1.2.3b - cross elasticity of demand
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
abbreviation for cross elasticity of demand
XED
define XED
measures the responsiveness of demand for one good to a change in the price of another good
XED formula
percentage change in demand of good B/percentage change in price of good A
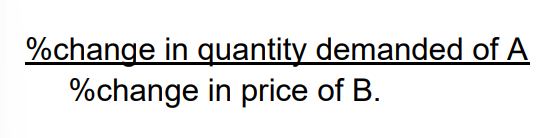
alternative formula for XED
(price of A/demand of B) X (change in quantity of B/change in price of A)
two types of relationships goods can have
substitutes (in competition with one another) = competitive demand
complements (one goes with the other) = joint demand
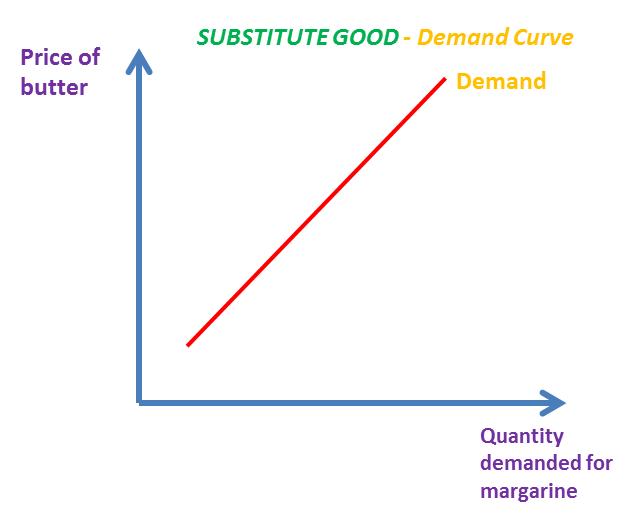
substitutes XED
will be positive
increase in strawberry price = increase in raspberry demand
reduction in iPhone price = decrease in Samsung demand
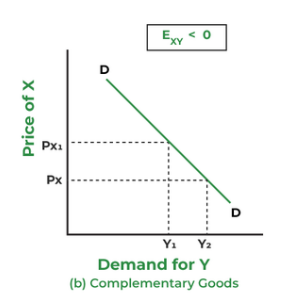
complements XED
will be negative (like a normal demand curve)
increase in strawberry price = decrease in cream demand
reduction in iPhone price = increase in AirPods demand
elastic XED
XED>1
means the good is responsive to the change in price of its complements or substitutes
(the two goods have a strong interrelationship in terms of price)
inelastic XED
XED<1
the good is unresponsive to the change in price of its complements or substitutes
(two goods have a weak interrelationship in terms of price)
unitary XED
XED = 1
percentage change in price of one good is exactly proportional to percentage change in demand of another good
XED = 0
two goods are unrelated
change in price in one has no effect on change in demand for another