PSYC 336 - Clinical
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Epidemiology
The prevalence and distribution of a disorder in a population.
Etiology
The cause(s) of a disorder.
Pathology
The underlying psychological/ neurobiological features of a disorder.
Transdiagnostic
factor that is part of serval diagnosis
The essentialist approach to mental disorders
Mental disorders are natural categories whose true nature can be discovered and described
Categories represent empirically verifiable similarities among and differences between people
The social constructionist approach of mental disorders
Concepts of mental disorders (of categories) are social constructions
Syndrome Heterogeneity
different causal mechanisms may relate to the same disorder, and multiple outcomes of interest can occur within one individual.
Comorbidity
the co-occurrence of two or more disorders in a single individual
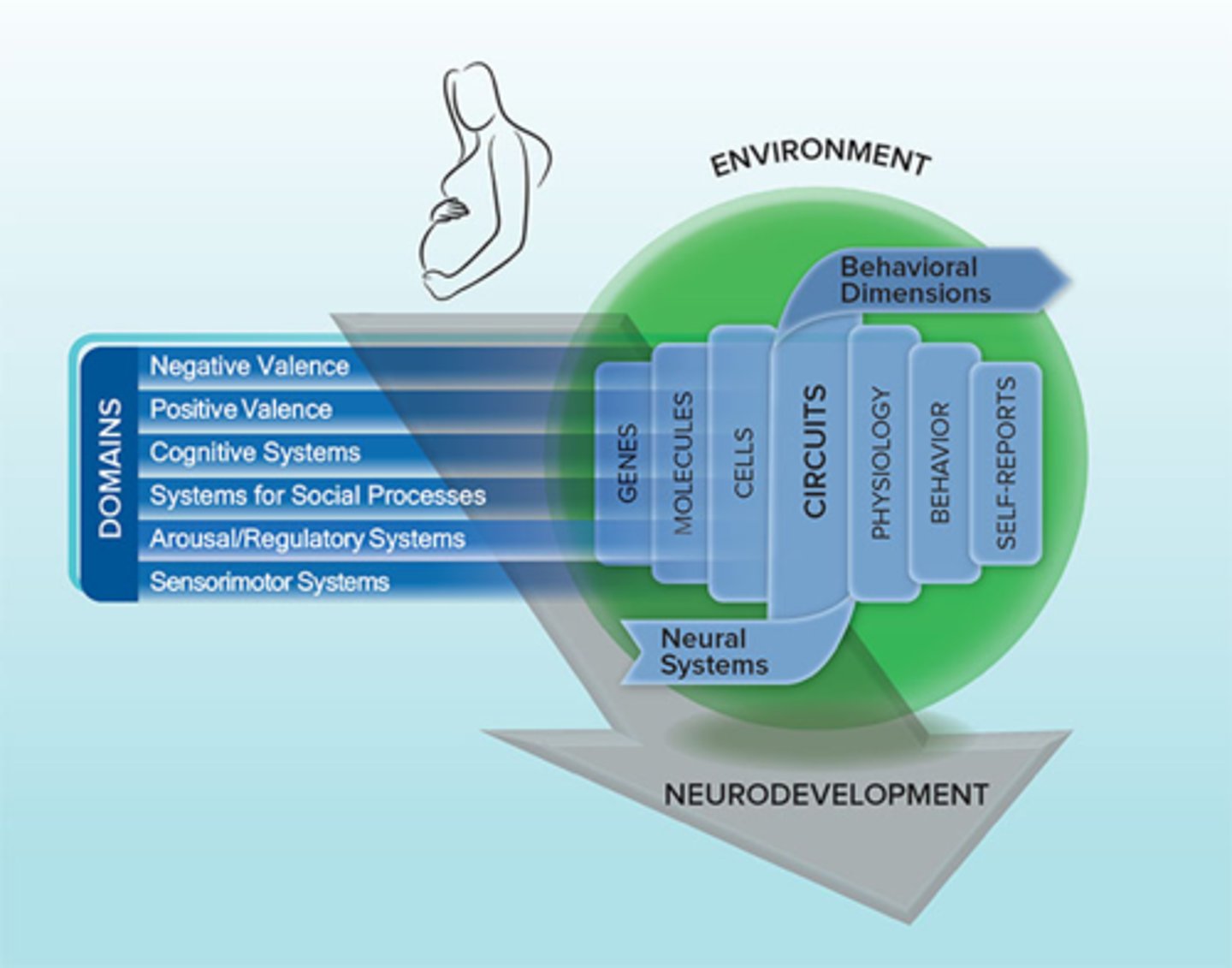
RDoC
Psychopathology research moving toward transdiagnostic domains of functioning that have a clear neurobiological/cognitive basis (bottom up)
acrophobia
two of the following symptoms
Public transportation
Open spaces
Enclosed spaces
Standing in line
Being in a crowd
Being outside of the home alone
interoceptive avoidance
Strong sensitivity to and avoidance of internal bodily symptoms associated with anxiety and panic
Exercise, sex, caffeine, alcohol, saunas, wearing neckties, anger, scary movies
safety behaviors
Behaviors intended to avoid disaster, dysfunctional emotion regulation strategies
Check pulse
Be near hospital
Carrying antianxiety medication
Having a safe person
Experiential avoidance
Person is unwilling to remain in contact with private experiences
Watching TV, Eating
Avoiding feelings
categories of obsessions
Contamination
Guilt and responsibility of harm
Uncertainty
Taboo thoughts about sex
Violence and blasphemy
Need for order and symmetry
Categories of compulsions
Decontamination
Checking
Ordering and arranging
Mental rituals
Body Dismorphic Disorder
Intrusive, distressing thoughts concerning one's appearance
Repeated checking
Two types of CBT
ERP
CT
exposure and response prevention
Entails confrontation with stimuli that provoke obsessional fear, but that objectively pose a low risk of harm
delivery of ERP
A few hours of assessment and treatment planning
Assessment of obsessions, compulsive rituals, avoidance strategies and anticipated consequences of confronting feared situations
15 hours of treatment sessions, about 90 minutes each
key requirements for ERP success
Physiological arousal and subjective fear must be evoked
Fear responses must gradually diminish during exposure
Initial fear response at the beginning of each exposure session
should decline across sessions
efficiency of ERP
Improvement rates 50-70%
Motivational Enhancement theory
a therapy designed to quickly produce internally motivated change, helps to develop internal motivation to change
in vivo exposure
Gradual exposure to feared situations in order to extinguish fear
Examples for panic disorder in vivo exposure:
Driving
Public Transporation
Bridges
Waiting in lines
Nomothetic
on average what happens in certain treatments and how they work
Idiographic
what is going to work for that particular person
Experiment to prove sub-threshold Psychopathology
2000 female twin pairs with symptoms of depression
Tested:
Risk of depression recurrence over 5 years
Risk of depression in co-twin over 5 years
Conclusion:
DSM diagnostic criteria are not reflective of natural discontinuity in depressive symptoms as experienced in the general population
Line separating no diagnosis from diagnosis is arbitrary - a convection not a fact
Traumatic stressors stats
quite common with a lifetime prevalence of trauma being 60.7% for men and 51.2% for women
strong predictors of unhealthy trauma recovery
- Severity of event
- Lack of social support
- Ongoing post-event stress
Acute Stress Disorder (ASD)
occurs within a month after exposure to traumatic stress
Sensory representations (S-reps)
Inflexible, involuntary, sensation bound, disintegrated from the autobiographical memory base and are connected to the superior partial areas, amygdala, insula areas of the brain
Memories of the trauma are over represented in S-reps
prolonged grief disorder
Prevent the individual from fully processing and accepting the loss of a loved one
Stress disorder
exposure based interventions for trauma
Help reduce trauma related distress by facilitating new learning about the meaning of the trauma and altering maladaptive beliefs about oneself, others, and the world
Prolonged exposure
In vivo exercise
Imagined exposure
ex:
EMDR
NET
Cognitive treatments for trauma
Changes in the person's understanding of the trauma and its meaning in their life
Update the trauma memory
Discussion of key themes:
Challenges to safety
Trust
Power
Self esteem
pre trauma
characteristics of the individual and environment that preceded trauma exposure
-Lower socio-economic status
-Lower intelligence
-Childhood trauma
-Prior adult or child trauma
-Prior worse adjustment
peri-trauma
Characteristics of the trauma and the environmental and individual response to the trauma
Things about the trauma that makes them likely to develop
- Trauma severity
- Perceived life threat
- Peri-traumatic emotions
post-trauma
Individual and environmental factors that occur after the trauma
Things that happened after event that makes them more likely to develop
- Ongoing life stress
- Lack of social support
- Negative cognitions
resilience factors to trauma development
Spirituality
Connections to family
Close bonds with others as a result of shared history, experiences, and culture
Nature of trauma memory
Intentional recall is poor:
- Trouble intentionally recalling complete memory of trauma
- Memory is poorly integrated into autobiographical memory base (no clear context in time, place, other memories)
Vivid unintentional recall:
- Involuntary and intrusive memories (flashbacks)
- Flashbacks experienced as if in the present
- Flashbacks experienced despite more recently learned contradictory info
- Flashbacks triggered by wide range of stimuli (fear generalization)
prolonged exposure
Exposure to trauma-related memories(imaginal exposure) and situations (in vivo exposure)
imaginal exposure
a part of prolonged exposure
Repeatedly tell story of trauma in as vividand detailed a manner as possible- emotional engagement (activate trauma memory)- habituation- cognitive restructuring
CISD (Critical Incident Stress Debriefing)
severe events are discussed within teams; peer driven process; confidential; after a major incident; conducted 24-72 hours after
does not work!!!!!