Types of Joints and Conditions
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary with included pictures
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
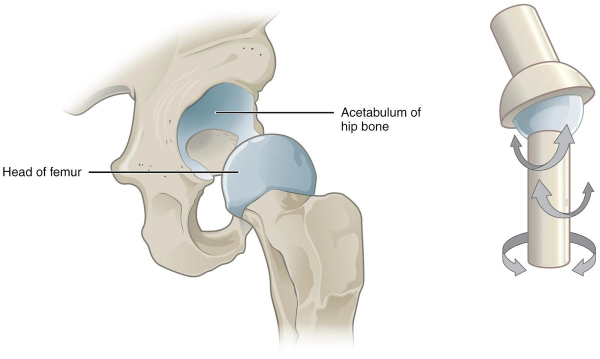
Ball and socket joints
The rounded head of one bone fits into the indentation of another, allowing for movement in all directions
the shoulder and hip
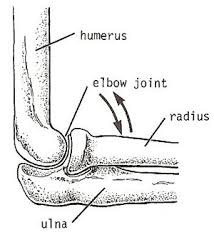
Hinge joints
Allow for movement in only one direction, like a door hinge
Elbow, knee, and fingers
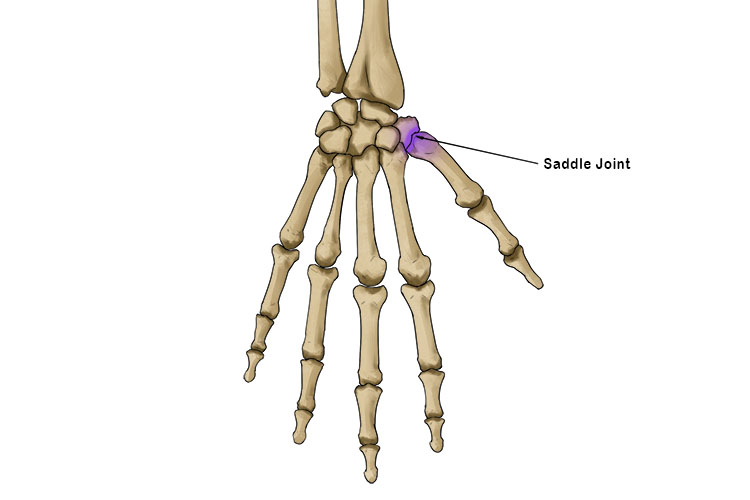
Saddle joints
Allow for movement in any direction, but not rotation
The joint at the base of your thumb
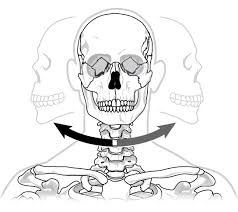
Pivot joints
Enable rotation in place
e.g. joints the neck that allows you to turn your head
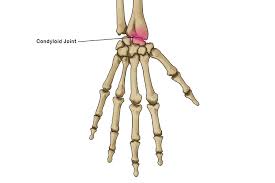
Condyloid joints
Made of two oval-shaped bones that fit together, allowing for a wide range of motion but not rotation
joints in the wrist and between the toes and the rest of the foot, knuckles
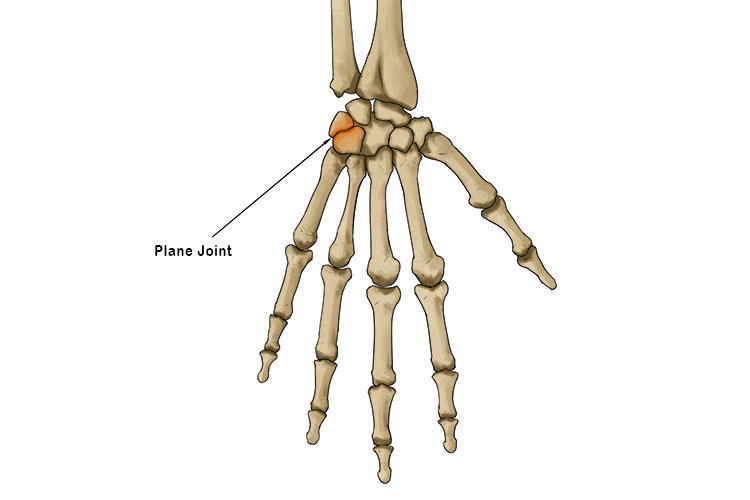
Planar (gliding) joints
Permit bones to slide over one another in one plane
e.g. joints between the carpal bones in the wrist
Osteogenesis imperfecta
a congenital present at birth
inability to produce a type of collagen needed in bone tissue
Osteoporosis
a to decrease in bone mass
holes in spongy bone are wider
most often occurs in women after menopause due to a decrease in sex hormone circulation
scoliosis
an abnormal sideways curvature of the spine in the thoracic or lumbar region
severe cases can reduce the volume of the thoracic cavity leading to a difficulty breathing
osteoarthritis
a wearing down of articular cartilage (could be a result of aging)
results in pain stiffness, loss of flexibility in joints
hypermobility
a condition where range of motion in joints is possible due to abnormally shaped ends of bones
genetic connective tissue defect leading to weakened cartilage and/or tendons
transverse
a straight break that runs across the bone
spiral
a break that spirals across the bone
oblique
a diagonal break across the bone
greenstick
an incomplete break where the bone bends but doesn’t break all the way through (common in children)
comminuted
the bone is broken into fragments (three or more pieces)
compression
the bone is crushed or compressed, not broken by a sharp line
open (compound)
the broken bone breaks through the skin, requiring immediate treatment to prevent infection
closed (simple)
the skin remains intact and there is no open wound
displaced
the broken ends of the bones are not aligned with each other
non-displaced
the bone may be cracked or broken, but the two ends stay in the correct alignment