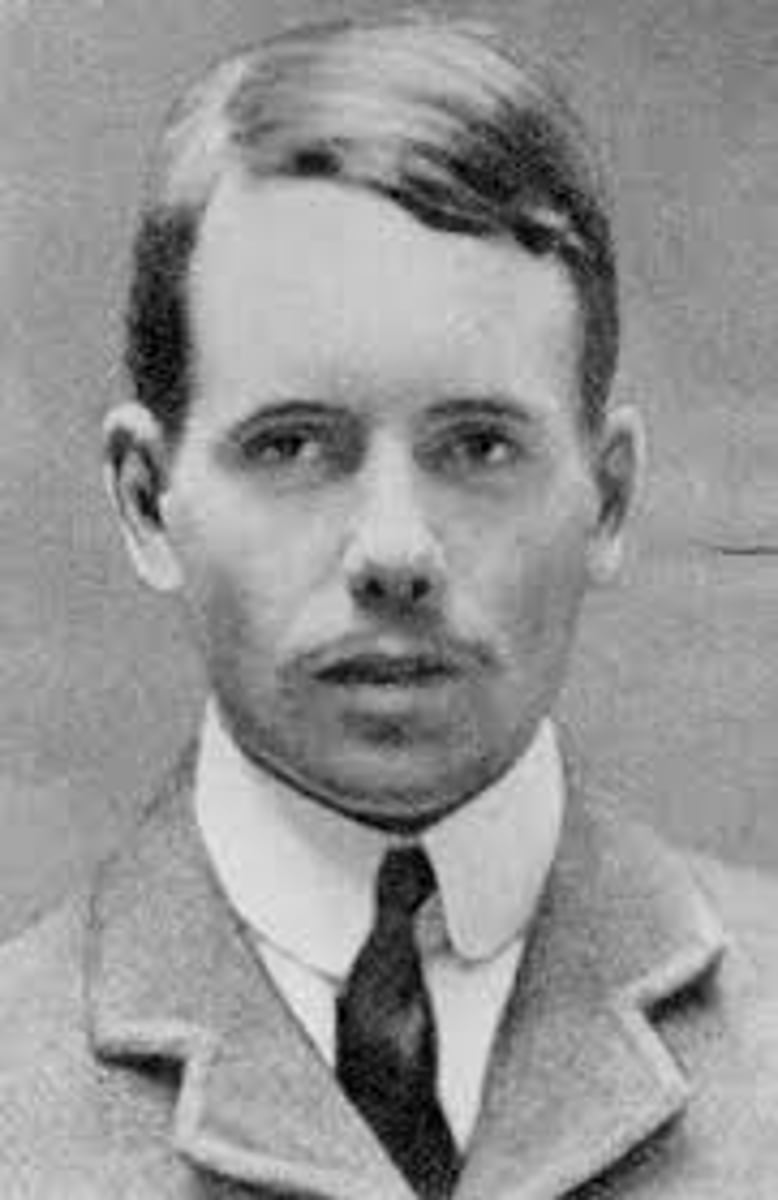
Henry Moseley
Arranged the periodic table by atomic number instead of mass number

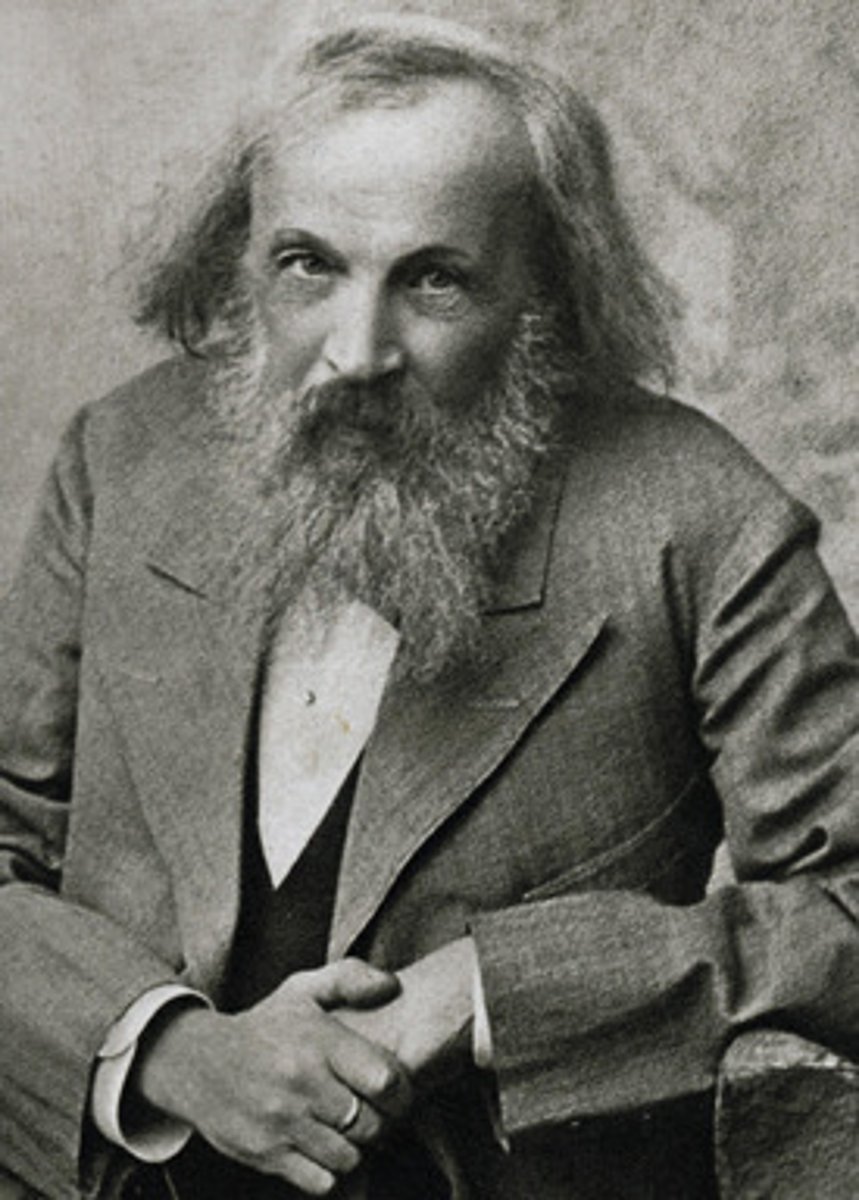
Dimitri Mendeleev (1869)
Developed the first periodic table of elements, organized by atomic mass

shielding
inner level electrons block attraction from the nucleus
nuclear charge
number of protons in the nucleus