BIOS 1300 - Chapter 13 Part 1 - Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
What are meninges?
3 connective tissue membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord.
What are the 3 layers of meninges?
Dura mater (Outer) , Arachnoid mater (Web like), Pia mater (In contact with connective tissue.
What is a subdural Hematoma?
It is subdural hemorrhage with bleeding under the dura mater.
What is epidural space?
Cushion of fat and network of veins in space between vertebrae and spinal dura mater made of adipose, loose connective tissue, and blood vessels.
-Its where epidural is inserted.
What is the subarachnoid space?
space between arachnoid and pia mater filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
What are the cervical and lumbar enlargements?
Sites where nerves arise serving upper limbs (cervical) and lower limbs (lumbar).
What is the Conus medullaris?
The caudal end of the spinal cord on level L1 - L2 of the vertebrea.
What is the lumbar cistern?
An extension of subarachnoid. Include the filum terminale and cauda equina.
What is a lumbar puncture?
It is a CSF sample from the lumbar cistern (L3/L4) OR (L4/L5). You are meant to avoid the spinal cord.
What is the Filum terminale?
An extension fo pia mater from conus medullaris. It merges with dura mater and creates the coccygeal ligament at level S2. It provides support and connection.
What is the Cauda equina.
It is a horse tail and has roots of 11 pairs of spinal nerves. It extends inferiorly from conus medullaris.
What is the central canal?
It is what contains cerebrospinal fluid, where CSR nourish and cushions entities.
What are ependymal cells?
They line the central canal and circulate CSF using cilia.
Spinal Cord Cross-section (label)
Spinal Cord Cross-section (label)
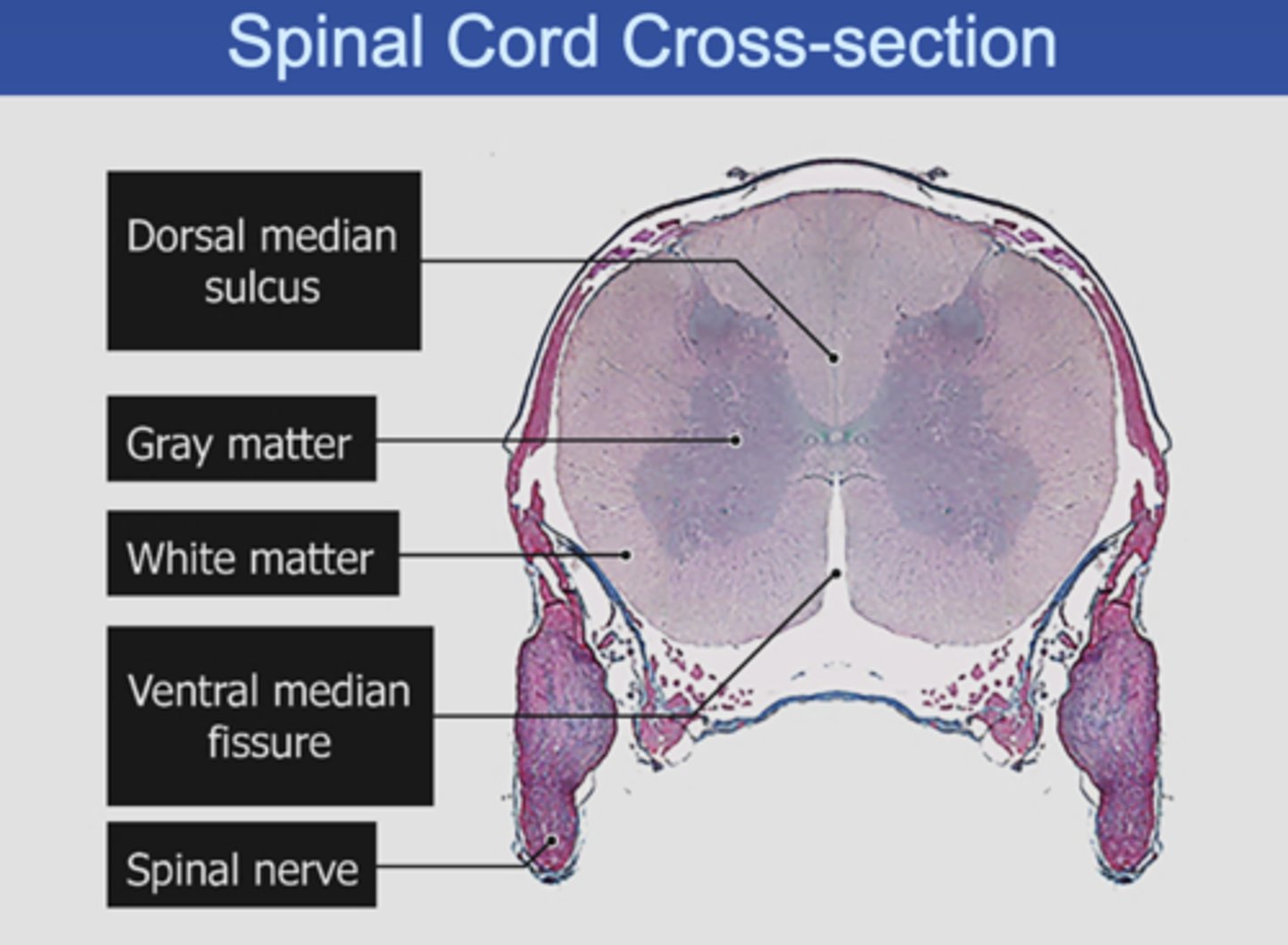
Label
Label
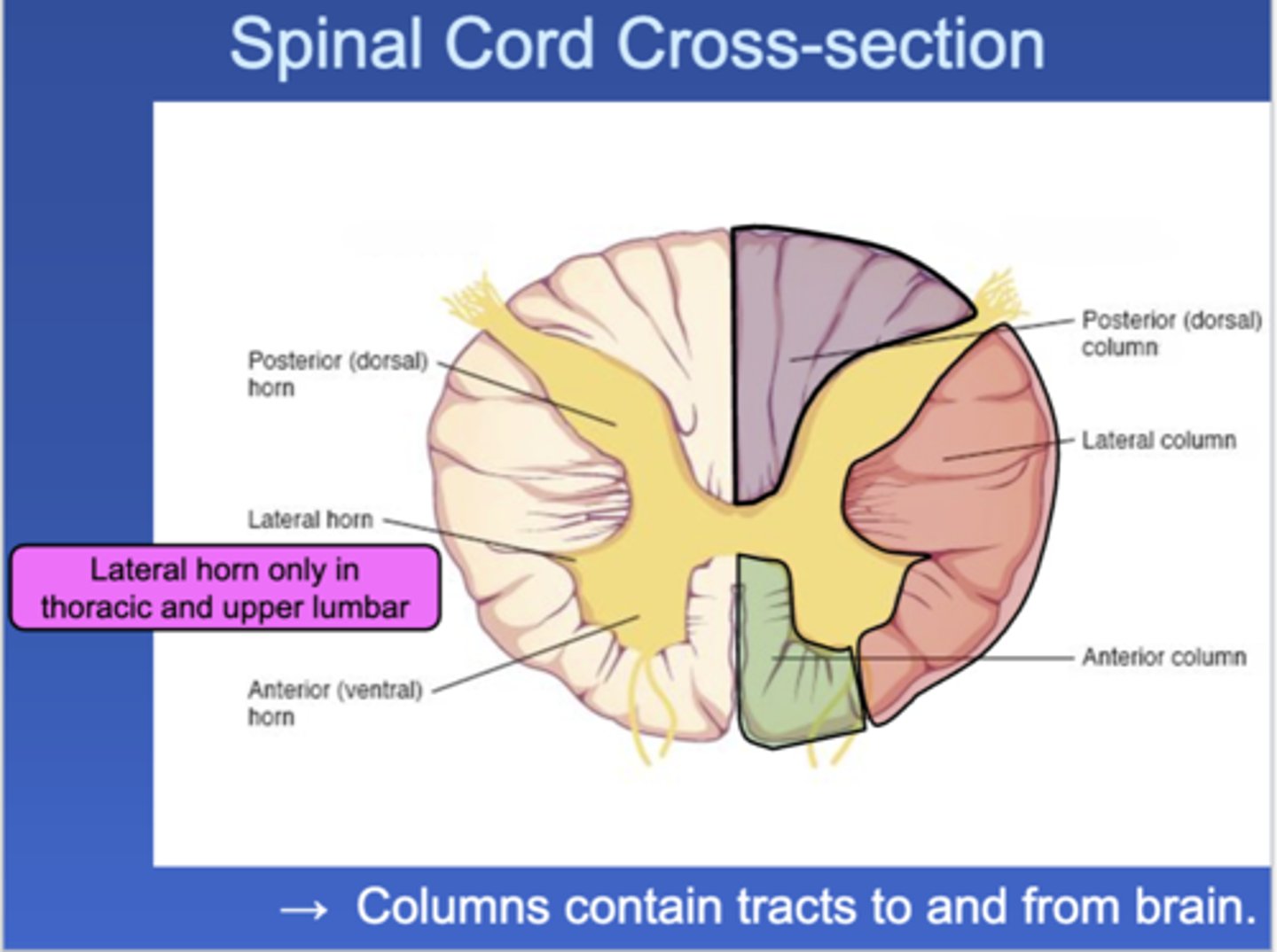
What are all of the horns?
The ventral (anterior) horn, dorsal (posterior) horn, and lateral horn.
What does the Ventral horn do?
It contains MOTOR neurosomas
What does the dorsal horn do?
It contains the SENSORY neurosomas.
What does the lateral horn do.
It contains the neurosomas of sympathetic NS.
What are white matter tracts?
Bundles of axons in CNS that are to and from brain. Each tract has similar origin, destination and function.
What is white matter?
Made out of mainly myelinated axons with white columns that contain tracts.
What is grey matter?
They are made of mainly neuron cell bodies and dendrites.
Where is white and gray matter?
In the cerebellum
What is a ganglion?
Cluster of neural cell bodies outside the CNS that looks like a bulge.
EX: Dorsal root ganglia; cell bodies of sensory neurons.
What is cerebral cortex?
outer layer of the brain
What does the brainstem do?
It processes and relays signals. It gives rise to CN III-XII
What does the thalamus do?
It relays and organizes sensory information.
What are nuclei in the brain?
Clusters of neurosomas deep in brain.
What are afferent signals?
The are sensory signals that use ascending tracts with 3 neurons to relay info to cerebral cortex.
What does decussation mean?
Crossing from one side to the other.
What does contralateral
On opposite sides
What does Ipsilateral mean?
On the same side.
What are common symptoms in strokes?
Contralateral numbness, weakness, or paralysis.
What are efferent signals?
They are motor signals that use descending tracts and go to upper and low motor neurons.