dental radiography
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
milliammeter (mA)
determines the number of electros available to produce x-rays
7-15mA
kilovolt peak (kVp)
force used to move electrons
60-90kVp
tube head
houses mechanical, electrical, and safety components
extension (support) arm
allows for placement of position indicating device and houses electrical cords that connect the control panel and tube head
position indicating device (PID)
aims the x-rays
round or rectangular
reduces amount of tissue exposed to x-rays
central rays (CR)
x-rays in the center of the useful beam
collimator
lead washer that restricts the size of the x-ray beam
located within the PID
density
amount of light transmitted through the film
dark films have higher density than light films
contrast
difference between shades of the radiograph
short-scale contrast
few gray shades
many black and white shades
long-scale contrast
many gray shades
many black and white shades
definition
detail
how sharp the outline of structures on a radiograph is
exposure
measurement of ionization in air produced by x-rays
absorbed dose
amount of energy deposited in any matter, living or not
dose equivalent
absorbed dose in living tissue
measured in Sv and rems
latent period
period of time before the first clinically observable symptoms occur
exposure, latent period, period of injury, recovery period
four stages of exposure
acute exposure
produces short-term effects seen within months
chronic exposure
produces long-term effects seen years after exposure
ALARA
as low as reasonably achievable
using the least amount of radiation to get appropriate diagnostic results
artifacts
blemishes or images on the radiograph that are not present in the actual object
scatter radiation
comes from the patient's head
maximum permissible dose (MPD)
maximum exposure level
50mSv per year - radiation workers
5mSv per year - pregnant workers and general public
1mSv per day
output
amount of radiation a machine produces at the end of the PID
stepwedge
tests the output of an x-ray machine
determines amounts of radiation reaching the film by measurements of film density
tests when to change solutions
lead foil attached to cardboard or tongue depressor
film speed D
Ultra-Speed
slower than F
film speed F
Kodak InSight
faster than D
requires less exposure time
lateral jaw exposure
shows either left or right half of the jaw
latent image
image made on film when expose to x-rays
must be processed to turn into a visible image
coronoid process of the mandible
bone seen on films taken in the far back of a pts mouth
radiopaque
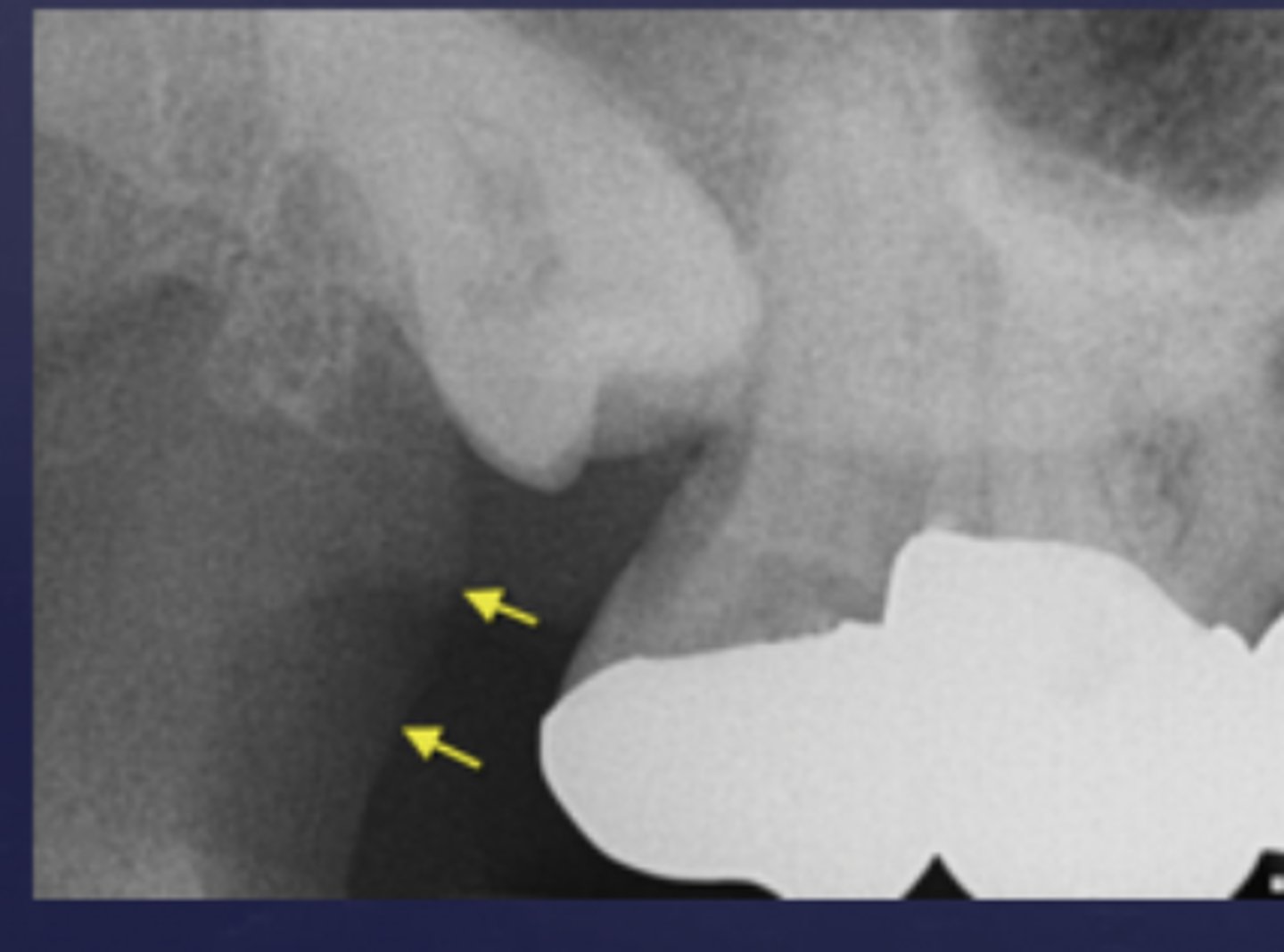
hamular process
spike of bone seen behind the last molar
radiopaque
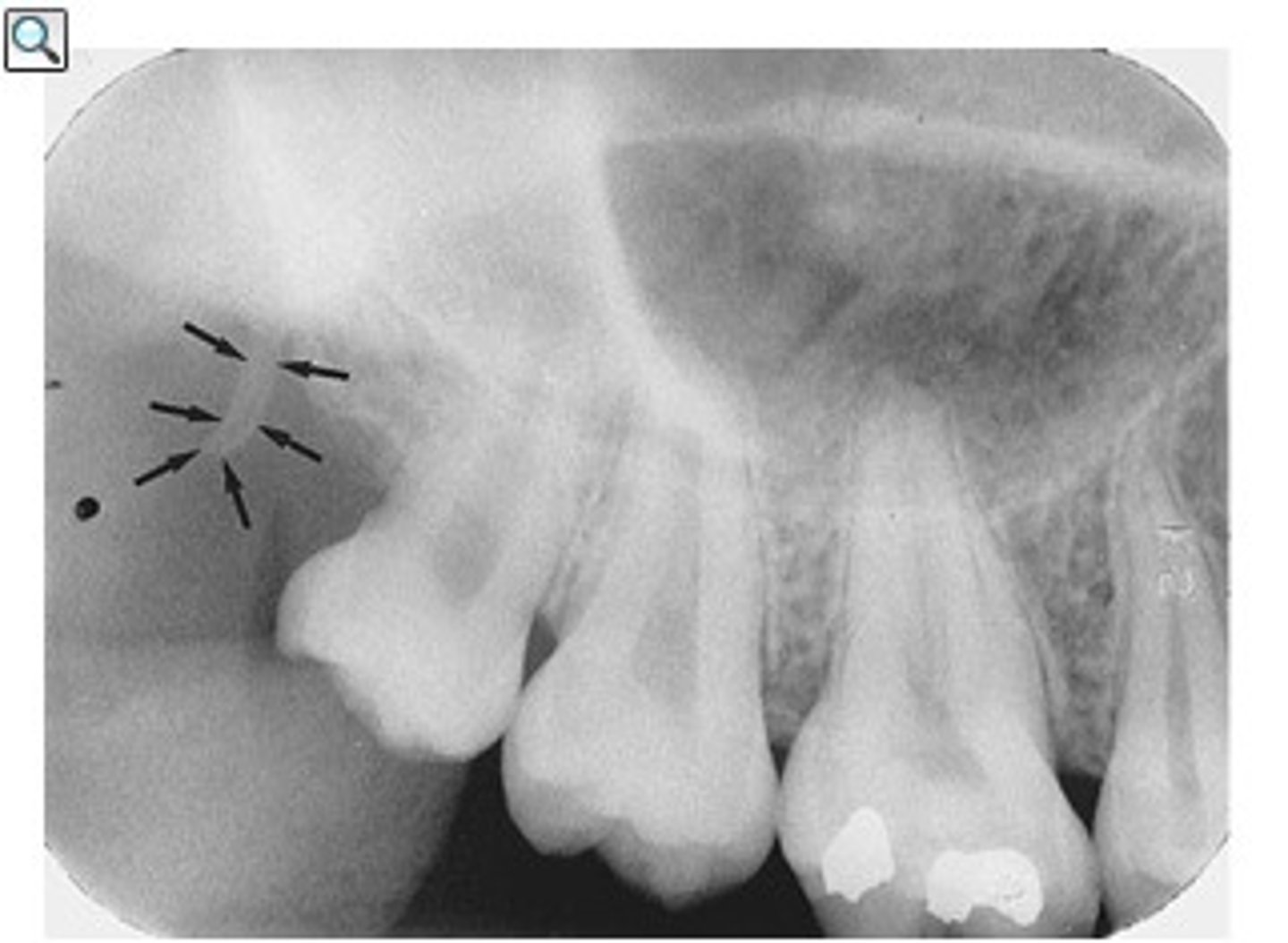
maxillary tuberosity
rounded portion of bone behind the last tooth
radiopaque
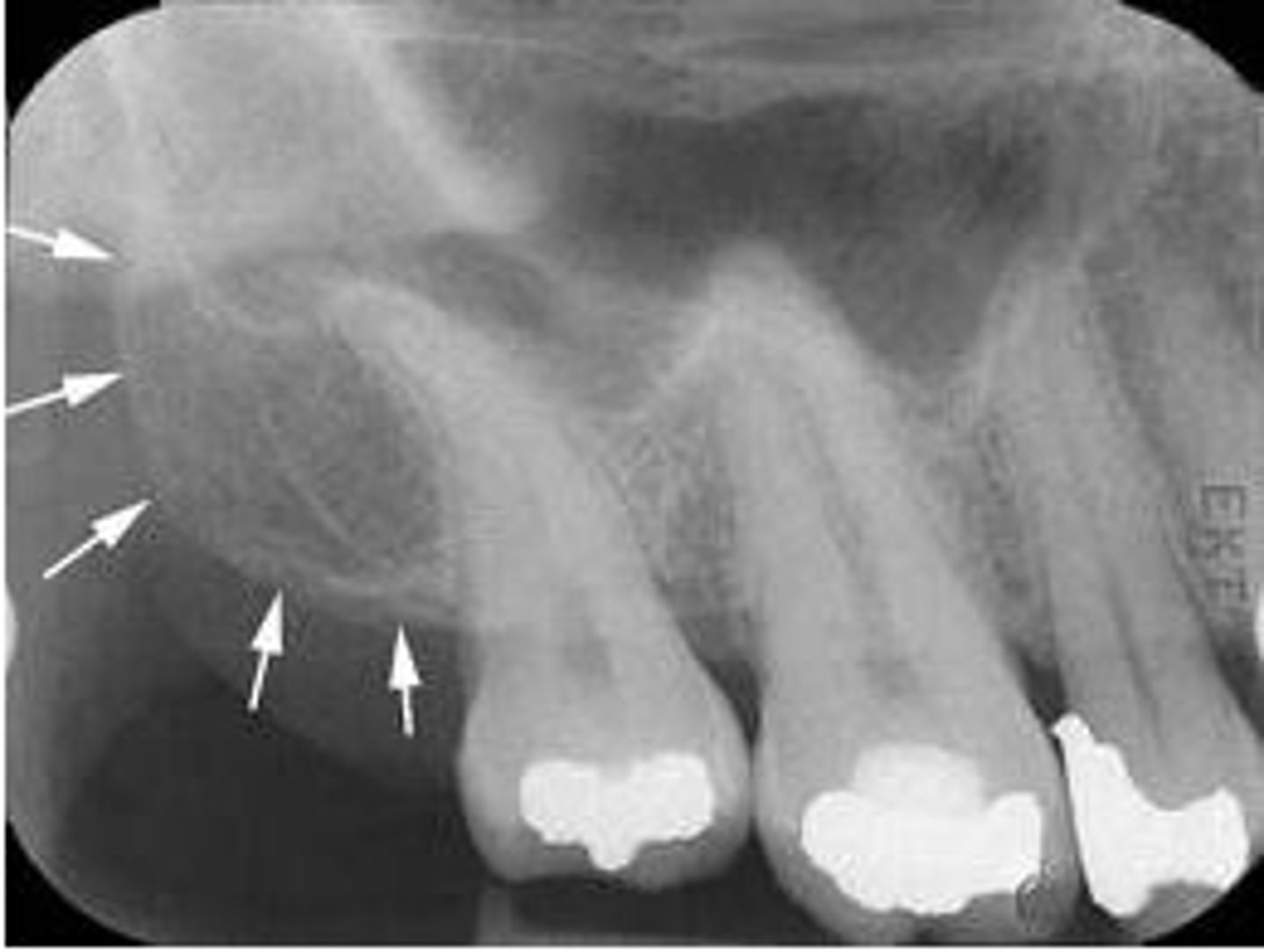
zygoma
portion of the cheek bone
radiopaque
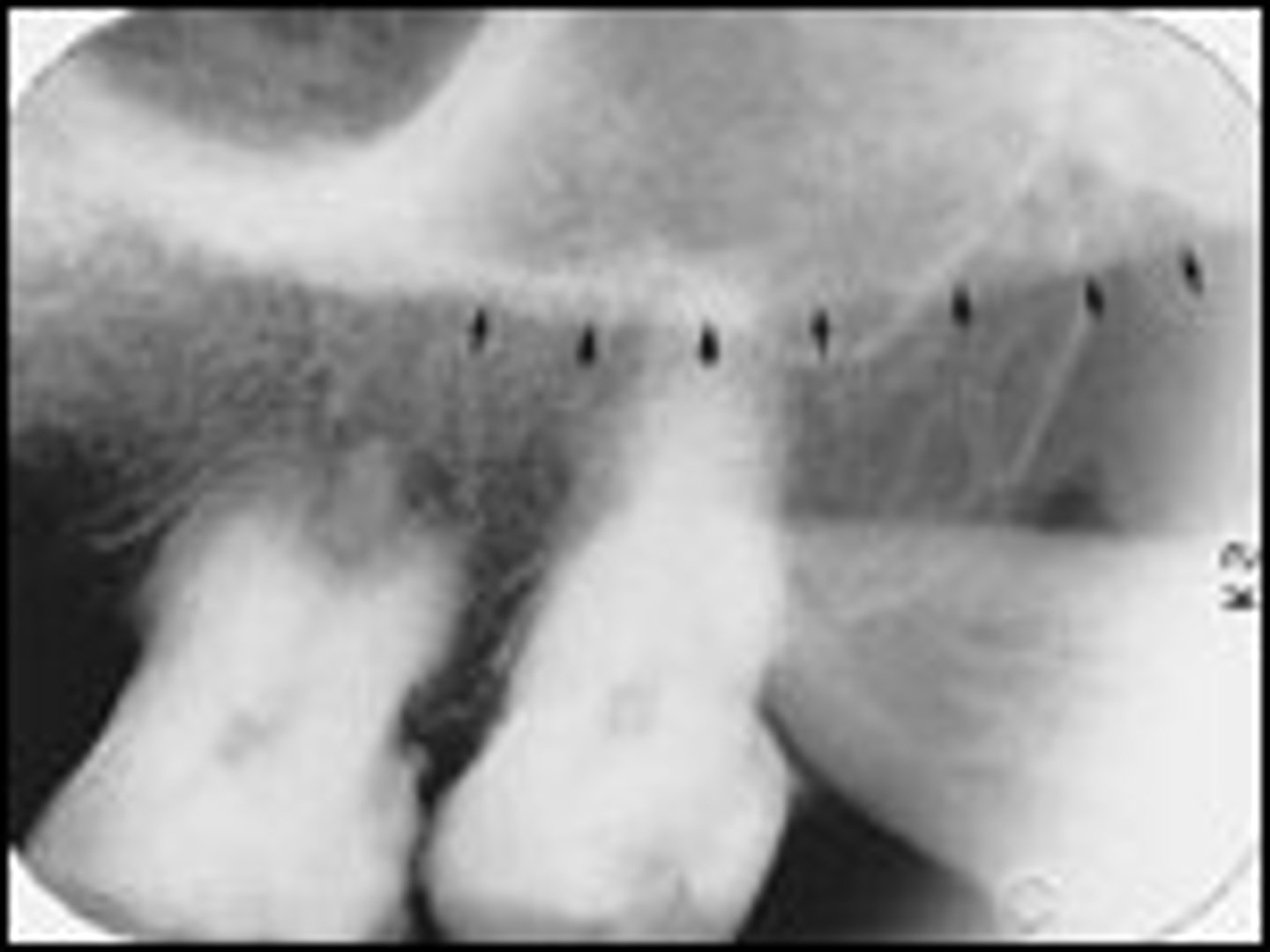
sinus septum
thin bone separating the sinuses
radiopaque
floor of the sinus
lower border of the sinuses
radiopaque
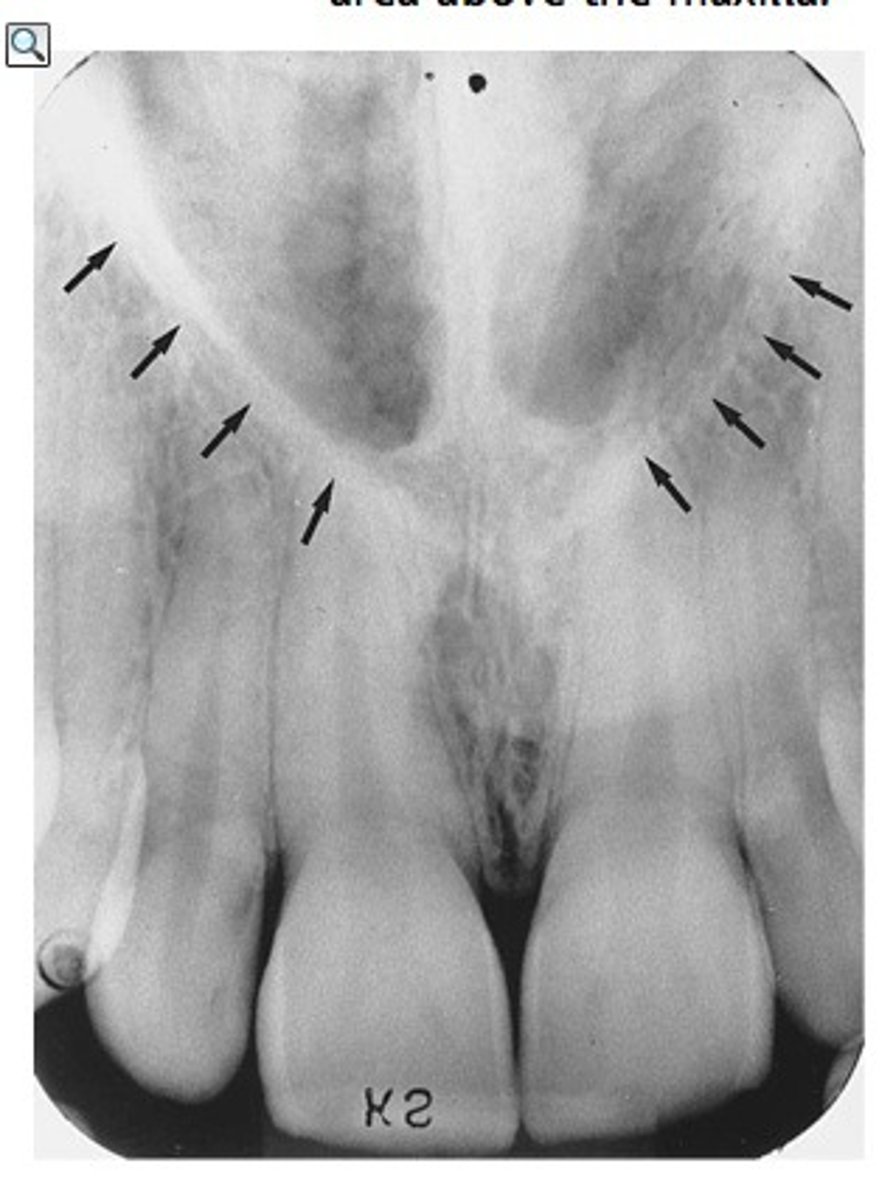
nasal fossa
nasal cavity
radiolucent
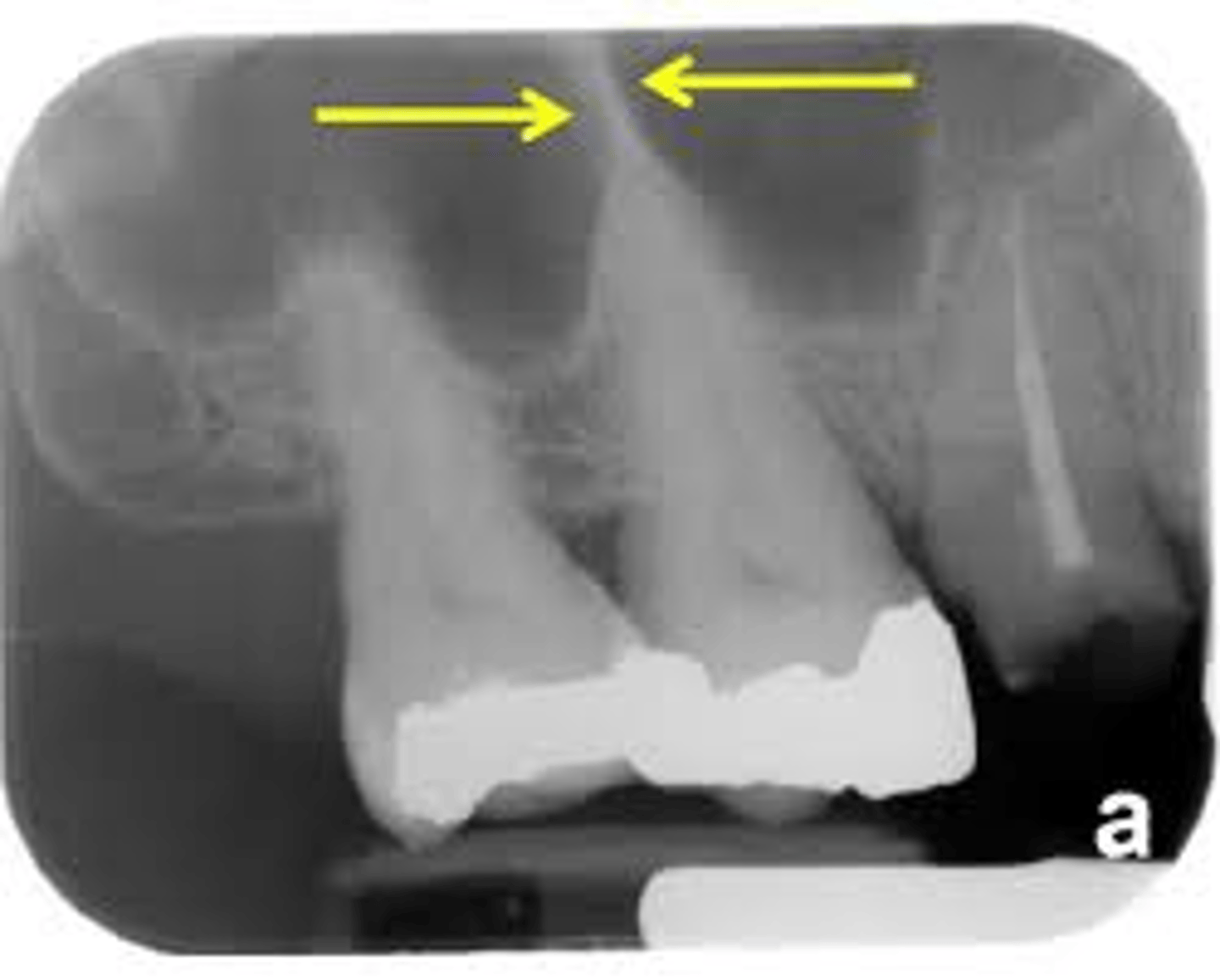
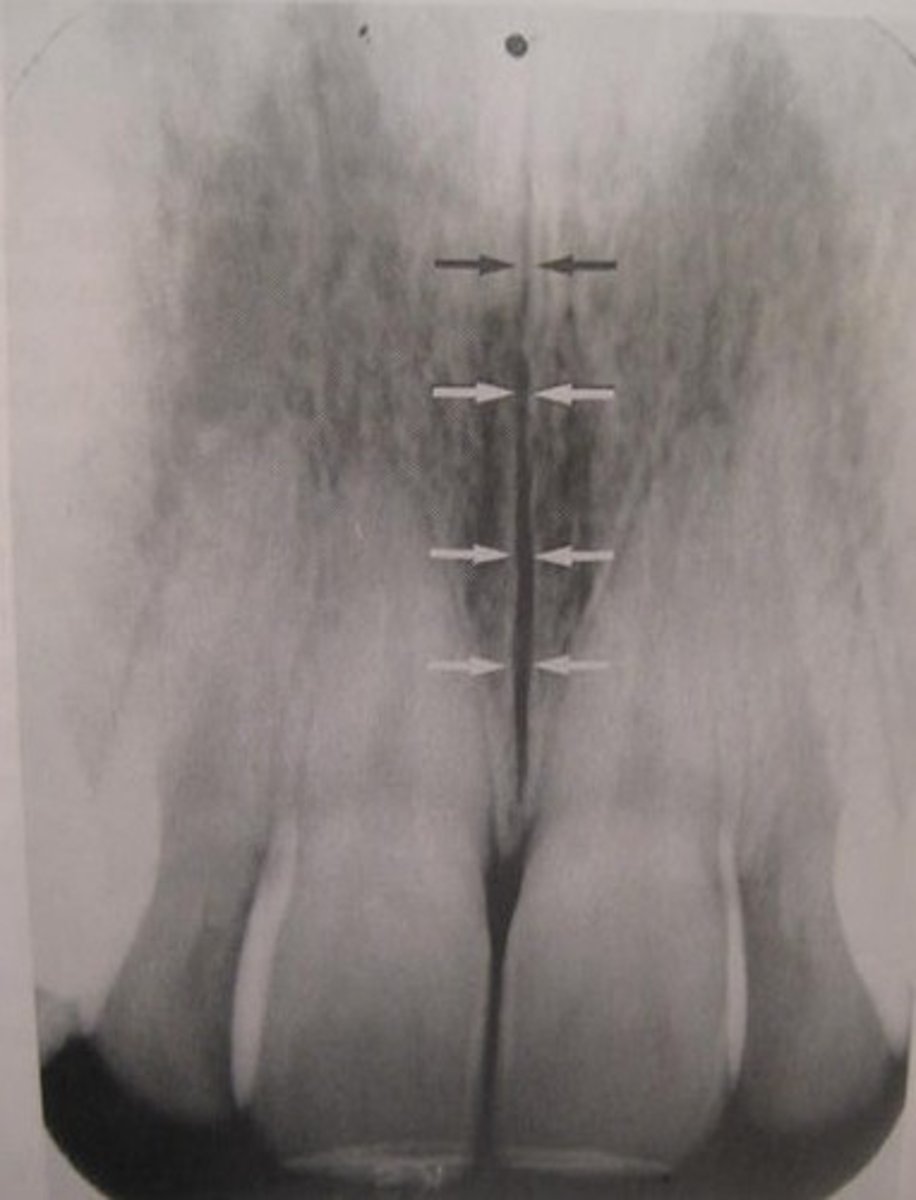
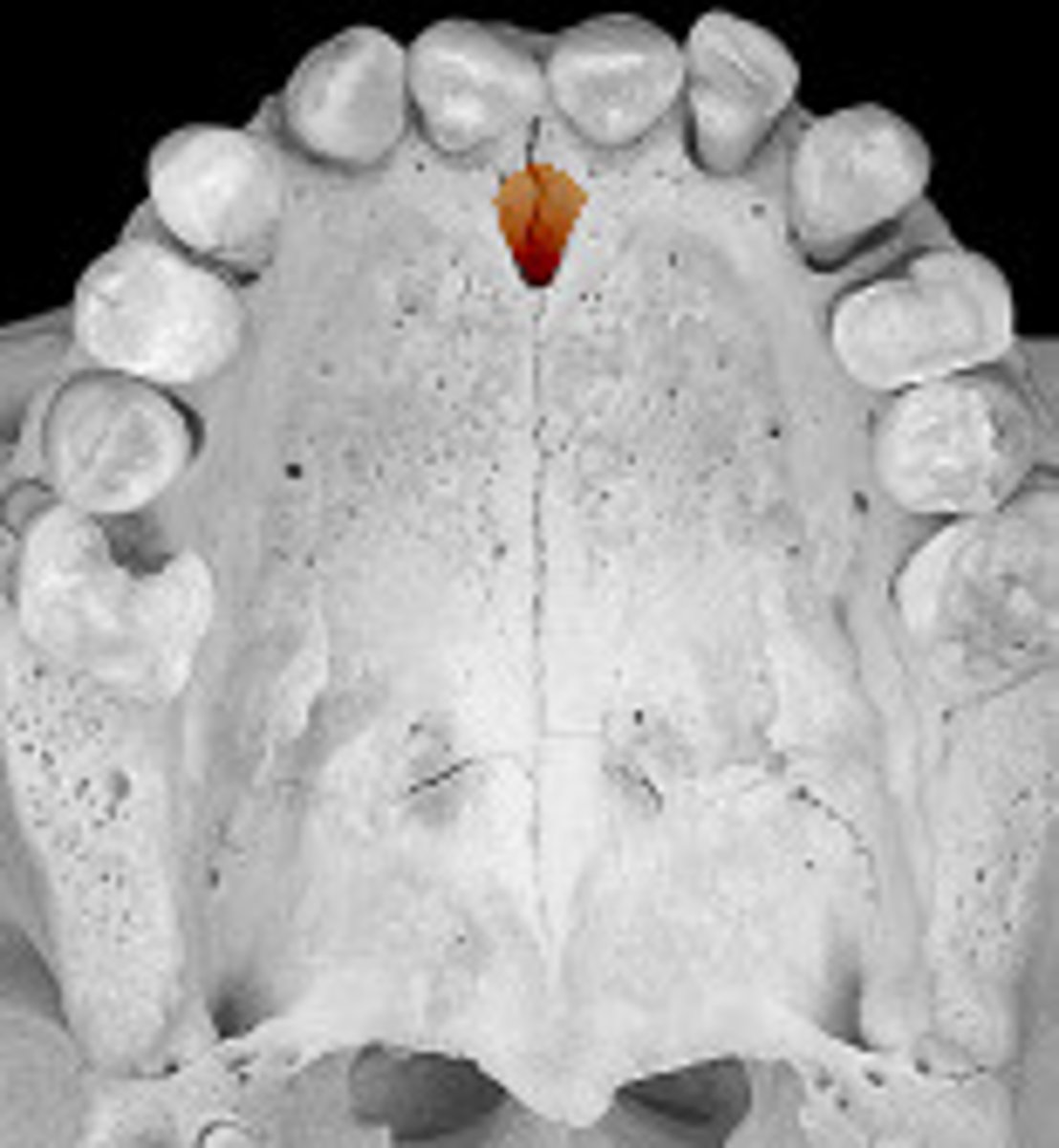
median suture
"crack" between roots of maxillary central incisors
area of incomplete fusion
radiolucent
incisive foramen
hole in the bone of the maxilla and between roots of incisors
radiolucent
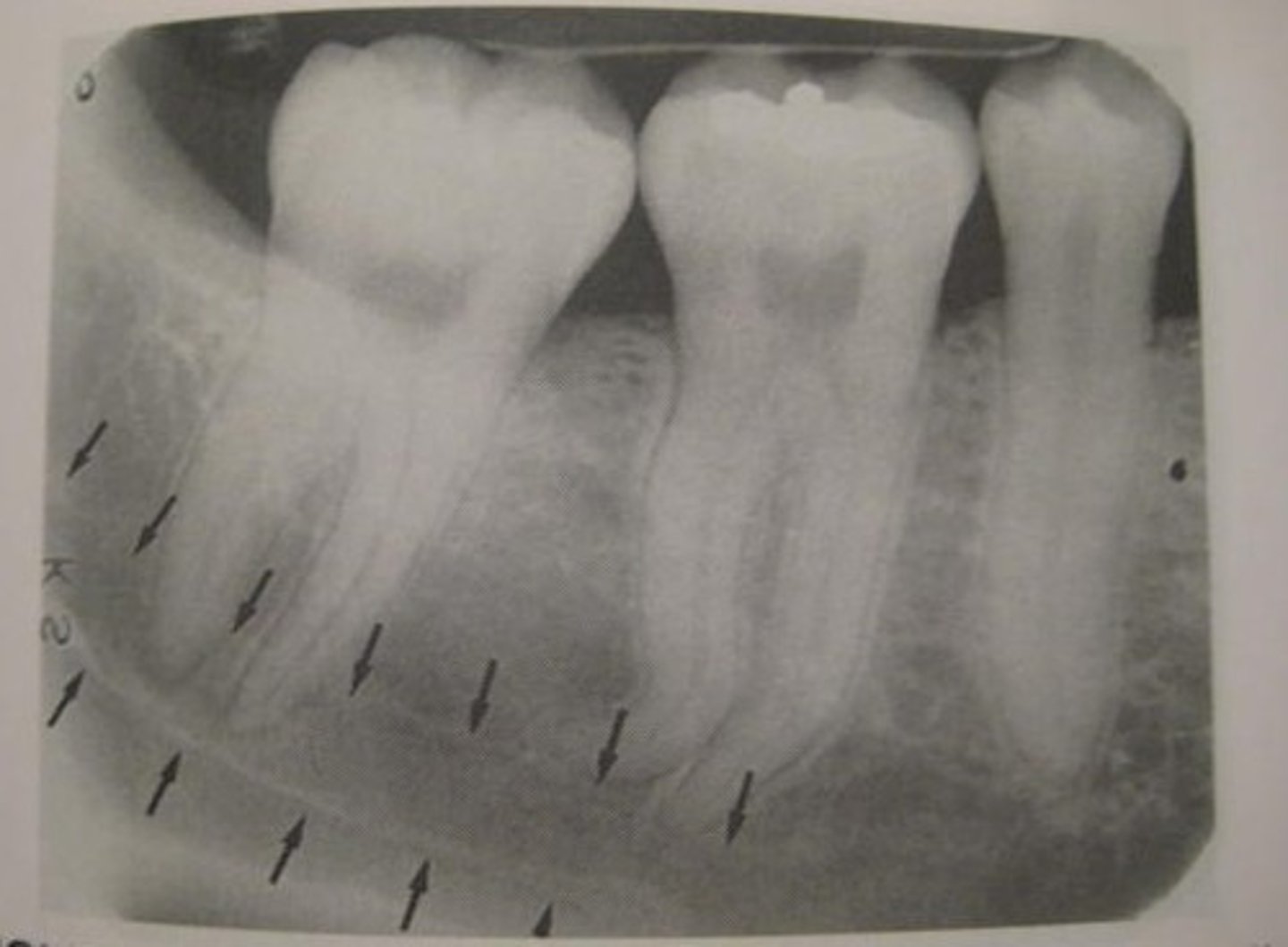
external oblique ridge
dense white line distal to the last molar and moving across root of molars
internal oblique ridge
located below the external oblique ridge
less dense
ridge of bone that extends across roots
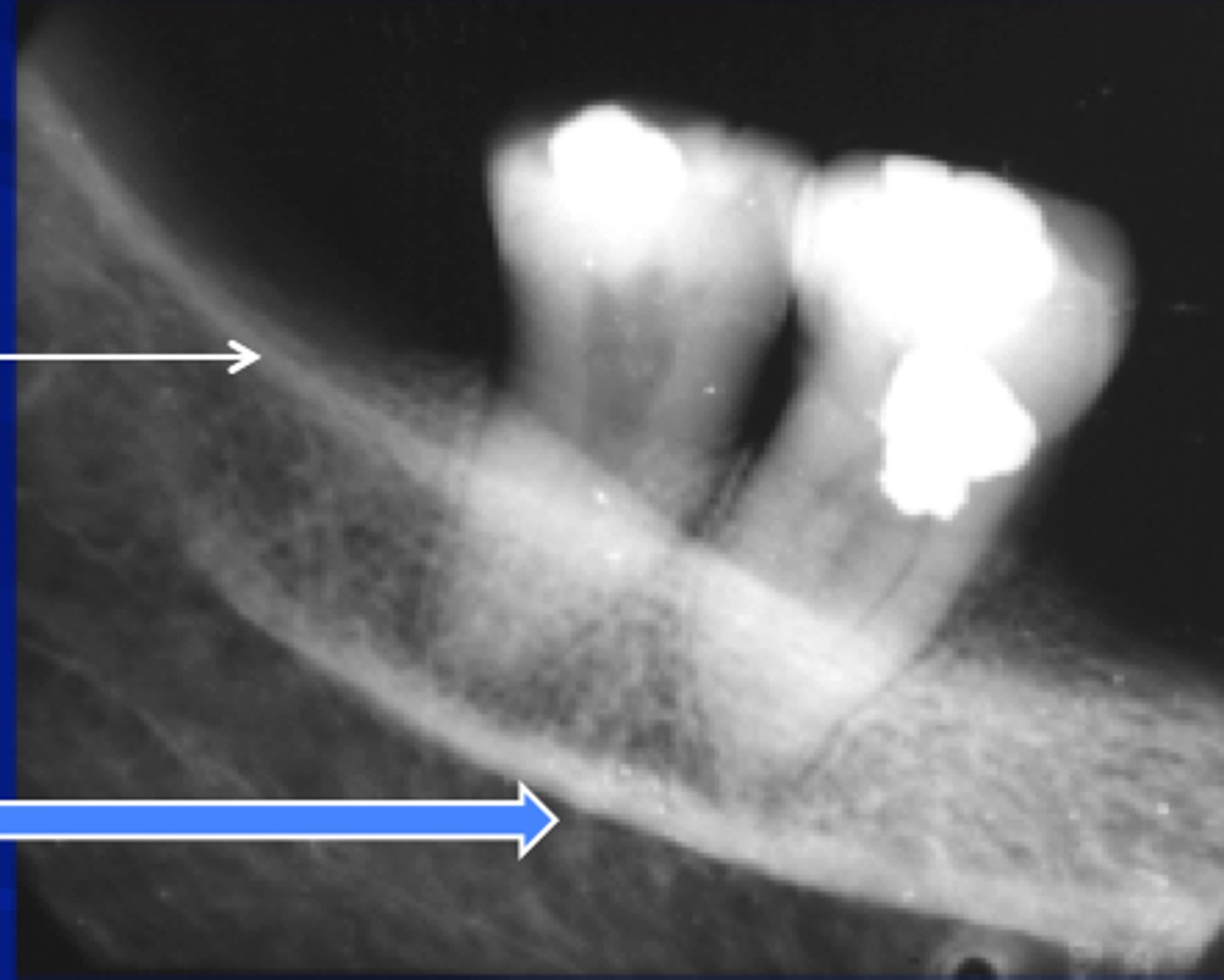
mandibular canal
border on top and bottom by a white line
passageway for nerves and blood vessels
submandibular gland fossa
rounded area of bone
less dense
space for submandibular salivary gland
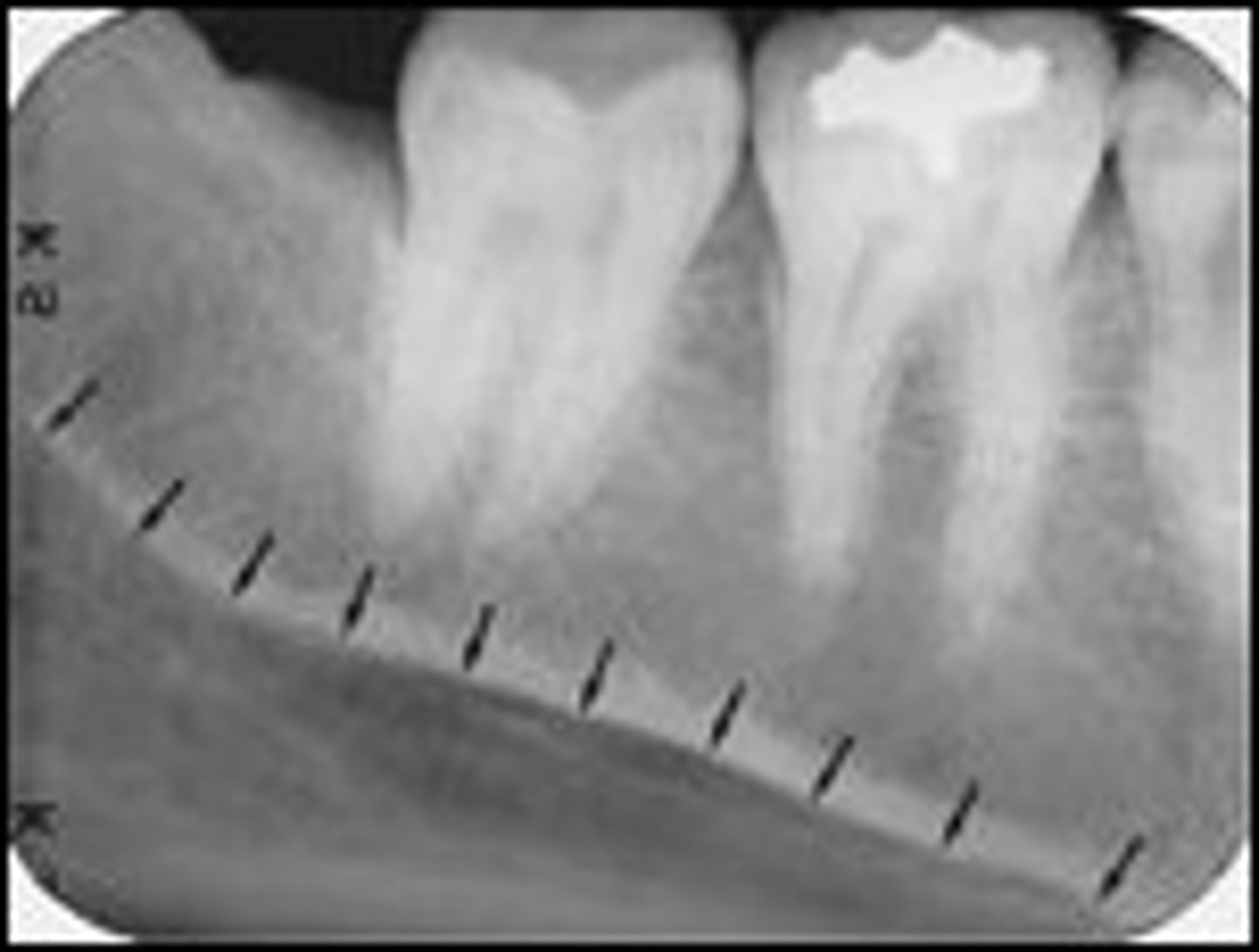
mental foramen
hole between roots of premolars
mental ridge
runs from the premolar region to the midline of the mandible
prominence in bone forming chin
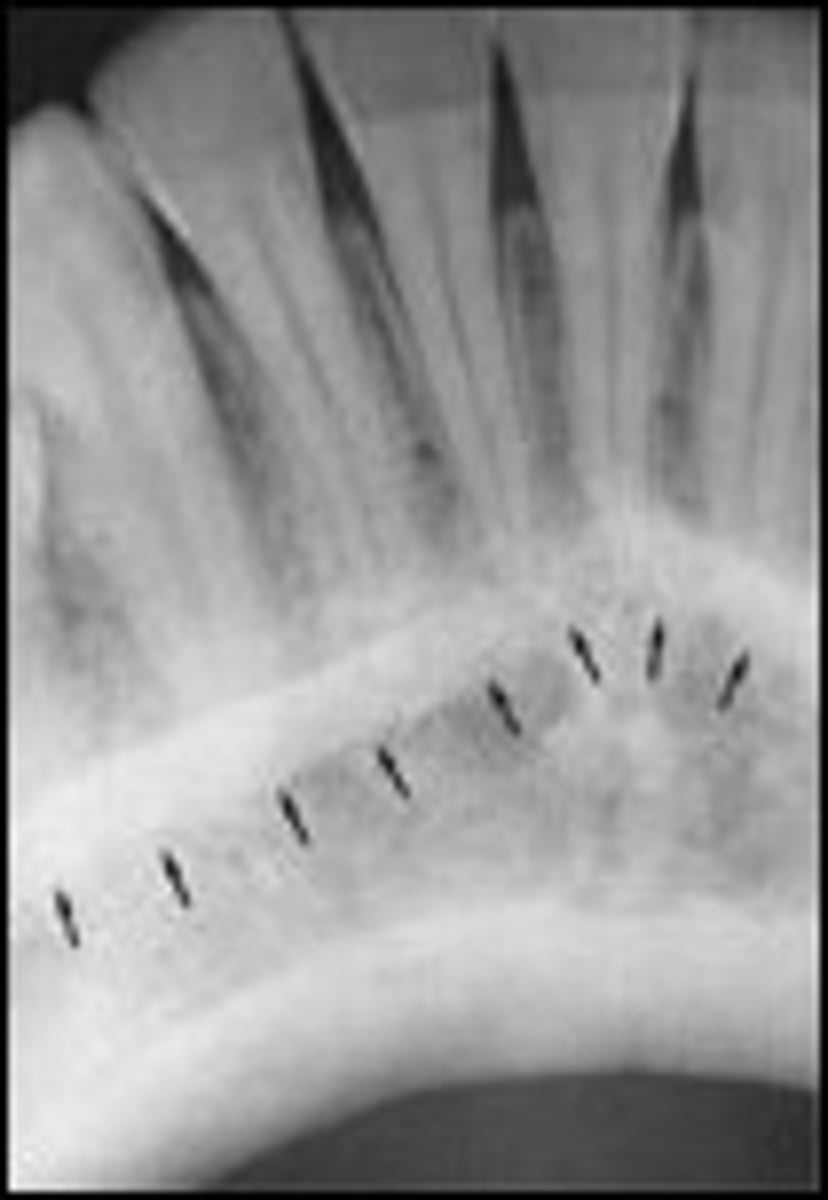
genial tubercles
bone spikes on the inner surface of the mandible
appear as a circle in images
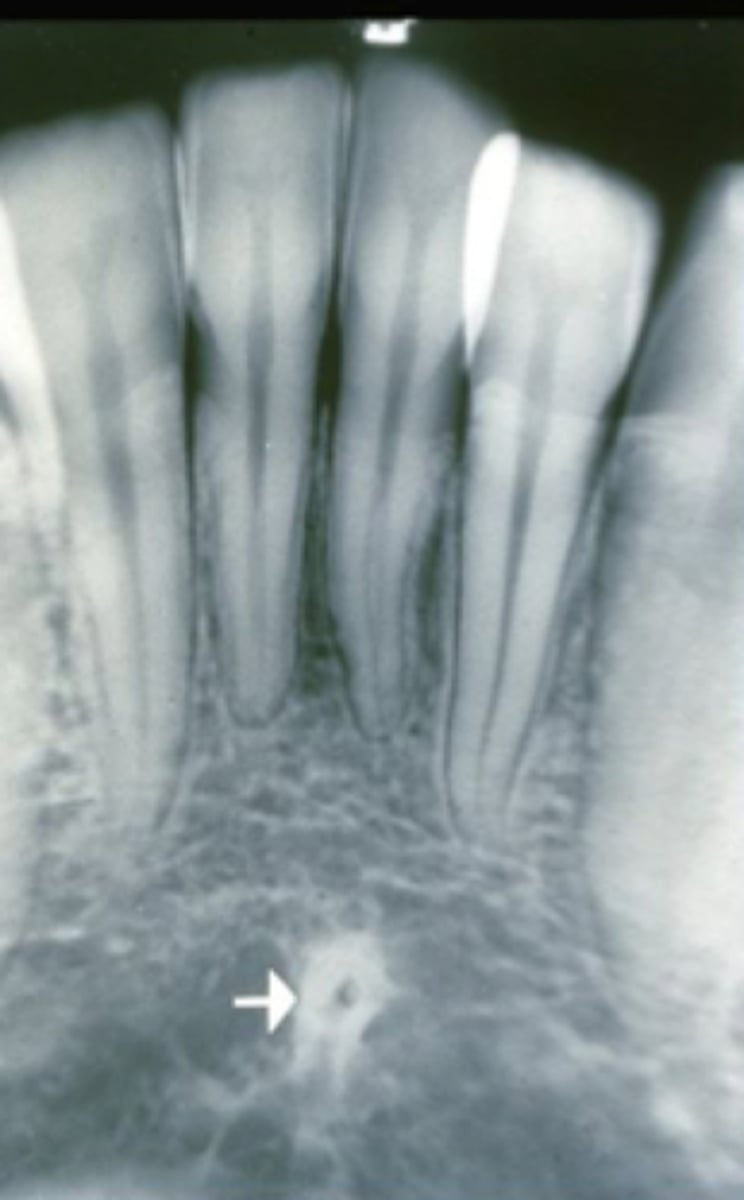
lingual foramen
located within genial tubercles
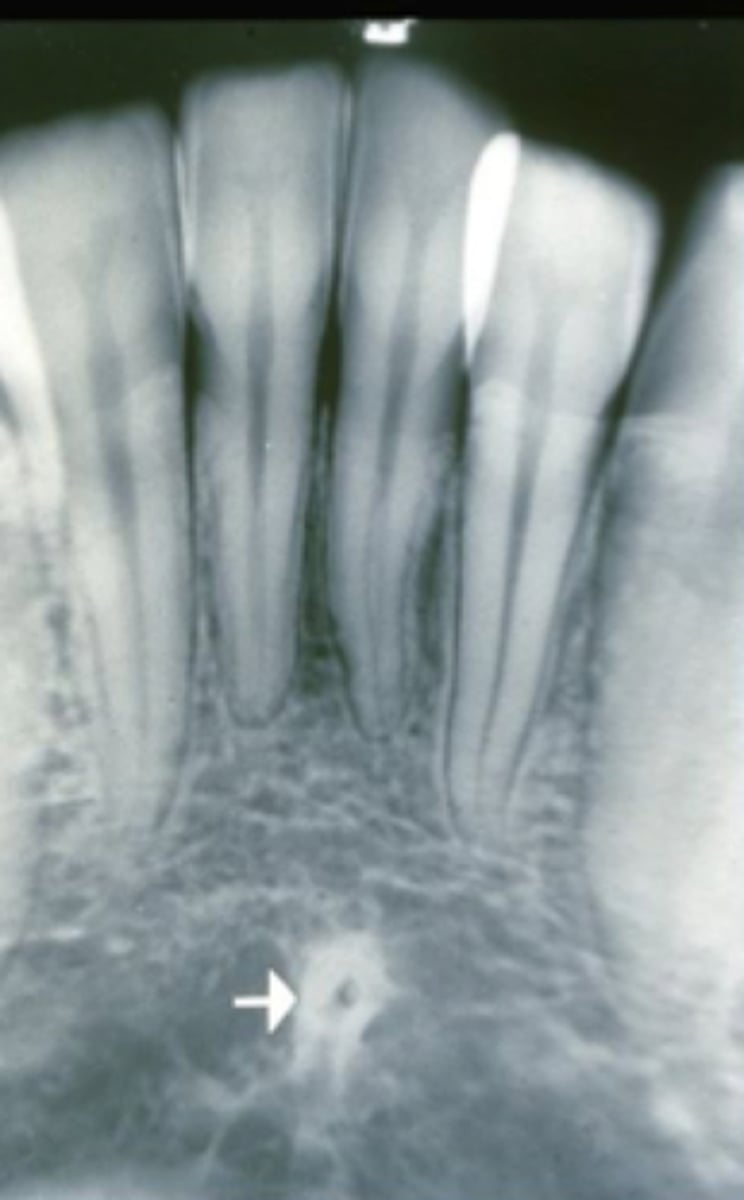
inferior border of the mandible
rounded edge/border of the mandible
cephalostat
standardizes and stabilizes head positioning with a cephalometric machine
films used by ortho, oral surg, and prostho
charged-coupled device (CCD)
sensor used in place of film for digital imaging
edentulous
areas of the jaw with no teeth
bent film
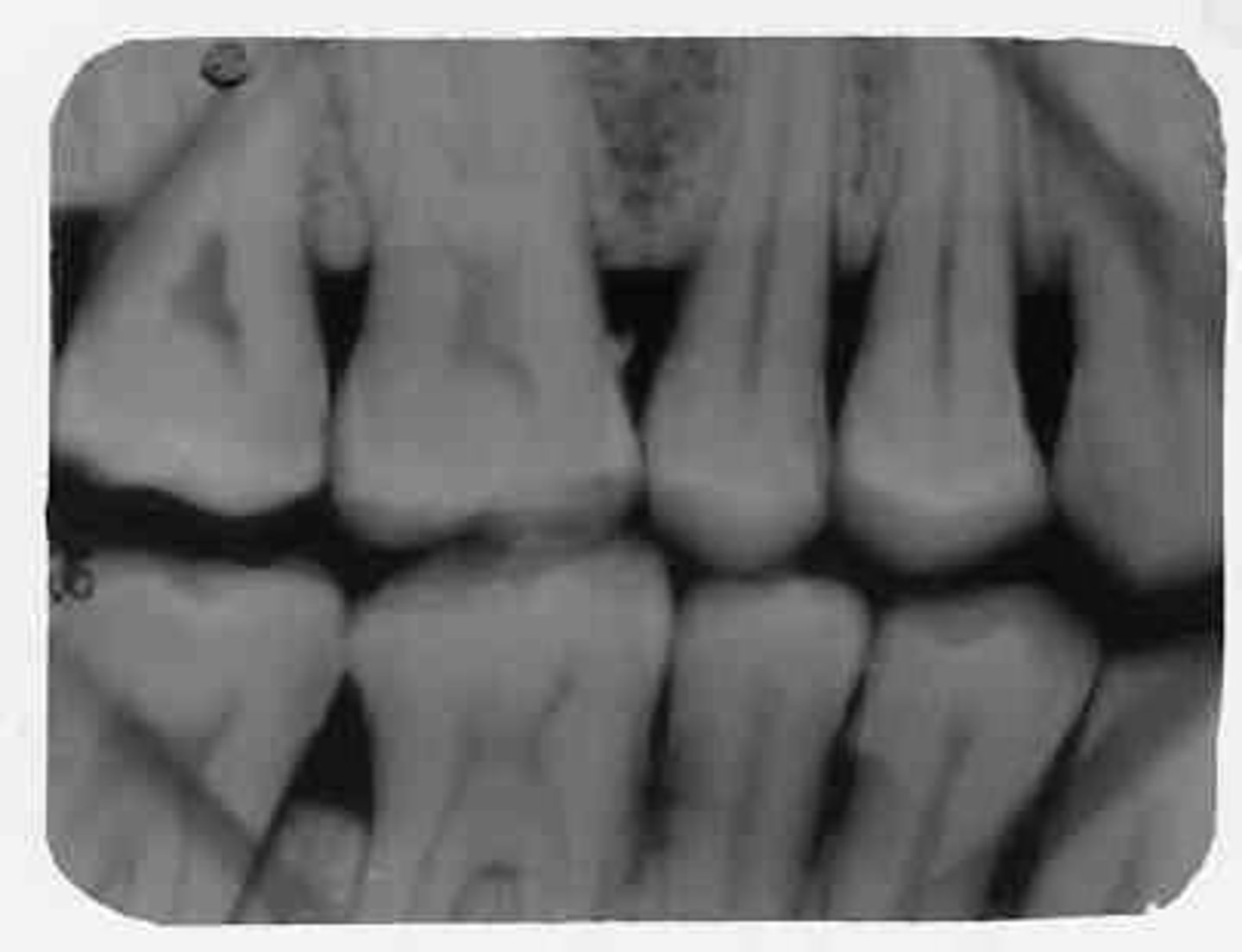
scratched emulsion
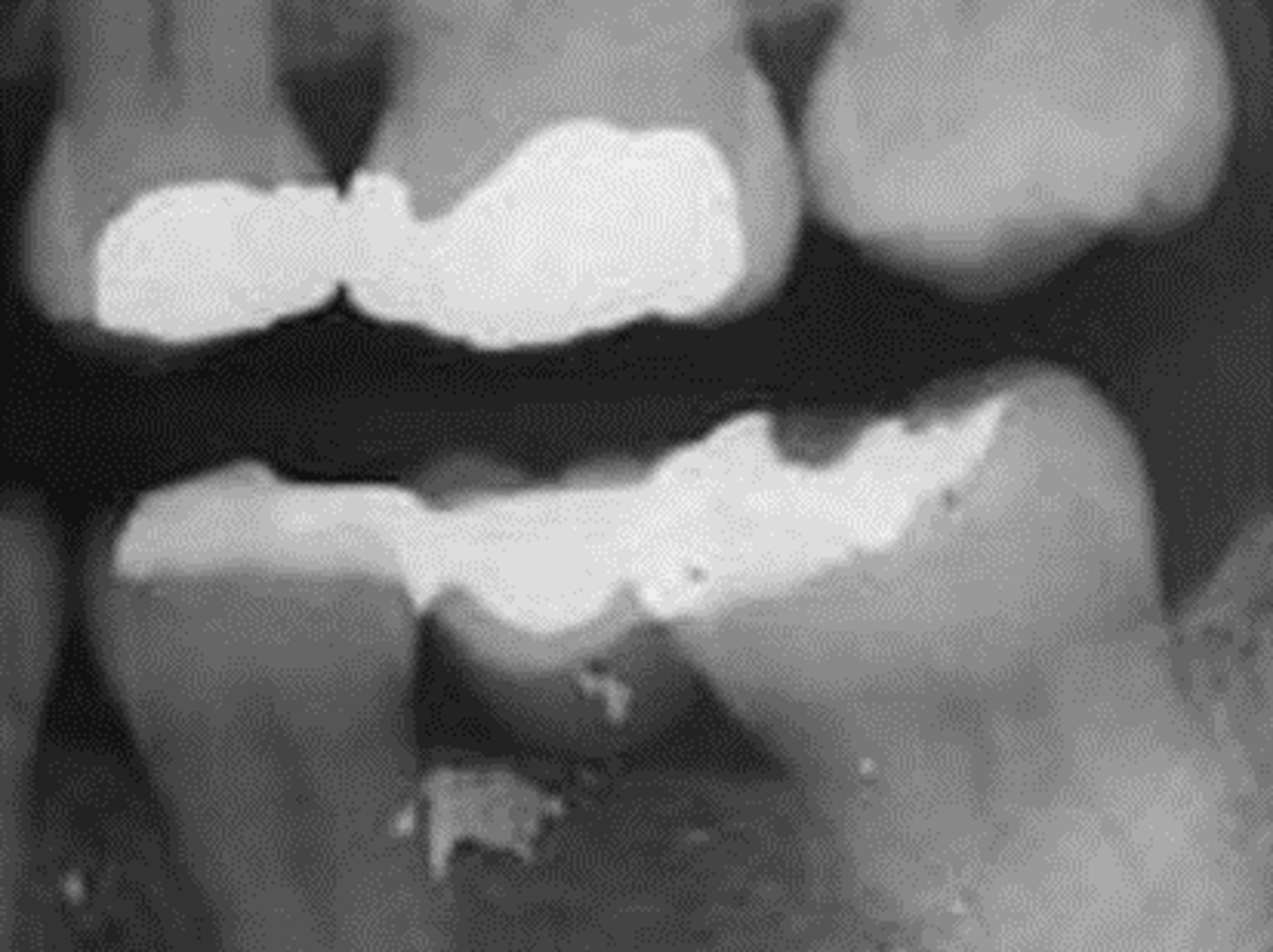
slanted occlusal plane
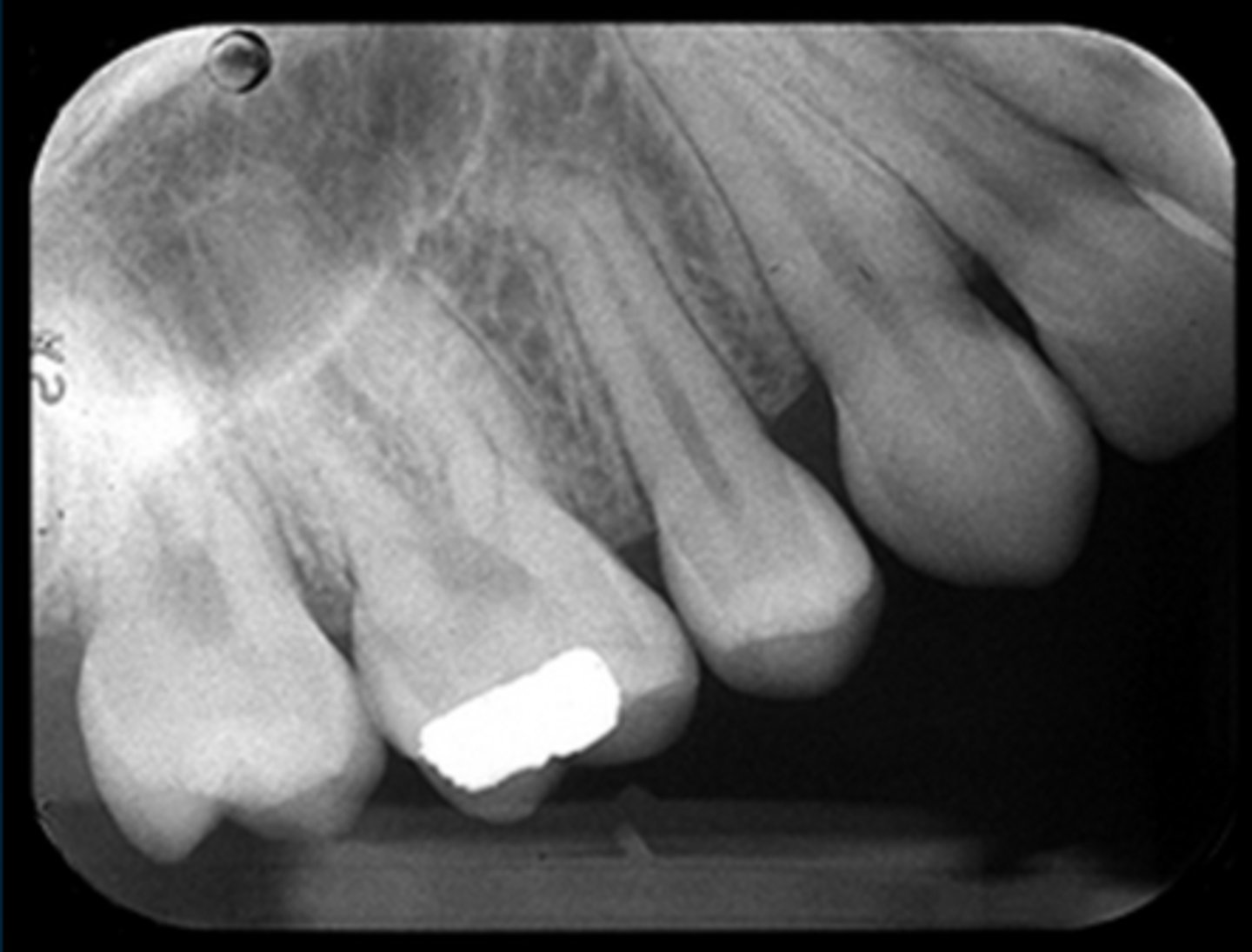
herringbone
film placed backwards (concave instead of convex)
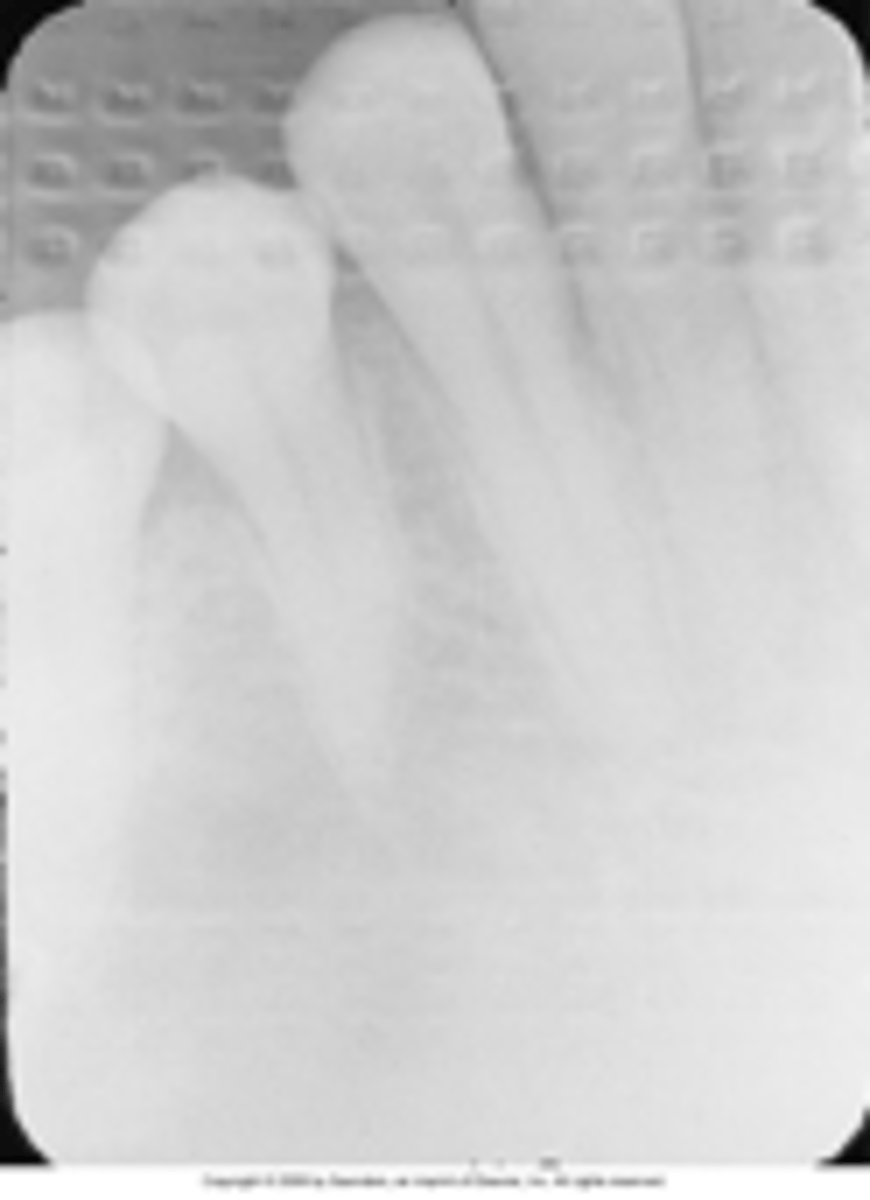
overlapping
crowns appear to be on top of each other
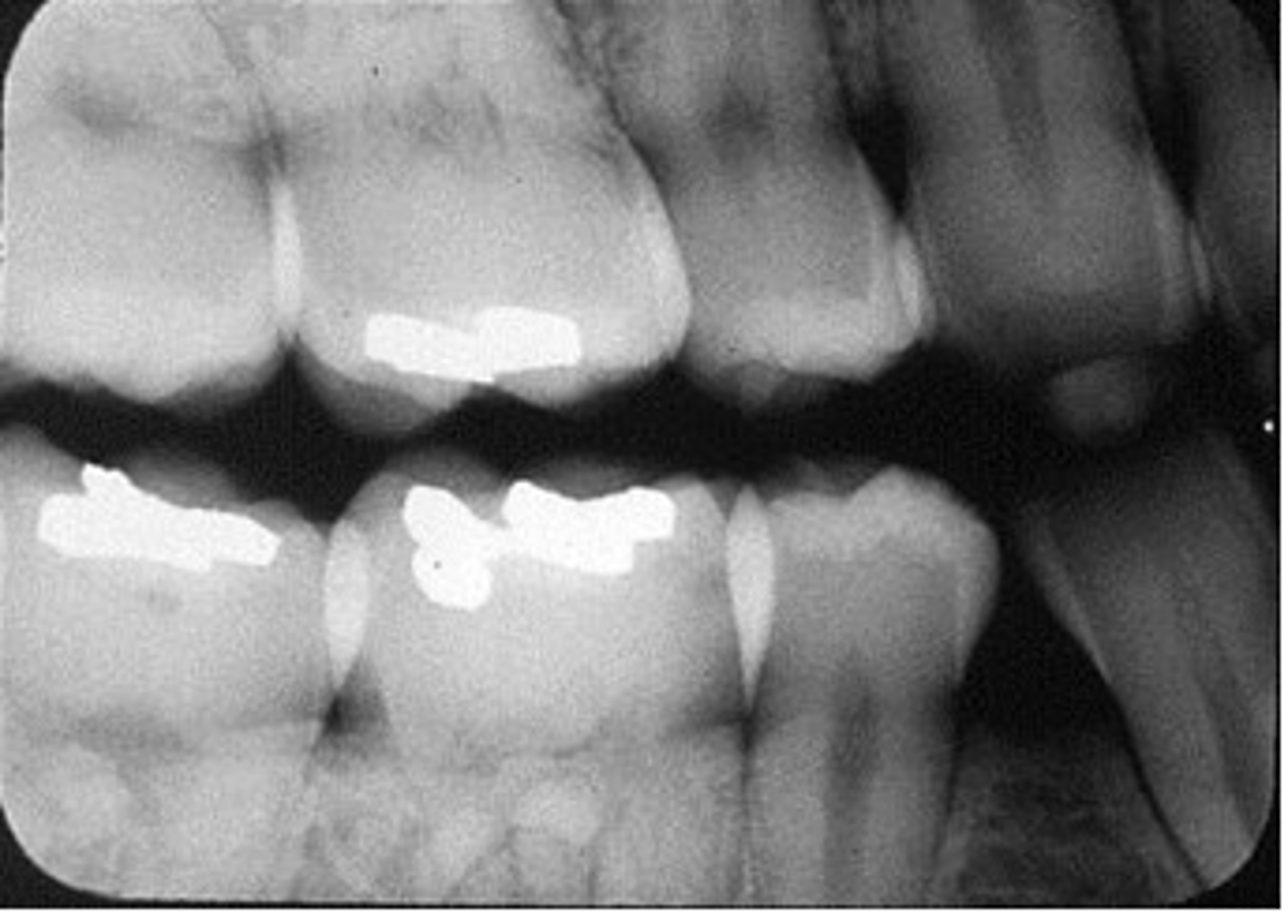
cone cut
PID not centered over film
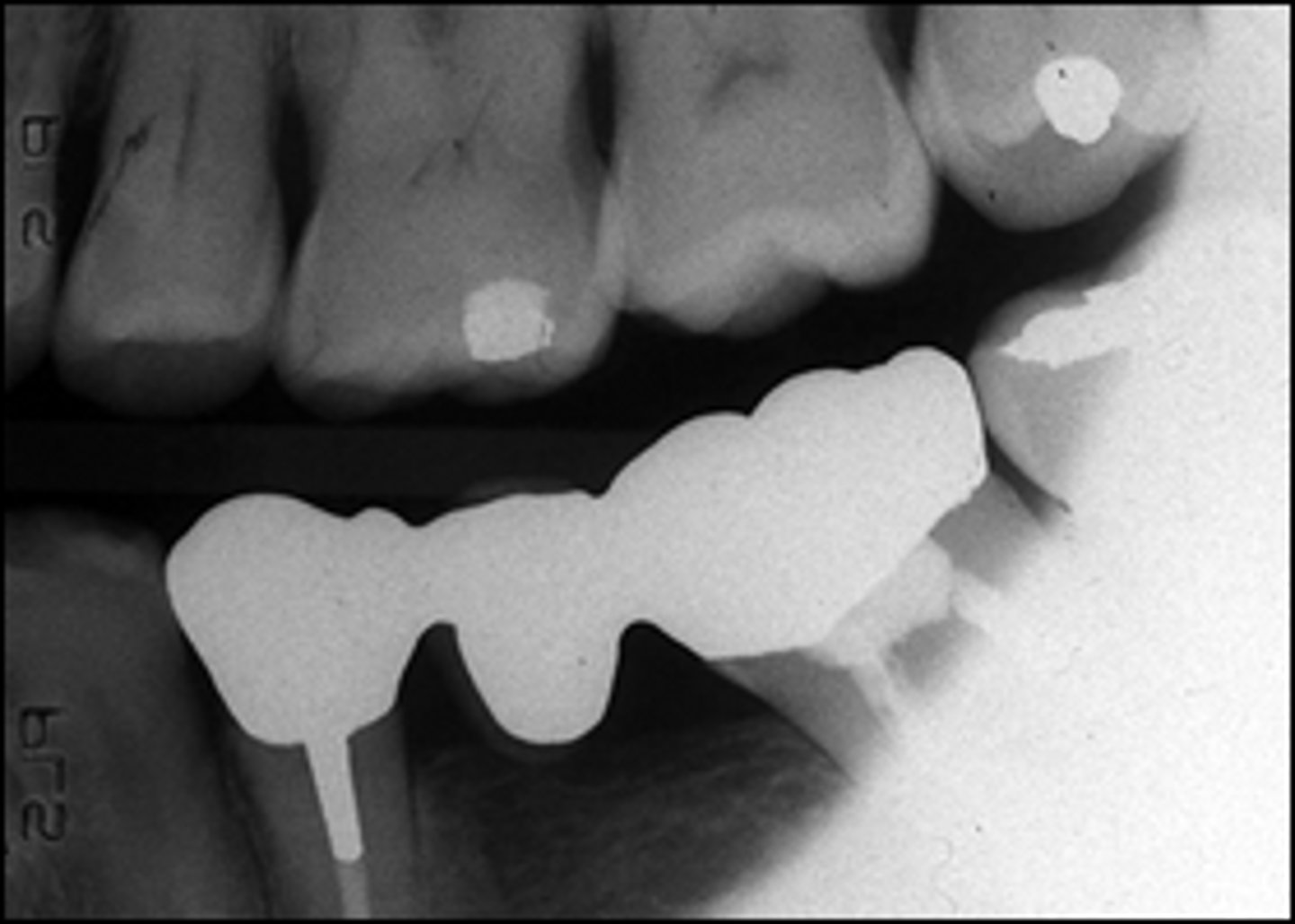
elongation
insufficient vertical angulation
teeth appear longer than actual size
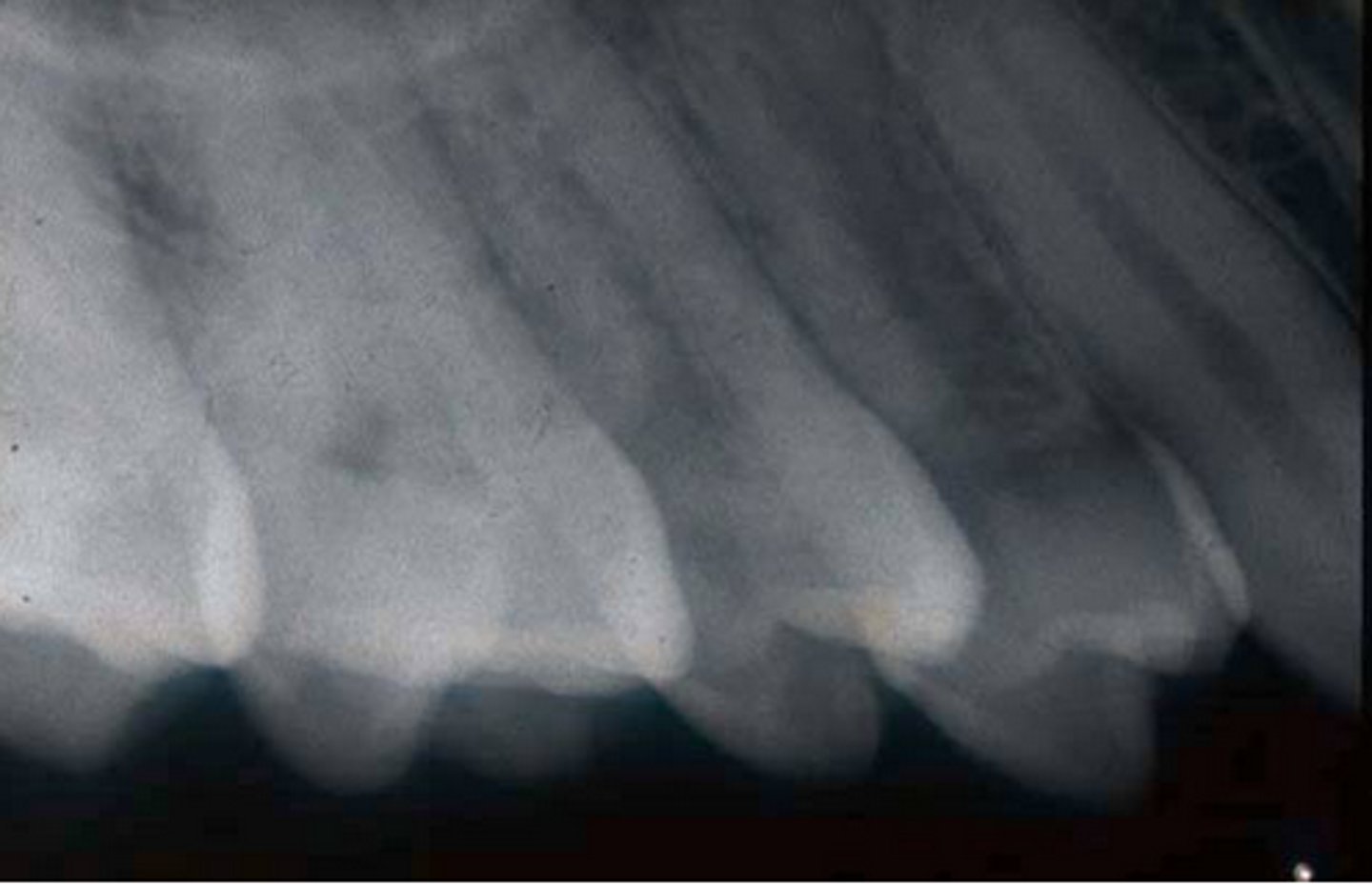
foreshortening
vertical angulation too high
teeth appear shorter than actual size
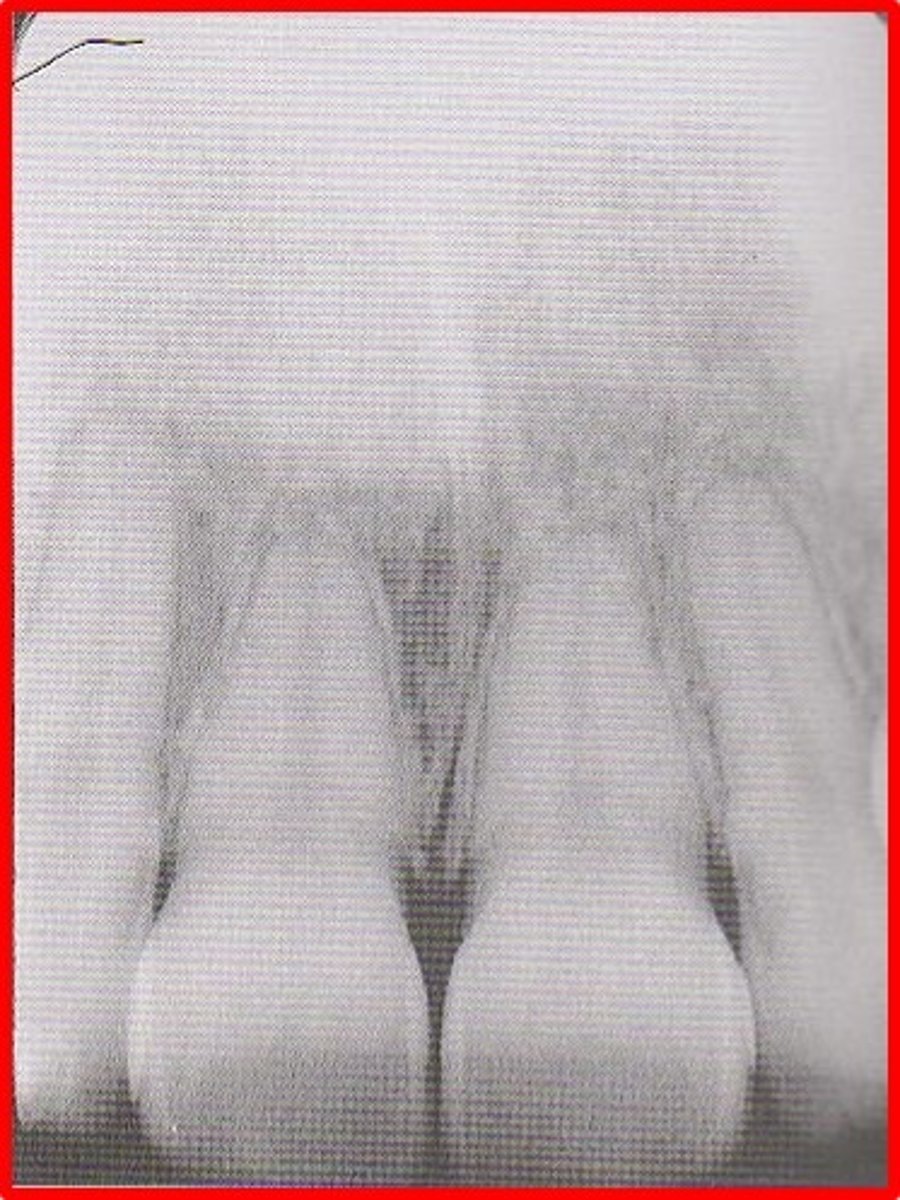
fog
hazy appearance on film
many causes
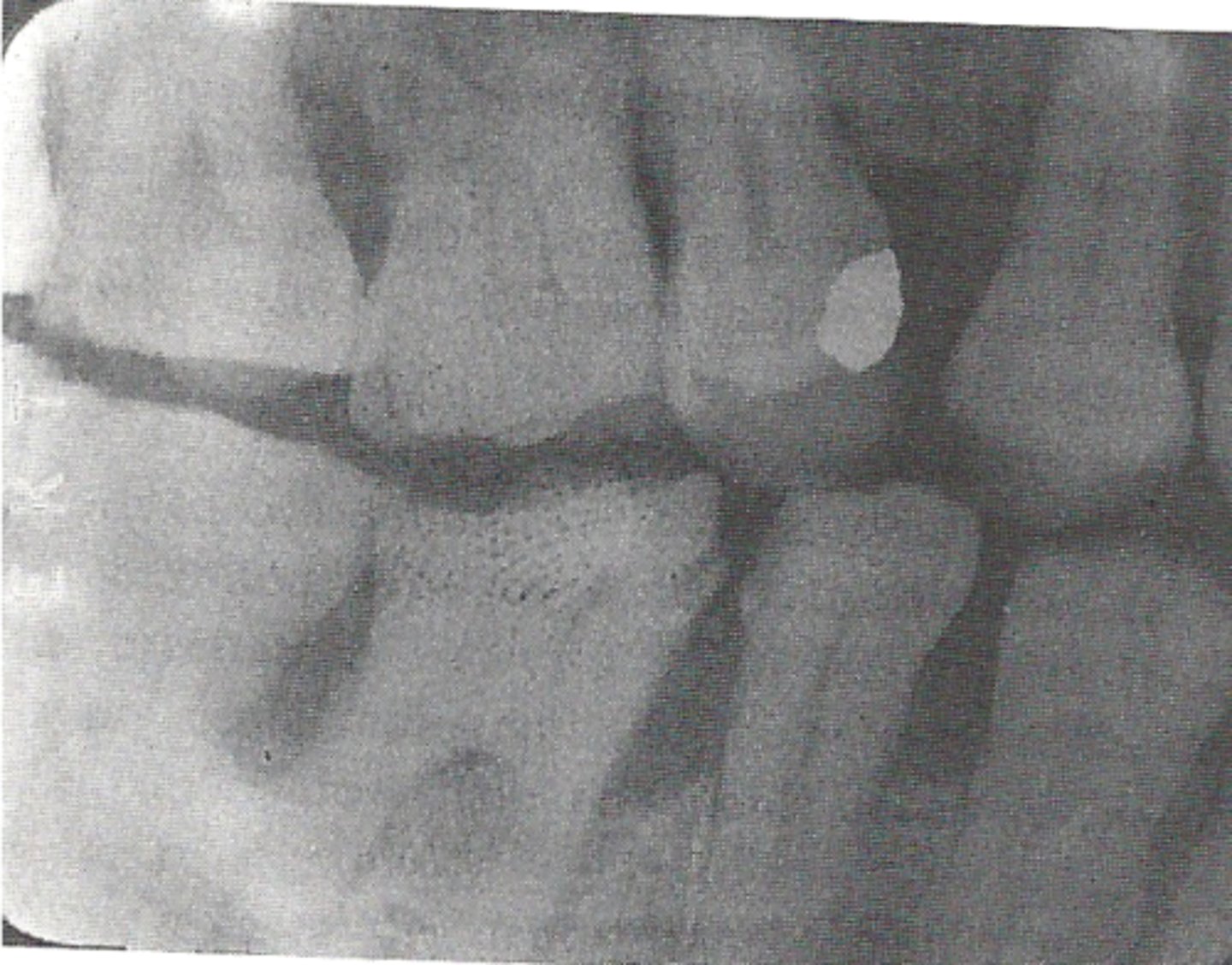
black film
can be caused by overdeveloping, developer too hot, or exposure to white light after x-ray exposure
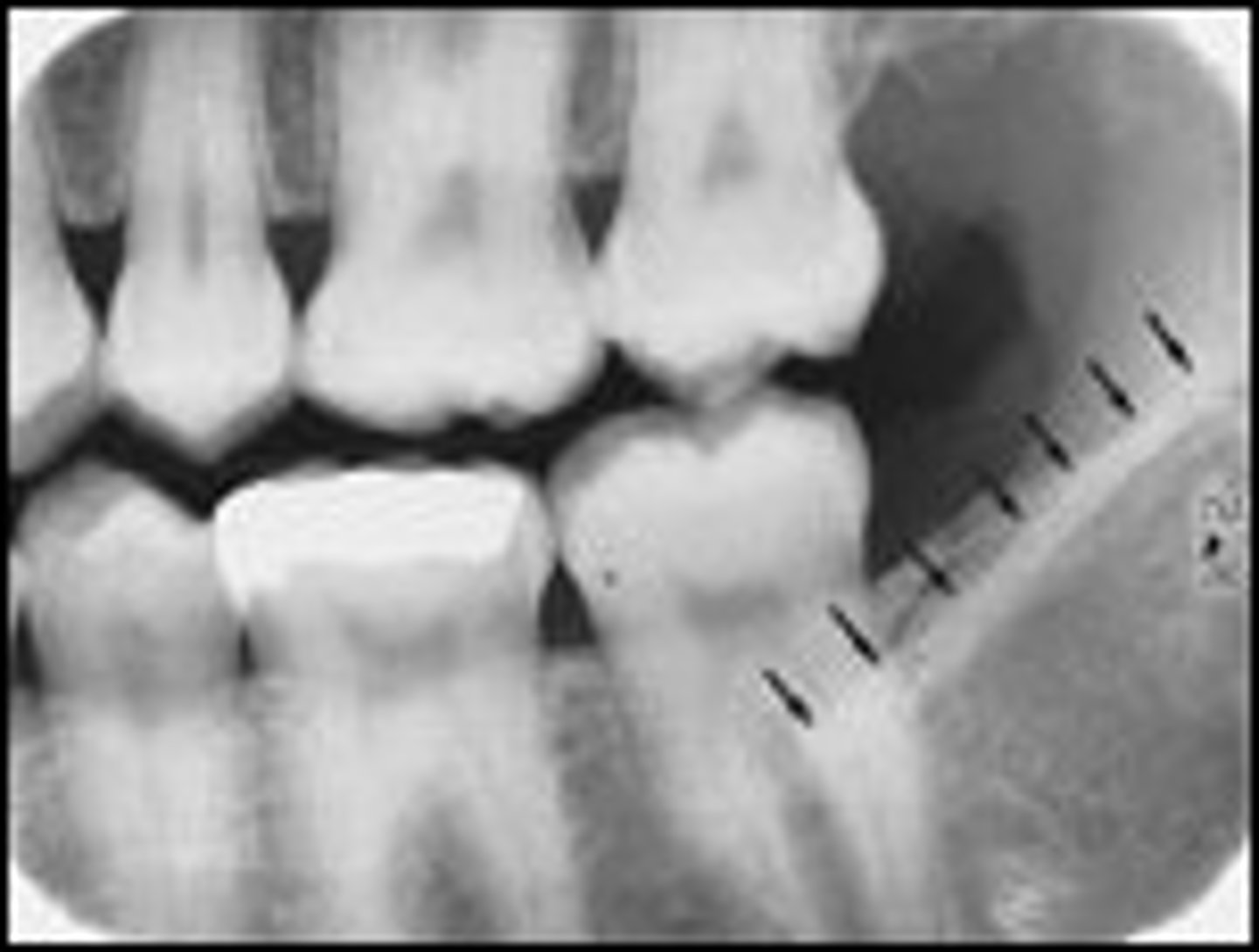
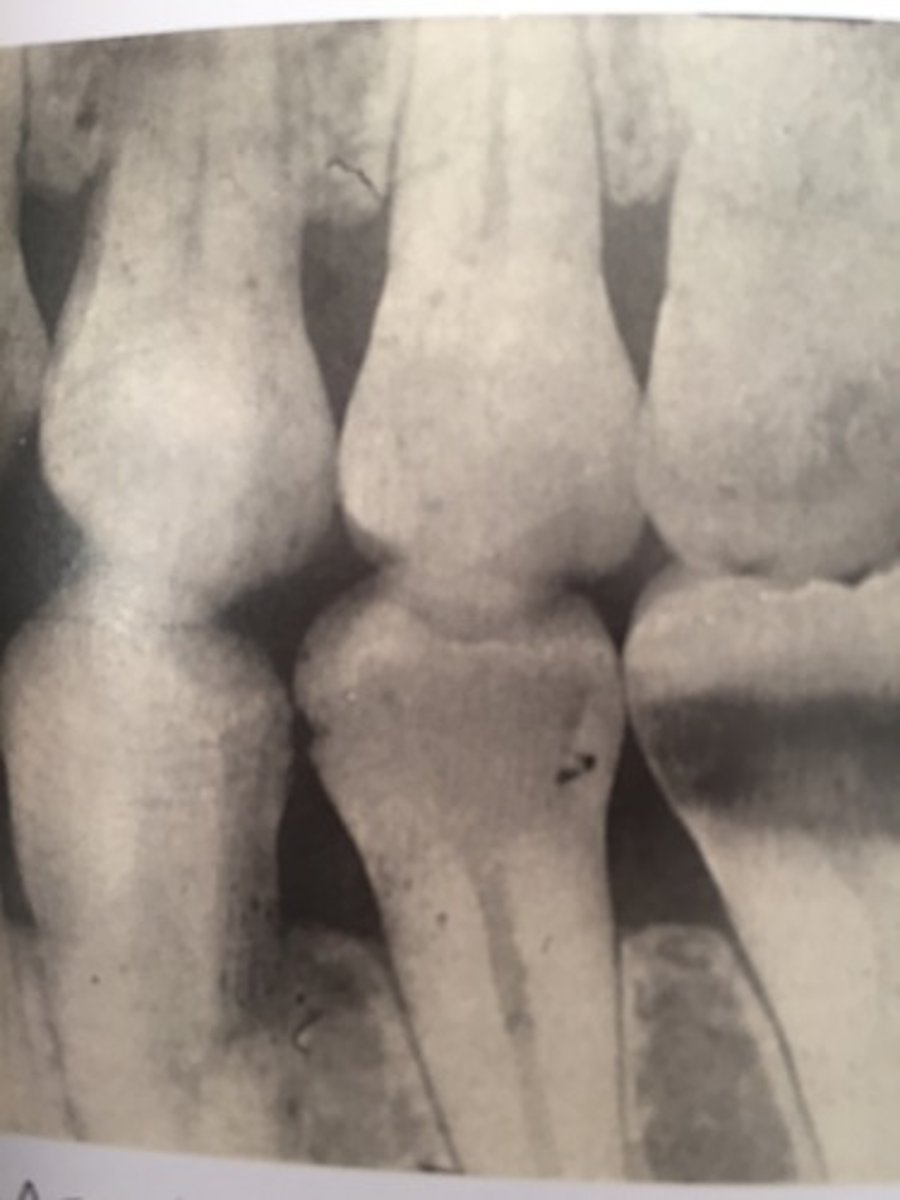
exhausted chemicals
cause film to be too light, fogged, or tinted brown
exhausted fixer pictured
developer too cool
film too light
developer too warm
film too dark
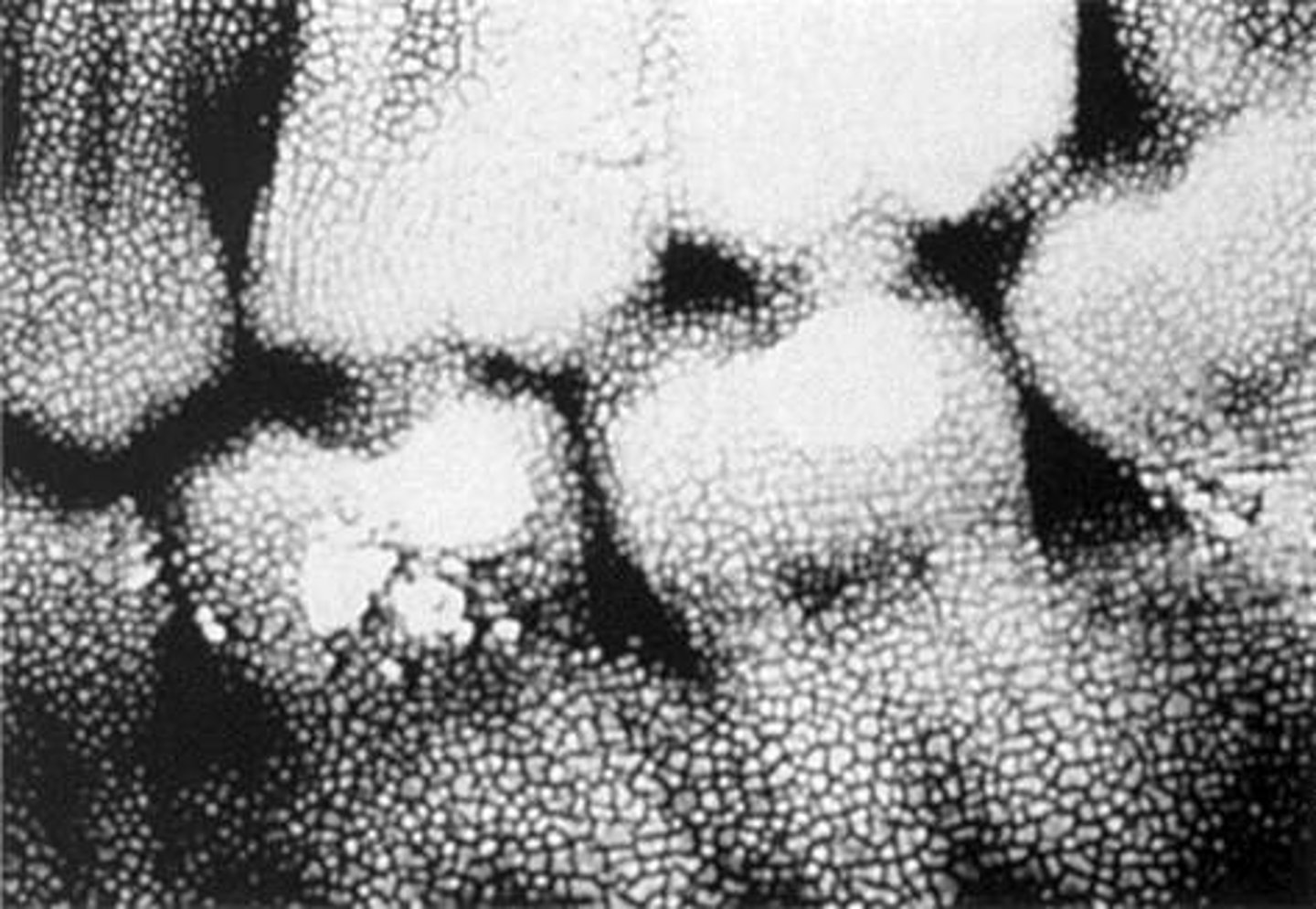
reticulation
crackled appearance
caused by extreme difference in solution temperatures
films stuck together
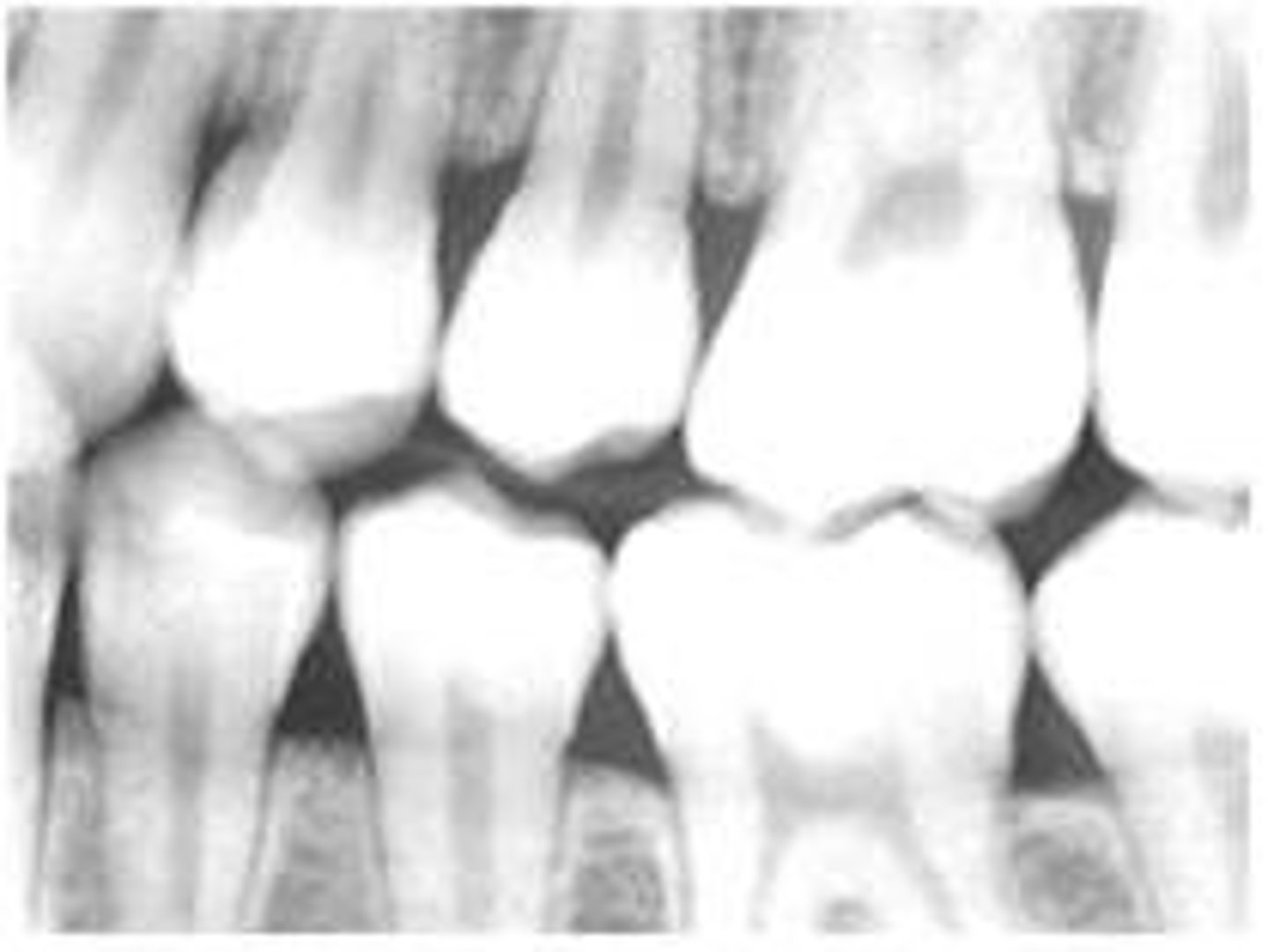
interproximal film
bitewing
shows crowns of both upper and lower teeth on same film
used to diagnose interproximal caries
sizes 0, 1, 2, or 3
radiolucent
portion of film that is dark due to lack of structural density
substance permits passage of x-rays with little to no resistance
radiopaque
portion of film that is light due to higher structural density
substance resists passage of radiation
secondary radiation
given off my any matter irradiated with x-rays
created when the primary beam interacts with matter and gives off energy
soft x-rays
rays of low energy and long wavelengths
have little penetrating power
removed from beam by filtration
Roentgen (R)
unit of exposure to radiation measured in air
replaced by coulombs/kg
Sievert (Sv)
measures the dose equivalent
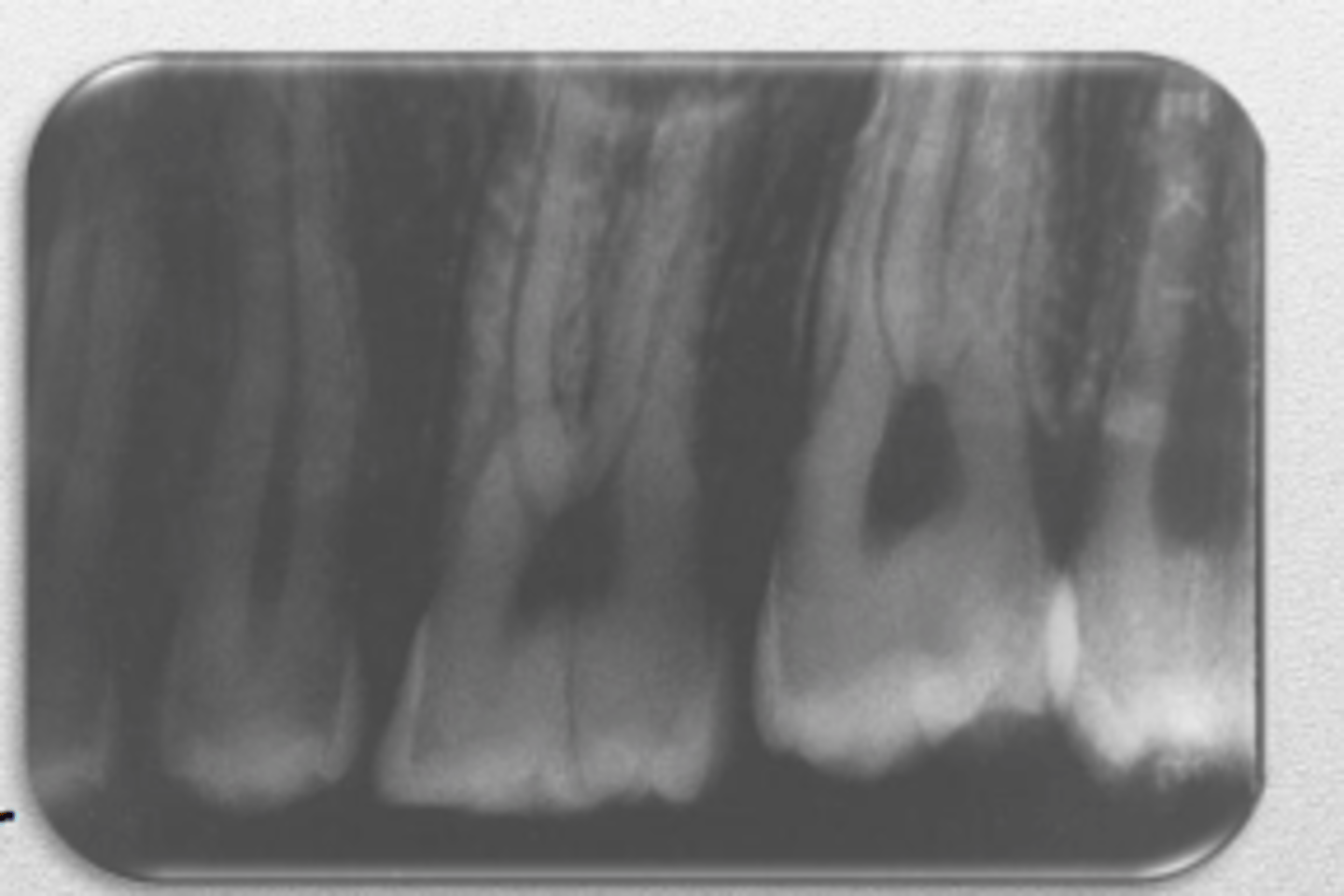
periapical film
shows the entire tooth or teeth and surrounding tissues
PPE (personal protective equipment)
personal barriers worn to prevent contamination
gloves, mask, eyewear, and gowns
occlusal plane
plane between maxillary and mandibular teeth
forms a slight upward curve - Curve of Spee
TLD
monitoring device containing crystalline compounds that store energy when struck by x-rays
determine amount of radiation exposure
RAD
unit of absorbed dose equal to 0.01 joule/kg of tissue
approximately equal to R
replaced by Gray
Gray (Gy)
measures absorbed dose
1 Gy = 100 rad
REM
measures the dose equivalent
compares biological effects of various types of radiation
replaced by Sievert (Sv)
Iowa Department of Public Health
state radiation control agency
inspects facilities
Iowa Dental Board
ensures dental assistants meet minimum training standards
issues qualification in dental radiography
conditions for an assistant to take radiographs
assistant is qualified in dental radiography or is on trainee status
dentist orders films
dentist provides supervision
conditions for trainee to take radiographs
dentist orders films
dentist provides personal supervision
requirements to obtain radiography qualification
course of study with clinical training
examination
application with fee
radiography qualification renewal
renewed with registration by August 31 of odd-numbered years
renewal requirements
proof of 2 hours of con ed in dental radiography and renewal fee
penalties for violating requirements
disciplinary action by the dental board
criminal charges or civil action
false
a dentist should always prescribe radiographs every six months to review a patients dental condition
false
certified dental assistant does not need to obtain a separate radiography qualification from the Board to take x-rays
true
dental assistant trainees can train in dental radiography during trainee period
false
Iowa Dental Board inspects dental radiography machines
control panel
timer
mA setting
kVp setting
detail/definition
if a pt is moving, what film quality is affected
decrease mA or decrease time
how to lighten a film's density
increase kVp
how to increase the number of shades
proper density
contrast
detail
shows entire area and surrounding structures
four factors of a diagnostically acceptable radiograph
movement of pt, film, or tube head during exposure
length of PID
causes of poor detail
filters
absorbing material that remove some radiation
usually aluminum
placed in path of beam
muscle
nerve and brain
bone
connective
skin
immature reproductive cells
blood cells
tissue sensitivity from most to least resistant
effects of chronic exposure
shortened life span
cataract formation
embryologic defects
genetic mutations
cancer