Structure of Flowering Plants - Chp 23
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Is the shoot system above or below ground?
above
Is the root system above or below ground?
below
Tap roots
- primary root grows from the radicle
- lateral/fibrous/secondary roots are formed from the primary root, and have tiny hairs on them
- present in most dicots
Tap root: example
carrot
Fibrous roots
- form when the radicle dies
- equal sized roots emerge from the base of the stem
- most common in monocots
Fibrous roots: example
grass, daffodils
Adventitious roots
- do not develop from a radicle
- grow in strange places
Adventitious roots: example
roots at the base of an onion
Function of Roots
- anchor the plant
- absorbs water and minerals from the soil, through the root hairs
- transports materials to the shoot
- store food
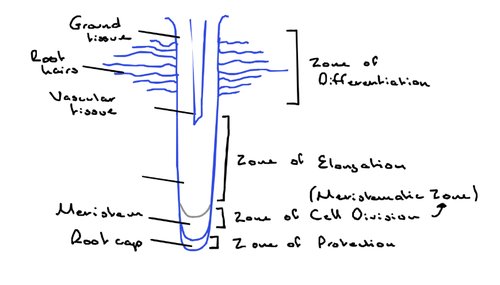
What are the 4 zones in a root?
- zone of protection
- zone of cell production/meristematic zone
- zone of elongation
- zone of differentiation
Zone of protection
the root cap protects the root as it pushes through the soil
Zone of cell production/Meristematic zone
- apical meristems are found here
- constantly undergoing mitosis to produce new cells so the roots can grow
Meristem
plant tissue that is capable of mitosis
Zone of elongation
- the new cells formed by the meristem are very small and need to grow
- plant growth regulators such as auxin stimulate the cells to grow larger
Zone of differentiation
elongated cells are specialised and divided into 3 different types of tissues
Herbaceous plant
- usually soft and green
- does not contain lignin
Woody plant
- hard and woody
- does contain lignin
Stem structure: nodes, internodes, apical bud, axial, auxilliary/lateral buds, lenticel
nodes - where leaves and branches emerge from the stem
internodes - part between nodes
apical bud - the tip of the stem which is responsible for plant growth
axial - the angle between the leaf and the stem
auxilliary/lateral buds - found at each axial, responsible for the growth of new leaves or branches
lenticel - opening found in the stems that allows gas exchange to occur
Functions of the stem
- supports aerial parts of the plant
- transports water and minerals from roots to leaves
- transports foot from leaves to roots
- carries out photosynthesis
- store food
Example of a stem adapted to store food
Potato tuber
Leaf structure: petiole, lamina, midrib, veins
petiole - the stalk of the leaf, contains transport tissues
lamina - thin flat blade structures, aka the leaves
midrib - petiole continues through the lamina, contains transport tissues
veins - contains transport tissues
Venation
The pattern vein in a leaf
Parallel venation + Example
- the veins run along side each other
- grass, daffodils
Net/reticulate venation + Example
- veins form a branching structure throughout the leaf
- roses
Functions of leaves
- make food by photosynthesis
- exchange gases with atmosphere
- lose water by transpiration
- store food
Example of a plant adapted to store food in the leaves
Spinach
3 types of plant tissue
- dermal tissue
- ground tissue
- vascular tissue
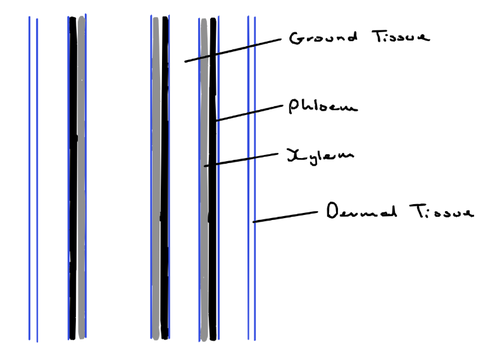
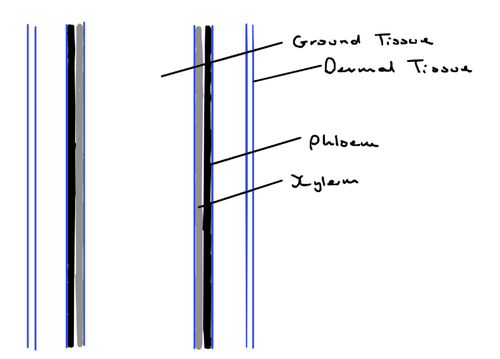
Dermal tissue + Function
- outer layer of the plant (epidermis) protects the plant
- some plants have a waxy cuticle which prevents water loss in hot climates
Ground tissue + Function
- cortex is the area occupied by the ground tissue
- makes up the bulk of the plant
- carries out photosynthesis, provides strength and support to aerial parts of the plant, stores food (only some plants)
Vascular tissue + Function
- made up of the xylem and phloem, contained in vascular bundles
- xylem transports water and minerals
- phloem transports food
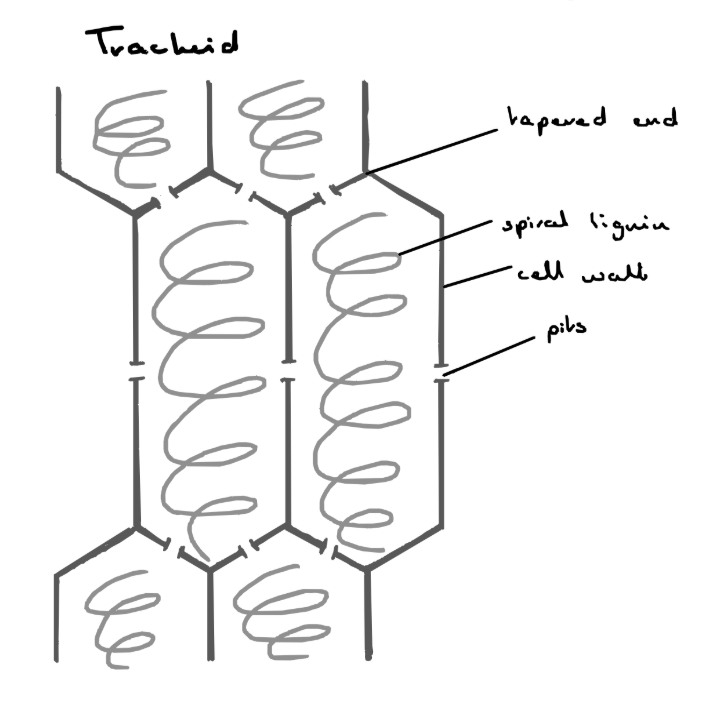
Structure of xylem
- consists of tracheids and vessels
Is xylem living or dead?
considered a dead tissue as the living contents die before maturity
Function of xylem
- responsible for the transport of water from the roots to the leaves
- spiral lignin provides support for the plant
Location of xylem
- found in the roots, stem, leaves, flowers
- found in vascular bundles
Tracheids
- long, tapered, hollow cells
- overlap and allow water to pass from one to the other through tiny slits called pits
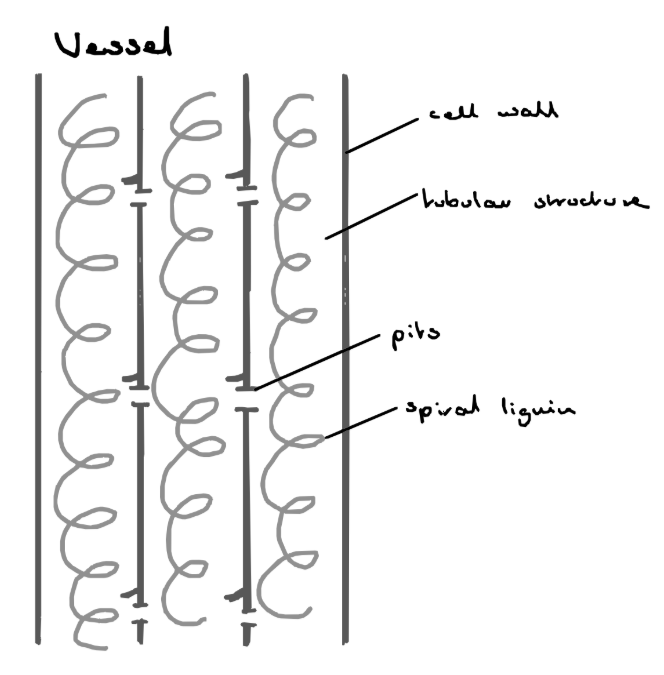
Vessels
Tubular structures - a number of cells join end to end, the end wall is broken down to form a continuous tube
Pits - allows water to pass from side to side
- more efficient than tracheids due to being wider and continuous tubes
Structure of phloem
made up of sieve tubes and companion cells
Function of Phloem
transports food made by photosynthesis form the leaves to the rest of the plant
Location of phloem
- found in roots, stems, leaves
- found in vascular bundles
Sieve tubes - structure
Sieve tube elements - individual elements that are long tubular structures joined on top of eachother, they contain cytoplasm but do not have a nucleus
Sieve plates - end walls that contain pores to allow the passage of materials from one element to another
Cell wall - made of cellulose and no lignin is present
Companion cells
- for every sieve tube there is a companion cell
- contains a nucleus and a dense cytoplasm
- control the activity of the sieve tube
Is phloem living or dead?
living due to the presence of the companion cell, and its nucleus
Transverse section of a root diagram

Longitutindal section of a root diagram
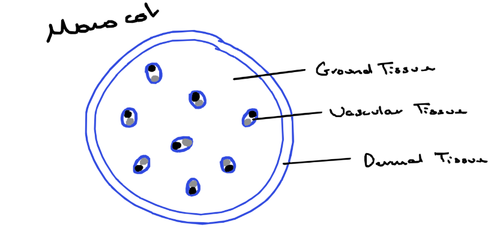
Transverse section of a monocot stem diagram
Transverse section of a dicot stem diagram
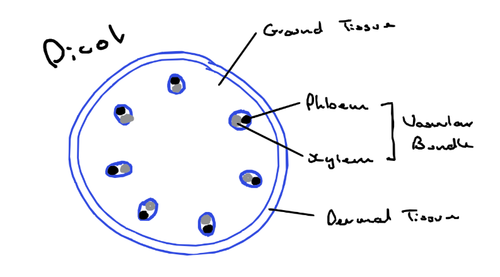
Longitudinal section of a monocot stem diagram
Longitudinal section of a dicot stem diagram
Longitudinal tracheid diagram
Longitudinal vessel diagram
Longitudinal phloem diagram
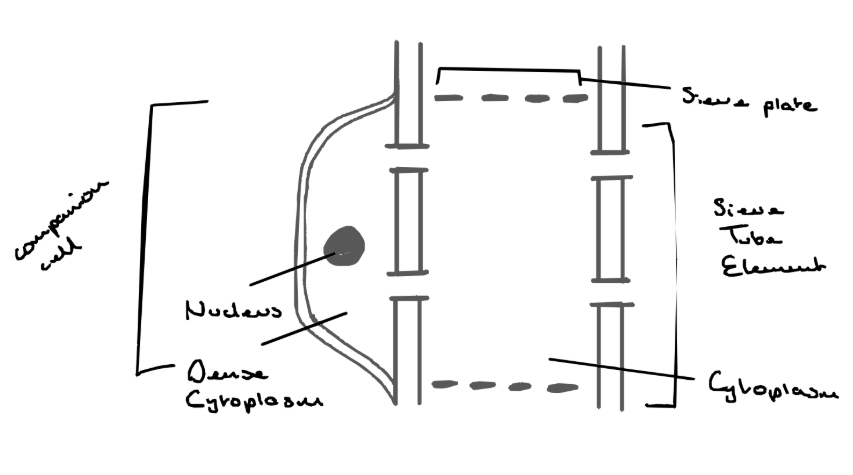
Transverse phloem diagram
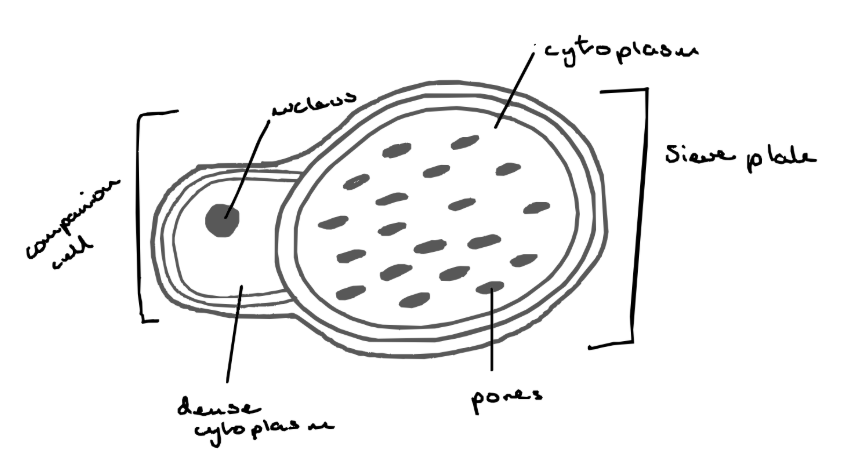
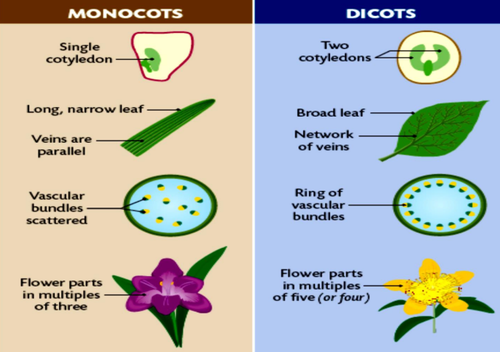
Characteristics of a Monocotyledon
- contain 1 seed leaf
- mostly herbaceous, soft and not woody
- parallel venation
- vascular bundles are placed at random along the stem
- flowering plants are arranged in multiples of 3
- eg daffodils, grasses
Cotyledon
a leaf in the seed specialised for food storage
Characteristics of a Dicotyledon
- contain 2 seed leaves
- herbaceous or woody
- broad leaves with net venation
- vascular bundles arranged in rings
- petal arrangement in multiples of fours or fives
Differences between Monocots + Dicots