STANDARDIZATION AND TITRATION CURVES
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
volumetric standards (4 criterias)
the ideal standard solution for a titrimetric method will:
be sufficiently STABLE so that it is necessary to determine its concentration only once
react RAPIDLY with the analyte so that the time required between additions of reagent is minimized
react more or less COMPLETELY with the analyte so that satisfactory endpoints are realized
undergo a SELECTIVE reaction with the analyte that can be described by a balanced equation
Should concentrations of volumetric standard solutions be ascertained?
YES
Standardization
The concentration of a volumetric solution is determined by titrating it against a carefully measured quantity of
a primary standard
secondary standard
an exactly known volume of another standard solution
Primary Standards
highly purified compound that serves as a reference material in titrations and in other analytical methods
6 Characteristics of Primary Standards
high purity. established methods for confirming purity should be available
atmospheric stability (does not react easily when kept in its pure form; low reactivity; does not react easily with atmospheric oxygen)
absence of hydrate water so that the composition of the solid does not change with variations in humidity
modest cost
reasonable solubility in the titration medium
reasonably large molar mass so that the relative error associated with weighing the standard is minimized
In older editions of the USP, sodium carbonate is used as the primary standard instead of tromethamine. What advantages does tromethamine have over sodium carbonate?
Tromethamine as Primary Standard (THAM or TRIS): 121.4 g/mol
Sodium Carbonate: 105.99 g/mol
higher molecular weight (sodium carbonate has a lower equivalent weight)
batter atmospheric stability (sodium carbonate is hygroscopic)
Secondary Standards
compound whose purity has been determined by chemical analysis. the secondary standard serves as the working standard material for titrations and for many other analyses
how are weaker or stronger volumetric solutions prepared
by using the official procedure with proportionate amounts
what glassware is used for volumetric solutions
are always prepared with volumetric glassware for volume measurement and a suitable analytical balance for weighing
They are precisely calibrated glassware used to measure and transfer specific volumes
Volumetric solutions are to be prepared at the standard temperature of?
25 degrees Celcius, if carried out at a markedly different temperature, standardize the volumetric solution used as a the titrant at that different temperature or make a suitable temperature correction
Empirical Concentration
refers to the actual, experimentally determined concentration of a solution, which may differ from its theoretical or nominal concentration due to factors like impurities, reaction side effects, or environmental influences
Stnadardization of Volumetric Solution
the volumetric solution’s concetration is STILL unknown
Hydrate compounds
contain variable water content which changes over time due to absorption or loss of moisture
anhydrous substances
ensure that the measured mass corresponds exactly to the number of moles of the substance
drying the standard is often necessary for some primary standards True or False
True
A higher molecular weight means less substance is needed per mole, making errors less significant true or false
False ; more substance is needed
example of secondary standards
NaOH is one example of a secondary standard. Commercially available NaOH contains impurities of NaCl, Na 2 CO3 , and Na 2 SO4 , and readily absorbs H2O from the atmosphere. To determine the concentration of NaOH in a solution, we titrate it against a primary standard weak acid, such as potassium hydrogen phthalate
acetic, hydrochloric, and sulfuric acids may be standardized against a sodium hydroxide solution that recently has been standardized against a certified primary standard
Titer value
mass of a substance (in grams) that reacts with 1 mL of a standard
solution during a titration. It helps determine the exact concentration of an analyte in solution.
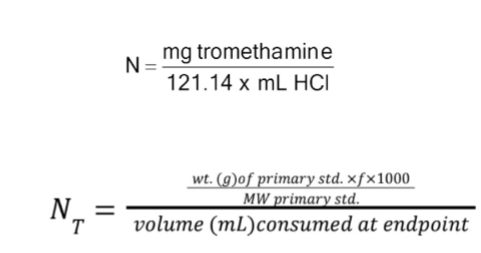
Normality factor
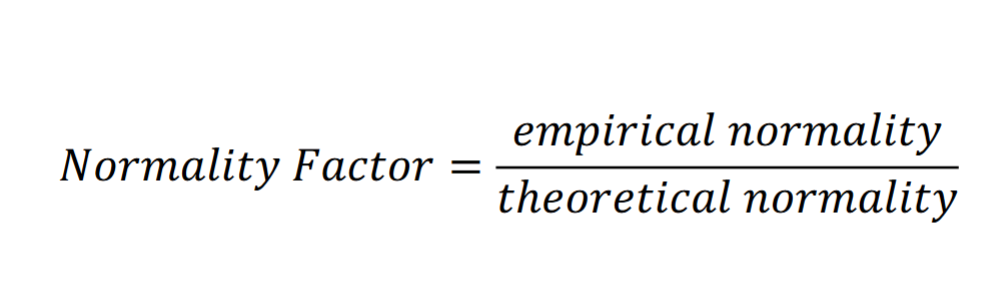
titration curve
plot of some function of the analyte or titrant
concentration on the y axis versus titrant volume on the x axis.
Two types of titration curve
sigmoidal titration curve
line segment curve
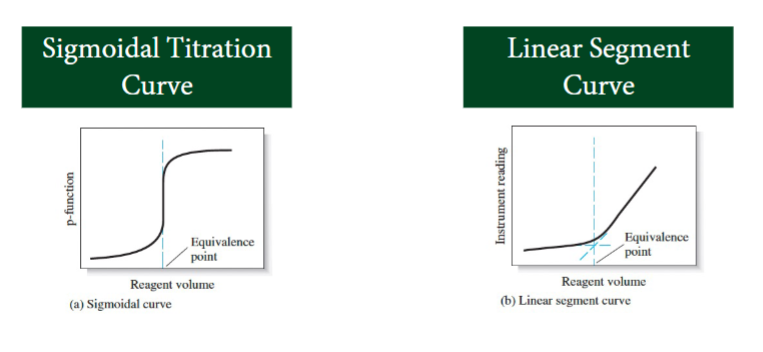
sigmoidal curve
A sigmoidal curve in which the p-function of analyte (or sometimes the titrant) is plotted as a function of titrant volume
linear segment curve vertical axis
instrument signal
that is proportional to the concentration of the analyte or titrant.
advantages of sigmoidal titration curve
speed and convenience
Linear Segment Curve
The linear segment type is advantageous for reactions that are complete only in the presence of a considerable excess of the reagent or analyte
In a sigmoidal titration curve, where is the equivalence point?
At the inflection points:
point on a curve
where the concavity
changeshighest slope
the point in the curve
where the second
derivative changes
sign.
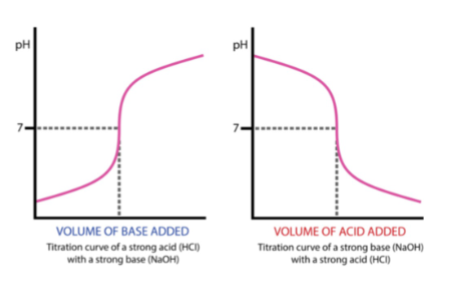
drawing titration curve
check ppt