Chapter 15: Nervous System diseases and disorders
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
Stroke Related Facts and Stats
Every 40 seconds, someone in the U.S. has a stroke.
Every 3.25 minutes, someone dies from a stroke.
In 2022, 1 in every 6 deaths from cardiovascular disease was due to stroke.
Stroke is a leading cause of serious long-term disability.
Risk of having a first stroke is nearly twice as high for blacks as for whites, and blacks have the highest rate of death due to stroke.
A stroke is sometimes called a brain attack
2 million brain cells die during a stroke, increasing the risk of permanent brain damage, disability, or death
Someone in the US dies of CVD every 34 seconds → 2552 deaths each day
Someone in the US dies of a stroke every 3 minutes and 14 seconds →446 deaths each day
The stroke belt includes ________.
Alabama, Arkansas, Georgia, Indiana, Kentucky, Louisiana, Mississippi, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee, and Virginia
Stroke map overlaps with hypertension map; highest stroke death rates in states are the one with the most HBP and diabetes
Parkinson’s Stats and Facts
Nearly one million people in the U.S. are living with Parkinson's disease (PD).
Approximately 60,000 Americans are diagnosed with PD each year.
Men are 1.5 times more likely to have Parkinson's disease than women.
Most people are diagnosed with Parkinson’s around age 60 → 20-50 is considered early onset
Alzheimer’s Facts and Stats
More than 6 million Americans are living with Alzheimer’s by 2050. This is projected to rise to 13 million.
In the US, Alzheimer’s and dementia deaths have increased 16% during the COVID-19 pandemic.
1 in 3 seniors dies with Alzheimer’s or another form of dementia. It kills more than breast cancer and prostate cancer combined.
In 2021, Alzheimer’s and dementia will cost the nation $355 billion. By 2050, it will be as high as $1 trillion.
More than 11 million Americans provide unpaid care for people with Alzheimer’s and dementia.
In 2020, these caregivers provided an estimated 15.3 billion hours of care valued at nearly $257 billion.
Only 53% of black Americans trust that a future cure of Alzheimer’s will be shared equally.
3 in 1 Hispanics do not believe they will live long enough to develop dementia.
Between 2000 and 2019, Deaths from heart diseases decreased by 7.3% while deaths from Alzheimer’s increased by 145%.
Shingles Facts and Stats
Nearly 500,000 people over 60 get shingles every year in the US.
Almost 1 in 3 adults will get shingles during their lifetime.
98% of adults have had chickenpox and are at risk for shingles.
Multiple Sclerosis Facts and Stats
MS is more prominent in females than males (74% females and only 26% males)
Nearly 1 million people in the US have MS
Nervous System
Consists of brain, spinal cord, and nerves
Central nervous system: Brain and Spinal cord
Peripheral nervous system: Autonomic nervous system and Cranial and spinal nerves
Parts of the Brain
Cerebrum
Cerebellum
Brainstem
Part of the CNS
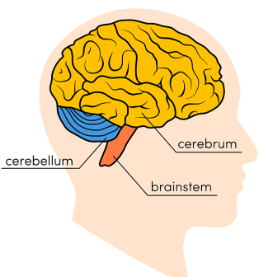
The cerebrum initiates ______.
and coordinates movement and regulates temperature, enables speech, judgment, thinking and reasoning, problem-solving, emotions and learning. Functions related to vision, hearing, touch and other senses.
Cerebellum
Coordinates voluntary muscle movements and to maintain posture, balance and equilibrium.
The brainstem connects the ________.
cerebrum with the spinal cord and includes the midbrain, the pons and the medulla. Many activities are controlled here including involuntary actions such as breathing, heart beating, blood flowing, etc.
The way the brain responds to trauma and recovery is _______.
different for every person
Spinal cord
Part of CNS
Conduit for signals between the brain and the rest of the body.
Controls simple musculoskeletal reflexes without input from the brain.
Some cells of the central nervous system are so specialized that they cannot divide and create new cells.
As a result, recovery from a brain or spinal cord injury is much more difficult.
Peripheral Nervous System
Peripheral nerves reside outside your brain and spinal cord. Relays information between your brain and the rest of your body.
2 main parts: Autonomic nervous system (ANS) and Somatic nervous system (SNS)
Autonomic Nervous system
Controls involuntary bodily functions and regulates glands.
Sympathetic = controls the body’s changes in response to stressors, such as increasing heart rate or blood pressure aka fight or flight response
Parasympathetic = controls the changes in the body needed to relax and restore function such as returning blood pressure to normal
Somatic Nervous system (SNS)
Controls muscle movement and relays information from ears, eyes, and skin to the central nervous system.
Common signs and symptoms of nervous system disorders
headache
nausea and vomiting
mood swings
weakness
fever
Symptoms specific to CNS
Dysphasia or inability to speak
stiffness in neck, back, or extremities
inability to move any part of the body
paralysis
seizures or convulsions
visual difficulties
unconsciousness
amnesia or extreme forgetfulness
extreme or prolonged tiredness
Diagnostic tests
Motor/Reflex Tests: mallet touching knees and elbows
Sensory Tests: put something warm or cold or use a needle to see if you can feel it
Neurological Exams:
Cerebrospinal fluid = to test for infections
Measurement of intracranial pressure = for brain injury/trauma
X-rays of skull and vertebral column
Myelogram = inject dye in spinal column
Angiogram = inject dye into bloodstream to see if it flows properly
Electroencephalography (E E G)
CT and MRI
Encephalitis
Inflammation of brain tissue caused by bacteria and viruses, and bite of mosquitoes
Symptoms:
Headache
Sensitivity to light
Elevated temperature
Stiff neck and back
Lethargy
Mental confusion
Coma
Treatment:
Treatment may be supportive and first determine what is the cause
happens more in young people
early diagnosis and treatment is key for survival
Antiviral medication may be effective
Meningitis
Inflammation of meninges or coverings of brain and spinal cord
Causes:
Bacteria
Virus
Fungi
Toxins
E.g., lead, arsenic
At - Risk groups –
Under 5 = more in groups and sharing
16 – 25 = more in groups, sharing, and college
Over 55 = immunocompromised
Can be life threatening
Meningitis (cont.)
Symptoms:
Stiffness and resistance in neck (nuchal rigidity)
Coma
Rash
Seizures
Fever
Sleepy
Dislike lights
Confusion and vomiting
Diagnosis
Lumbar puncture to find causative agent
Treatment
Antibiotics for bacterial infection
Antipyretics
Anticonvulsants
Quiet, dark environment
The best prevention for meningitis is ______.
vaccines (for A & E meningitis)
Poliomyelitis (polio) (cont.)
Symptoms:
Muscle weakness
Neck stiffness
Nausea and vomiting
Muscles atrophy and become paralyzed
Diagnosis
Virus culture from throat, feces, and/or spinal fluid
Supportive treatment:
Analgesics
Bedrest during acute phase
Long-term physical therapy and braces may be needed
If respiratory system involved, mechanical ventilation may be needed
Polio spreads by _______.
air droplets and airborne particles from fecal matter
Polio was eradicated in the US until 2022 when ______.
there was a case in an un-vaccinated individual in New York who traveled to a foreign country
Tetanus
Highly fatal infection of nerve tissue
Cause
Bacteria Clostridium tetani
First symptom:
Jaw stiffness
Commonly called lockjaw (can’t talk or eat)
muscle spasms
stomach pain and seizures
Treatment:
Human Tetanus Immune Globulin (TIG)
Aggressive wound care
Antibiotics
Tetanus Vaccine
Vaccines for tetanus are recommended _______.
to take every 10 years
available for every age group
Rabies
An often fatal encephalomyelitis
Caused by a virus
Primarily affects animals: E.g., raccoons, foxes, skunks, BATS
Transmitted to humans through bite of infected animal
1-3 cases of rabies in humans annually
Rabies is usually from _______.
contact with bats; most bites from bats go unnoticed cause of their small teeth which is dangerous
2023 7 y/o in Texas died last year, bit by bat but no noticeable marks so parents did not take action, died about 3 months later, this past November art teacher in CA also bitten by infected bat found in her classroom, died less than a month later
Rabies (cont.)
Symptoms: Fever, Pain, Paralysis, Convulsions, Rage, Spasms and paralysis of muscles for swallowing, Throat spasms leading to hydrophobia, Inability to swallow, and Drooling of frothy saliva
Treatment: Immediate washing of area with soap and water, give immunoglobin, and then Anti-rabies injections – Series of 4 shots over 14 day period
No cure; once symptoms appears it’s too late
Shingles
Viral disease caused by herpes zoster (chicken pox virus)
Symptoms
Burning or tingling pain
Itchy, painful, red rash
Rash becomes fluid filled blisters
Symptoms last 10 days to several weeks
Diagnosis
Made based on the appearance of lesions → visual examination
Viral culture test
Anyone who has had chickenpox can develop this
Shingles (cont.)
Treatment:
There is no cure
Treatment is symptomatic
Antivirals
Analgesics
Antipyretics
Antipruritic
Two shot vaccine recommended for adults over age 50
Cerebrovascular Accident
Also known as stroke
Is due to a poor blood supply to the brain
Causes
Cerebral thrombus = plaque in brain blocks arteries or veins
Cerebral embolism = blood clot travels to the brain
Cerebral hemorrhage
Cerebrovascular attack (cont.)
Symptoms: numerous symptoms depending on the area of the brain affected and the severity of the C V A
Sudden loss of consciousness
Confusion
Poor coordination
Dysphasia
Dysphagia
Hemiparesis (paralysis on one side of the body)
Spotting a stroke acronym
Balance
Eyesight changes: can only see bottom vision or only part of vision is dark
Face dropping
Arm weakness: can’t hold up their arms
Speech difficulties: all of a sudden can’t talk or understand speech
Time: call 911 and look at the time and tell paramedics when they arrive → certain medications have to be given in a certain window of time
Stroke on the right of the brain ______.
affects the left side of the body
left-side paralysis
memory deficits
impulsive behavior
attention span
movements on the left side of the body
emotional stability
awareness on left side of the body
Stroke on the left side of the brain _________.
affects the right side of the body
right side paralysis
memory deficits
slow behavior
speech impairment
motor speech, understanding math, and writing
recognizing objects and remembering written info
emotional control
CVA (cont.)
Diagnosis
Physical exam, E E G, C T scan, and M R I
Treatment:
Anticoagulant
Hypertensive medications
Rehabilitation program
Risk factors:
Smoking
High-fat diet
Obesity
Lack of exercise
High Blood Pressure
Surgical prevention treatment:
Carotid endarterectomy
Transient Ischemiac attacks (TIAs)
Also known as mini-strokes
Due to insufficient blood supply to brain for a short time between 1-24 hours
Symptoms:
Weakness of arm and/or leg
Dizziness
Slurred speech
Mild loss of consciousness
Symptoms last few minutes to 1 hour
Diagnosis by angiogram
Treatment:
Surgery to improve blood flow
Degenerative Disk Disease
Degeneration or wearing away of intervertebral disk
Allows vertebrae to bump or rub against each other
Symptoms:
Difficulty walking
Radiating pain in back and in one or both legs
Diagnosis by X-ray, myelogram, C T scan, and M R I
Treatment:
Rest back and legs
Back brace
Physical therapy
Analgesics
Anti-inflammatories
Exercise to ease pain
Surgery is last resort
MRI is the most common for _______.
degenerative disk diseases as it gives a better picture of the spinal cord
Headaches
One of the most common disorders in humans
Usually, a symptom of another disease rather than a disorder in and of itself
Disorders that typically have headaches as a symptom include:
Sinusitis
Meningitis
Encephalitis
Hypertension
Anemia
Constipation
Premenstrual tension
Tumors
Caffeine withdrawal
Headaches stem from two common ________.
mechanisms: Tension on facial, neck, and scalp muscles and Vascular changes in arterial size of vessels inside head
Contributing factors: Stress, Toxic fumes (harsh or overpowering smells), Noise, Lack of sleep, and Alcohol consumption
Headaches may be ______.
acute (occur every once in a while) or chronic (consistent or for a long period of time)
Pain may be mild to unbearable and incapacitating
Pain may be constant, pressure, throbbing, stabbing, or intermittent
Common Types:
Tension: “stress headache”; pain in occipital area
Cluster
Following lumbar puncture
Migraine
Headache (cont.)
Diagnosis:
History and physical, X-ray, E E G, M R I, and C T
Treatment:
Lifestyle changes – improved diet, sleep, exercise
Analgesics
Bedrest
Muscle massage
Muscle relaxants
Warm baths
Biofeedback: see how brain reacts which helps for treatment
Cluster headache
These headaches occur at night after falling asleep. Can be caused by stress, emotional trauma, or unknown reasons. Severe throbbing pain behind the nose and one eye.
Migraine headache
Severe incapacitating headache commonly accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and visual disturbances. Individuals can experience a visual aura, a sensation that preceded the event, flashing lights or photophobia. Occur 2X more in women than men.
Epilepsy
Chronic disease of brain
Intermittent episodes of abnormal electrical activity in brain
Symptoms:
Seizure
Convulsions
Common types of seizures
Focal onset-seizures (Petit mal)
Generalized onset-seizures (Grand mal)
Status epilepticus
Diagnosis by EEG, CT scan, cerebral angiogram, and blood tests
Treatment:
Anticonvulsive medications
Close monitoring and adjusting of medication
If conclusions last for 5 minutes call 911
Focal onset-seizures (Petit mal)
Brief change in consciousness without convulsions
Still have awareness of surroundings
Generalized onset-seizures (Grand mal)
Convulsions
Loss of consciousness
Loss of control on bladder and fecal matter
See visual rainbow aura before event
Status epilepticus
Life threatening
Continuous series of convulsions
No recovery
Bell’s Palsy
Affects facial nerve (7th cranial) leading to unilateral (one-sided) paralysis
Affects individuals 20 to 60 years of age →pregnant women or people with diabetes, flu, Covid, etc.
Symptoms:
Drooping weakness of eye and mouth
Inability to close the affected eye → given patch to cover eye
Drooling of saliva
Unable to whistle or smile
Distorted facial appearance
Diagnosis by history and symptoms
Treatment:
Analgesics
Anti-inflammatories
Ball’s Palsy begins _______.
suddenly and worsens over 24 hours
last 2-8 weeks
Parkinson’s Disease
Slow, progressive brain degeneration
Cause is unknown, but may be related to a decrease of brain neurotransmitter – dopamine
Symptoms: Rigidity and immobility of hand, Very slow speech pattern, Pill-rolling motion of fingers, Expressionless facial appearance, Abnormal bent-forward posture; Short, fast-running steps with shuffling appearance, and Bradykinesia
Symptoms appear after age 55 or earlier
Symptomatic treatment: Dopamine replacement, Physical, and psychological therapy
No Prevention
Dementias
Loss of mental ability due to loss of neurons or brain cells
Types of dementia
Senile (old age)
Alzheimer’s disease – the most common type of senile dementia
Senile and Alzheimer’s disease are often used synonymously, but they are not the same.
Vascular
Head trauma
Substance induced
Alzheimer’s Disease
A form of senile dementia
Usually affects individuals age 60 and older → in younger people its early onset (have a shorter life expectancy)
Early symptoms:
Short-term memory loss
Inability to concentrate
Slight changes in personality
Diagnosis: Positive only by autopsy and Initially, diagnosis may be made by ruling out other brain diseases
Treatment: Supportive, no known cure; Focused on safety, maintaining nutrition, hydration, personal hygiene; Emotional support for family and caregivers
Early-stage Alzheimer’s
Function independently - may still drive, work and socialize. May experience memory lapses, such as forgetting familiar words or the location of everyday objects.
Symptoms - not widely apparent at this stage, - family and close friends may notice and a doctor would be able to identify symptoms using certain diagnostic tools.
Some may be eligible to receive U.S. Food and Drug Administration-approved treatments that can change the course of disease progression.
Middle-stage Alzheimer’s
Longest stage - can last for many years.
Sx become more pronounced,
Require a greater level of care → need to be watched constantly by family or caregiver
Damage to brain nerve cells make it difficult to express thoughts and perform routine tasks without assistance.
In this stage, the person living with Alzheimer's can still participate in daily activities with assistance.
Late-stage Alzheimer’s
Dementia symptoms are severe.
May forget people or confuse their identity.
Lose the ability to respond to their environment, to carry on a conversation and, eventually, to control movement. They may still say words or phrases, but communicating pain becomes difficult.
As memory and cognitive skills continue to worsen, significant personality changes may take place, requiring individuals to need extensive care.
May not be able to initiate much engagement during this stage, still benefit from interaction in ways that are appropriate, like listening to relaxing music or receiving reassurance through gentle touch.
4 Pillars of Prevention
Diet and supplements—healthy diet, including lean proteins, fruits and vegetables,.
Stress management—including meditation, deep breathing, massage, and prayer.
Exercise and brain aerobics—150 minutes cardio and strength training. Brain aerobics – reading, crossword puzzles
Spiritual fitness - connectedness
The duration of stages for Alzheimer’s ________.
vary for each person
Vascular Dementia
2nd most common form of dementia
Atrophy and death of brain cells due to decreased blood flow
Atherosclerotic plaque can cause decreased blood flow → common with aging
Symptoms: Changes in memory, personality, and judgment, Irritability, Depression, Sleeplessness, and Lack of personal hygiene
Diagnosis: History and physical, blood flow testing
Treatment: Increasing blood flow to brain and Carotid endarterectomy
Head trauma
Death of brain cells due to head trauma
Symptoms:
Decrease in mental intellect and cognitive function
Loss of ability to reason, remember, or show appropriate emotions
Changes in personality
Diagnosis:
History, cranial X-rays, C T scan, and M R I
Treatment:
Correct damage, if possible
Therapy and rehabilitation
Prevention:
Is often easy to prevent with proper use of protective equipment
Head trauma is more common in _______.
males aged 14-24
Subtstance-Induced Dementia
Brain cell death from drug toxicity and toxins in the environment
aka “Pseudo dementia” →symptoms are usually temporary
Toxic substances include: Alcohol, Cocaine, Heroine, Lead, Mercury, Paint fumes and thinner, and Insecticides
Symptoms: Mental impairment and Decreased cognitive ability
For toxins in the environment, such as lead and mercury, symptoms go away based on how much of it is in your system.
Sleep Apnea
Characterized by periods of breathlessness
Causes:
More common in men
Obesity
Hypertension
Airway obstruction
Alcohol ingestion
Cigarette smoking
Symptoms:
Daytime sleepiness
Extreme snoring
Changes in personality
Depression
Impotence in men
Diagnosis:
Monitoring affected individual during sleep for apnea (sleep study) and low blood oxygen levels → must have 5 periods of not breathing for 10 minutes over several hours
Sleep Apnea (cont.)
Treatment: Based on cause, Weight loss, Surgery to correct nasal obstruction, Oxygen during sleep, and Medications to stimulate breathing
Prevention: Most cases can be prevented by maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding alcohol, not smoking, and avoiding environmental smoke.
Brain tumor
Classified as primary and secondary
Primary tumors are called brain tumors
Secondary tumors are named after the organ of origin
Cause:
Unknown
Symptoms: Vary based on what part of the brain is affected
Headache
Vomiting
Seizures
Changes in mood and personality
Visual disturbance
Loss of memory
Concussions and Contusions
Concussion less serious than contusion, no injury to the brain
Contusion is a physical bruising of the brain tissue
Cause
Blow to head by object, fall, or other trauma
E.g., automobile accident
Symptoms:
Disruption of normal electrical activity in brain – unconsciousness
Unconsciousness may last a few seconds to several hours
Headache
Blurred vision
Concussions and Contusions (cont.)
Symptoms:
Irritability
Draw up knees and begin vomiting
Contusions can lead to:
Hematoma
Increased intracranial pressure (I C P) → from brain swelling
Permanent brain damage
Coup and contrecoup contusions
Diagnosis: History of injury, neurologic examination, cranial X-ray, C T scan, and M R I
Coup Contusion
A bruise on the brain directly where the head is struck.
Contrecoup Contusion
A bruise or contusion on the brain on the opposite side of the initial impact.
After the initial impact, the brain continues to move and slams against the opposite side of the skull.
Ex: Whiplash in a car accident
Treatment for Concussions and Contusions
Bedrest
Direct observation
Individual should be checked every 2 to 4 hours
Monitoring of changes in consciousness, eye pupil size, mood, and behavior
Decrease screentime
Analgesics, stimulants, and sedatives should not be given
Medications may mask symptoms and make assessment difficult
Skull Fracture
A break in a cranial (skull) bone
Greatest danger:
Brain tissue damage from bony fragments
Potential of cutting brain tissue, severing vessels causing hematoma
Brain damage may be temporary or permanent
Symptoms: Variety of symptoms depending on location of fracture, Fracture near base of skull may cause impaired breathing, Hemiparesis, Seizures, and Infection
Treatment: Dependent on type and position of fracture, Craniotomy may be necessary to relieve I C P, and Protective headgear may be necessary until fracture healed
Epideural Hematoma
A collection of blood between the bony skull and dura mater (outer meninges).
Cause:
Usually, the result of a fight or accident
Blood vessels rupture and hemorrhage or seep blood usually rapidly over a period of hours
Symptoms:
Usually occur within a few hours
Headache
Dilated pupils
Nausea
Vomiting
Symptoms:
Dizziness
As the hematoma grows:
Loss of consciousness
Increase in I C P
Subdural Hematoma
A collection of blood between the dura mater (outer layer) and the arachnoid (middle layer).
Occurs twice as often as epidural.
Blood vessels rupture and seep blood slowly, usually over a period of days.
Cause:
Usually, the result of head hitting stationary object → As is seen with falls when the head hits the floor
Symptoms:
Hemiparesis
Nausea and vomiting
Dizziness
Convulsions
Loss of consciousness
Epidural and Subdural Hematoma
Diagnosis:
Cerebral hematoma is made by
Clinical history
Cranial X-ray
C T or M R I
Treatment:
Goal is to decrease I C P
Pressure can be relieved by
Special craniotomy called burr holes
Electrical cauterization
Head injuries have ______.
increased in the US
Spinal Cord Injury
Usually results when the bony spinal column is injured or fractured
Happen more in men
The cord can be injured at any level
Neck area is most vulnerable → C1 to C4
Cause:
Automobile accidents – leading cause
Gunshot and knife wounds
Falls and sports injuries
Symptoms of Spinal Cord Injury
Symptoms:
Varying degrees of injury
Injury to C1-C3 is usually fatal
Quadriplegia – spinal cord paralysis
Loss of movement and feeling in trunk and all four extremities
Loss of bowel, bladder, and sexual function
If severe, respiratory ventilation
Paraplegia
Loss of movement and feeling in trunk and both legs
Loss of bowel, bladder, and sexual function
Spinal Cord Injury (cont.)
Diagnosis:
History of injury, neurologic exam, spinal X-rays, CT scan, and MRI
Emergency treatment:
Immediate treatment necessary
Do not move individual unless surroundings unsafe
Maintain position of spine with special collars and backboards
Treatment:
Realignment and stabilization of bony spinal column
Decompression or release of pressure on spinal cord
Prevent further injury
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
Also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease
More in men over 50
Destructive disease of motor or movement neurons
Atrophy of muscles leading to progressive loss of movement of hands, arms, and legs
Issues with speaking and breathing
Supportive treatment →about keeping them comfortable
Timeline varies for each person
No cure
Guillain Barre Syndrome
Acute, progressive disease affecting spinal nerves
Cause - unknown; maybe from certain viruses or infections
Most people have a full recovery
Recommend people with this disease to not take flu shots.
Begins 10 to 21 days after febrile illness
Early symptoms:
Nausea
Fever
Malaise
Guillain Barre Syndrome (cont.)
Within 24 to 72 hours, paresthesia, muscle weakness, and paralysis usually begin.
Symptoms may progress for several days to weeks.
Once progression ceases, recovery begins.
Supportive treatment
Recovery usually complete
Huntington’s Chorea
Inherited disease
Appears during middle age
Progressive degenerative disease of brain
Leads to mental deterioration
Symptoms:
Loss of muscle control and chorea
Changes in personality mood, and behavior
Loss of memory and dementia
Supportive treatment
No cure
Multiple Sclerosis
Causes:
Demyelination of C N S nerves → damage to outer casing of nerves causing messages to not flow properly
Allows information to leak from nerve pathway
Leads to poor or absent nerve transmission
Symptoms:
Muscle weakness and lack of coordination
Paresthesia
Speech difficulty
Loss of bladder function
Visual disturbance, especially diplopia
Multiple Sclerosis (cont.)
Affects adults between ages 20 and 40.
Periods of remission and exacerbation → autoimmune disease
Treatment: Physical therapy and Muscle relaxants to maintain muscle tone and reduce spastic movement
Effects of Aging
DECREASED NERVOUS SYSTEM ACTIVITY IN BRAIN AND SPINAL CORD.
LOSS OF SHORT-TERM MEMORY.
LOSS OF VISUAL ACUITY AND PERIPHERAL VISION.
ALTERED SLEEP PATTERNS.
Parts of the brain
Brainstem, cerebrum, and cerebellum
Shingles typically occurs in which population?
Adults
Rabies is curable as long as you recognize the symptoms within the first week of the bite.
True or False
False
Women who experience gestational diabetes are at a higher risk for developing Type 2 diabetes later on in life.
True or False.
True
Common types of Headaches
Migraine, cluster, and tension
The first symptom of Bell's Palsy is lockjaw.
true or false
false
Bell’s palsy is unilateral paralysis of the face caused by paralysis of the _____ cranial nerve.
7th
A sleep disorder characterized by bouts of breathlessness is ______.
Sleep Apnea
The disease that causes demyelination of the nerves of the Central Nervous System is ________________.
Multiple Sclerosis
Diabetes INSIPIDUS is the most common major disease of the endocrine pancreas.
true or false
false
What microorganisms can cause meningitis?
Bacteria, fungi, and viruses