Artifacts
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
What are artifacts?
Anything in an ultrasound image that is not properly indicative of the structure being imaged.
What is the basic cause for artifacts?
The pulse/echo behaves in a manner that breaks a design assumption inherent in the scanner.
What are some design assumptions that are made that artifacts break?
Sound attenuates at the same rate throughout the field
Sound travels in a straight line
The speed of sound travels 1540 m/s
Echoes only originates from along the thin central beam axis in the main beam
The beam is very narrow in all dimensions
Sound travels directly to a reflector and back to the transducer
Are artifacts good or bad?
Both.
What are some useful artifacts?
Enhancement
Shadowing (sometimes)
Speed of sound (sometimes)
Comet tail
Ring-down (sometimes)
What are some confusing artifacts?
Beam width and slice thickness
Refractive duplication
Many others
What categories can artifacts be placed in?
Not real
Missing
Wrong location
Wrong brightness
Wrong shape
Wrong size
Those artifacts that are “added to the display” (reverb slice thickness, side lobe, etc.) tend to be seen where?
In regions of the screen that would typically be anechoic (ie. bladder, gallbladder, lumen of large vessels, cysts, ascites, etc.)
The weak artificial echoes are seen against what?
A black background.
Most artifacts occur due to what?
The relationship between the beam and the underlying anatomy.
What are some ways you can reduce confusing artifacts?
Reposition the transducer (find another window, try compression, try respiration), and try to anticipate whether or not an artifact will occur.
When looking at an ultrasound image, it is important to not assume what?
Do not assume everything you see is real.
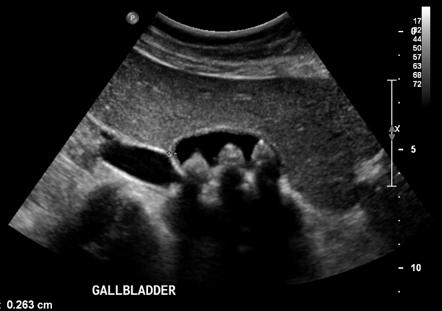
What is shadowing?
Significant lack of echoes seen deep to a highly attenuating structure/interface.
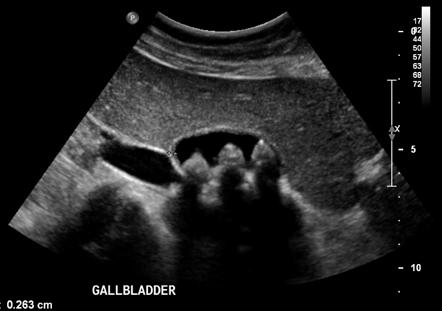
What is the cause of shadowing?
Removal of echo intensity due to absorption, reflection, or scattering.
Shadowing is seen deep to what kind of attenuating structure?
A strongly attenuating structure.
What category of artifacts is shadowing placed under?
“Wong brightness” or “missing”.
Is shadowing helpful or not?
Both, depending on the situation.
Shadowing can be caused by what objects?
Stones, calcifications, bone, as well as fibrous tissue and barium, as well as gas.
What causes edge shadowing?
An oblique incidence or a change in the speed of sound.
Stones and bones produce what kind of shadows?
Clean shadows (anechoic).
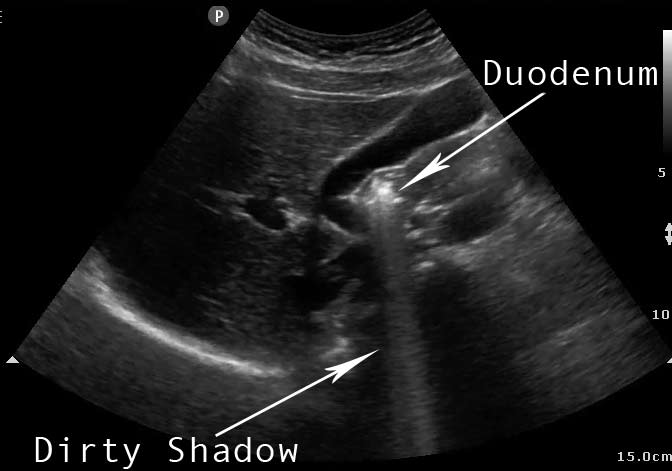
Gas produces what kind of shadow?
A dirty shadow (not anechoic).
How can you optimize shadowing?
Use high frequency
Focus
Reduce overall gain
What is enhancement also known as?
Through transmission.
What is the appearance of enchancement?
An area of increased brightness deep to a low attenuating structure (cystic or solid).
What is the cause of enhancement?
Decreased attenuation produces echoes deep to the structure that have a higher amplitude than their neighbours.
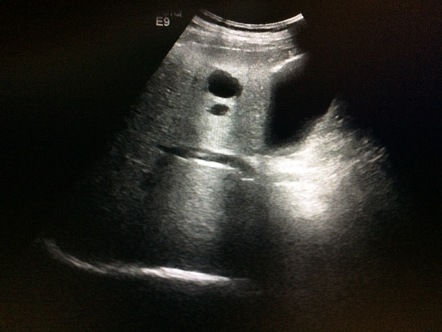
What category of artifacts is enhancement found in?
“wrong brightness”
Is enhancement helpful?
Sometimes helpful, sometimes not.
What is the appearance of reverberation?
It is a series of multiple equally spaced linear echoes. It has a stepladder appearance and is typically seen in the near field.
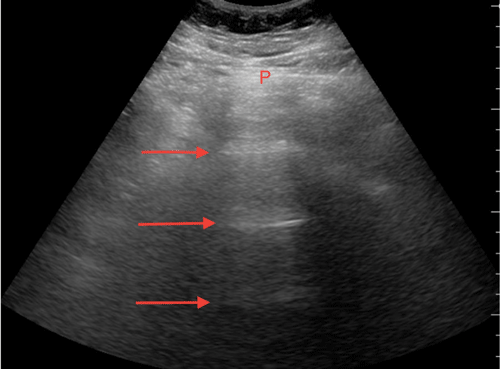
What causes reverberation?
Sound bouncing back and forth between two strong, specular reflectors.
What category of artifacts is reverberation found in?
Not real.
Is reverberation confusing or helpful?
Confusing.
What is the solution for reverberation artifact?
Reposition the transducer.
What are the two types of reverberation?
Long range reverberation (typical reverberation we see in the near field)
Short range reverberation (comet tail)
What does comet tail artifact look like?
A short series of closely-spaced linear echoes.
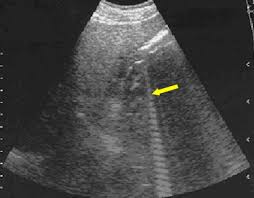
What is the cause for comet tail artifact?
Short range reverberation between two very closely spaced, specular interfaces.
What category of artifacts is comet tail artifact found in?
Not real.
Is comet tail artifact helpful or confusing?
Helpful.
Comet tail artifact is seen behind what objects?
Metal chips
Staples
IUCD
Metal pellets
Thin layers of calcium
Cholesterol crystals
What is ring-down artifact?
A long series of very closely spaced bright echoes.
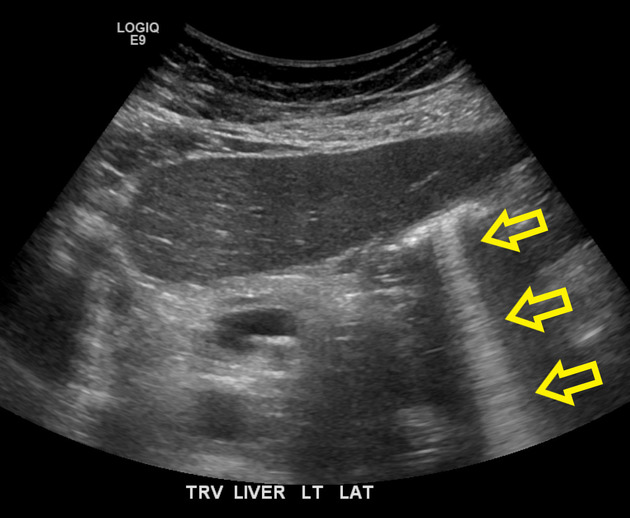
Ring down artifact often changes with what?
Peristalsis.
What is the cause of ring down artifact?
Resonance artifact from gas. When the sound hits gas, it resonates and emits a continuous stream of echoes.
What category of artifacts is ring down found in?
Not real.
Is ring down helpful?
It can be helpful, but it can also be not helpful.
Comet tail is a reverberation artifact whereas ring down is what kind of artifact?
A resonance artifact.
What are reverberation artifacts in lung ultrasound called?
A-lines.
What are ring-down or resonance artifacts in lung ultrasound called?
B-lines.
What is the appearance of mirror artifact?
The duplication of echoes from one side of a strong spectral reflector onto the other side.
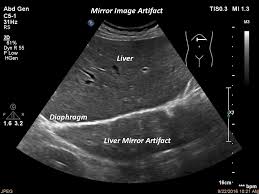
Mirror image artifact most commonly occurs where?
At the diaphragm, but can occur anywhere where there is a strong reflector.
What is the cause for mirror image artifact?
Sound is reflected from a strong reflector into tissue, thus creating a “multipath” image where the resulting echoes are mislocated farther along the scanline. The result causes a duplication of structures on the other side of the strong reflector.
What category of artifacts is a mirror image artifact found in?
Not real.
Mirror artifacts are helpful or confusing?
CONFUSING!!
What are some solutions to avoid mirror image artifact?
Change windows
Bypass the strong reflector
Change the angle
Reduce the gain
Mirror image artifacts are common or uncommon?
Common.
What should you watch out for when encountering possible mirror image artifacts?
Strong specular reflectors like bone and metal, as well as air and gas.
Is anything deep to gas real?
No! Nothing is real deep to gas.
What are the four beam dimension artifacts?
Side lobe/grating lobe
Beam width
Point spreading
Slice thickness
What is side lobe/grating lobe artifact?
Linear echoes that are added to an image on either side of a bright specular reflector.
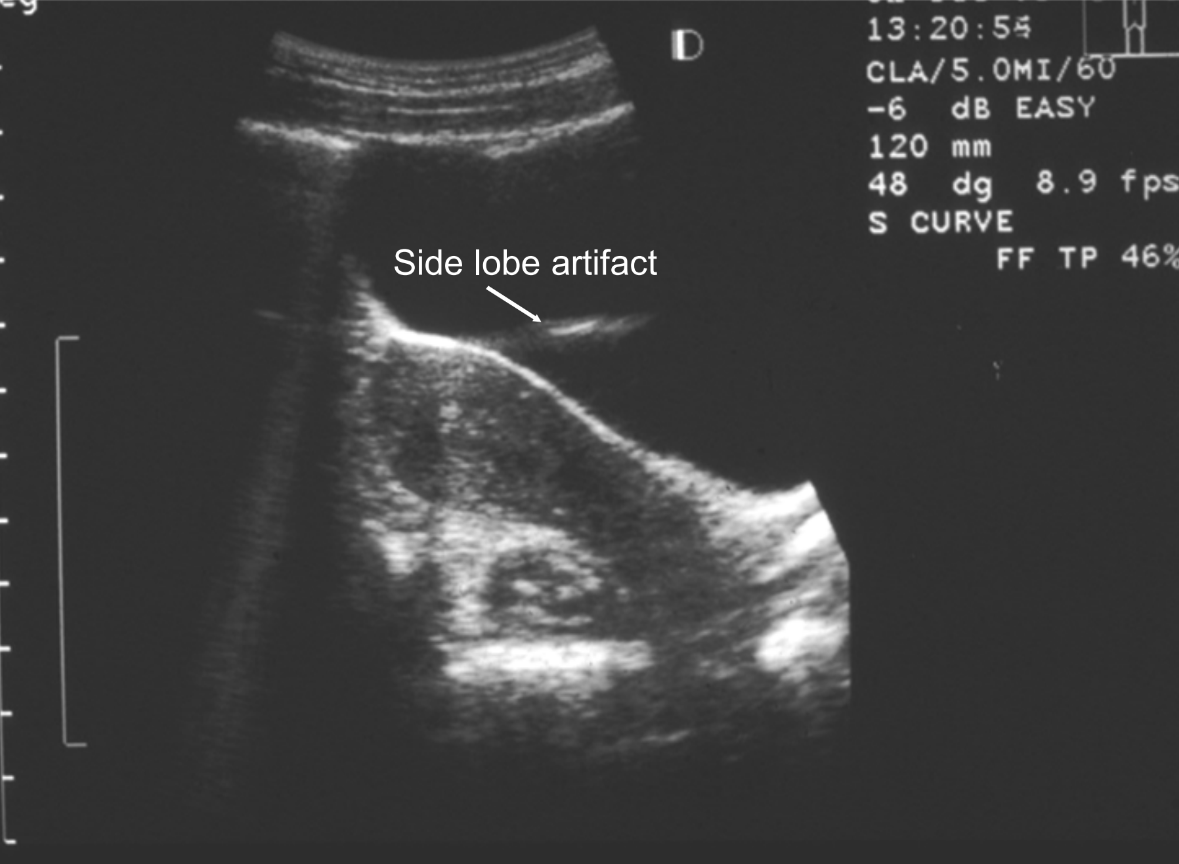
What is cause of side lobe and grating lobe artifacts?
Echoes returned from the weak side lobes or grating lobes or grating lobes after striking a strong reflector or if the echoes are erroneously positioned along central beam axis.
What category of artifacts is side lobes/grating lobes found in?
Not real.
Side lobe and grating lobe artifacts are considered helpful or confusing?
Confusing.
How can you remove side lobe/grating lobe artifacts?
By repositioning the transducer.
What does slice thickness artifact look like?
Low level scattered echoes filling in an anechoic area.
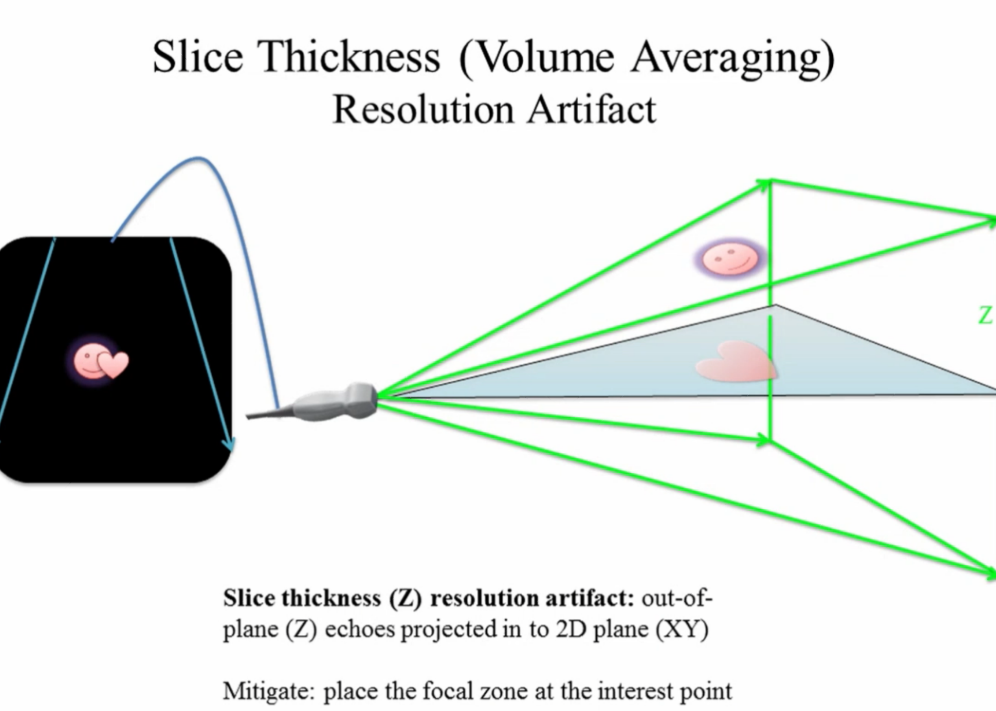
What is the cause of slice thickness artifact?
Echoes returned from the edges of beam within tissue. They are erroneously positioned along the central beam axis.
What category of artifacts is slice thickness artifact found in?
Not real.
Is slice thickness artifact confusing or helpful?
Confusing.
What is the solution for slice thickness artifact?
Changing your focus.
What is beam width artifact?
Low level scattered echoes ‘filling in’ an anechoic area OR point spreading.
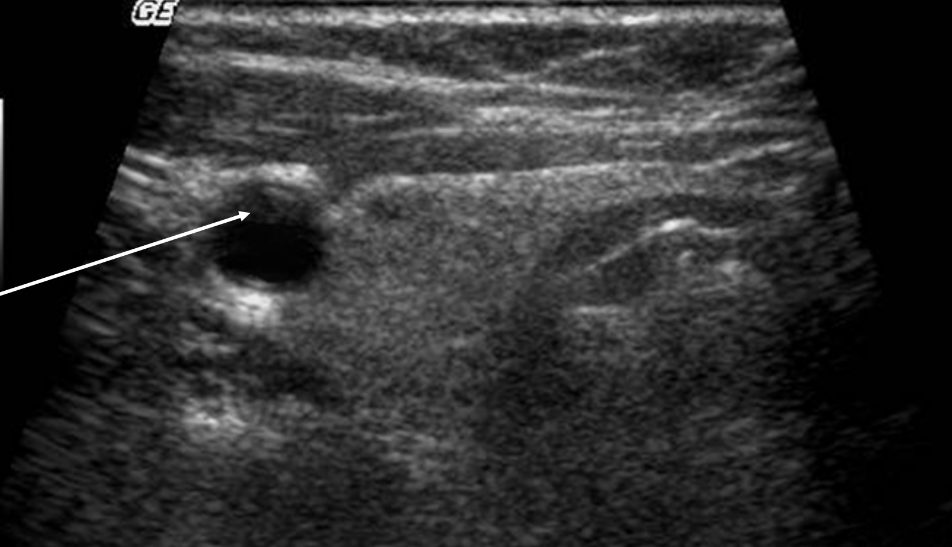
What is the cause of beam width artifact?
Echoes returned from edges of beam within the tissue or erroneously positioned along the beam axis.
What category of artifacts is beam width artifact found in?
Not real.
Is beam artifacts helpful or confusing?
Confusing.
What is point spreading artifact?
Small point interfaces appear as short linear interfaces due to poor lateral resolution.
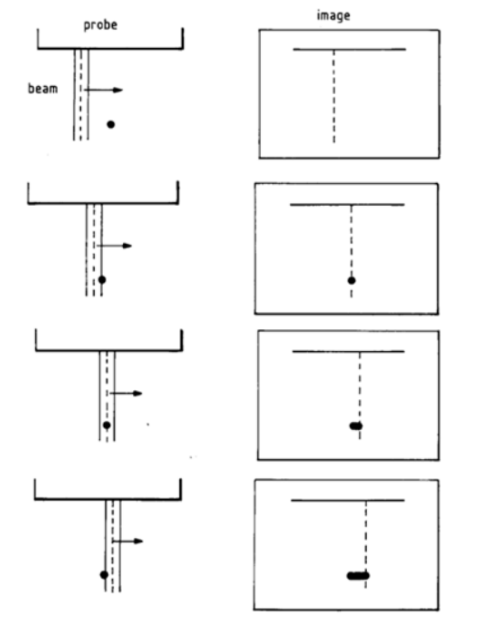
What is the cause of point spreading artifact?
Beam width “stretches” the interface as it sweeps through.
What category is point spreading artifacts found under?
Too large.
Point artifacts are helpful or confusing?
Confusing.
What is the solution for point spreading artifacts?
Changing your focus to the region of interest.
What is the appearance of speed of sound artifact?
Mislocation of interfaces deep to tissue that has a different propagation speed.
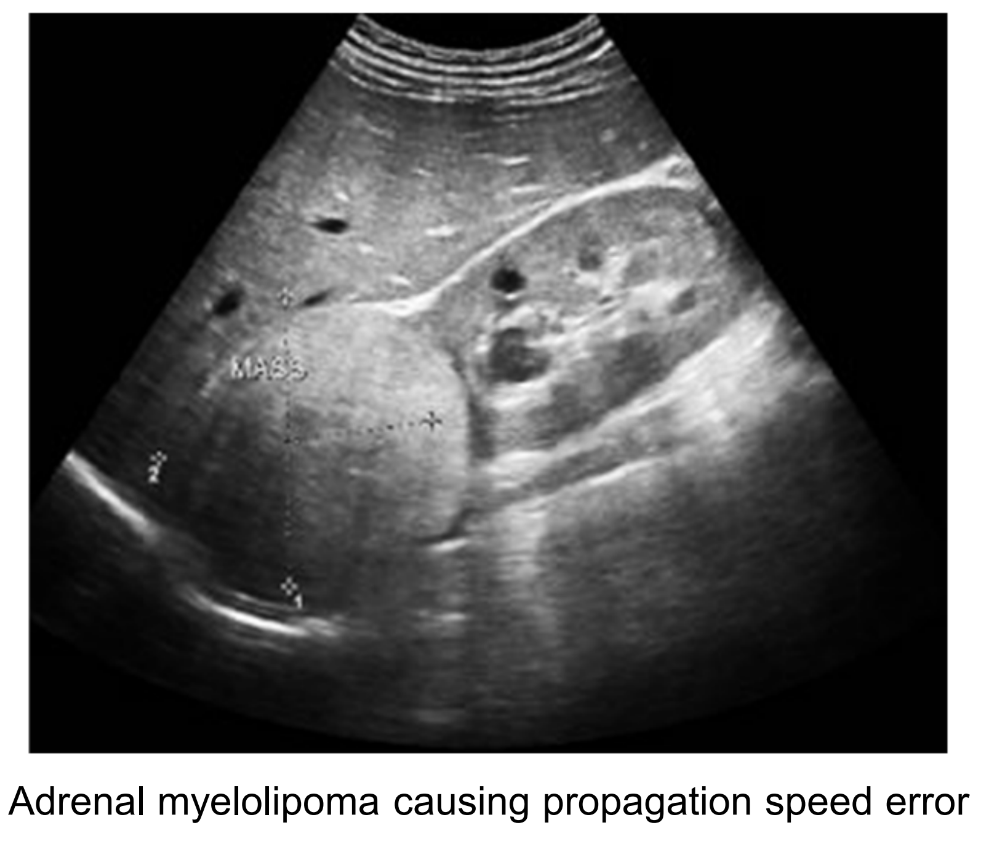
What are some other names for speed of sound artifact?
Propagation speed error or misregistration.
What is the cause of speed of sound artifact?
A significant change in speed will change the go-return time, thus changing where the echoes are seen.
An increase in the speed of sound will do what to the go-return time and will place echoes where?
Decrease the go-return time and place echoes too close to the transducer.
An decrease in the speed of sound will do what to the go-return time and will place echoes where?
Increase the go-return time and place echoes too far from the transducer.
What category of artifacts does speed of sound artifact belong in?
Wrong location or wrong shape. This is confusing and not helpful.
Some machines permit a speed of sound correction setting to be applied which does what?
If the imaging modality is frequently scanning through fat (1440 m/s), the speed of sound can be adjusted to prevent speed of sound artifact.
What are the three refractive artifacts?
Edge shadowing
Refractive mispositioning
Refractive duplication
What two criteria is required for refraction to occur?
Oblique incidence
Change in speed
What is the appearance of refractive edge shadowing?
Edge shadows at the edges of curved interfaces. It is very common.
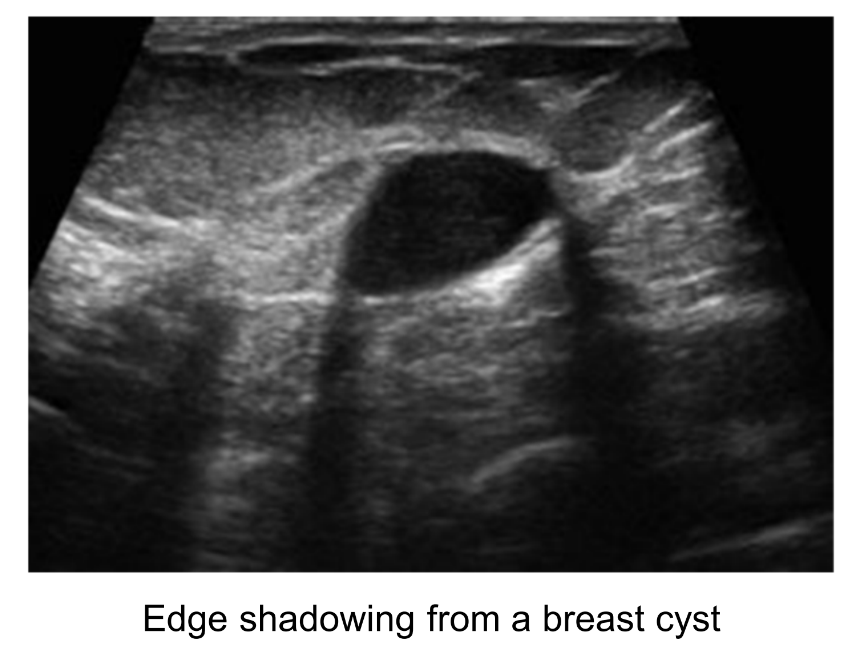
What is the cause of refractive edge shadowing?
Refraction and reflection of the beam at grazing incidence.
What category of artifacts is refractive edge shadowing found in?
Missing. It can be helpful and/or confusing.
What is the solution when dealing with refractive edge shadowing?
Reposition the transducer.
What is refractive mispositioning?
Where the interface is mispositioned lateral to its true position.
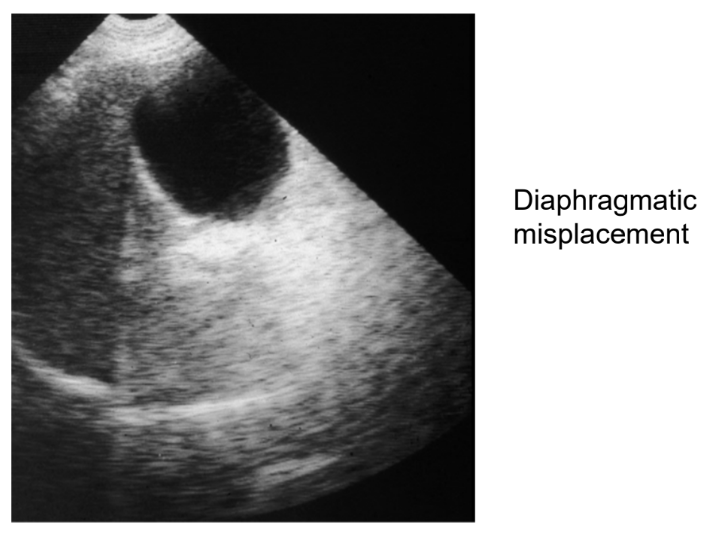
What is the cause of refractive mispositioning?
The ‘bent’ beam generates an echo which is erroneously positioned along the beam axis.
What category of artifacts is refractive mispositioning found in?
“Wrong location”, and is therefore confusing.
What is the solution to refractive mispositioning?
Get perpendicular.
What is refractive duplication or ghosting?
Where there is lateral duplication of the interface on either side of its true location.
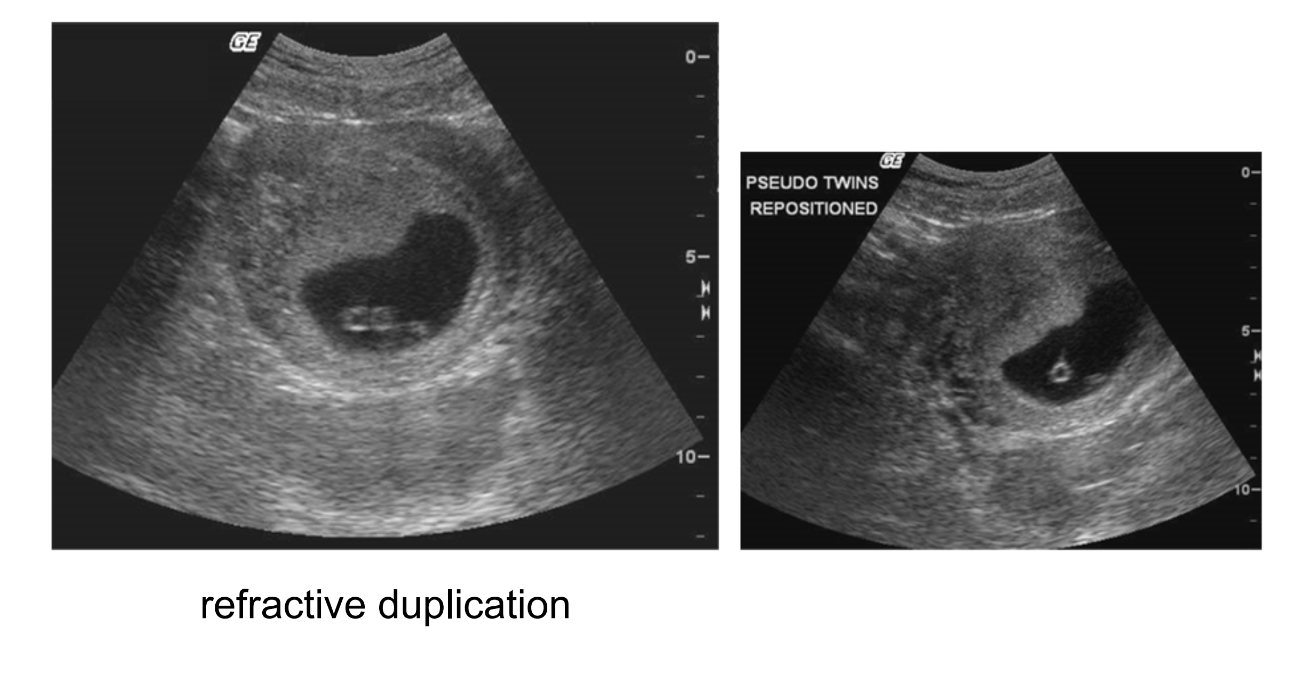
What are some examples of refractive duplication?
Pseudo-twins, copper 14, double SMA, duplicated kidney, etc.
What is the cause of refractive duplication?
Refraction occurring twice as the beam is swept through the region of interest. This commonly occurs through “acoustic lens: of the rectus abdominis.
What category of artifacts is refractive duplication found in?
“Wrong location”. This is confusing.
What is the solution for refractive duplication?
Get perpendicular.
With refractive artifact, the mispositioning is what?
LATERAL.
What is the appearance of focal zone artifact?
False brightening of an area, and adding echoes to a normally anechoic region (focal zone banding).
What is the cause of focal zone artifact?
Intensity due to focal zone.