chapter 16 immune system- Adaptive Immunity
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
innate immunity
present at birth
immediate
nonspecific
Adaptive Immunity
develops after exposure to antigen
slower
higly specific
memory response - involve in immunizations
two types of adaptive immunity
humoral and cell mediated
humoral immunity
antibodies produced
B cells
plasma and memory cells
cell-mediated immunity
team of t cells
direct cell killing
intracellular pathogens
important for viral infections
kill infected cells
What type of cell is a B cell?
A lymphocyte
What do B cells differentiate into?
Antibody-producing plasma B cells
When do B cells encounter antibodies?
When they encounter an antigen
What is the role of plasma cells?
To produce antibodies
antibody
host defense protein produced in response to foreign structures, circulates in the bloodstream
What is cell-mediated immunity?
A type of immunity that involves T cell lymphocytes.
What do helper T cells do?
They stimulate B cells.
What do cytotoxic T cells do?
They kill infected host cells.
Antigen
molecules that elicit the production of antibodies
-can exist in a singular structures
Epitope
A small segment of antigen that can elicit an immune response
-can have more than one in this
haptens
very small molecule that must bind to another immunogen in order to be recognized
-alone will not, not large enough, must be bound to another large immunogen
APC and examples
antigen-presenting cell
ex: dendritic cells, B cells
What does antigenicity measure?
How well antigens elicit an immune response.
What is the threshold for each antigen?
The just right amount of antigen required to generate the best response.
What happens with low antigen levels?
They only activate a few B cells.
What can high antigen levels lead to?
Peripheral tolerance.
order of proteins, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids; lipids in immune response
1. proteins= vairety
2. Carbohydrates - dont really stimulate immune response
3.nucleic acid lipids
What is immunological specificity in adaptive immunity?
Antibodies are generated for specific antigens.
Can antigenetically related organisms provide immune protection against each other?
Yes, some antigenetically related organisms may generate immune protection against each other.
Which two viruses are known to provide cross-protection due to immunological specificity?
Cowpox and Smallpox.
What must key virulence proteins share to allow for cross-protection?
They must share similar structures.
antibodies
-provide immunological response
-Circulate in blood and lymph can be found on surface of B cells (numeral)
antibodies consist of 4 polypeptide chains
2 long heavy chains, and I short light chains
Two identical antigen-binding sites
variable and constant regions
Five classes of antibodies determined by heavy chain
IgM, IgA, IgG, IgE, IgD
Heavy chain constant regions play a role in
function of antibodies
heavy chain of all IgA is the same but different of IgG
same structure different heavy chain
Isotype
different antibodies of species
allotype
antibody differences between individuals of a specie
Idiotype
different antibodies within an individual (depends on antigen)
What is the most abundant antibody in blood and tissue fluids?
IgG
What is one function of IgG?
Opsonizes microbes to improve phagocytosis
How does IgG interact with viruses?
Neutralizes viruses
What pathway does IgG activate in the complement system?
Activates the classical pathway
What is a unique characteristic of IgG regarding the placenta?
IgG can cross the placenta
can be good and bad
IgD
commonly found on Surface of B cells
IgE
mainly found on surface of most cells and basophils
Allergic Responses
IgA
secretory antibody that is secreted across mucosal surfaces
-dimer held together by chain; found in tears, Saliva, breast milk
IgM
often circulates
Ferris wheel shaped pentameter
usually first antibody detected
heavy chains
monomers
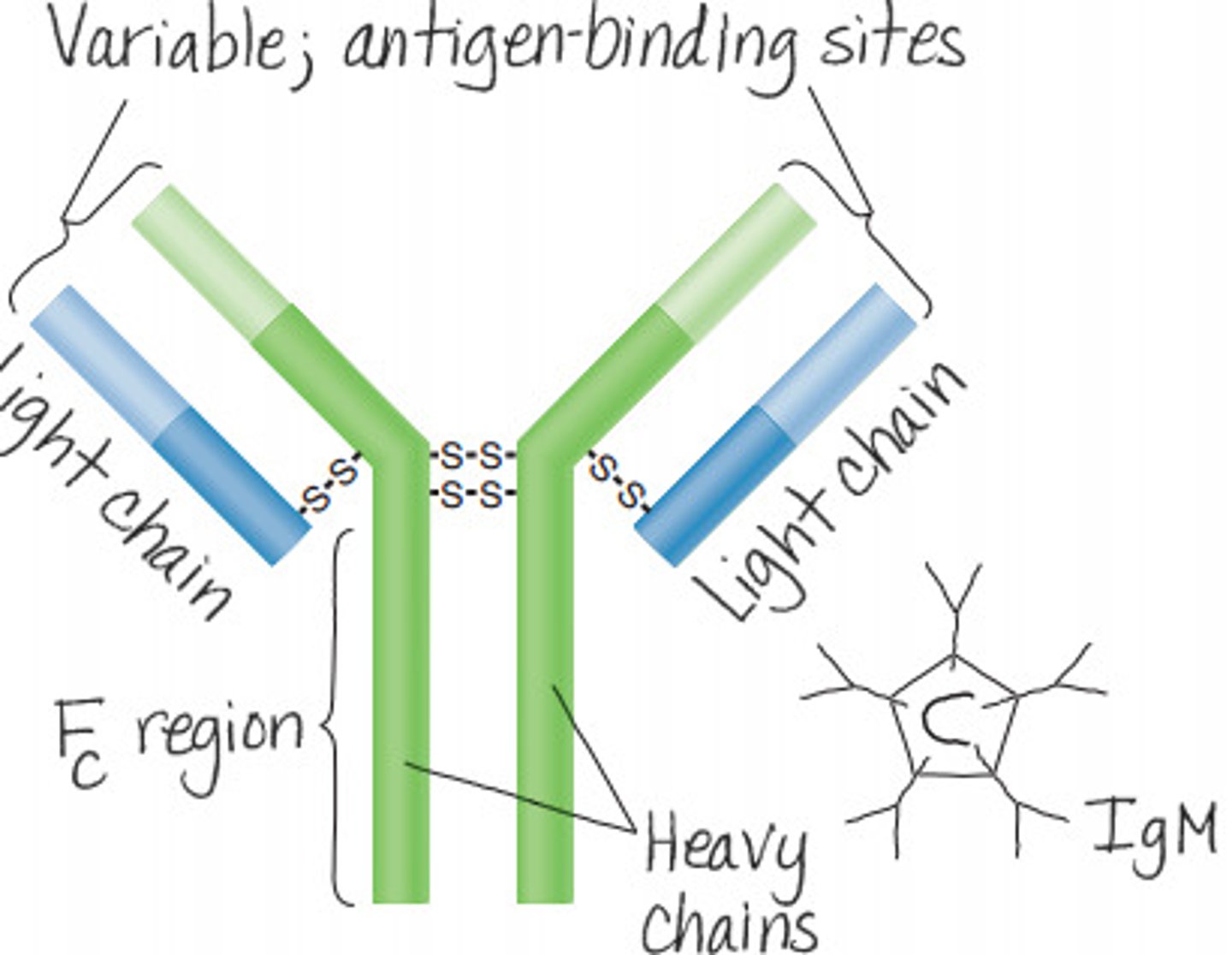
IgM -> IgG
A more efficient antibody very adapted
What is the primary antibody response?
Antigen binds to B cells that only make antibodies against that antigen, primarily producing IgM.
What happens to B cells during the primary antibody response?
B cells proliferate and differentiate into antibody-secreting plasma cells and memory B cells.
What type of antibody is produced first in the primary response?
IgM is produced first.
What is the eventual class switch in antibody production after the primary response?
The class switch is to IgG.
How does the abundance and efficiency of IgM compare to IgG?
IgM is abundant but not efficient compared to IgG.
Some activated B cells become
memory cells
memory cells that encounter antigen again quickly trigger
secondary antibody response
Immunization
Exposure
-vaccine or natural memory cells created allow for a rapid response when the pathogen is encountered again
B cell receptors
-Found on B cells to help identify correct antigen
-Typically have IgD or IgM
-may be 50, 000 receptors specific for the same antigen
-can be coded to produce antibodies for certain antigen
How can B cells be activated?
B cells can be activated in two ways: T cell independent and T cell dependent.
What is T cell independent activation of B cells?
B cell receptors bind antigen with multiple copies of epitope, resulting in capping.
What is T cell dependent activation of B cells?
Antigen binds to B cells; CD40 ligand on T cells binds to CD40 on B cell surface.
capping
cluster binding of B cell receptors on B cell
capping
cluster binding of B cell receptors on B cell
cd4o
receptor on T cell
What is the role of T cells in the immune system?
T cells are critical to directing and balancing the immune system.
What are the two groups of T cells based on differentiation proteins?
Helper T cells and Cytotoxic T cells.
What surface protein do Helper T cells display?
CD4 antibody.
What surface protein do Cytotoxic T cells display?
CD8.
What type of immunity do Helper T cells mediate?
Cell-mediated immunity.
What type of immunity do Cytotoxic T cells mediate?
Cell-mediated immunity only.
cytotoxic
kill cells
coreceptors mediate how
T cells recognize antigen
How T cell recognize
T cell activation is dependent upon antigen presenting cells (APC's
-T cell only recognize antigens presented on MHCs
What is the function of Class I MHC?
Class I MHC are found on all nucleated cells (not RBC).
Where are Class II MHC found?
Class II MHC are found on antigen presenting dendritic cells, macrophages, and B cells.
How T cells recognize antigens
Antigen made by intracellular pathogens (endogenous antigens)are presented on MHC1 molecules
↳ results in destruction of infected cell
-By CD8 T-cells
-Antigen produced outside of the APC(exogenous antigens)are engulfed and attach to MHC2 molecules
↳ results in antibody production
What do T cell receptors (TCRs) bind to?
Antigens
Where are T cell receptors (TCRs) located?
On the surface of T cells
What must antigens be attached to for TCRs to bind?
MHC proteins on APCs
What complex do T cell receptors (TCRs) form with CD3?
CD3 complex
What do CD3 proteins do when activated by TCRs?
Signal the nucleus and trigger proliferation of the T cell
What is the role of CD4 in activating cells?
binds to MHC II/antigen complex.
What is the role of CD8 in activating cells?
binds to MHC I/antigen complex.
What is the second signal required for T cell activation?
CD28 on T cell binds to B7 on APC.
B7
ligand
helps activate T cells
T cell must be able to recognize and differentiate self from nonself
process of selection
-learn to recognize in thymus
regulatory cells
negative selection that survived
positive selecton of t cell
t cells that weakly recognize self are allowed to live
-weak response to antigens, enter peripheral self
negative selection of T cells
t cells that bind to strongly to self are destroyed
- go through apoptosis
Some self-reactive t cells live and become
Regulatory T cells
-prevent autoimmune disease
-block activation of self-reactive lymphocytes
-protect from self-reactive cells
Superantigens do not
require processing and presentation by APCs
What do superantigens bind to?
Outside of T cell receptors on T cells and MHC molecules on antigen-presenting cells (APCs).
What is the effect of superantigens on T cell activation?
They can activate many more T cells than usual, with no antigen specificity involved.
How many T cells can be activated at once by superantigens?
Up to 30% T cells can be activated at once.
What can excessive T cell activation by superantigens lead to?
A cytokine storm.
What type of immunity is mediated by Cytotoxic T cells?
Cell mediated immunity
What must Cytotoxic T cells bind to for activation?
Antigen presented on APCs via MHC I molecule
Which cytokine is required for the activation of Cytotoxic T cells?
IL-2 produced by Th1 helper cells
What do activated Cytotoxic T cells do after leaving the lymph node?
They travel to the site of infection to kill infected cells
What type of pathogens are Cytotoxic T cells important for clearing?
Intracellular pathogens
Which cells express MHC I molecules?
All nucleated cells
What process do Cytotoxic T cells induce in infected cells?
Apoptosis
induce apoptosis
perforin
granzymes
perforin
create pore in host cell