Edexcel B GCSE Geography Paper 1
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
What are ocean currents?
When cold, salty water sinks at the Poles, it then flows towards the Equator and is warmed again, creating a convection current.
What do pressure differences result in?
Land and sea end up heating differently. Land generally forms areas of low pressure in the summer and high pressure in winter. Sea forms high pressure in summer and low pressure in winter.
Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ)
Occurs between the two Hadley Cells, where warm tropical air rises at the Equator. The Sun’s radiation is most intense at the Equator, causing warm tropical air to rise rapidly.
Near the ITCZ, is there more rainfall or less?
More because the heat creates an area of low pressure that brings heavy rainfall. As the rising air moves away from Equator, it loses its moisture and density, falling to form arid regions.
Where is the Ferrell cell?
The Ferrel Cell is (30°-60°N and S)
Where is the Polar cell?
The Polar Cell is (60°-90°N and S)
Does the eruption theory explain the heating or cooling of the Earth? Explain your choice
It cools the planet, as volcanoes produce ash that rises into the stratosphere, reflecting sunlight back into space.
Does the asteroid collision theory explain the heating or cooling of the Earth? Explain your choice
It cools the planet. as asteroids hit Earth, sending ash and dust into the atmosphere, blocking sunlight.
Does the sunspot theory explain the heating or cooling of the Earth? Explain your choice
Warming the planet, as lots of sunspots means more solar energy
Does the Orbital change theory explain the heating or cooling of the Earth? Explain your choice
Both- The Earth has natural warming and cooling periods caused by Milankovitch cycles or variations in the tilt and/or orbit of the Earth around the Sun (Wobble, roll and stretch theory).
How do ice cores tell us about past climates?
Air bubbles in large samples of ice extracted from deep in the ground contain CO2, that tells us there have been previous warm and cold periods.
How do tree rings tell us about past climates?
Each ring in a tree shows a year’s growth. In warmer and wetter years, a tree grows more.
How do historical sources tell us about past climates?
Historical records from ancient cave paintings, diaries and written observations have provide evidence of climate change through accounts of harvests.
How does pollen analysis tell us about past climates?
Study of plant pollen preserved in sediment can show changes in the type of vegetation in a particular area. They type of vegetation tells us the conditions of the climate
Explain the enhanced greenhouse effect
Human activities (industry, transport, energy, farming) produce greenhouse gases (carbon dioxide, methane) that trap heat from the Sun and warm the planet.
Give evidence for enhanced greenhouse effect
1°C rise in average temperature since the early 1900s
Sea levels have risen over 200mm (thermal expansion)
Arctic sea ice has halved in area since 1980
90% of the world’s valley glaciers are shrinking
Climate change could cause:
more frequent floods and droughts
stronger storms (tropical cyclones)
changes to farming (unreliable rainfall)
Why is predicting future climate change difficult?
As there are too many unknown factors like people’s lifestyle choices and consumption of fossil fuels versus renewable energy
Give the definition of a tropical cylcone
It is a rotating system of clouds and storms forming over tropical waters
What the the three conditions for a tropical cyclone?
A warm ocean, exceeding 26.5°C allowing a warm body of air to develop
Strong winds that draw the warm air up rapidly from the ocean surface
A strong Coriolis force created by Earth’s rotation (so not formed on or close to Equator where the force is too weak).
Hazards caused by tropical cyclones
Strong winds bring down trees and power lines
Storm surges (a large scale increase in sea level due to a storm)
Landslides occur because saturated hillsides can slump.
For a named developing country, explain why it is vulnerable to cyclones.
Named developing country: Bangladesh
much of its population is rural, living on low-lying flood-prone farmland
urbanisation means increased surface runoff so more rain water reaches rivers
settlements have been built on low-lying land prone to flooding
its Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is low, so it is less able
to invest in costly flood defences.
85% of the world’s cyclone deaths are in Bangladesh
For a named developing country, explain how it prepares for cyclones
Named developing country: Bangladesh
forecasting (forecast issued through tv and radio)
satellite technology (to track cyclones and issue warnings)
warning systems in villages (as not everyone has access to technology)
evacuation strategies (cyclone shelters)
surge defences (embankments, costly but effective).
For a named developing country, explain the impacts of a tropical cyclone
Bangladesh: May 2009, Cyclone Aila
killed 190 people
left 750,000 people homeless
60 000 animals killed
sickness spread from contaminated water
3.5 million people affected due to high pop. density
For a named developed country, explain how it prepares for cyclones
Named developed country: USA
over 20 satellites operate everyday
evacuation systems are in place
awareness of the public (eg awareness weeks)
artificial levees
not perfect as during hurricane Sandy, satellites software was out of date and thus warning people took longer, so it was costly
For a named developed country, explain the impacts of cyclones
Named developing country: USA, Hurricane Sandy 2012
2nd costliest hurricane in the US ($6.5)
250 people killed
100 000+ homes damaged
10 million without power
no access to bank accounts due to power cuts
23 fires across NYC due to dependence on candles
What are the four main layers of the Earth's structure?
The four main layers of the Earth's structure are the crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core.
The inner core:
Solid sphere of iron and nickel
Temperatures reaching up to 5700°C.
Most dense
The outer core:
liquid iron and nickel
responsible for generating Earth's magnetic field.
Lower mantle and the Upper mantle:
Lower mantle: solid - thickest section of the Earth
Upper mantle - the asthenosphere, the “lubricating layer” (a porridge-like mass of molten rock and solid rock)
Explain how convection currents cause tectonic plates to move
Radioactive decay in the core causes heat to rise and fall in the mantle
This movement pushes/pulls/drags the overlying plates
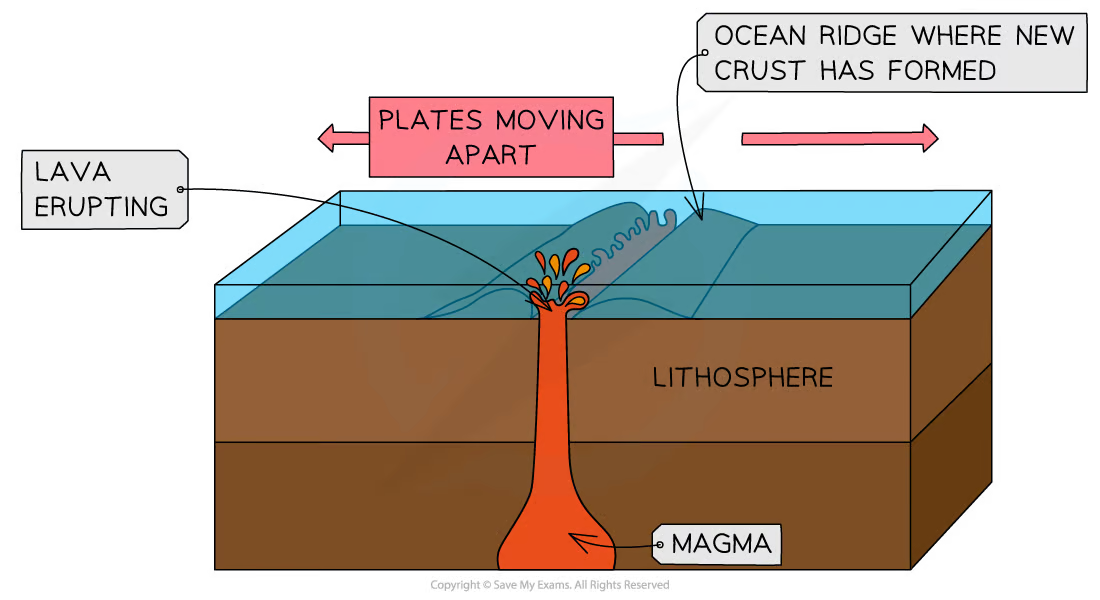
Divergent
The plates are moving apart and magma rises to fill the gap
Shield volcanoes and small earthquakes
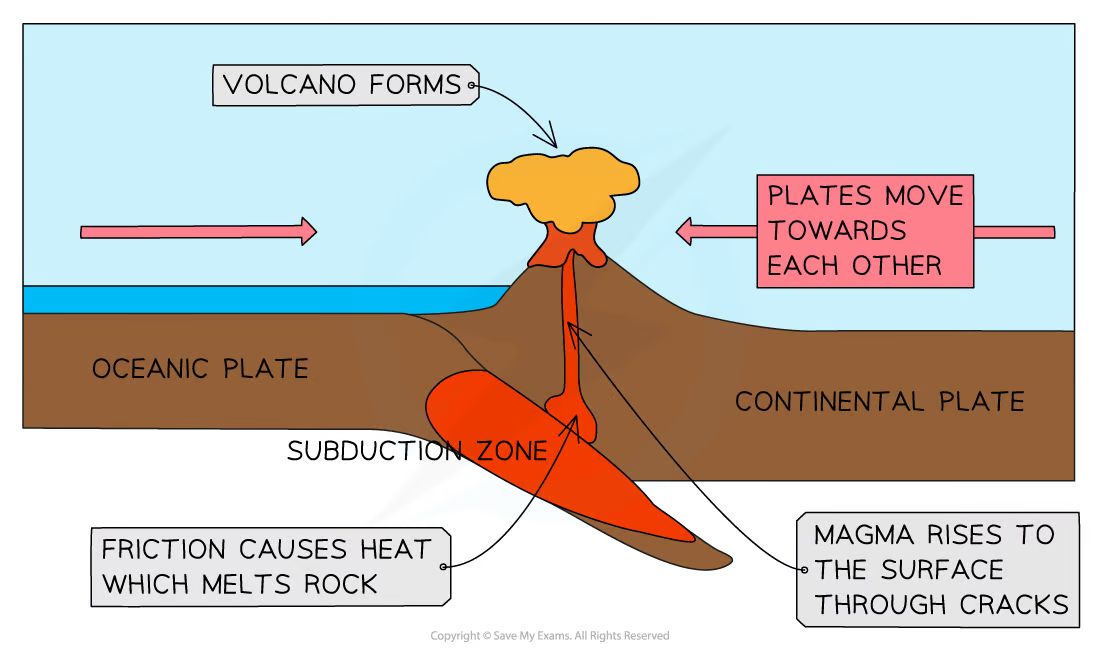
Convergent
Plates push together, and the denser oceanic plate is subducted
Composite volcanoes, and violent earthquakes
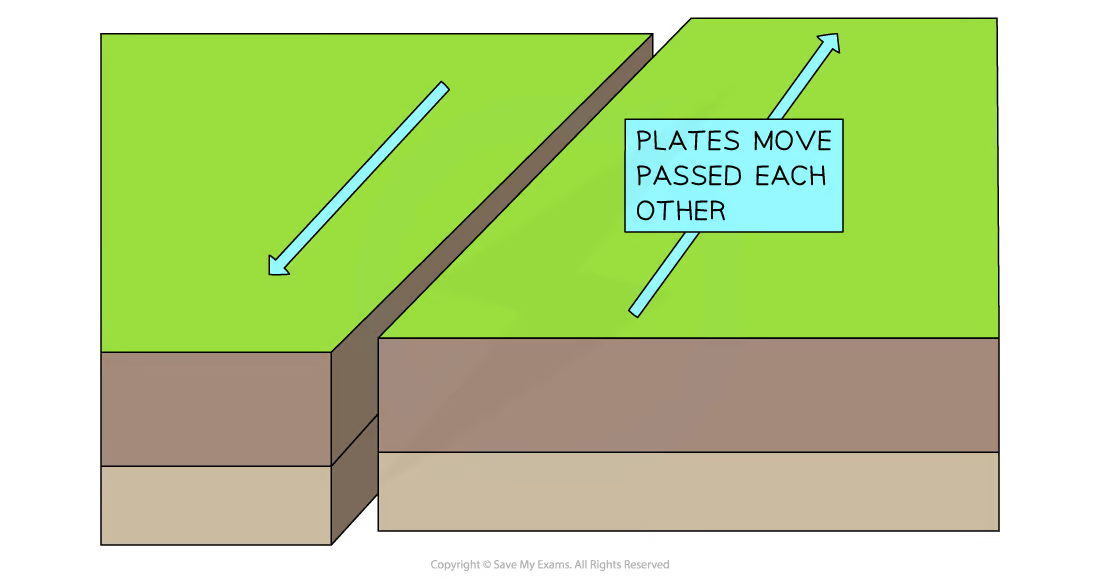
Conservative
Plates slide past each other
Friction between the plates causes earthquakes
The magnitude of an earthquake is measured on the…
Richter Scale! 😍😍😍
Explain the distribution of earthquakes globally
Pacific Ring of Fire
Could happen at all plate boundaries
Composite volcanoes
Tall, steep-sided volcanoes
Convergent plate boundaries
Shield volcanoes
Broad, gently sloping volcanoes
Hot spots and divergent boundaries
For a named developing country, explain why it is vulnerable to earthquakes.
Named developing country: Haiti
Low wages, 70% of people lives under $2 a day
Building quality, 86% lived in slum conditions and buildings could easily topple
Healthcare, 0.25 doctors per 1000 people
For a named developing country, explain the impact of earthquakes.
Named developing country: Haiti, Port-au-prince 2010
300 000 deaths
1 million made homeless
Cholera due to lack of clean water, killed a further 8,000 people
$13.7 billion for repairs
For a named developed country, explain the impact of earthquakes.
Named developed country: Japan, Sendai 2011
20,000 people were killed
Tsunami waves caused US$235 billion of damage
350,000 people were made homeless
2 nuclear reactors went into meltdown
Development can be measured using:
economic indicators (for example, GDP per capita)
social indicators (for example, literacy rate)
political indicators (for example, corruption).
Human Development Index (HDI)
An average of
life expectancy
literacy
average length of schooling
GDP per capita.
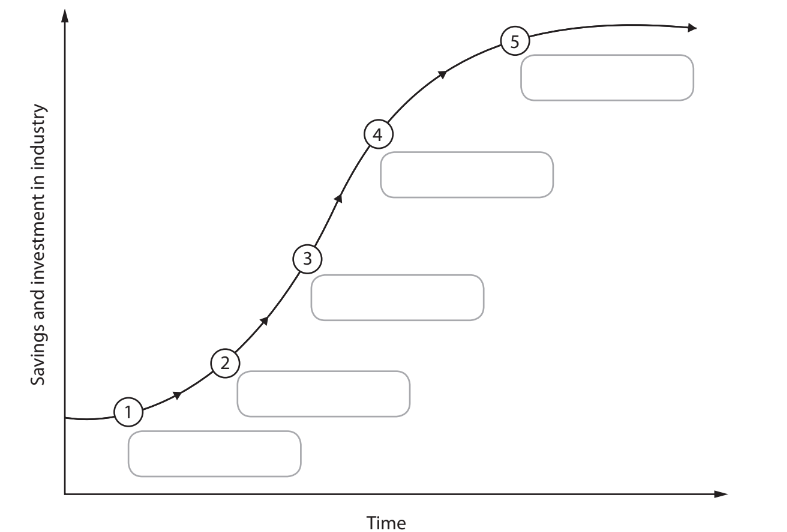
Rostows Development Theory:
Traditional society – most people work in agriculture, a subsistence economy (for example, Malawi).
Pre-conditions for take-off – a shift from farming to manufacturing, trade increases
Take-off – investment creates new industries (for example,
India), growth is rapid.
Drive to maturity – industries produce consumer goods and technology is used throughout the economy.
Age of high mass consumption – wealth is spent on the service sector such as healthcare (for example, the UK).
Frank’s dependency theory argues that:
development is about a core and periphery
core = developed nations
periphery = ‘others’, producing raw materials
to sell to the core
periphery depends upon the core for their
market
What does a Top-Down development scheme involve and give an example
Governments or Transnational Companies (TNCs) plan changes which are often large and expensive, using loans from Inter-Governmental Organisations (IGOs).
An example is the Sardar Sarovar Dam
Sardar Sarovar Dam , advantages and disadvantages
Advantages :
India’s cities – hydroelectric power (HEP)
Farmers – irrigation water for crops
Disadvantages :
Local residents – Villages and farmland have been flooded
by the dam.
Western India – Religious and historic sites have been
flooded.
What does a Bottom-Up development scheme involve and give an example
NGO’s (non-governmental organisations) work with communities and identify their needs
E.g Biogas plants in India
Biogas plants , advantages and disadvantages
Advantages :
Cooking with gas is smoke-free, reducing respiratory
illnesses.
Girls have more time to go to school rather than collecting
fuelwood.
Disadvantages :
Small-scale
For a named emerging country, explain the significance of its location in its development
Large coastline - east-west shipping routes are essential for trade and India’s growth.
India’s location in Asia - close to the “Asian Tigers“
India is also a member of the United Nations, the World Trade
organisation and the Commonwealth.
How does globalisation help India?
Globalisation has increased India’s exports and output.
Exports increased by almost 20 times in 23 years
500% increase in GDP
Reduced unemployment and poverty.
Where does most FDI (foreign direct investment) come from in India
From TNC’s (Transnational Companies)
Megacities
Have over 10 million people (for example, Mumbai).
urban primacy
A city that has an importance and bigger influence than their size suggests (for example, London).
Informal economy vs formal economy
Informal economy
Millions of people sell goods or offer services on the street (for example, selling fruit)
Formal economy
Has an organised system of employment with clear written rules of recruitment, agreement and job responsibilities.
India Case study : Core
Maharashtra
India Case study : Periphery
Bihar