Surface Water 3
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
bedrock and surficial geology on water chemistry
weathering products, groundwater water storage and flow paths may change water chemistry
climate on water chemistry
runoff magnitude and flow paths
rate of chemical and biological activity and evaporative enrichment all change water chemistry
increasing climate will increase turnover and weathering
ecosystems on water chemistry
soils - OM, controls on water balance, redox conditions, wetlands (anoxic) may all change water chemistry
land use on water chemistry
altered water balance, flow paths, point source and diffuse pollution
changes in water chemistry
based on connectivity of different source waters
surface run off can cause erosion or sediments
throughflow can have high concentrations of OM, nutrients and pollutants
ground water can have high concentrations of dissolved salts
also can be due to biological activity - photosynthesis, decomp, redox chemistry
variability in water chemistry
light and photosynthesis changes pH, oxygen, temp day and night
changes in flowpaths, can increase throughflow and surface runoff during storms
seasonal temp changes, plant nutrient uptake, and discharge
fire, human land use, climate change
physical water quality
total suspended solids, turbidity, colour, taste, odour, temp, electrical conductivity
chemical water quality
pH, hardness, alkalinity, salinity, total dissolved solids, major cations and anions, dissolved OM, nutrients, metals, dissolved gases, biological oxygen demand
synthetic organic compounds, pesticides, pharmaceuticals, microplastics
biological water quality
bacteria, protozoa, virus, algae
pathogens - total coliform, e coli, giardia, chloera, salmonella, shigella
turbidity
optical measure of light dispersion
cloudy samples have higher
mainly clay/silt, w contribution from algae and natural organic compounds
measured in nephelometric turbidity units (NTU)
turbidity vs TSS
turbidity is easier to measure, of interest for water/habitat quality
TSS of interest for sediment transport and land management
primary productivity and turbidity
algal/macrophyte productivity inhibited by turbidity - restricted to near surface (less O2 production)
but sediments also carry nutrients like phosphorous which can cause eutrophication when they settle
habitat quality and turbidity
fish cant see and catch prey, gills get clogged, eggs can be buried, macroinvertebrates are also buried
increases heat absorption, esp in shallow water, reduces oxygen, increases thermal stratification
water treatment and turbidity
suspended sediment can carry pathogens, heavy metals, organic contaminants
removal of turbidity a requirement prior to disinfection
anthropogenic increases of turbidity and TSS
construction/ag/forestry increase availability of sediments for erosion
urbanization increases stream channel erosion by increasing peak flow
can also increase with invasive, bottom feeding fish - carp
water temperature
influences metabolic rate (productivity), optimal habitat (varies), dissolved O2 (max solubility decreases with temp), solubility of salts and EC, water density (thermal strat), compound toxicity (of heavy metals)
thermal pollution
cooling of power plants returns warm water
urban industrial discharge
forestry/ag - removal of shading
impoundments or reservoirs, increases residence time, absorption of solar radiation
total dissolved solids and salinity
a measure of the mass of dissolved solids/salts
often estimated from EC
ex road salts in the north sask when passing through edmonton
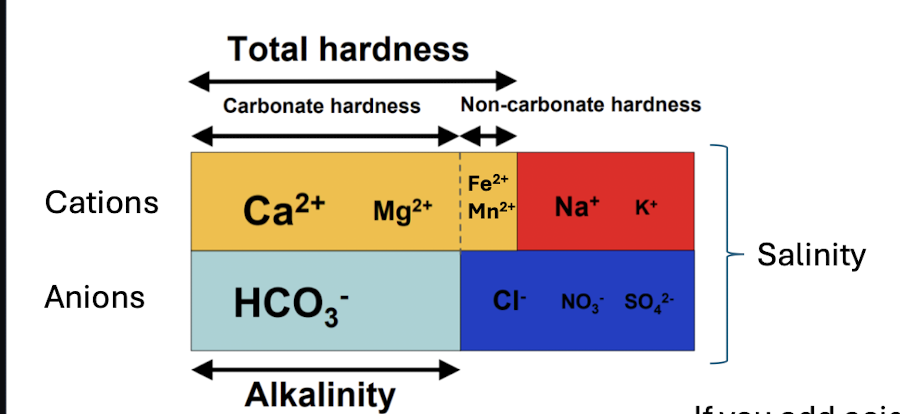
electrical conductivity
a measure of how well a sample can conduct electricity, which increases with greater amounts of dissolved salts and temperature
easily measured, in microsiemens/cm
often normalized to 25 degrees and made specific
differs for different salts
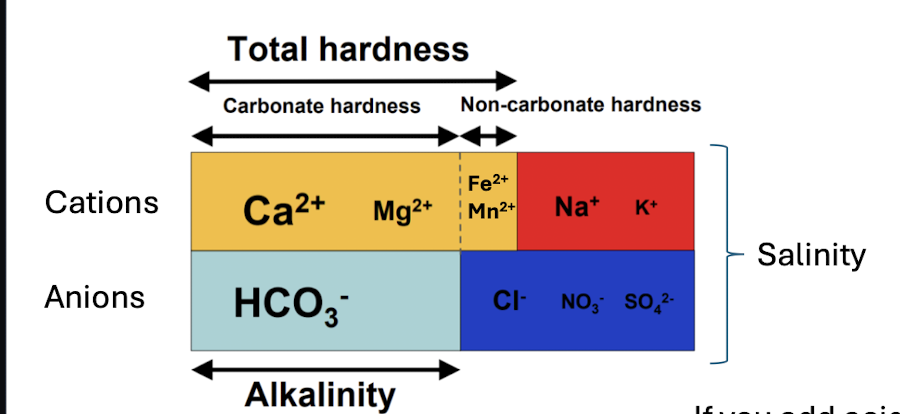
alkalinity
when limestone and dolomite (carbonate bedrock) is dissolved
concentration of HCO3-
waters capacity to resist changes in pH - buffering capacity
will change with acid added to a sample
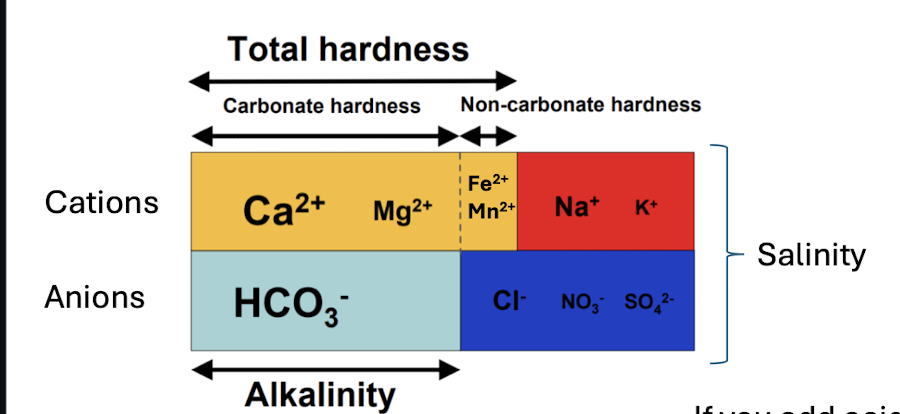
hardness
when limestone and dolomite (carbonate bedrock) is dissolved
concentration of Ca2+ and Mg2+
buildups of carbonates in water systems, effectiveness of detergents, higher can reduce toxicity of metals to aquatic life
can be reported in terms of HCO3-
will not change w acids
pH
indicates acidity, measured as log concentrations of hydrogen ions in water
range from 0-16
normal rain is 5.6, surface water 6-8 (buffered by alkalinity)
bog water is 4, ocean is 8.2
importance of pH
animals and plants have specific ranges they can tolerate (aquatic 6.5-9)
influences solubility and toxicity of metals in water
aluminium can increase at low pH and can kill fish
above 8 is hard to disinfect
solubility of phosphorus is highest at 6.5 which leads to eutrophication
acid rain
pH in rain as low as 4.2
peaked in 80s and 90s mainly where there was high emissions and low alkalinity (decreased buffering)
recovery has been slow and uneven, biologically has been slow
where does acid rain have a large impact
low alkalinity (decreased buffering) and higher emissions
maritime canada, canadian shield
how does acid rain occur
so2 and nox emissions from industry - burning coal, metal smelting
led to deposition of sulfuric and nitric acids
metals and water
many can be beneficial in moderate concentrations, but others with few biological uses are considered toxic
acid mine drainage, tailing ponds, ag, domestic waste, etc all lead to contamination in water
acid mine drainage
very acidic - pyrite and FeS
and often very high metal concentrations but depend on the mine
point source pollution of water
methylmercury
mercury is transmitted frmo industry operations into the environment, converted to methylmercury under anoxic conditions by microbial activity
so often increases in wetlands and
bioaccumulates or magnifies
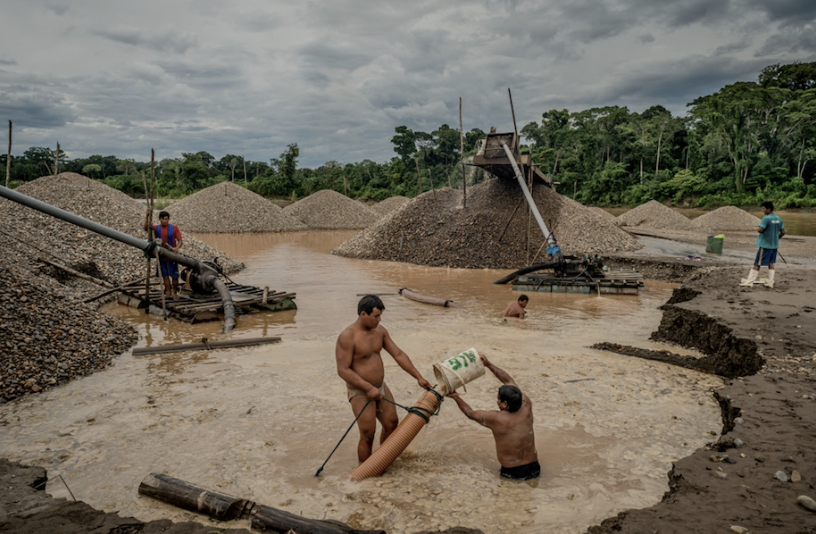
tropical alluvial mining
increasing process for gold and other metals have led to small scale mining in tropical regions
mercury is used to separate the gold - source of pollution
also increases turbidity in rivers

selenium concern
an emerging concern from coal mines in rocky mountains
causes deformities in fish
bioaccumulates and biomagnifies
fluoride concern
added to municipal water for oral health
but pollution from industries, fertilizers, smelters go into surface water
directly toxic, affects metabolism
tailing ponds have high concentration
bioaccumulates and biomagnifies
dissolved organic matter (DOM)
derived from plant material as it decomposes
diverse chemical composition - sugars, carbs, proteins, fats, humic acids, fulvic acids
contains dissolved organic phosphorus, carbon and nitrogen
peatlands are a large source
water treatment and DOM
removal is necessary
unpleasant taste, vector for pathogens
needs to be removed prior to chlorination or carcinogenic compounds created
DOM and aquatic functions
determines light conditions - habitat quality, algal productivity, thermal conditions
contains imp nutrients, enters food web through microbial activity
recovery of acid rain and DOM
higher pH increased solubility of DOM
caused brownification in the recent years, increases costs for water treatment
climate warming also contributes
phytoplankton
contains chlorophyll A and can photosynthesize
filtration and measurement of chl a is used to measure the abundance
cyanobacteria
warm, high phosphorus conditions lead to blooms
nitrogen fixing from the atmosphere
can release toxins
dissolved oxygen (DO)
in surface water can come from diffusion and mixing with atmosphere or produced as byproduct of photosynthesis - varies seasonally and day to night
used by animals and microbes for decomp
often have threshold for requirements, stratification can lead to depletion at depth
biological oxygen demand (BOD)
amount of oxygen used by bacteria to decompose organic mater - indicates risk for o2 depletion
done at standardized temp (20 C) for 5 days
waste water, pulp and paper mill waste can increase
but DOM from terrestrial sources usually have low numbers
coliform bacteria
found in intestines
total amount can indicate fecal pathogens (environmental contamination)
some specific e coli can be pathogenic themselves
sources are leaking sewer lines, wildlife waste, septic/pet waste, and farm wastes
persistent organic pollutants (POPs)
hydrocarbons from coal, oil, gas or synthesized
PAHs - maybe carcinogenic
industrial chemicals like PCBs largely banned
pesticides like organochlorines (DDT)
can evaporate and deposit back into the mountains etc
pahs and oil sands
atmospheric deposition up to 10X at oil sands mines
may have increased from mining, but also wild fires