Bio H 24-25 - Ecology
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
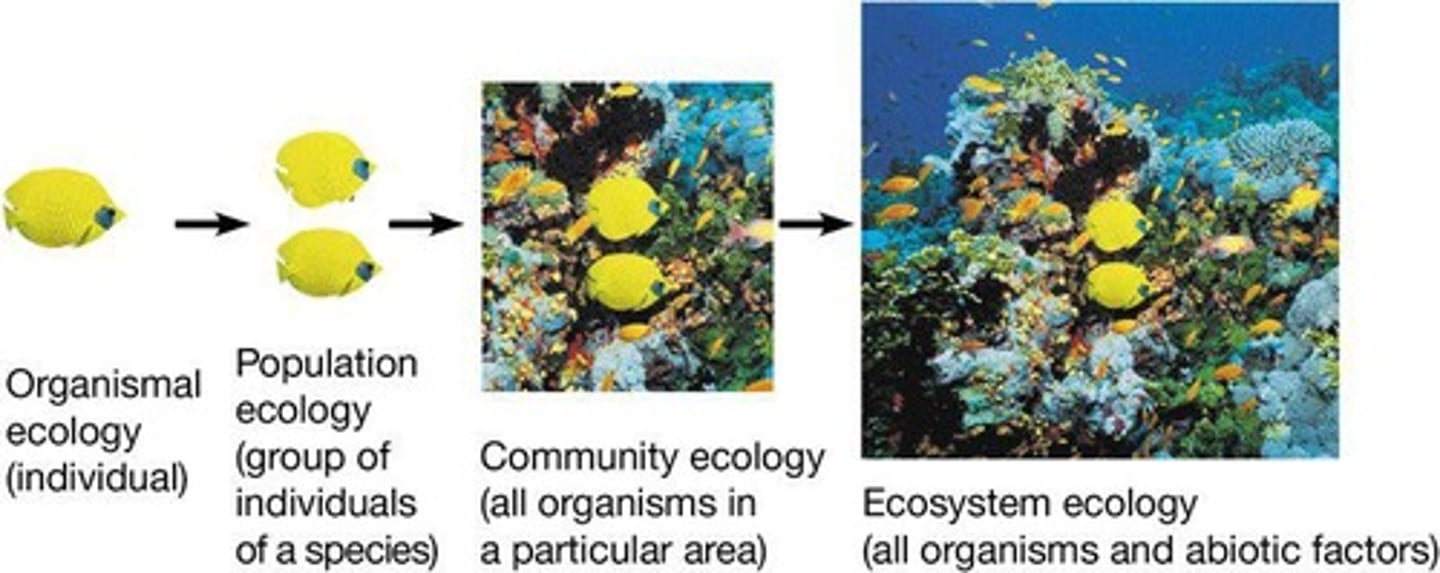
What is ecology?
The study of interactions of organisms with each other and their physical surroundings.
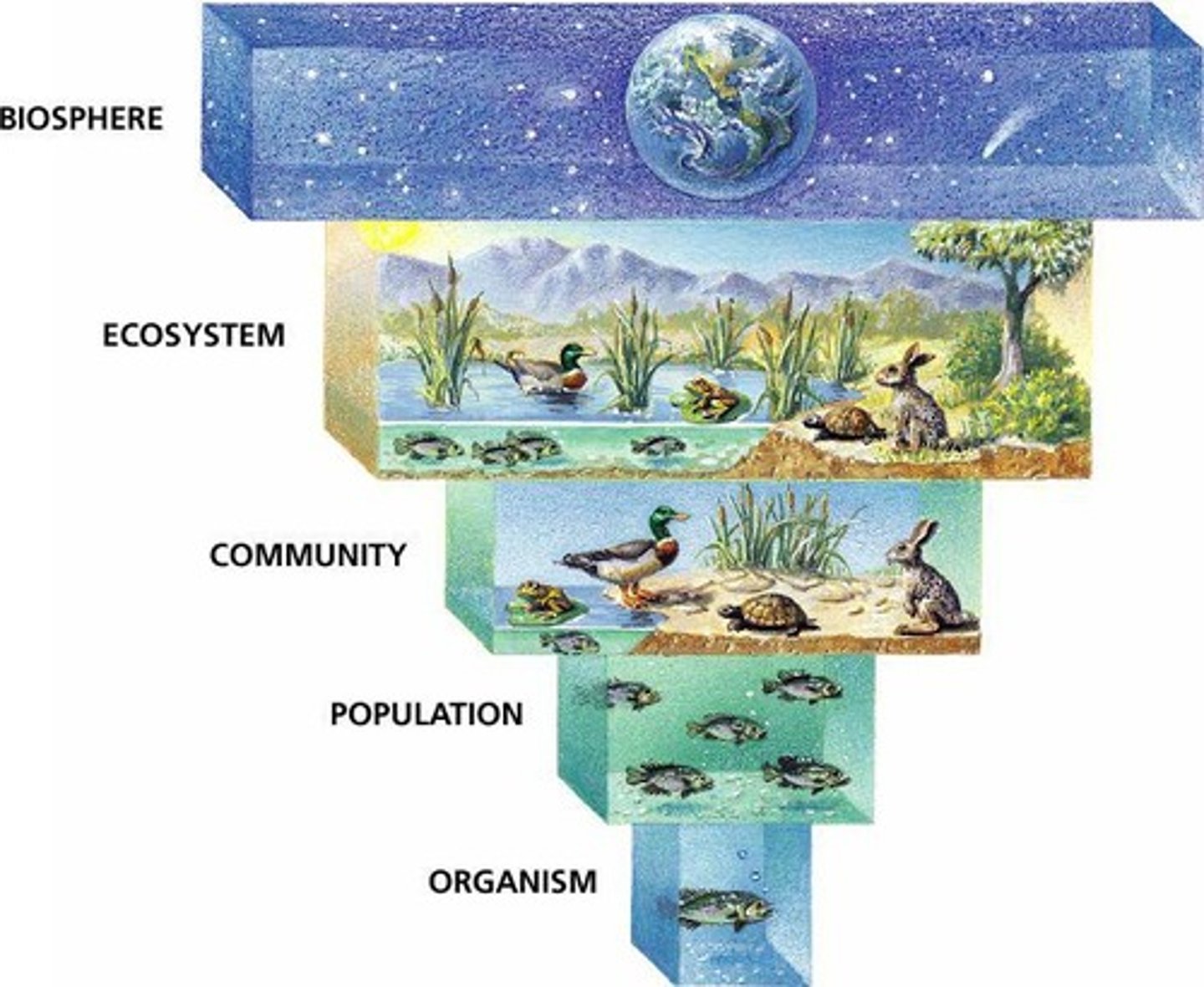
What is a biosphere?
The part of the Earth where life exists.
Define ecosystem.
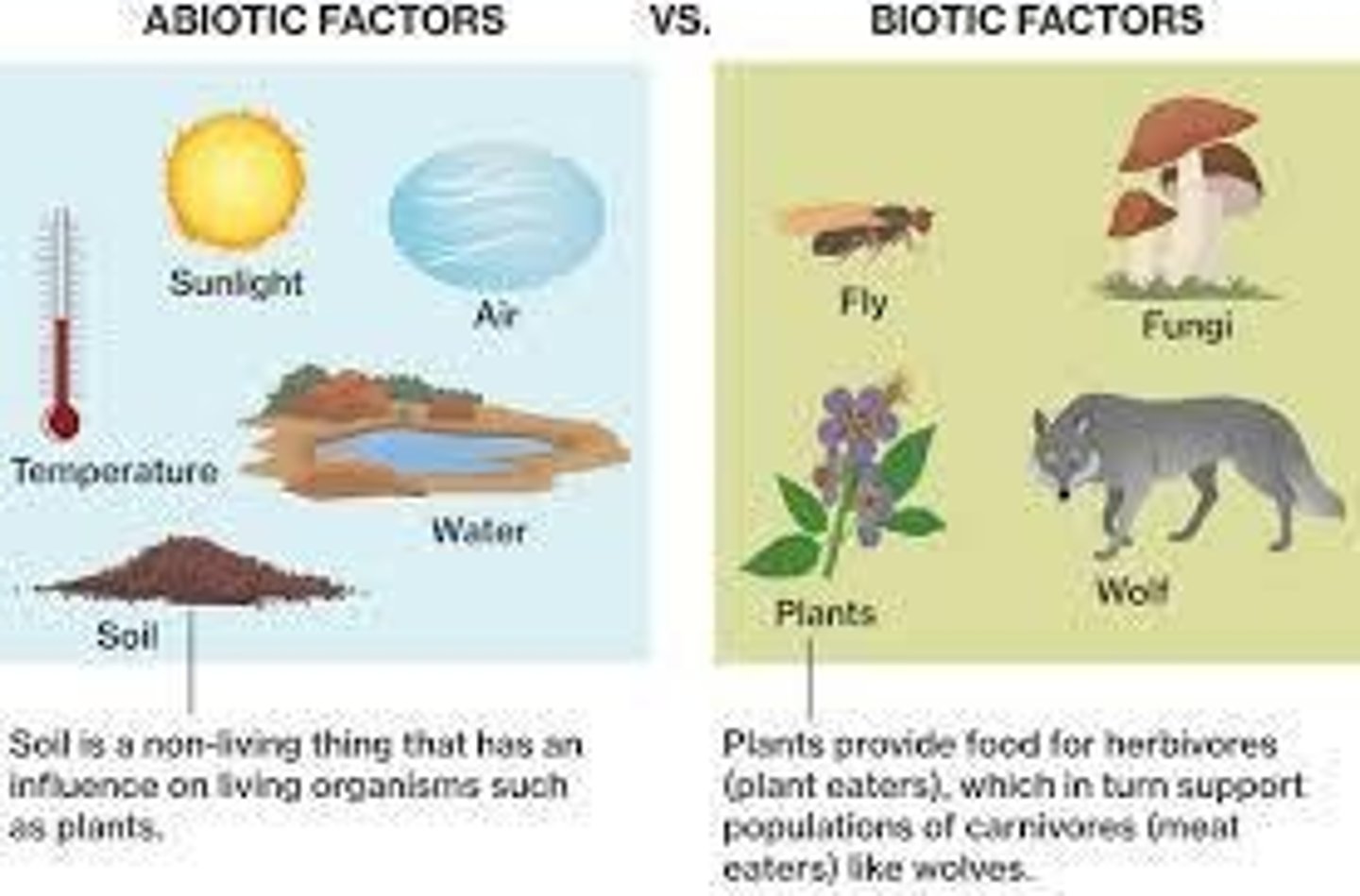
A given physical area (abiotic) and the living organisms (biotic factors) that inhabit that area.
What is a niche in ecology?
The role or function of an organism within its ecosystem, including its habitat, resource use, and interactions with other organisms.
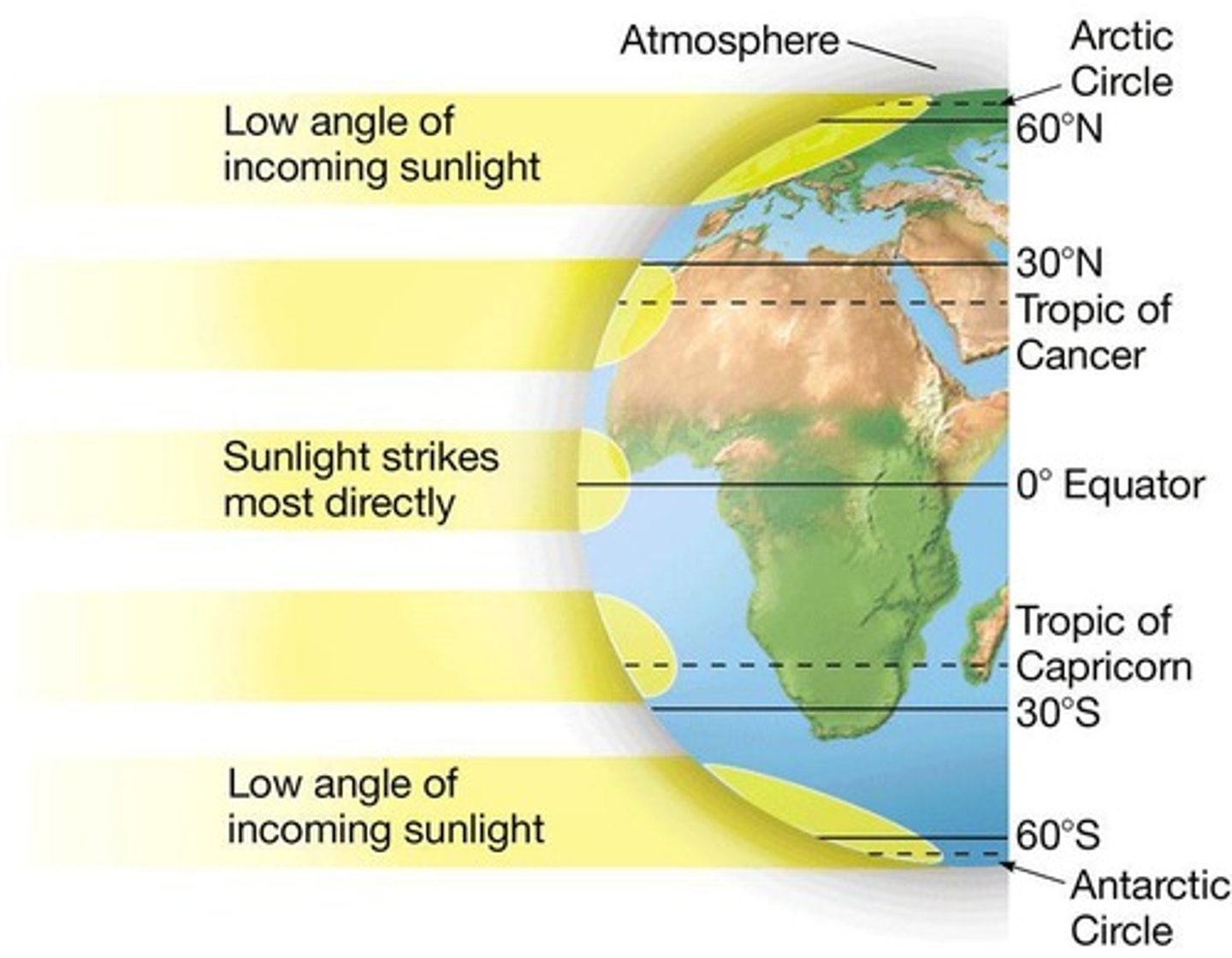
How does sunlight affect climate?
The angle at which sunlight hits the Earth is a major factor in determining climate.
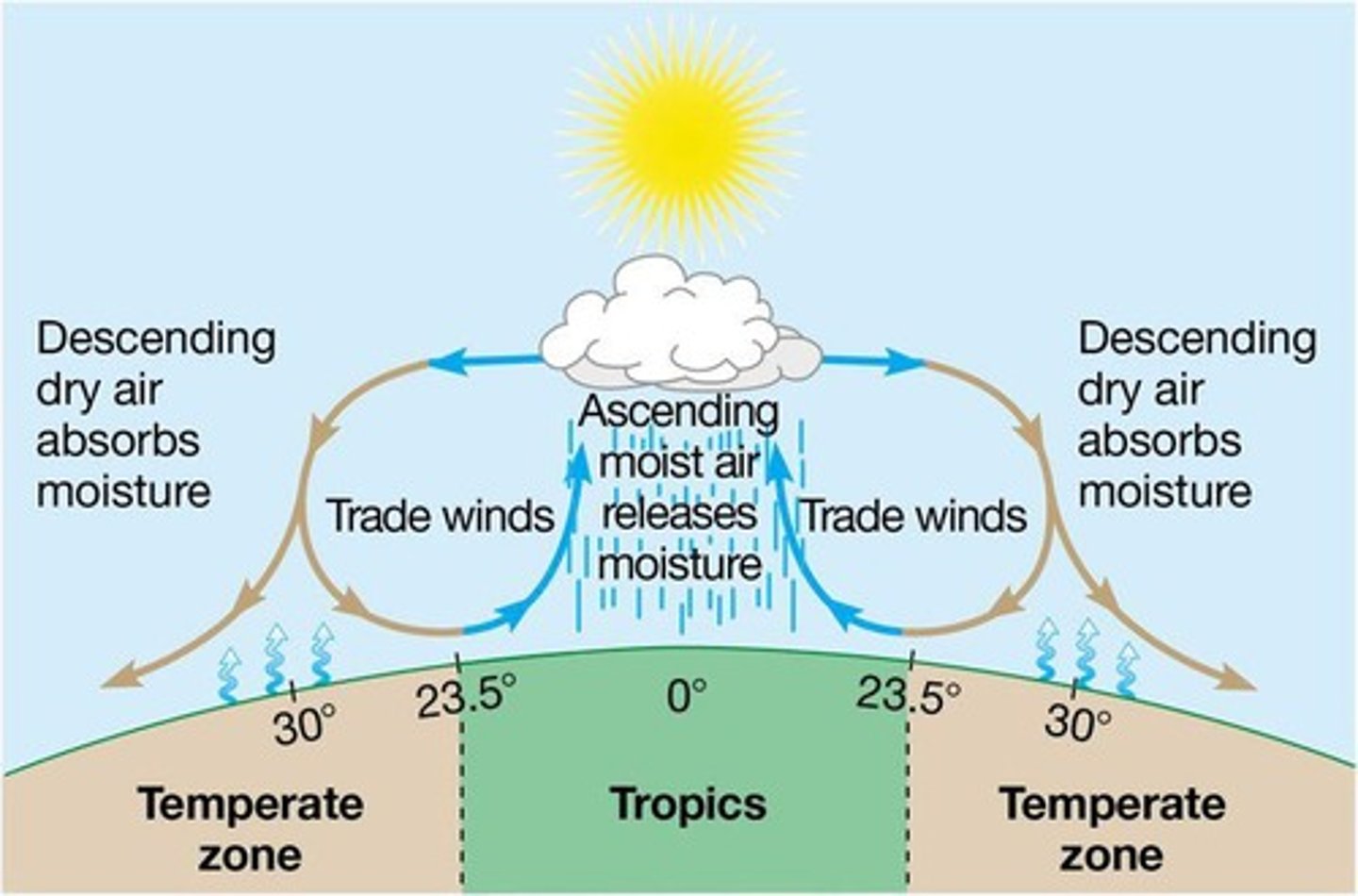
What drives wind and ocean currents?
Wind is driven by hot air rising and cooler air falling, and the unequal heating of the Earth's surface.
What is the difference between weather and climate?
Weather refers to day-to-day atmospheric conditions, while climate refers to average year-to-year conditions of temperature and precipitation.

What are producers in an ecosystem?
Organisms that capture energy from the sun or inorganic sources, such as photosynthetic algae or chemosynthetic bacteria.
What are primary consumers?
Organisms that feed on producers.
What are secondary consumers?
Organisms that feed on primary consumers.
What is the role of decomposers in an ecosystem?
Decomposers break down dead organisms, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem.
What is the 10% rule of energy flow?
Only about 10% of the energy from one trophic level is transferred to the next level; the rest is used for metabolic processes or lost as heat.
What is biomass?
The total mass of organisms at one trophic level.
What is a food web?
A system of interdependent food chains that shows how energy and nutrients flow through an ecosystem.
What is a keystone species?
An organism that helps define an entire ecosystem; without it, the ecosystem would be dramatically different or cease to exist.
What are herbivores?
Animals that eat plants.
What are carnivores?
Animals that eat other animals.
What are omnivores?
Animals that eat both plants and animals.
What are detritivores?
Organisms that eat dead organic matter, such as crabs, mites, and earthworms.
What is the pyramid of biomass?
A graphical representation showing that there is less biomass at higher trophic levels.
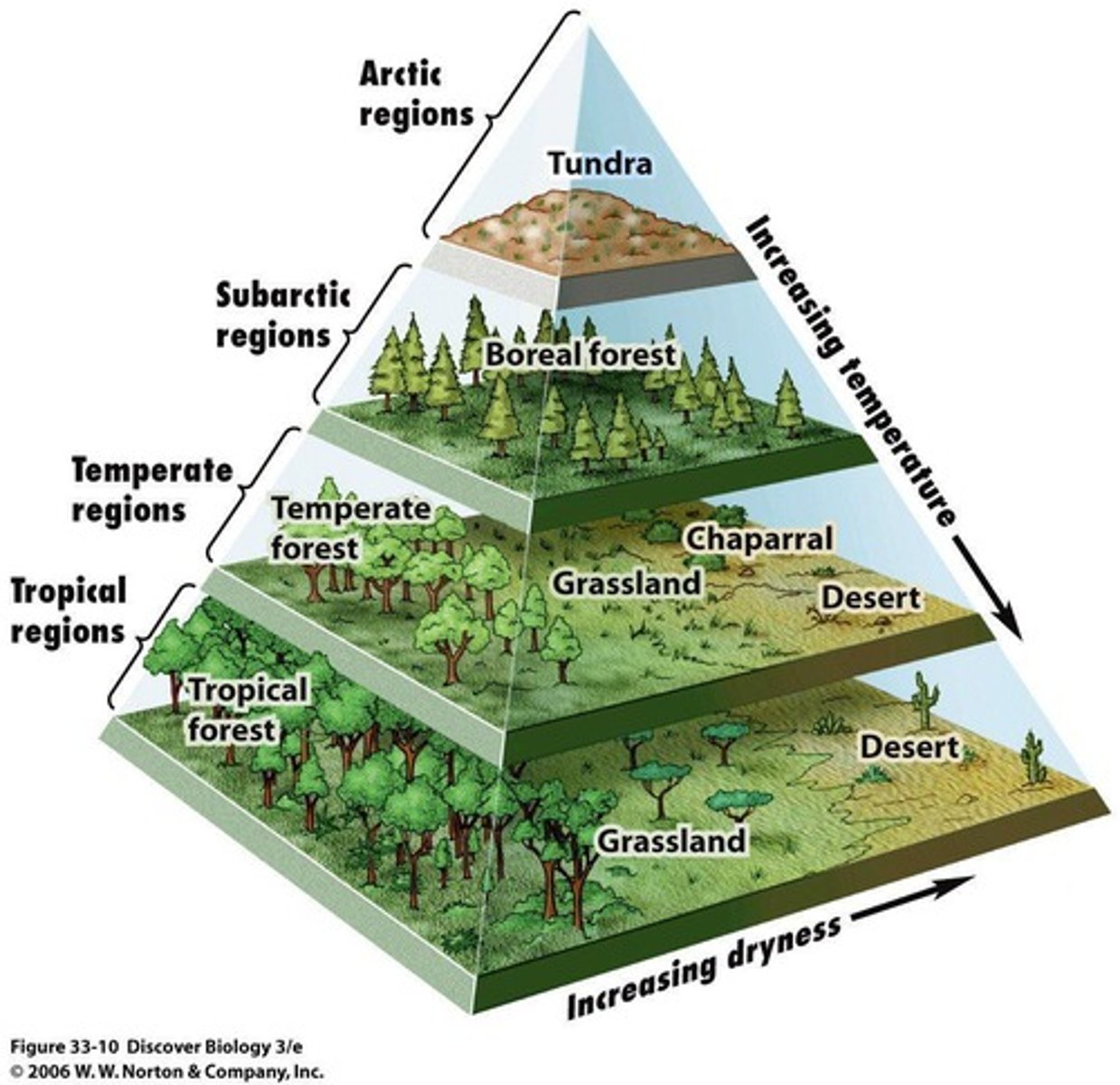
What is the significance of plant life in an ecosystem?
Lots of plant life is needed to support a few consumers.
What happens to energy as it flows through an ecosystem?
Energy flows but is not recycled; nutrients can be recycled.
What happens to energy during transfer between trophic levels?
Always some energy is lost during an energy transfer.
What is the 10% Rule in ecology?
When energy is passed from one trophic level to the next, only 10% (on average) of the energy will be passed on.
What is biomagnification?
Biomagnification refers to the increase in concentration of a substance (such as a pesticide) in the tissues of organisms at successively higher levels in a food chain.
What are the two types of biomagnification?
Primary and secondary.
What is primary succession?
Primary succession is the start of a new community where no life existed before.
What is secondary succession?
Secondary succession occurs when one community replaces another.
Give an example of ecological succession.
A pond begins to fill with organic matter and becomes marshland, then solid land over time.
What are pioneer species?
Pioneer species are organisms that begin to colonize areas that did not have living things before, starting primary succession.
What is a climax community?
A climax community is a stable collection of organisms in an area.
What are typical pioneer species in a harsh environment?
Lichens, moss, and grass.
What is nutrient limitation in ecosystems?
Nutrient limitation refers to the scarcity of nutrients, often nitrogen or phosphorus, that limits primary productivity.
What is the primary productivity of an ecosystem?
The rate at which organic matter is created by producers.
What can excess introduced nutrients cause in aquatic ecosystems?
Excess nutrients can cause algal blooms.
What characterizes biomes?
Biomes are environments that have a characteristic climax community.
What are some characteristics of the tundra biome?
Almost treeless, with lichens, moss, grass, and a permafrost layer that stunts plant growth.
What types of animals are typical in the tundra biome?
Reindeer and caribou.
What are the major seasonal changes in temperate forests?
Major seasonal changes occur, with winter halting most plant regrowth.
What is the chaparral biome known for?
Vegetation adapted to periodic fires, often caused by lightning.
How do some plant species in chaparral respond to fire?
Some plant species produce seeds that will germinate only after exposure to a hot fire.
What is a common feature of the polar ice caps biome?
It is characterized by extreme cold and limited vegetation.
What biome is located in the Midwest US, south of tundra, and features black bears and wolves?
Temperate Deciduous Forest
What type of forest is characterized by conifers, pines, and spruce?
Temperate Deciduous Forest
What is the typical climate of the Temperate Deciduous Forest?
Mild summers and cold winters with most rain falling in one season.
What is a significant factor that limits succession in the Temperate Deciduous Forest?
Grazing.
What biome is known for having periodic fires and less variation in temperature than grasslands?
Temperate Grasslands.
What is the average annual rainfall in deserts?
Less than 25 cm of rain per year.
What biome features warm temperatures (around 25 °C) and consistent rainfall year-round?
Tropical Rain Forests.
What is a characteristic of the Tropical Rain Forest's soil?
Nutrient-poor soils despite large diversity in organisms.
What aquatic biome provides much of our drinking water and food?
Freshwater Biomes.
What is the aphotic zone in aquatic biomes?
A zone where no light penetrates.
What is the photic zone in marine biomes?
The area where light can penetrate, allowing phytoplankton and algae to grow.
What are coral reefs primarily composed of?
Tiny animals called corals that secrete a hard calcium-rich exterior.
What is a defining feature of the Neritic Zone in marine biomes?
It extends from the low tide line to the open sea and falls within the photic zone.
What type of aquatic biome is characterized by shallow waters and high photosynthesis?
Estuaries.
What are mangrove swamps dominated by?
Salt-tolerant trees called mangroves.
What is the main process through which water is recycled in the environment?
The Water Cycle.
What nutrient cycle is affected when nitrogen balance is thrown off?
The Nitrogen Cycle.
What are limiting factors in an ecosystem?
Nutrients that limit growth within an ecosystem.
What is the role of chemosynthesis in the deep sea zone?
Some organisms use it to produce energy in the absence of sunlight.
What is the significance of the water cycle in ecosystems?
It recycles water through evaporation, condensation, and precipitation.
What is the primary characteristic of the Deep Sea Zone?
High pressure, cold temperatures, and no sunlight.
What types of organisms are typically found in the intertidal zones?
Organisms that can withstand radical daily changes in the environment, such as barnacles.
What is the primary source of photosynthesis in the open sea?
Phytoplankton.
What is nitrification in the nitrogen cycle?
The process where soil bacteria convert ammonia (NH3) into nitrites (NO2) and then into nitrates (NO3), which are more often taken in by plants.
What is the primary form of nitrogen in the atmosphere?
Nitrogen (N2), which makes up 80% of our atmosphere.
Why do living organisms need nitrogen?
Nitrogen is essential for the assembly of molecules like amino acids and nucleotides.
What is nitrogen fixation?
The process by which certain bacteria convert atmospheric nitrogen (N2) into a usable form, such as ammonia (NH3), often in symbiosis with plants.
What is the role of denitrifying bacteria in the nitrogen cycle?
They use nitrates as the final electron acceptor in their electron transport chain, converting them back to nitrogen gas (N2).
What is ammonification?
The decomposition of organic nitrogen into ammonia (NH4) by bacteria and fungi.
What is eutrophication?
A process in which a body of water becomes overly enriched with nutrients, leading to excessive growth of simple plant life.
What is mutualism in symbiotic relationships?
A relationship where both species involved benefit, such as plants and their pollinators.
What is commensalism?
A symbiotic relationship where one species benefits and the other is neither helped nor harmed, like barnacles on whales.
What is parasitism?
A relationship where one species benefits at the expense of another, such as mistletoe on a host plant.
What characterizes exponential population growth?
Population growth that occurs under ideal conditions, leading to a J-shaped curve.
What is logistic population growth?
Population growth that is limited by environmental factors, resulting in an S-shaped curve.
What is carrying capacity?
The maximum number of individuals that an environment can support.
What are density-dependent factors?
Factors that limit population size based on the population's density, such as disease and competition.
What are density-independent factors?
Factors that affect all populations similarly regardless of size, such as natural disasters and extreme weather conditions.
What happens when the birth rate exceeds the death rate in a population?
The population will grow.
What happens when the death rate exceeds the birth rate in a population?
The population will shrink.
How do human activities impact the nitrogen cycle?
Through mining, deforestation, and combustion of fossil fuels.
What is the significance of the nitrogen cycle in ecosystems?
It recycles nitrogen, which is crucial for the growth and survival of living organisms.
How do plants obtain nitrogen?
Plants absorb nitrates (NO3) from the soil, which are then consumed by animals that eat plants.
What is the role of photosynthesis in biogeochemical cycles?
Photosynthesis is a biological process that contributes to the carbon-oxygen cycle.
What is the impact of decomposition on the nitrogen cycle?
Decomposition returns nitrogen to the soil in the form of ammonia (NH4), making it available for plants.