Animal cells 𝜗ৎ
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What organelles does an animal cell have?
Nucleus
Mitochondria
Ribosome
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Golgi body
Lysosomes
Cell membrane
Cytoplasm
Function of the nucleus
Largest organelle in the cell - contains genetic information which codes for protein synthesis
Structure of nucleus
Nuclear envelope of
Nucleoplasm
Nucleolus

Nuclear envelope
Double membrane with pores to allow the transport of mRNA and ribosomes out of the nucleus to the cytoplasm
Nucleoplasm
Cytoplasm like material which contain chromatin - which condenses to form chromosomes during cell division
Nucleolus
Small spherical body that synthesises ribosomal RNA
Function of mitochondria
Release ATP energy during aerobic respiration
Structure of mitochondria
Outer/ inner/inter membrane
Cristae
Matrix
Ribosome
Circle of DNA.
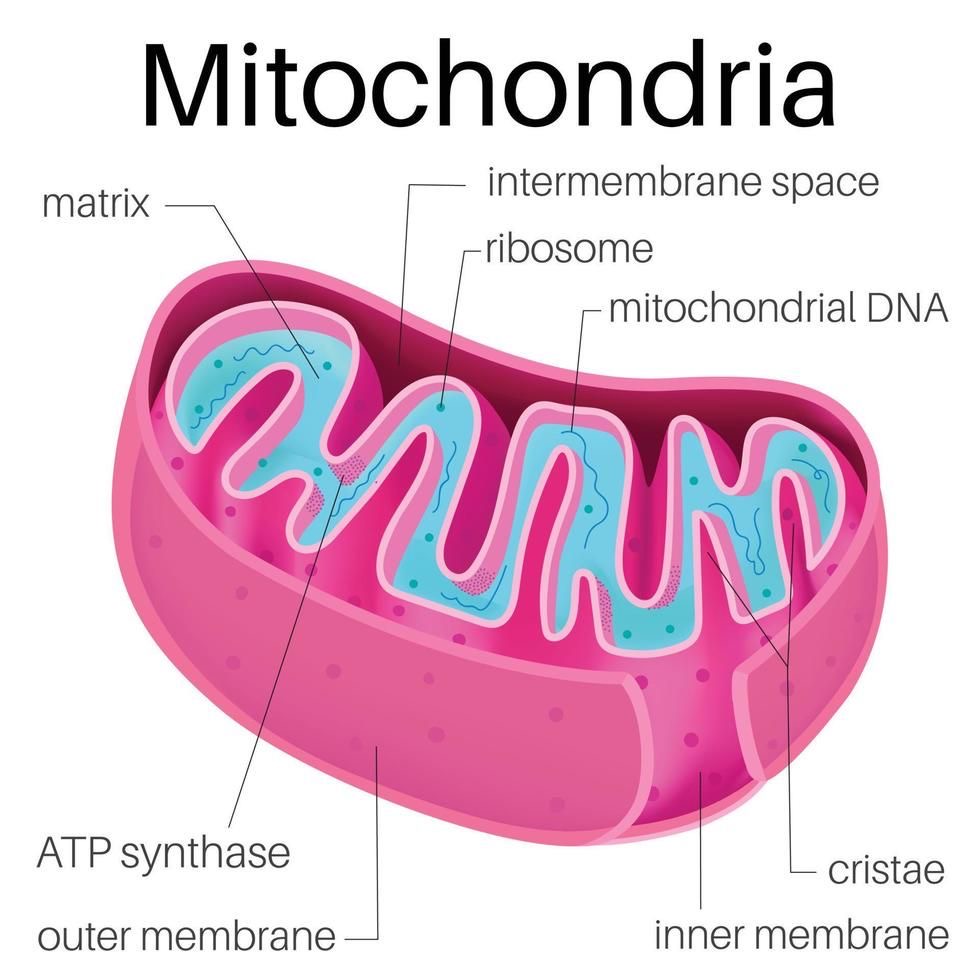
Outer/ inner/inter membrane
Double membrane with a narrow, fluid-filled inter membrane space
Cristae
Inner membrane folds into Cristal which increases surface area for ATP production
Matrix
Contains enzymes - stages of aerobic respiration occur here
Ribosomes
Small 70s ribosomes for ATP production
Circle of DNA
Allows self replication
Function of ribosomes
Synthesise proteins by reading the code on mRNA in the cytoplasm ( translation ) - some attach to the RER for protein secretion
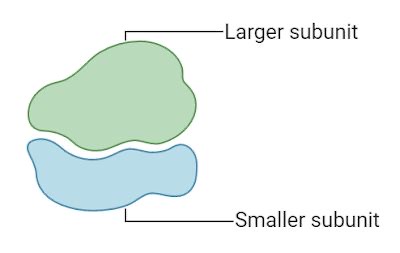
Structure of ribosome
Large subunit
Small subunit
What are the subunits made of
rRNA and protein
Where are ribosomes typically found
Free in the cytoplasm
Associated with rough endoplasmic reticulum
Function of Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Protein synthesis + transport of proteins
Structure of rough endoplasmic reticulum
Network of flattened membrane sacs ( cisternae ) connected to the nuclear envelope - studded with ribosomes
Function of smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Building + transporting lipids - prominent in cells loaded with carbohydrates, proteins, or fats
Function of Golgi body
Modifying + packaging proteins into secretory vesicles for secretion from the cell by exocytosis
Producing glycoprotein
Forming lysosomes
Structure of Golgi body
Network of interconnected flattened sacs, receives protein filled vesicles from the RER
Structure of lysosomes
Single membrane sacs packed with hydrolytic (digestive) enzymes made by Golgi body
Why are these enzymes kept separate
Safety of the cell and then unleashed to break down old cell parts or infested materials eg bacteria
Function of Centrioles
During cell division centrioles move to opposite poles of the cell forming spindles - crucial role in ensuring equal distribution of genetic material
Structure of centrioles
Cylindrical organelles composed of micro tubes positioned at right angles